简介:通过IK分词器分词并生成词云。
本文主要介绍如何通过 IK 分词器进行词频统计。使用分词器对文章的词频进行统计,主要目的是实现如下图所示的词云功能,可以找到文章内的重点词汇。后续也可以对词进行词性标注,实体识别以及对实体的情感分析等功能。
词频统计服务具体模块如下:
- 数据输入:文本信息
- 数据输出:词 - 词频(TF-IDF等) - 词性等内容
- 使用的组件:分词器、语料库、词云展示组件等
- 功能点:白名单,黑名单,同义词等
现存的中文分词器有 IK、HanLP、jieba 和 NLPIR 等几种,不同分词器各有特点,本文使用 IK 实现,因为 ES 一般使用 medcl 等大佬封装的 IK 分词器插件作为中文分词器。
由于 ES 的 IK 分词器插件深度结合了 ES,仅对文本分词使用不到 ES 的内容,所以文本采用申艳超大佬版本的 IK。
1. IK 分词统计代码
IK 的代码相对比较简单,东西不多,将 String 拆分为词并统计代码如下:
单纯统计词频:
/**
* 全文本词频统计
*
* @param content 文本内容
* @param useSmart 是否使用 smart
* @return 词,词频
* @throws IOException
*/
private static Map countTermFrequency(String content, Boolean useSmart) throws IOException {
// 输出结果 Map
Map frequencies = new HashMap<>();
if (StringUtils.isBlank(content)) {
return frequencies;
}
DefaultConfig conf = new DefaultConfig();
conf.setUseSmart(useSmart);
// 使用 IKSegmenter 初始化文本信息并加载词典
IKSegmenter ikSegmenter = new IKSegmenter(new StringReader(content), conf);
Lexeme lexeme;
while ((lexeme = ikSegmenter.next()) != null) {
if (lexeme.getLexemeText().length() > 1) {// 过滤单字,也可以过滤其他内容,如数字和单纯符号等内容
final String term = lexeme.getLexemeText();
// Map 累加操作
frequencies.compute(term, (k, v) -> {
if (v == null) {
v = 1;
} else {
v += 1;
}
return v;
});
}
}
return frequencies;
}
统计词频和文档频率:
/**
* 文本列表词频和词文档频率统计
*
* @param docs 文档列表
* @param useSmart 是否使用只能分词
* @return 词频列表 词-[词频,文档频率]
* @throws IOException
*/
private static Map countTFDF(List docs, boolean useSmart) throws IOException {
// 输出结果 Map
Map frequencies = new HashMap<>();
for (String doc : docs) {
if (StringUtils.isBlank(doc)) {
continue;
}
DefaultConfig conf = new DefaultConfig();
conf.setUseSmart(useSmart);
// 使用 IKSegmenter 初始化文本信息并加载词典
IKSegmenter ikSegmenter = new IKSegmenter(new StringReader(doc), conf);
Lexeme lexeme;
// 用于文档频率统计的 Set
Set terms = new HashSet<>();
while ((lexeme = ikSegmenter.next()) != null) {
if (lexeme.getLexemeText().length() > 1) {
final String text = lexeme.getLexemeText();
// 进行词频统计
frequencies.compute(text, (k, v) -> {
if (v == null) {
v = new Integer[]{1, 0};
} else {
v[0] += 1;
}
return v;
});
terms.add(text);
}
}
// 进行文档频率统计:无需初始化 Map,统计词频后 Map 里面必有该词记录
for (String term : terms) {
frequencies.get(term)[1] += 1;
}
}
return frequencies;
} 2. 获取词云 TopN 个词
获取 TopN 个词用于词云展示有多种排序方式,可以直接根据词频、文档频率或者 TF-IDF 等算法进行排序,本文仅根据词频求取 TopN。
M 个数字获取 TopN 有以下算法:
- M 小 N 小:快速选择算法
- M 大 N 小:小顶堆
- M 大 N 大:归并排序
本文采用小顶堆方式实现,对应JAVA中的优先队列数据结构 PriorityQueue:
/**
* 按出现次数,从高到低排序取 TopN
*
* @param data 词和排序数字对应的 Map
* @param TopN 词云展示的 TopN
* @return 前 N 个词和排序值
*/
private static List> order(Map data, int topN) {
PriorityQueue> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(data.size(), new Comparator>() {
@Override
public int compare(Map.Entry o1, Map.Entry o2) {
return o2.getValue().compareTo(o1.getValue());
}
});
for (Map.Entry entry : data.entrySet()) {
priorityQueue.add(entry);
}
//TODO 当前100词频一致时(概率极低)的处理办法,if( list(0).value == list(99).value ){xxx}
List> list = new ArrayList<>();
//统计结果队列size和topN值取较小值列表
int size = priorityQueue.size() <= topN ? priorityQueue.size() : topN;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
list.add(priorityQueue.remove());
}
return list;
} 3. IK 代码浅析
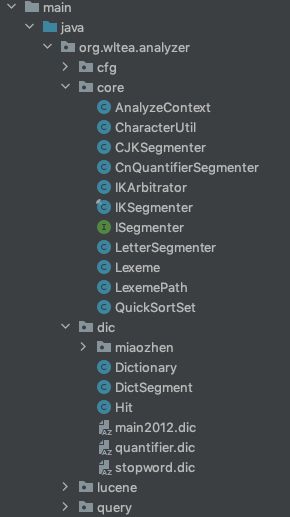
核心主类为IKSegmenter,需要关注的点有dic包也就是词典相关内容以及字符处理工具类CharacterUtil的identifyCharType()方法,目录结构如下:
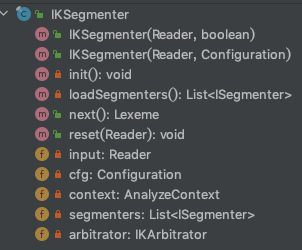
IKSegmenter类结构如下图,其中 init() 为私有方法,初始化加载词典采用非懒加载模式,在第一次初始化IKSegmenter实例时会调用并加载词典,代码位于结构图下方。
// IKSegmenter 类构造方法
public IKSegmenter(Reader input, Configuration cfg) {
this.input = input;
this.cfg = cfg;
this.init();
}
// IKSegmenter 类初始化
private void init() {
//初始化词典单例
Dictionary.initial(this.cfg);
//初始化分词上下文
this.context = new AnalyzeContext(this.cfg);
//加载子分词器
this.segmenters = this.loadSegmenters();
//加载歧义裁决器
this.arbitrator = new IKArbitrator();
}
// Dictionary 类初始化词典
public static Dictionary initial(Configuration cfg) {
if (singleton == null) {
synchronized (Dictionary.class) {
if (singleton == null) {
singleton = new Dictionary(cfg);
return singleton;
}
}
}
return singleton;
}词典私有构造方法Dictionary()内会加载 IK 自带的词典以及扩展词典,我们也可以把自己线上不变的词典放到这里这样IKAnalyzer.cfg.xml中就只需要配置经常变更词典即可。
private Dictionary(Configuration cfg) {
this.cfg = cfg;
this.loadMainDict();// 主词典以及扩展词典
this.loadmiaozhenDict();// 自定义词典加载,仿照其他方法即可
this.loadStopWordDict();// 扩展停词词典
this.loadQuantifierDict();// 量词词典
}在IKSegmenter类调用next()方法获取下一个词元时,会调用CharacterUtil类中的identifyCharType()方法识别字符种类,这里我们也可以自定义一些字符种类针对处理新兴的网络语言,如@、##等内容:
static int identifyCharType(char input) {
if (input >= '0' && input <= '9') {
return CHAR_ARABIC;
} else if ((input >= 'a' && input <= 'z') || (input >= 'A' && input <= 'Z')) {
return CHAR_ENGLISH;
} else {
Character.UnicodeBlock ub = Character.UnicodeBlock.of(input);
//caster 增加#为中文字符
if (ub == Character.UnicodeBlock.CJK_UNIFIED_IDEOGRAPHS
|| ub == Character.UnicodeBlock.CJK_COMPATIBILITY_IDEOGRAPHS
|| ub == Character.UnicodeBlock.CJK_UNIFIED_IDEOGRAPHS_EXTENSION_A ||input=='#') {
//目前已知的中文字符UTF-8集合
return CHAR_CHINESE;
} else if (ub == Character.UnicodeBlock.HALFWIDTH_AND_FULLWIDTH_FORMS //全角数字字符和日韩字符
//韩文字符集
|| ub == Character.UnicodeBlock.HANGUL_SYLLABLES
|| ub == Character.UnicodeBlock.HANGUL_JAMO
|| ub == Character.UnicodeBlock.HANGUL_COMPATIBILITY_JAMO
//日文字符集
|| ub == Character.UnicodeBlock.HIRAGANA //平假名
|| ub == Character.UnicodeBlock.KATAKANA //片假名
|| ub == Character.UnicodeBlock.KATAKANA_PHONETIC_EXTENSIONS) {
return CHAR_OTHER_CJK;
}
}
//其他的不做处理的字符
return CHAR_USELESS;
}由于 IK 内容不多,建议大家可以从头捋一遍,包括各个实现ISegmenter接口的各个自分词器等内容。
4. 进行词云展示
词云展示可以使用 Kibana 自带的词云 Dashboard,或者比较热门的 WordCloud。自己测试可以使用线上的微词云快速便捷查看词云效果:导入两列的 XLS 文件即可,左侧控制栏也可以对形状字体等进行配置美化。
展示效果如下图所示:
5. 总结
本文主要通过 IK 分词器实现了词频统计功能,用于词云的展示,不仅仅适用于 ES,任何数据源文档都可以进行词频统计。但是功能比较基础,感兴趣的同学可以实现一下词排序方式变更(tf/idf)、词性标注、实体识别和情感分析等功能;IK 分词器较为局限,需要使用 HanLP(自带词性标注)等更高级的分词器以及 NLP 相关知识来辅助,也可以参考百度 AI 的词法分析模块。
原文链接
本文为阿里云原创内容,未经允许不得转载。