Android 弹窗浅谈
我们知道 Android 弹窗中,有一类弹窗会在应用之外也显示,这是因为他被申明成了系统弹窗,除此之外还有2类弹窗分别是:子弹窗与应用弹窗。
应用弹窗:就是我们常规使用的 Dialog 之类弹窗,依赖于应用的 Activity;子弹窗:依赖于父窗口,比如 PopupWindow;系统弹窗:比如状态栏、Toast等,本文所讲的系统悬浮窗就是系统弹窗。
系统悬浮窗具体实现
权限申请
代码设计
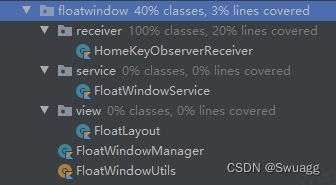
下面的包结构截图,简单展示了实现系统悬浮窗的代码结构,更复杂的业务需要可在此基础上进行扩展。
FloatWindowService:系统悬浮窗在此 Service 中弹出;
FloatWindowManager:系统悬浮窗管理类;
FloatLayout:系统悬浮窗布局;
HomeKeyObserverReceiver:
监听 Home 键;
FloatWindowUtils:系统悬浮窗工具类。
具体实现
FloatWindowService 类
class FloatWindowService : Service() {
private val TAG = FloatWindowService::class.java.simpleName
private var mFloatWindowManager: FloatWindowManager? = null
private var mHomeKeyObserverReceiver: HomeKeyObserverReceiver? = null
override fun onCreate() {
TLogUtils.i(TAG, "onCreate: ")
mFloatWindowManager = FloatWindowManager(applicationContext)
mHomeKeyObserverReceiver = HomeKeyObserverReceiver()
registerReceiver(mHomeKeyObserverReceiver, IntentFilter(Intent.ACTION_CLOSE_SYSTEM_DIALOGS))
mFloatWindowManager!!.createWindow()
}
override fun onBind(intent: Intent?): IBinder? {
return null
}
override fun onStartCommand(intent: Intent?, flags: Int, startId: Int): Int {
return START_NOT_STICKY
}
override fun onDestroy() {
TLogUtils.i(TAG, "onDestroy: ")
mFloatWindowManager?.removeWindow()
if (mHomeKeyObserverReceiver != null) {
unregisterReceiver(mHomeKeyObserverReceiver)
}
}
}
FloatWindowManager 类
包括系统悬浮窗的创建、显示、销毁(以及更新)。
public void addView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params); // 添加 View 到 Window public void updateViewLayout(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params); //更新 View 在 Window 中的位置 public void removeView(View view); //删除 View
FloatWindowManager 类代码
class FloatWindowManager constructor(context: Context) {
var isShowing = false
private val TAG = FloatWindowManager::class.java.simpleName
private var mContext: Context = context
private var mFloatLayout = FloatLayout(mContext)
private var mLayoutParams: WindowManager.LayoutParams? = null
private var mWindowManager: WindowManager = context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE) as WindowManager
fun createWindow() {
TLogUtils.i(TAG, "createWindow: start...")
// 对象配置操作使用apply,额外的处理使用also
mLayoutParams = WindowManager.LayoutParams().apply {
type = if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.O) {
// Android 8.0以后需要使用TYPE_APPLICATION_OVERLAY,不允许使用以下窗口类型来在其他应用和窗口上方显示提醒窗口:TYPE_PHONE、TYPE_PRIORITY_PHONE、TYPE_SYSTEM_ALERT、TYPE_SYSTEM_OVERLAY、TYPE_SYSTEM_ERROR。
WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_APPLICATION_OVERLAY
} else {
// 在Android 8.0之前,悬浮窗口设置可以为TYPE_PHONE,这种类型是用于提供用户交互操作的非应用窗口。
// 在API Level = 23的时候,需要在Android Manifest.xml文件中声明权限SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW才能在其他应用上绘制控件
WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_PHONE
}
// 设置图片格式,效果为背景透明
format = PixelFormat.RGBA_8888
// 设置浮动窗口不可聚焦(实现操作除浮动窗口外的其他可见窗口的操作)
flags = WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_FOCUSABLE
// 调整悬浮窗显示的停靠位置为右侧置顶
gravity = Gravity.TOP or Gravity.END
width = 800
height = 200
x = 20
y = 40
}
mWindowManager.addView(mFloatLayout, mLayoutParams)
TLogUtils.i(TAG, "createWindow: end...")
isShowing = true
}
fun showWindow() {
TLogUtils.i(TAG, "showWindow: isShowing = $isShowing")
if (!isShowing) {
if (mLayoutParams == null) {
createWindow()
} else {
mWindowManager.addView(mFloatLayout, mLayoutParams)
isShowing = true
}
}
}
fun removeWindow() {
TLogUtils.i(TAG, "removeWindow: isShowing = $isShowing")
mWindowManager.removeView(mFloatLayout)
isShowing = false
}
}
FloatLayout 类及其 Layout
系统悬浮窗自定义View:FloatLayout
class FloatLayout @JvmOverloads constructor(context: Context, attrs: AttributeSet? = null, defStyleAttr: Int = 0, defStyleRes: Int = 0) :
ConstraintLayout(context, attrs, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes) {
private var mTime: TCLTextView
private var mDistance: TCLTextView
private var mSpeed: TCLTextView
private var mCalories: TCLTextView
init {
val view = LayoutInflater.from(context).inflate(R.layout.do_exercise_view_float_layout, this, true)
mTime = view.findViewById(R.id.float_layout_tv_time)
mDistance = view.findViewById(R.id.float_layout_tv_distance)
mSpeed = view.findViewById(R.id.float_layout_tv_speed)
mCalories = view.findViewById(R.id.float_layout_tv_calories)
}
}
布局文件:float_layout_tv_time
HomeKeyObserverReceiver 类
class HomeKeyObserverReceiver : BroadcastReceiver() {
override fun onReceive(context: Context?, intent: Intent?) {
try {
val action = intent!!.action
val reason = intent.getStringExtra("reason")
TLogUtils.d(TAG, "HomeKeyObserverReceiver: action = $action,reason = $reason")
if (Intent.ACTION_CLOSE_SYSTEM_DIALOGS == action && "homekey" == reason) {
val keyCode = intent.getIntExtra("keycode", KeyEvent.KEYCODE_UNKNOWN)
TLogUtils.d(TAG, "keyCode = $keyCode")
context?.stopService(Intent(context, FloatWindowService::class.java))
}
} catch (ex: Exception) {
ex.printStackTrace()
}
}
companion object {
private val TAG = HomeKeyObserverReceiver::class.java.simpleName
}
}
FloatWindowUtils 类
object FloatWindowUtils {
const val REQUEST_FLOAT_CODE = 1000
private val TAG = FloatWindowUtils::class.java.simpleName
/**
* 判断Service是否开启
*/
fun isServiceRunning(context: Context, ServiceName: String): Boolean {
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(ServiceName)) {
return false
}
val myManager = context.getSystemService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE) as ActivityManager
val runningService = myManager.getRunningServices(1000) as ArrayList
runningService.forEach {
if (it.service.className == ServiceName) {
return true
}
}
return false
}
/**
* 检查悬浮窗权限是否开启
*/
@SuppressLint("NewApi")
fun checkSuspendedWindowPermission(context: Activity, block: () -> Unit) {
if (commonROMPermissionCheck(context)) {
block()
} else {
Toast.makeText(context, "请开启悬浮窗权限", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
context.startActivityForResult(Intent(Settings.ACTION_MANAGE_OVERLAY_PERMISSION).apply {
data = Uri.parse("package:${context.packageName}")
}, REQUEST_FLOAT_CODE)
}
}
/**
* 判断悬浮窗权限权限
*/
fun commonROMPermissionCheck(context: Context?): Boolean {
var result = true
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 23) {
try {
val clazz: Class<*> = Settings::class.java
val canDrawOverlays = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("canDrawOverlays", Context::class.java)
result = canDrawOverlays.invoke(null, context) as Boolean
} catch (e: Exception) {
TLogUtils.e(TAG, e)
}
}
return result
}
}
总结
本文并未详细讨论系统悬浮窗的拖动功能,实现系统悬浮穿基本功能可以总结为以下几个步骤:
1. 声明及申请权限;
2. 构建悬浮窗需要的控件 Service、Receiver、Manager、Layout、Util;
3. 使用 WindowManager 创建、显示、销毁(以及更新)Layout。
到此这篇关于Kotlin实现Android系统悬浮窗详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Android Kotlin系统悬浮窗内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!