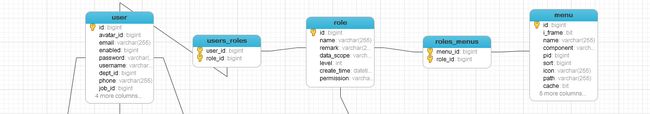
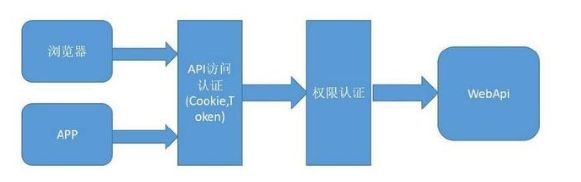
权限控制采用 RBAC思想。简单地说,一个用户拥有若干角色,每个角色拥有一个默认的权限,每一个角色拥有若干个菜单,菜单中存在按钮权限,这样,就构造成“用户-角色-菜单” 的授权模型。在这种模型中,用户与角色、角色与菜单之间构成了多对多的关系,如下图
1.简介
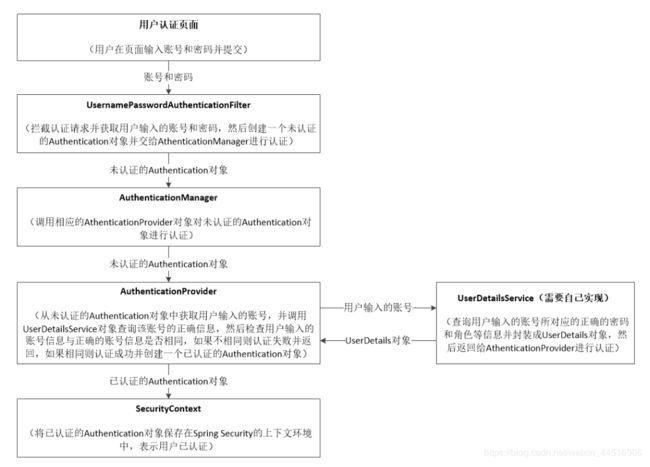
对访问权限进行控制,应用的安全性包括用户认证(Authentication)和用户授权(Authorization)两个部分。用户认证指的是验证某个用户是否为系统中的合法主体,也就是说用户能否访问该系统。用户授权指的是验证某个用户是否有权限执行某个操作。spring-security的主要核心功能为 认证和授权,所有的架构也是基于这两个核心功能去实现的。
2.原理
对Web资源进行保护,最好的办法莫过于Filter,要想对方法调用进行保护,最好的办法莫过于AOP。spring-security在我们进行用户认证以及授予权限的时候,通过各种各样的拦截器来控制权限的访问,从而实现安全。
spring-security的filter如何启用的,参考Spring Security实现原理剖析(一):filter的构造和初始化
3.核心组件
| 组件 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| SecurityContextHolder | 提供对SecurityContext的访问 |
| SecurityContext | 持有Authentication对象和其他可能需要的信息 |
| AuthenticationManager | 可以包含多个AuthenticationProvider |
| ProviderManager | AuthenticationManager接口的实现类 |
| AuthenticationProvider | 进行认证操作的类 调用其中的authenticate()方法去进行认证操作 |
| Authentication | Spring Security方式的认证主体 |
| GrantedAuthority | 对认证主题的应用层面的授权,含当前用户的权限信息,通常使用角色表示 |
| UserDetails | 构建Authentication对象必须的信息,可以自定义,可能需要访问DB得到 |
| UserDetailsService | 通过username构建UserDetails对象,通过loadUserByUsername根据userName获取UserDetail对象 (可以在这里基于自身业务进行自定义的实现 如通过数据库,xml,缓存获取等) |
4.加载机制
4.1 自定义配置类,继承WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter,重写configure方法
package com.zhouy.modules.security.config;
import com.zhouy.annotation.AnonymousAccess;
import com.zhouy.modules.security.security.JwtAuthenticationEntryPoint;
import com.zhouy.modules.security.security.JwtAuthorizationTokenFilter;
import com.zhouy.modules.security.service.JwtUserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.http.HttpMethod;
import org.springframework.security.access.prepost.PreAuthorize;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationManager;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.method.configuration.EnableGlobalMethodSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.WebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
import org.springframework.security.config.core.GrantedAuthorityDefaults;
import org.springframework.security.config.http.SessionCreationPolicy;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter;
import org.springframework.web.method.HandlerMethod;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.RequestMappingInfo;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true)
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Value("${jwt.header}")
private String tokenHeader;
// 登录验证类
private final UserDetailsService jwtUserDetailsService;
// token过滤器来验证token有效性类
private final JwtAuthorizationTokenFilter authorizationTokenFilter;
// 认证失败处理类
private final JwtAuthenticationEntryPoint unauthorizedHandler;
// spring上下文
private final ApplicationContext applicationContext;
public SecurityConfig(@Qualifier("jwtUserDetailsService") UserDetailsService jwtUserDetailsService,
JwtAuthorizationTokenFilter authorizationTokenFilter,
JwtAuthenticationEntryPoint unauthorizedHandler,
ApplicationContext applicationContext){
this.jwtUserDetailsService = jwtUserDetailsService;
this.authorizationTokenFilter = authorizationTokenFilter;
this.unauthorizedHandler = unauthorizedHandler;
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
@Autowired
public void configureGlobal(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.userDetailsService(jwtUserDetailsService).passwordEncoder(passwordEncoderBean());
}
// @Bean
// GrantedAuthorityDefaults grantedAuthorityDefaults() {
// // Remove the ROLE_ prefix
// return new GrantedAuthorityDefaults("");
// }
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoderBean() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
@Bean
@Override
public AuthenticationManager authenticationManagerBean() throws Exception { return super.authenticationManagerBean(); }
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity httpSecurity) throws Exception {
// 搜寻 匿名标记 url: PreAuthorize("hasAnyRole('anonymous')") 和 PreAuthorize("@el.check('anonymous')") 和 AnonymousAccess
Map handlerMethodMap = applicationContext.getBean(RequestMappingHandlerMapping.class).getHandlerMethods();
Set anonymousUrls = new HashSet<>();
for (Map.Entry infoEntry : handlerMethodMap.entrySet()) {
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = infoEntry.getValue();
AnonymousAccess anonymousAccess = handlerMethod.getMethodAnnotation(AnonymousAccess.class);
PreAuthorize preAuthorize = handlerMethod.getMethodAnnotation(PreAuthorize.class);
if (null != preAuthorize && preAuthorize.value().toLowerCase().contains("anonymous")) {
anonymousUrls.addAll(infoEntry.getKey().getPatternsCondition().getPatterns());
} else if (null != anonymousAccess && null == preAuthorize) {
anonymousUrls.addAll(infoEntry.getKey().getPatternsCondition().getPatterns());
}
}
httpSecurity
// 禁用 CSRF
.csrf().disable()
// 授权异常
.exceptionHandling().authenticationEntryPoint(unauthorizedHandler).and()
// 不创建会话
.sessionManagement().sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS).and()
// 过滤请求
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers(
HttpMethod.GET,
"/*.html",
"/**/*.html",
"/**/*.css",
"/**/*.js"
).anonymous()
// 放行OPTIONS请求
.antMatchers(HttpMethod.OPTIONS, "/**").permitAll()
// 自定义匿名访问所有url放行 : 允许 匿名和带权限以及登录用户访问
.antMatchers(anonymousUrls.toArray(new String[0])).permitAll()
// 除了上面外其他所有请求都需要认证
.anyRequest().authenticated()
// 防止iframe 造成跨域
.and().headers().frameOptions().disable();
httpSecurity
.addFilterBefore(authorizationTokenFilter, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);
}
}
4.2 spring-security认证过程
重写WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter的configureGlobal(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth)方法。
UserDetailsService实现
package com.zhouy.modules.security.service;
import com.zhouy.exception.BadRequestException;
import com.zhouy.modules.security.security.JwtUser;
import com.zhouy.modules.system.service.UserService;
import com.zhouy.modules.system.service.dto.DeptSmallDTO;
import com.zhouy.modules.system.service.dto.JobSmallDTO;
import com.zhouy.modules.system.service.dto.UserDTO;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UsernameNotFoundException;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.Optional;
@Service
public class JwtUserDetailsService implements UserDetailsService{
private final UserService userService;
private final JwtPermissionService jwtPermissionService;
public JwtUserDetailsService (UserService userService,JwtPermissionService jwtPermissionService){
this.userService = userService;
this.jwtPermissionService = jwtPermissionService;
}
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
UserDTO user = userService.findByName(username);
if (user == null){
throw new BadRequestException("账号不存在");
}else{
return createJwtUser(user);
}
}
public UserDetails createJwtUser(UserDTO user) {
return new JwtUser(user.getId(),
user.getUsername(),
user.getPassword(),
user.getAvatar(),
user.getEmail(),
user.getPhone(),
Optional.ofNullable(user.getDept()).map(DeptSmallDTO::getName).orElse(null),
Optional.ofNullable(user.getJob()).map(JobSmallDTO::getName).orElse(null),
jwtPermissionService.mapToGrantedAuthorities(user),
user.getEnabled(),
user.getCreateTime(),
user.getLastPasswordResetTime());
}
}
UserDetails
package com.zhouy.modules.security.security;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonIgnore;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Getter;
import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import java.sql.Timestamp;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
/**
* UserDetails
*/
@Getter
@AllArgsConstructor
public class JwtUser implements UserDetails {
@JsonIgnore
private final Long id;
private final String username;
@JsonIgnore
private final String password;
private final String avatar;
private final String email;
private final String phone;
private final String dept;
private final String job;
//所拥有的权限
@JsonIgnore
private final Collection authorities;
private final boolean enabled;
private Timestamp createTime;
@JsonIgnore
private final Date lastPasswordResetDate;
@JsonIgnore
@Override
public boolean isAccountNonExpired() {
return true;
}
@JsonIgnore
@Override
public boolean isAccountNonLocked() {
return true;
}
@JsonIgnore
@Override
public boolean isCredentialsNonExpired() {
return true;
}
@JsonIgnore
@Override
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
@Override
public boolean isEnabled() {
return enabled;
}
public Collection getRoles() {
return authorities.stream().map(GrantedAuthority::getAuthority).collect(Collectors.toSet());
}
}
UserDetails的权限信息
package com.zhouy.modules.security.service;
import com.zhouy.modules.system.domain.Menu;
import com.zhouy.modules.system.domain.Role;
import com.zhouy.modules.system.mapper.MenuMapper;
import com.zhouy.modules.system.mapper.RoleMapper;
import com.zhouy.modules.system.service.MenuService;
import com.zhouy.modules.system.service.dto.UserDTO;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheConfig;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.authority.SimpleGrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
@Service
@CacheConfig(cacheNames = "role")
public class JwtPermissionService {
private final RoleMapper roleMapper;
private final MenuService menuService;
public JwtPermissionService(RoleMapper roleMapper,MenuService menuService){
this.roleMapper = roleMapper;
this.menuService = menuService;
}
/**
* #p0.username:入参的第一个参数的username属性值
* @param userDTO
* @return
*/
@Cacheable(key = "'loadPermissionByUser:'+ #p0.username")
public Collection mapToGrantedAuthorities(UserDTO userDTO){
Set roles = roleMapper.findByUsers_Id(userDTO.getId());
Set permissions = roles.stream()
.filter(role -> StringUtils.isNoneBlank(role.getPermission()))
.map(Role::getPermission)
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
Set menu_permissions = roles.stream()
.flatMap(role -> menuService.findByRoleId(role.getId()).stream())
.filter(menu -> StringUtils.isNoneBlank(menu.getPermission()))
.map(Menu::getPermission)
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
// Set menu_permissions = new HashSet<>();
// for (Role role:roles) {
// List 4.3 “记住我”
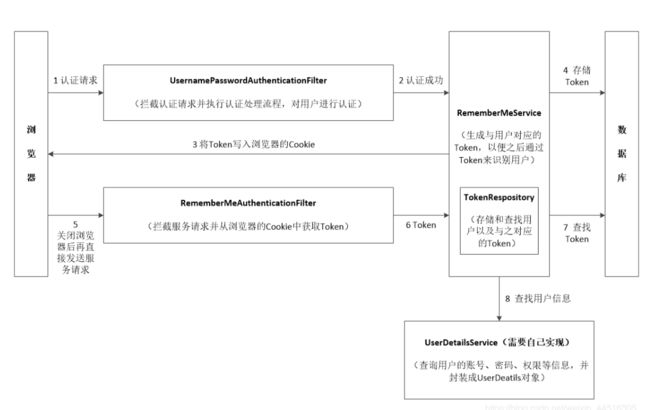
用户可以使用账号和密码进行认证,但是如果用户使用账号和密码进行认证时选择了“记住我”功能,则在有效期内,当用户关闭浏览器后再重新访问服务时,不需要用户再次输入账号和密码重新进行认证,而是通过“记住我”功能自动认证。
上述的用户认证处理逻辑都是基于Spring Security提供的默认实现,我们只需要自己实现一个UserDetailsService接口用于获取用户认证信息即可,十分简便。
4.4 spring-security权限控制过程
安全配置类上添加@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true)注解,开启方法级别的权限控制,在方法上添加@PreAuthorize("@el.check('job:list')")类似注解,实现在方法之前先做权限验证。
4.4.1 接口权限
Spring Security 提供了Spring EL表达式,允许我们在定义接口访问的方法上面添加注解,来控制访问权限,常用的 EL如下
| 表达式 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| hasRole([role]) | 当前用户是否拥有指定角色 |
| hasAnyRole([role1,role2]) | 多个角色是一个以逗号进行分隔的字符串。如果当前用户拥有指定角色中的任意一个则返回true。 |
下面的接口表示用户拥有 admin、menu:edit 权限中的任意一个就能能访问update方法,如果方法不加@preAuthorize注解,意味着所有用户都需要带上有效的 token 后能访问 update 方法
@Log(description = "修改菜单")
@PutMapping(value = "/menus")
@PreAuthorize("hasAnyRole('admin','menu:edit')")
public ResponseEntity update(@Validated @RequestBody Menu resources){
// 略
}
4.4.2 自定义权限验证
由于每个接口都需要给超级管理员放行,而使用 hasAnyRole('admin','user:list') 每次都需要重复的添加 admin 权限,因此有自定义权限验证方式,在验证的时候默认给拥有admin权限的用户放行。
源码:
package me.zhengjie.config;
import me.zhengjie.utils.SecurityUtils;
import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
/**
* 自定义权限验证:
*
* 由于每个接口都需要给超级管理员放行,
* 而使用 hasAnyRole('admin','user:list') 每次都需要重复的添加 admin 权限,
* 因此加入了自定义权限验证方式,
* 在验证的时候默认给拥有admin权限的用户放行。
*/
@Service(value = "el")
public class ElPermissionConfig {
public Boolean check(String ...permissions){
// 如果是匿名访问的,就放行
String anonymous = "anonymous";
if(Arrays.asList(permissions).contains(anonymous)){
return true;
}
// 获取当前用户的所有权限
List elPermissions = SecurityUtils.getUserDetails().getAuthorities().stream().map(GrantedAuthority::getAuthority).collect(Collectors.toList());
// 判断当前用户的所有权限是否包含接口上定义的权限
return elPermissions.contains("admin") || Arrays.stream(permissions).anyMatch(elPermissions::contains);
}
}
使用方式:
@PreAuthorize("@el.check('user:list')")
4.4.3 匿名访问
在我们使用的时候,有些接口是不需要验证权限,这个时候就需要我们给接口放行,使用方式如下
1.修改配置文件方式
// 关键代码,部分略
protected void configure(HttpSecurity httpSecurity) throws Exception {
httpSecurity
// 支付宝回调
.antMatchers("/api/aliPay/return").anonymous()
// 所有请求都需要认证
.anyRequest().authenticated();
httpSecurity
.addFilterBefore(authenticationTokenFilter, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);
}
2.使用注解方式
// 自定义匿名接口
@AnonymousAccess
package com.zhouy.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface AnonymousAccess {
}
重写WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter的configure(HttpSecurity httpSecurity)方法
1.权限验证之前先做jwt验证
//权限验证之前先JWT验证,验证token有效性、对等性
httpSecurity.addFilterBefore(authenticationTokenFilter, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);
自定义基于JWT的安全过滤器
package com.zhouy.modules.security.security;
import com.zhouy.modules.security.utils.JwtTokenUtil;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken;
import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContextHolder;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.WebAuthenticationDetailsSource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.filter.OncePerRequestFilter;
import sun.plugin.liveconnect.SecurityContextHelper;
import javax.servlet.FilterChain;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* token 校验
*/
@Component
public class JwtAuthorizationTokenFilter extends OncePerRequestFilter {
@Value("${jwt.online}")
private String onlineKey;
private final UserDetailsService userDetailsService;
private final JwtTokenUtil jwtTokenUtil;
private final RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
public JwtAuthorizationTokenFilter(@Qualifier("jwtUserDetailsService")UserDetailsService userDetailsService, JwtTokenUtil jwtTokenUtil, RedisTemplate redisTemplate){
this.userDetailsService = userDetailsService;
this.jwtTokenUtil = jwtTokenUtil;
this.redisTemplate = redisTemplate;
}
/**
* 这里无论访问哪个api都会进到这里,不管带不带token
* @param httpServletRequest
* @param httpServletResponse
* @param filterChain
* @throws ServletException
* @throws IOException
*/
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws ServletException, IOException {
String authToken = jwtTokenUtil.getToken(httpServletRequest);
OnlineUser onlineUser = null;
try{
onlineUser = (OnlineUser) redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(onlineKey + authToken);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (onlineUser!= null & SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication() ==null){
JwtUser userDetails = (JwtUser) this.userDetailsService.loadUserByUsername(onlineUser.getUserName());
if (jwtTokenUtil.validateToken(authToken,userDetails))
{
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(userDetails, null, userDetails.getAuthorities());
authentication.setDetails(new WebAuthenticationDetailsSource().buildDetails(httpServletRequest));
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authentication);
}
}
filterChain.doFilter(httpServletRequest,httpServletResponse);
}
}
权限验证配置
//权限验证
httpSecurity
// 禁用 CSRF
// https://blog.csdn.net/xiaoxinshuaiga/article/details/80766369
.csrf().disable()
// 没通过jwt验证,则执行自定义的响应处理
.exceptionHandling().authenticationEntryPoint(unauthorizedHandler).and()
// 不创建会话,要使用jwt托管安全信息,所以把Session禁止掉
/**
* ALWAYS,//总是会新建一个Session。
* NEVER,//不会新建HttpSession,但是如果有Session存在,就会使用它。
* IF_REQUIRED,//如果有要求的话,会新建一个Session。
* STATELESS;//不会新建,也不会使用一个HttpSession。
*/
.sessionManagement().sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS).and()
// 过滤请求
//使用 anonymous() 所有人都能访问,但是带上 token 访问后会报错
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers(
HttpMethod.GET,
"/*.html",
"/**/*.html",
"/**/*.css",
"/**/*.js"
).anonymous()
// swagger start
//使用 permitAll() 方法所有人都能访问,包括带上 token 访问
.antMatchers("/swagger-ui.html").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/swagger-resources/**").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/webjars/**").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/*/api-docs").permitAll()
// swagger end
// 文件
.antMatchers("/avatar/**").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/file/**").permitAll()
// 放行OPTIONS请求
.antMatchers(HttpMethod.OPTIONS, "/**").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/druid/**").permitAll()
// 自定义匿名访问所有url放行 : 允许 匿名和带权限以及登录用户访问
.antMatchers(anonymousUrls.toArray(new String[0])).permitAll()
// 所有请求都需要认证
.anyRequest().authenticated()
// 防止iframe 造成跨域
.and().headers().frameOptions().disable();
授权异常处理( 没通过jwt验证,则执行自定义的响应处理)
package com.zhouy.modules.security.security;
import org.springframework.security.core.AuthenticationException;
import org.springframework.security.web.AuthenticationEntryPoint;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.Serializable;
@Component
public class JwtAuthenticationEntryPoint implements AuthenticationEntryPoint,Serializable {
@Override
public void commence(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, AuthenticationException e) throws IOException, ServletException {
// 当用户尝试访问安全的REST资源而不提供任何凭据时,将调用此方法发送401 响应
httpServletResponse.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_UNAUTHORIZED, e==null?"Unauthorized":e.getMessage());
}
}
5.JWT生成token
5.1 简介
JSON Web Token(JWT)是目前分布式系统中最流行的跨域身份验证解决方案。
5.2 跨域身份验证
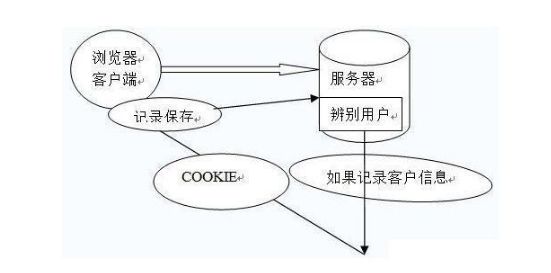
Internet服务无法与用户身份验证分开。一般过程如下。
1.用户向服务器发送用户名和密码。
2.验证服务器后,相关数据(如用户角色,登录时间等)将保存在当前会话中。
3.服务器向用户返回session_id,session信息都会写入到用户的Cookie。
4.用户的每个后续请求都将通过在Cookie中取出session_id传给服务器。
5.服务器收到session_id并对比之前保存的数据,确认用户的身份。
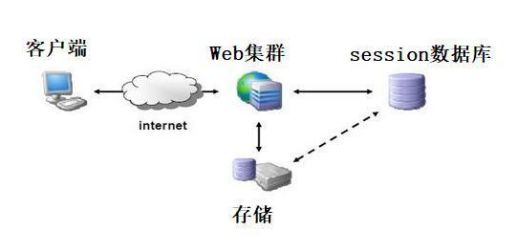
这种模式最大的问题是,没有分布式架构,无法支持横向扩展。如果使用一个服务器,该模式完全没有问题。但是,如果它是服务器群集或面向服务的跨域体系结构的话,则需要一个统一的session数据库库来保存会话数据实现共享,这样负载均衡下的每个服务器才可以正确的验证用户身份。
例如一个实际中常见的单点登陆的需求:站点A和站点B提供同一公司的相关服务。现在要求用户只需要登录其中一个网站,然后它就会自动登录到另一个网站。怎么做?
一种解决方案是听过持久化session数据,写入数据库或文件持久层等。收到请求后,验证服务从持久层请求数据。该解决方案的优点在于架构清晰,而缺点是架构修改比较费劲,整个服务的验证逻辑层都需要重写,工作量相对较大。而且由于依赖于持久层的数据库或者问题系统,会有单点风险,如果持久层失败,整个认证体系都会挂掉。
另外一种灵活的解决方案,通过客户端保存数据,而服务器根本不保存会话数据,每个请求都被发送回服务器。 JWT是这种解决方案的代表。
5.3 JWT原则
JWT的原则是在服务器身份验证之后,将生成一个JSON对象并将其发送回用户,如下所示。
{
"UserName": "Chongchong",
"Role": "Admin",
"Expire": "2018-08-08 20:15:56"
}
之后,当用户与服务器通信时,客户在请求中发回JSON对象。服务器仅依赖于这个JSON对象来标识用户。为了防止用户篡改数据,服务器将在生成对象时添加签名(有关详细信息,请参阅下文)。
服务器不保存任何会话数据,即服务器变为无状态,使其更容易扩展。
5.4 JWT数据结构
典型的,一个JWT看起来如下图。
改对象为一个很长的字符串,字符之间通过"."分隔符分为三个子串。注意JWT对象为一个长字串,各字串之间也没有换行符,此处为了演示需要,我们特意分行并用不同颜色表示了。每一个子串表示了一个功能块,总共有以下三个部分:
JWT的三个部分如下。JWT头、有效载荷和签名,将它们写成一行如下。
我们将在下面介绍这三个部分。
5.5 JWT头
JWT头部分是一个描述JWT元数据的JSON对象,通常如下所示。
{
"alg": "HS256",
"typ": "JWT"
}
在上面的代码中,alg属性表示签名使用的算法,默认为HMAC SHA256(写为HS256);typ属性表示令牌的类型,JWT令牌统一写为JWT。
最后,使用Base64 URL算法将上述JSON对象转换为字符串保存。
5.6 有效载荷
有效载荷部分,是JWT的主体内容部分,也是一个JSON对象,包含需要传递的数据。 JWT指定七个默认字段供选择。
iss:发行人
exp:到期时间
sub:主题
aud:用户
nbf:在此之前不可用
iat:发布时间
jti:JWT ID用于标识该JWT
除以上默认字段外,我们还可以自定义私有字段,如下例:
{
"sub": "1234567890",
"name": "chongchong",
"admin": true
}
请注意,默认情况下JWT是未加密的,任何人都可以解读其内容,因此不要构建隐私信息字段,存放保密信息,以防止信息泄露。
JSON对象也使用Base64 URL算法转换为字符串保存。
5..7 签名哈希
签名哈希部分是对上面两部分数据签名,通过指定的算法生成哈希,以确保数据不会被篡改。
首先,需要指定一个密码(secret)。该密码仅仅为保存在服务器中,并且不能向用户公开。然后,使用标头中指定的签名算法(默认情况下为HMAC SHA256)根据以下公式生成签名。
HMACSHA256(base64UrlEncode(header) + "." + base64UrlEncode(payload),
secret)
在计算出签名哈希后,JWT头,有效载荷和签名哈希的三个部分组合成一个字符串,每个部分用"."分隔,就构成整个JWT对象。
5.8 Base64URL算法
如前所述,JWT头和有效载荷序列化的算法都用到了Base64URL。该算法和常见Base64算法类似,稍有差别。
作为令牌的JWT可以放在URL中(例如api.example/?token=xxx)。 Base64中用的三个字符是"+","/"和"=",由于在URL中有特殊含义,因此Base64URL中对他们做了替换:"="去掉,"+"用"-"替换,"/"用"_"替换,这就是Base64URL算法,很简单把。
5.9. JWT的用法
客户端接收服务器返回的JWT,将其存储在Cookie或localStorage中。
此后,客户端将在与服务器交互中都会带JWT。如果将它存储在Cookie中,就可以自动发送,但是不会跨域,因此一般是将它放入HTTP请求的Header Authorization字段中。
Authorization: Bearer
当跨域时,也可以将JWT被放置于POST请求的数据主体中。
5.10 JWT问题和趋势
1、JWT默认不加密,但可以加密。生成原始令牌后,可以使用改令牌再次对其进行加密。
2、当JWT未加密方法是,一些私密数据无法通过JWT传输。
3、JWT不仅可用于认证,还可用于信息交换。善用JWT有助于减少服务器请求数据库的次数。
4、JWT的最大缺点是服务器不保存会话状态,所以在使用期间不可能取消令牌或更改令牌的权限。也就是说,一旦JWT签发,在有效期内将会一直有效。
5、JWT本身包含认证信息,因此一旦信息泄露,任何人都可以获得令牌的所有权限。为了减少盗用,JWT的有效期不宜设置太长。对于某些重要操作,用户在使用时应该每次都进行进行身份验证。
6、为了减少盗用和窃取,JWT不建议使用HTTP协议来传输代码,而是使用加密的HTTPS协议进行传输。
5.11 JWT工具类
package com.zhouy.modules.security.utils;
import com.zhouy.modules.security.security.JwtUser;
import com.zhouy.modules.system.domain.User;
import io.jsonwebtoken.Claims;
import io.jsonwebtoken.Clock;
import io.jsonwebtoken.Jwts;
import io.jsonwebtoken.SignatureAlgorithm;
import io.jsonwebtoken.impl.DefaultClock;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.security.Key;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.function.Function;
@Component
public class JwtTokenUtil {
private Clock clock = DefaultClock.INSTANCE;
@Value("${jwt.secret}")
private String secret;
@Value("${jwt.expiration}")
private Long expiration;
@Value("${jwt.header}")
private String tokenHeader;
// 生成token
public String generateToken(JwtUser user){
Key key = new SecretKeySpec(secret.getBytes(), SignatureAlgorithm.HS512.getJcaName());
final Date createdDate = clock.now();
final Date expirationDate = new Date(createdDate.getTime()+expiration);
return Jwts.builder()
.setClaims(Jwts.claims())
.setSubject(user.getUsername())
.setIssuedAt(createdDate)
.setExpiration(expirationDate)
.signWith(SignatureAlgorithm.HS512, key)
.compact();
}
// 获取token
public String getToken(HttpServletRequest request){
final String requestHeader = request.getHeader(tokenHeader);
if (requestHeader != null && requestHeader.startsWith("Bearer ")){
return requestHeader.substring(7);
}
return null;
}
// 获取token创建日期
private Date getIssuedAtDateFromToken(String token){
return getClaimFromToken(token,Claims::getIssuedAt);
}
private T getClaimFromToken(String token,Function claimsResolver){
Key key = new SecretKeySpec(secret.getBytes(), SignatureAlgorithm.HS512.getJcaName());
final Claims claims = Jwts.parser()
.setSigningKey(key)
.parseClaimsJws(token)
.getBody();
return claimsResolver.apply(claims);
}
private Boolean isTokenExpired(String token) {
final Date expiration = getClaimFromToken(token, Claims::getExpiration);;
return expiration.before(clock.now());
}
private Boolean isCreatedBeforeLastPasswordReset(Date created, Date lastPasswordReset) {
return (lastPasswordReset != null && created.before(lastPasswordReset));
}
public Boolean validateToken(String token, UserDetails userDetails) {
JwtUser jwtUser = (JwtUser) userDetails;
final Date created = getIssuedAtDateFromToken(token);
// 如果token存在,且token创建日期 > 最后修改密码的日期 则代表token有效
return (!isTokenExpired(token)
&& !isCreatedBeforeLastPasswordReset(created,jwtUser.getLastPasswordResetDate()));
}
}
6. spring-security与JWT引入
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
2.1.0.RELEASE
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-security
io.jsonwebtoken
jjwt
0.9.1
7.jwt的yaml配置
#jwt
jwt:
header: Authorization
secret: mySecret
# token 过期时间/毫秒,6小时 1小时 = 3600000 毫秒
expiration: 21600000
# 在线用户key
online: online-token
# 验证码
codeKey: code-key
8.前后端分离跨域处理
package com.zhouy.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.CorsRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.EnableWebMvc;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.ResourceHandlerRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc
public class ConfigurerAdapter implements WebMvcConfigurer{
/**
* 全局跨越配置,核心配置。
* 用于前后端分离,前端能成功调用后端api
*
* 2020-04-14 23:33:00
* 前天晚上和今天晚上一直卡在这个地方,一直以为spring-security没有配置正确,
* 可怎么配置都不行,其实现在想起来是我自己理解错了,一开始前端调用获取验证码api,
* 而该api我是在spring-security配置中做了放行的,可前端一直报跨域请求错误,
* 我就认为没有spring-security没有配置禁止跨域,因为一旦跨域那么spring-security的鉴权和认证都失效,
* 这么理解是完全错误的,即使允许了跨域spring-security还是会去认证和鉴权的,但是不允许跨域,
* 那前端根本就进不了后台,还谈何认证和授权。
* @param registry
*/
@Override
public void addCorsMappings(CorsRegistry registry) {
registry.addMapping("/**")
.allowCredentials(true)
.allowedHeaders("*")
.allowedOrigins("*")
.allowedMethods("GET","POST","DELETE");
}
@Override
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
registry.addResourceHandler("/**").addResourceLocations("classpath:/META-INF/resources/").setCachePeriod(0);
}
}