绪论
本期是对腾讯热播剧——雪中悍刀行的一次爬虫与数据分析,耗时一个小时,总爬取条数1W条评论,很适合新人练手,值得注意的一点是评论的情绪文本分析处理,这是第一次接触的知识。
爬虫方面:由于腾讯的评论数据是封装在json里面,所以只需要找到json文件,对需要的数据进行提取保存即可。
- 视频网址:https://v.qq.com/x/cover/mzc0...
- 评论json数据网址:https://video.coral.qq.com/va...
- 注:只要替换视频数字id的值,即可爬取其他视频的评论
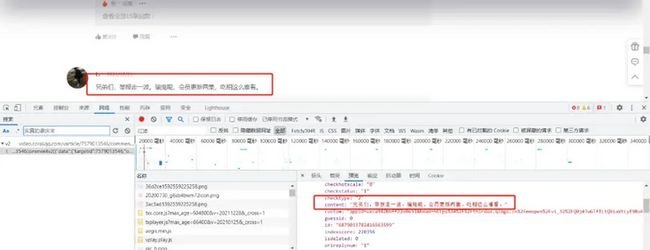
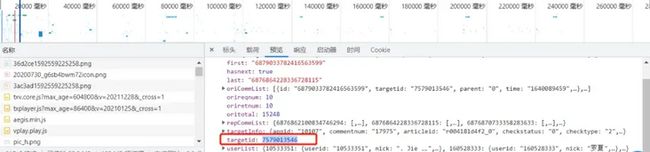
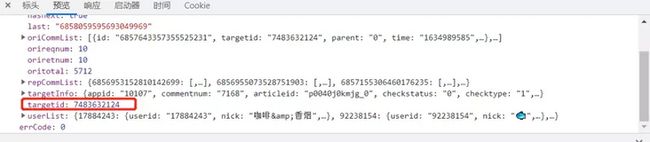
如何查找视频id?
项目结构:
一. 爬虫部分:
1.爬取评论内容代码:spiders.py
import requests
import re
import random
def get_html(url, params):
uapools = [
'Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_9_2) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/35.0.1916.153 Safari/537.36',
'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64; rv:30.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/30.0',
'Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_9_2) AppleWebKit/537.75.14 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/7.0.3 Safari/537.75.14'
]
thisua = random.choice(uapools)
headers = {"User-Agent": thisua}
r = requests.get(url, headers=headers, params=params)
r.raise_for_status()
r.encoding = r.apparent_encoding
r.encoding = 'utf-8'# 不加此句出现乱码
return r.text
def parse_page(infolist, data):
commentpat = '"content":"(.*?)"'
lastpat = '"last":"(.*?)"'
commentall = re.compile(commentpat, re.S).findall(data)
next_cid = re.compile(lastpat).findall(data)[0]
infolist.append(commentall)
return next_cid
def print_comment_list(infolist):
j = 0
for page in infolist:
print('第' + str(j + 1) + '页\n')
commentall = page
for i in range(0, len(commentall)):
print(commentall[i] + '\n')
j += 1
def save_to_txt(infolist, path):
fw = open(path, 'w+', encoding='utf-8')
j = 0
for page in infolist:
#fw.write('第' + str(j + 1) + '页\n')
commentall = page
for i in range(0, len(commentall)):
fw.write(commentall[i] + '\n')
j += 1
fw.close()
def main():
infolist = []
vid = '7579013546';
cid = "0";
page_num = 3000
url = 'https://video.coral.qq.com/varticle/' + vid + '/comment/v2'
#print(url)
for i in range(page_num):
params = {'orinum': '10', 'cursor': cid}
html = get_html(url, params)
cid = parse_page(infolist, html)
print_comment_list(infolist)
save_to_txt(infolist, 'content.txt')
main()2.爬取评论时间代码:sp.py
import requests
import re
import random
def get_html(url, params):
uapools = [
'Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_9_2) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/35.0.1916.153 Safari/537.36',
'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64; rv:30.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/30.0',
'Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_9_2) AppleWebKit/537.75.14 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/7.0.3 Safari/537.75.14'
]
thisua = random.choice(uapools)
headers = {"User-Agent": thisua}
r = requests.get(url, headers=headers, params=params)
r.raise_for_status()
r.encoding = r.apparent_encoding
r.encoding = 'utf-8'# 不加此句出现乱码
return r.text
def parse_page(infolist, data):
commentpat = '"time":"(.*?)"'
lastpat = '"last":"(.*?)"'
commentall = re.compile(commentpat, re.S).findall(data)
next_cid = re.compile(lastpat).findall(data)[0]
infolist.append(commentall)
return next_cid
def print_comment_list(infolist):
j = 0
for page in infolist:
print('第' + str(j + 1) + '页\n')
commentall = page
for i in range(0, len(commentall)):
print(commentall[i] + '\n')
j += 1
def save_to_txt(infolist, path):
fw = open(path, 'w+', encoding='utf-8')
j = 0
for page in infolist:
#fw.write('第' + str(j + 1) + '页\n')
commentall = page
for i in range(0, len(commentall)):
fw.write(commentall[i] + '\n')
j += 1
fw.close()
def main():
infolist = []
vid = '7579013546';
cid = "0";
page_num =3000
url = 'https://video.coral.qq.com/varticle/' + vid + '/comment/v2'
#print(url)
for i in range(page_num):
params = {'orinum': '10', 'cursor': cid}
html = get_html(url, params)
cid = parse_page(infolist, html)
print_comment_list(infolist)
save_to_txt(infolist, 'time.txt')
main()二.数据处理部分
1.评论的时间戳转换为正常时间 time.py
# coding=gbk
import csv
import time
csvFile = open("data.csv",'w',newline='',encoding='utf-8')
writer = csv.writer(csvFile)
csvRow = []
#print(csvRow)
f = open("time.txt",'r',encoding='utf-8')
for line in f:
csvRow = int(line)
#print(csvRow)
timeArray = time.localtime(csvRow)
csvRow = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", timeArray)
print(csvRow)
csvRow = csvRow.split()
writer.writerow(csvRow)
f.close()
csvFile.close()2.评论内容读入csv CD.py
# coding=gbk
import csv
csvFile = open("content.csv",'w',newline='',encoding='utf-8')
writer = csv.writer(csvFile)
csvRow = []
f = open("content.txt",'r',encoding='utf-8')
for line in f:
csvRow = line.split()
writer.writerow(csvRow)
f.close()
csvFile.close()3.统计一天各个时间段内的评论数 py.py
# coding=gbk
import csv
from pyecharts import options as opts
from sympy.combinatorics import Subset
from wordcloud import WordCloud
with open('../Spiders/data.csv') as csvfile:
reader = csv.reader(csvfile)
data1 = [str(row[1])[0:2] for row in reader]
print(data1)
print(type(data1))
#先变成集合得到seq中的所有元素,避免重复遍历
set_seq = set(data1)
rst = []
for item in set_seq:
rst.append((item,data1.count(item))) #添加元素及出现个数
rst.sort()
print(type(rst))
print(rst)
with open("time2.csv", "w+", newline='', encoding='utf-8') as f:
writer = csv.writer(f, delimiter=',')
for i in rst: # 对于每一行的,将这一行的每个元素分别写在对应的列中
writer.writerow(i)
with open('time2.csv') as csvfile:
reader = csv.reader(csvfile)
x = [str(row[0]) for row in reader]
print(x)
with open('time2.csv') as csvfile:
reader = csv.reader(csvfile)
y1 = [float(row[1]) for row in reader]
print(y1)4.统计最近评论数 py1.py
# coding=gbk
import csv
from pyecharts import options as opts
from sympy.combinatorics import Subset
from wordcloud import WordCloud
with open('../Spiders/data.csv') as csvfile:
reader = csv.reader(csvfile)
data1 = [str(row[0]) for row in reader]
#print(data1)
print(type(data1))
#先变成集合得到seq中的所有元素,避免重复遍历
set_seq = set(data1)
rst = []
for item in set_seq:
rst.append((item,data1.count(item))) #添加元素及出现个数
rst.sort()
print(type(rst))
print(rst)
with open("time1.csv", "w+", newline='', encoding='utf-8') as f:
writer = csv.writer(f, delimiter=',')
for i in rst: # 对于每一行的,将这一行的每个元素分别写在对应的列中
writer.writerow(i)
with open('time1.csv') as csvfile:
reader = csv.reader(csvfile)
x = [str(row[0]) for row in reader]
print(x)
with open('time1.csv') as csvfile:
reader = csv.reader(csvfile)
y1 = [float(row[1]) for row in reader]
print(y1)三. 数据分析
数据分析方面:涉及到了词云图,条形,折线,饼图,后三者是对评论时间与主演占比的分析,然而腾讯的评论时间是以时间戳的形式显示,所以要进行转换,再去统计出现次数,最后,新加了对评论内容的情感分析。
1.制作词云图
wc.py
import numpy as np
import re
import jieba
from wordcloud import WordCloud
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from PIL import Image
# 上面的包自己安装,不会的就百度
f = open('content.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8') # 这是数据源,也就是想生成词云的数据
txt = f.read() # 读取文件
f.close() # 关闭文件,其实用with就好,但是懒得改了
# 如果是文章的话,需要用到jieba分词,分完之后也可以自己处理下再生成词云
newtxt = re.sub("[A-Za-z0-9!%[],\。]", "", txt)
print(newtxt)
words = jieba.lcut(newtxt)
img = Image.open(r'wc.jpg') # 想要搞得形状
img_array = np.array(img)
# 相关配置,里面这个collocations配置可以避免重复
wordcloud = WordCloud(
background_color="white",
width=1080,
height=960,
font_path="../文悦新青年.otf",
max_words=150,
scale=10,#清晰度
max_font_size=100,
mask=img_array,
collocations=False).generate(newtxt)
plt.imshow(wordcloud)
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
wordcloud.to_file('wc.png')轮廓图:wc.jpg
在这里插入图片描述
词云图:result.png (注:这里要把英文字母过滤掉)
2.制作最近评论数条形图 DrawBar.py
# encoding: utf-8
import csv
import pyecharts.options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Bar
from pyecharts.globals import ThemeType
class DrawBar(object):
"""绘制柱形图类"""
def __init__(self):
"""创建柱状图实例,并设置宽高和风格"""
self.bar = Bar(init_opts=opts.InitOpts(width='1500px', height='700px', theme=ThemeType.LIGHT))
def add_x(self):
"""为图形添加X轴数据"""
with open('time1.csv') as csvfile:
reader = csv.reader(csvfile)
x = [str(row[0]) for row in reader]
print(x)
self.bar.add_xaxis(
xaxis_data=x,
)
def add_y(self):
with open('time1.csv') as csvfile:
reader = csv.reader(csvfile)
y1 = [float(row[1]) for row in reader]
print(y1)
"""为图形添加Y轴数据,可添加多条"""
self.bar.add_yaxis( # 第一个Y轴数据
series_name="评论数", # Y轴数据名称
y_axis=y1, # Y轴数据
label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=True,color="black"), # 设置标签
bar_max_width='100px', # 设置柱子最大宽度
)
def set_global(self):
"""设置图形的全局属性"""
#self.bar(width=2000,height=1000)
self.bar.set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts( # 设置标题
title='雪中悍刀行近日评论统计',title_textstyle_opts=opts.TextStyleOpts(font_size=35)
),
tooltip_opts=opts.TooltipOpts( # 提示框配置项(鼠标移到图形上时显示的东西)
is_show=True, # 是否显示提示框
trigger="axis", # 触发类型(axis坐标轴触发,鼠标移到时会有一条垂直于X轴的实线跟随鼠标移动,并显示提示信息)
axis_pointer_type="cross"# 指示器类型(cross将会生成两条分别垂直于X轴和Y轴的虚线,不启用trigger才会显示完全)
),
toolbox_opts=opts.ToolboxOpts(), # 工具箱配置项(什么都不填默认开启所有工具)
)
def draw(self):
"""绘制图形"""
self.add_x()
self.add_y()
self.set_global()
self.bar.render('../Html/DrawBar.html') # 将图绘制到 test.html 文件内,可在浏览器打开
def run(self):
"""执行函数"""
self.draw()
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = DrawBar()
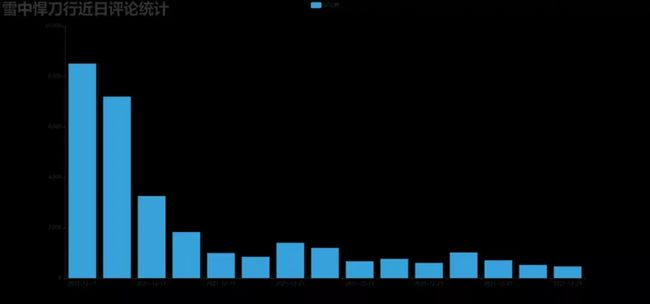
app.run()效果图:DrawBar.html
3.制作每小时评论条形图 DrawBar2.py
# encoding: utf-8
# encoding: utf-8
import csv
import pyecharts.options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Bar
from pyecharts.globals import ThemeType
class DrawBar(object):
"""绘制柱形图类"""
def __init__(self):
"""创建柱状图实例,并设置宽高和风格"""
self.bar = Bar(init_opts=opts.InitOpts(width='1500px', height='700px', theme=ThemeType.MACARONS))
def add_x(self):
"""为图形添加X轴数据"""
str_name1 = '点'
with open('time2.csv') as csvfile:
reader = csv.reader(csvfile)
x = [str(row[0] + str_name1) for row in reader]
print(x)
self.bar.add_xaxis(
xaxis_data=x
)
def add_y(self):
with open('time2.csv') as csvfile:
reader = csv.reader(csvfile)
y1 = [int(row[1]) for row in reader]
print(y1)
"""为图形添加Y轴数据,可添加多条"""
self.bar.add_yaxis( # 第一个Y轴数据
series_name="评论数", # Y轴数据名称
y_axis=y1, # Y轴数据
label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=False), # 设置标签
bar_max_width='50px', # 设置柱子最大宽度
)
def set_global(self):
"""设置图形的全局属性"""
#self.bar(width=2000,height=1000)
self.bar.set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts( # 设置标题
title='雪中悍刀行各时间段评论统计',title_textstyle_opts=opts.TextStyleOpts(font_size=35)
),
tooltip_opts=opts.TooltipOpts( # 提示框配置项(鼠标移到图形上时显示的东西)
is_show=True, # 是否显示提示框
trigger="axis", # 触发类型(axis坐标轴触发,鼠标移到时会有一条垂直于X轴的实线跟随鼠标移动,并显示提示信息)
axis_pointer_type="cross"# 指示器类型(cross将会生成两条分别垂直于X轴和Y轴的虚线,不启用trigger才会显示完全)
),
toolbox_opts=opts.ToolboxOpts(), # 工具箱配置项(什么都不填默认开启所有工具)
)
def draw(self):
"""绘制图形"""
self.add_x()
self.add_y()
self.set_global()
self.bar.render('../Html/DrawBar2.html') # 将图绘制到 test.html 文件内,可在浏览器打开
def run(self):
"""执行函数"""
self.draw()
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = DrawBar()
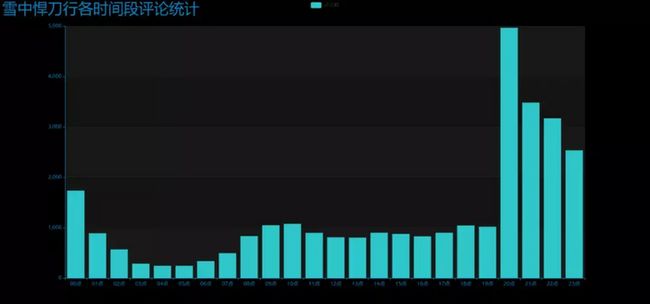
app.run()效果图:DrawBar2.html
4.制作近日评论数饼图 pie_pyecharts.py
import csv
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Pie
from random import randint
from pyecharts.globals import ThemeType
with open('time1.csv') as csvfile:
reader = csv.reader(csvfile)
x = [str(row[0]) for row in reader]
print(x)
with open('time1.csv') as csvfile:
reader = csv.reader(csvfile)
y1 = [float(row[1]) for row in reader]
print(y1)
num = y1
lab = x
(
Pie(init_opts=opts.InitOpts(width='1700px',height='450px',theme=ThemeType.LIGHT))#默认900,600
.set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="雪中悍刀行近日评论统计",
title_textstyle_opts=opts.TextStyleOpts(font_size=27)),legend_opts=opts.LegendOpts(
pos_top="10%", pos_left="1%",# 图例位置调整
),)
.add(series_name='',center=[280, 270], data_pair=[(j, i) for i, j in zip(num, lab)])#饼图
.add(series_name='',center=[845, 270],data_pair=[(j,i) for i,j in zip(num,lab)],radius=['40%','75%'])#环图
.add(series_name='', center=[1380, 270],data_pair=[(j, i) for i, j in zip(num, lab)], rosetype='radius')#南丁格尔图
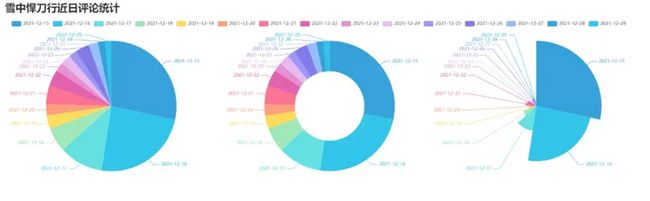
).render('pie_pyecharts.html')效果图
5.制作每小时评论饼图 pie_pyecharts2.py
import csv
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Pie
from random import randint
from pyecharts.globals import ThemeType
str_name1 = '点'
with open('time2.csv') as csvfile:
reader = csv.reader(csvfile)
x = [str(row[0]+str_name1) for row in reader]
print(x)
with open('time2.csv') as csvfile:
reader = csv.reader(csvfile)
y1 = [int(row[1]) for row in reader]
print(y1)
num = y1
lab = x
(
Pie(init_opts=opts.InitOpts(width='1650px',height='500px',theme=ThemeType.LIGHT,))#默认900,600
.set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="雪中悍刀行每小时评论统计"
,title_textstyle_opts=opts.TextStyleOpts(font_size=27)),
legend_opts=opts.LegendOpts(
pos_top="8%", pos_left="4%",# 图例位置调整
),
)
.add(series_name='',center=[250, 300], data_pair=[(j, i) for i, j in zip(num, lab)])#饼图
.add(series_name='',center=[810, 300],data_pair=[(j,i) for i,j in zip(num,lab)],radius=['40%','75%'])#环图
.add(series_name='', center=[1350, 300],data_pair=[(j, i) for i, j in zip(num, lab)], rosetype='radius')#南丁格尔图
).render('pie_pyecharts2.html')效果图
6.制作观看时间区间评论统计饼图 pie_pyecharts3.py
# coding=gbk
import csv
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.globals import ThemeType
from sympy.combinatorics import Subset
from wordcloud import WordCloud
from pyecharts.charts import Pie
from random import randintwith open(/data.csv') as csvfile:
reader = csv.reader(csvfile)
data2 = [int(row[1].strip('')[0:2]) for row in reader]
#print(data2)
print(type(data2))
#先变成集合得到seq中的所有元素,避免重复遍历
set_seq = set(data2)
list = []
for item in set_seq:
list.append((item,data2.count(item))) #添加元素及出现个数
list.sort()
print(type(list))
#print(list)
with open("time2.csv", "w+", newline='', encoding='utf-8') as f:
writer = csv.writer(f, delimiter=',')
for i in list: # 对于每一行的,将这一行的每个元素分别写在对应的列中
writer.writerow(i)
n = 4#分成n组
m = int(len(list)/n)
list2 = []
for i in range(0, len(list), m):
list2.append(list[i:i+m])
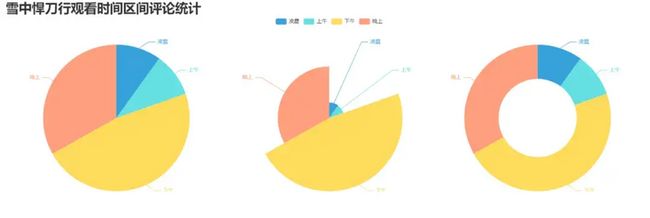
print("凌晨 : ",list2[0])
print("上午 : ",list2[1])
print("下午 : ",list2[2])
print("晚上 : ",list2[3])
with open('time2.csv') as csvfile:
reader = csv.reader(csvfile)
y1 = [int(row[1]) for row in reader]
print(y1)
n =6
groups = [y1[i:i + n] for i in range(0, len(y1), n)]
print(groups)
x=['凌晨','上午','下午','晚上']
y1=[]
for y1 in groups:
num_sum = 0
for groups in y1:
num_sum += groups
str_name1 = '点'
num = y1
lab = x
(
Pie(init_opts=opts.InitOpts(width='1500px',height='450px',theme=ThemeType.LIGHT))#默认900,600
.set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="雪中悍刀行观看时间区间评论统计"
, title_textstyle_opts=opts.TextStyleOpts(font_size=30)),
legend_opts=opts.LegendOpts(
pos_top="8%", # 图例位置调整
),
)
.add(series_name='',center=[260, 270], data_pair=[(j, i) for i, j in zip(num, lab)])#饼图
.add(series_name='',center=[1230, 270],data_pair=[(j,i) for i,j in zip(num,lab)],radius=['40%','75%'])#环图
.add(series_name='', center=[750, 270],data_pair=[(j, i) for i, j in zip(num, lab)], rosetype='radius')#南丁格尔图
).render('pie_pyecharts3.html')效果图
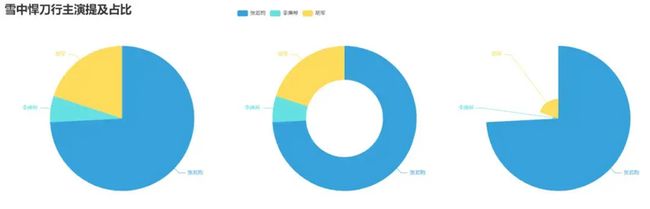
7.制作雪中悍刀行主演提及占比饼图 pie_pyecharts4.py
import csv
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Pie
from random import randint
from pyecharts.globals import ThemeType
f = open('content.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8') # 这是数据源,也就是想生成词云的数据
words = f.read() # 读取文件
f.close() # 关闭文件,其实用with就好,但是懒得改了
name=["张若昀","李庚希","胡军"]
print(name)
count=[float(words.count("张若昀")),
float(words.count("李庚希")),
float(words.count("胡军"))]
print(count)
num = count
lab = name
(
Pie(init_opts=opts.InitOpts(width='1650px',height='450px',theme=ThemeType.LIGHT))#默认900,600
.set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="雪中悍刀行主演提及占比",
title_textstyle_opts=opts.TextStyleOpts(font_size=27)),legend_opts=opts.LegendOpts(
pos_top="3%", pos_left="33%",# 图例位置调整
),)
.add(series_name='',center=[280, 270], data_pair=[(j, i) for i, j in zip(num, lab)])#饼图
.add(series_name='',center=[800, 270],data_pair=[(j,i) for i,j in zip(num,lab)],radius=['40%','75%'])#环图
.add(series_name='', center=[1300, 270],data_pair=[(j, i) for i, j in zip(num, lab)], rosetype='radius')#南丁格尔图
).render('pie_pyecharts4.html')效果图
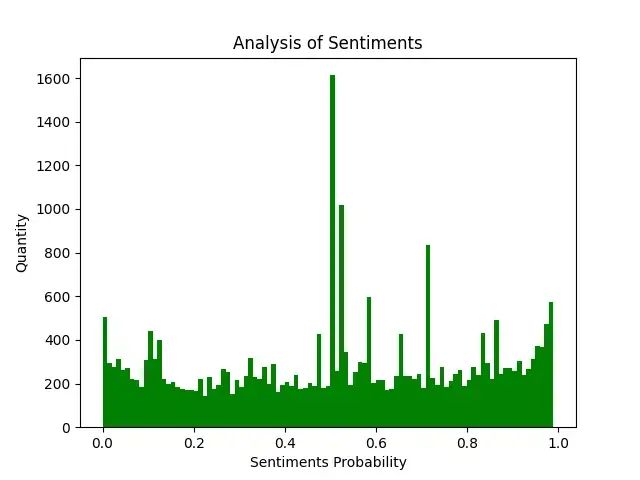
8.评论内容情感分析 SnowNLP.py
import numpy as np
from snownlp import SnowNLP
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
f = open('content.txt', 'r', encoding='UTF-8')
list = f.readlines()
sentimentslist = []
for i in list:
s = SnowNLP(i)
print(s.sentiments)
sentimentslist.append(s.sentiments)
plt.hist(sentimentslist, bins=np.arange(0, 1, 0.01), facecolor='g')
plt.xlabel('Sentiments Probability')
plt.ylabel('Quantity')
plt.title('Analysis of Sentiments')
plt.show()效果图(情感各分数段出现频率) SnowNLP情感分析是基于情感词典实现的,其简单的将文本分为两类,积极和消极,返回值为情绪的概率,也就是情感评分在[0,1]之间,越接近1,情感表现越积极,越接近0,情感表现越消极。