Redis持久化-RDB
目录
1 官网介绍
2 什么是RDB
3 Fork
4 dump.rdb 文件
4 如何触发RDB快照
5 RDB的优缺点
1 官网介绍
在指定的时间间隔内将内存中的数据集快照写入磁盘,也就是行话讲的Snapshot快照,它恢复时是将快照直接读到内存里
2 什么是RDB
Redis会单独创建一个(fork)子进程来进行持久化,会先将数据写到一个临时文件中,待持久化过程都结束了,在用这个临时文件替换上次持久化的文件。整个过程中,主进程是不进行任何IO操作的,这就确保了极高的性能,如果要进行大规模数据的恢复,且对于数据的恢复完整性不是十分敏感,那RDB方式要比AOF方式更加的高效。RDB的缺点是最后一次持久化的数据容易丢失
3 Fork
fork的作用是复制一个与当前进程一样的进程。新进程的所有数据(变量,环境变量、程序计数器)都和原进程一样,但是是一个全新的进程,并作为原进程的子进程
4 dump.rdb 文件
RDB保存的就是dump.rdb文件。一下是redis.conf中关于快照的部分配置文件
################################ SNAPSHOTTING ################################
# Save the DB to disk.
#
# save
#
# Redis will save the DB if both the given number of seconds and the given
# number of write operations against the DB occurred.
#
# Snapshotting can be completely disabled with a single empty string argument
# as in following example:
#
# save ""
#
# Unless specified otherwise, by default Redis will save the DB:
# * After 3600 seconds (an hour) if at least 1 key changed
# * After 300 seconds (5 minutes) if at least 100 keys changed
# * After 60 seconds if at least 10000 keys changed
#
# You can set these explicitly by uncommenting the three following lines.
#
# save 3600 1
# save 300 100
# save 60 10000
# By default Redis will stop accepting writes if RDB snapshots are enabled
# (at least one save point) and the latest background save failed.
# This will make the user aware (in a hard way) that data is not persisting
# on disk properly, otherwise chances are that no one will notice and some
# disaster will happen.
#
# If the background saving process will start working again Redis will
# automatically allow writes again.
#
# However if you have setup your proper monitoring of the Redis server
# and persistence, you may want to disable this feature so that Redis will
# continue to work as usual even if there are problems with disk,
# permissions, and so forth.
stop-writes-on-bgsave-error yes
# Compress string objects using LZF when dump .rdb databases?
# By default compression is enabled as it's almost always a win.
# If you want to save some CPU in the saving child set it to 'no' but
# the dataset will likely be bigger if you have compressible values or keys.
rdbcompression yes
# Since version 5 of RDB a CRC64 checksum is placed at the end of the file.
# This makes the format more resistant to corruption but there is a performance
# hit to pay (around 10%) when saving and loading RDB files, so you can disable it
# for maximum performances.
#
# RDB files created with checksum disabled have a checksum of zero that will
# tell the loading code to skip the check.
rdbchecksum yes
# Enables or disables full sanitation checks for ziplist and listpack etc when
# loading an RDB or RESTORE payload. This reduces the chances of a assertion or
# crash later on while processing commands.
# Options:
# no - Never perform full sanitation
# yes - Always perform full sanitation
# clients - Perform full sanitation only for user connections.
# Excludes: RDB files, RESTORE commands received from the master
# connection, and client connections which have the
# skip-sanitize-payload ACL flag.
# The default should be 'clients' but since it currently affects cluster
# resharding via MIGRATE, it is temporarily set to 'no' by default.
#
# sanitize-dump-payload no
# The filename where to dump the DB
dbfilename dump.rdb
# Remove RDB files used by replication in instances without persistence
# enabled. By default this option is disabled, however there are environments
# where for regulations or other security concerns, RDB files persisted on
# disk by masters in order to feed replicas, or stored on disk by replicas
# in order to load them for the initial synchronization, should be deleted
# ASAP. Note that this option ONLY WORKS in instances that have both AOF
# and RDB persistence disabled, otherwise is completely ignored.
#
# An alternative (and sometimes better) way to obtain the same effect is
# to use diskless replication on both master and replicas instances. However
# in the case of replicas, diskless is not always an option.
rdb-del-sync-files no
由以上的配置文件可知它的更改策略可以自己配置:
由以上的注释掉的策略来说在3600秒内修改1次,或300秒内修改100次,或60秒内修改10000次时会生成快照文件。
注意:如果在规定的时间内达到了修改次数,时间没到时不会生成dump.rdb文件的。另外:如果在规定时间内没有达到修改次数也想要生成快照文件,只需要执行save命令即可。
stop-writes-on-bgsave-error yes另外,redis.conf配置文件中关于快照的这一行表示:如果后台在save的时候出错了,那么前台就停止写的操作。如果不在乎数据的一致性可以将yes改为no
rdbcompression yes对于存储到磁盘中的快照,可以设置是否进行压缩存储。如果是的话redis会采用LZF算法进行压缩。如果你不行消耗CPU来进行压缩的话可以设置为关闭此功能。
rdbchecksum yes在存储快照后,还可以让redis使用CRC64算法来进行数据校验,但是这样做会增加大约10%的性能消耗,如果希望获取到最大的性能提升,可以关闭此功能。
4 如何触发RDB快照
1) 配置文件中默认的快照配置(在多少秒内,数据修改了多少次)
2) 命令save或者是bgsave(bgsave:redis会在后台异步进行快照操作,快照同时还可以响应客户端请求,可以通过lastsave命令获取最后一次成功执行快照的时间)
3) 执行flushdb命令,也会产生dump,rdb文件,但里面是空的,毫无意义
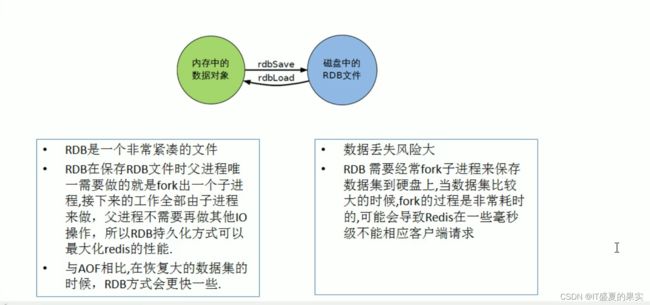
5 RDB的优缺点
优点:
1)适合大规模的数据恢复
2) 对数据完整性和一致性要求不高
缺点:
1)在一定时间间隔做一次备份,所以redis意外down掉的话,就会丢失最后一次快照后的所有修改
2)Fork的时候,内存中的数据被克隆了一份,大致两倍的膨胀性需要考虑
动态停止保存RDB规则的方法:redis-cli config set save ""