python提供了几种调用shell的命令,但是每个命令的功能不同,需要详细了解下,才可以比较方便的来应对不同的需求。
os.system
os.system(cmd)的返回值。如果执行成功,那么会返回0,表示命令执行成功。否则,则是执行错误。
使用os.system返回值是脚本的退出状态码,该方法在调用完shell脚本后,返回一个16位的二进制数,低位为杀死所调用脚本的信号号码,高位为脚本的退出状态码。
示例:
import osresult = os.system('cat /etc/passwd')print(result) # 0os.popen
os.popen()方法不仅执行命令而且返回执行后的信息对象(常用于需要获取执行命令后的返回信息),是通过一个管道文件将结果返回。通过 os.popen() 返回的是 file read 的对象,对其进行读取 read() 的操作可以看到执行的输出。
示例:
import osresult = os.popen('cat /etc/passwd')print(result.read())commands
commands模块是一个可执行shell命令的库,是python的内置模块
示例:
import commands
status = commands.getstatus('cat /etc/passwd')print(status)output = commands.getoutput('cat /etc/passwd')print(output)(status, output) = commands.getstatusoutput('cat /etc/passwd')print(status, output)subprocess
Subprocess是一个功能强大的子进程管理模块,当执行命令的参数或者返回中包含了中文文字,那么建议使用subprocess。
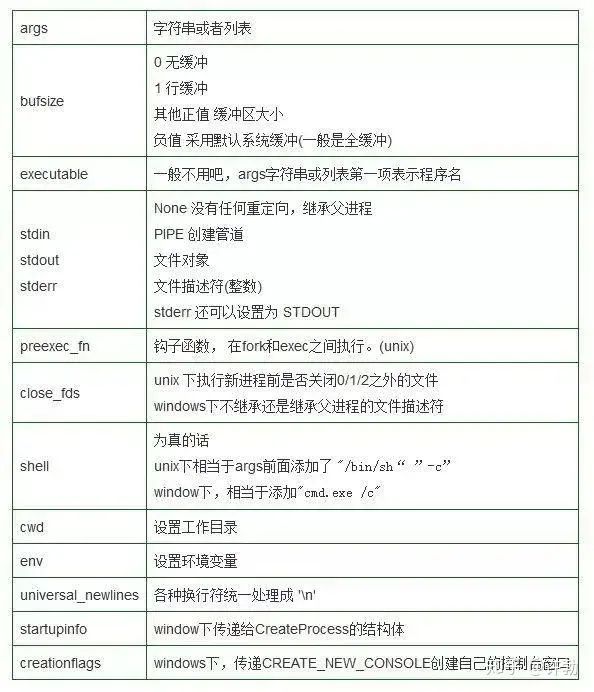
subprocess.Popen() 的参数解释
使用subprocess.call()
subporcess模块还有一个call() 方法,可以用于更加简单的调用外部命令。
subprocess.call (*popenargs , **kwargs )call的使用方法和Popen基本一致,没有太大的区别,在这里只是多介绍一种使用方式。
示例:
import subprocessres = subprocess.Popen('cat /etc/passwd', shell=True, stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.STDOUT) # 使用管道# print res.stdout.read() # 标准输出for line in res.stdout.readlines(): print lineres.stdout.close() # 关闭总结:
综上,除了os.system之外,其他的命令方式均可以获取执行之后的返回结果。
os.system()用于简单执行命令,可以显示执行结果。
os.popen()用于简单执行命令,不能显示执行结果,可以通过变量返回执行结果。
subprocess.Popen() 用于执行复杂命令,可以显示执行结果,可以设置输出内容。
subprocess.call() 用于执行复杂命令,可以显示执行结果,可以设置输出内容。