11、C#处理程序异常的技术
1、捕获异常
- 异常是程序运行中发生的错误,异常处理是程序设计的一部分。错误的出现并不总是编写应用程序者的原因,有时应用程序会因为终端用户操作而发生错误。无论如何,在编写程序前,都应预测应用程序和代码出现的错误。
1.1处理异常三种语句
try……catch^=…… //捕获异常
try……fianlly…… //清除异常
try……catch……finally //处理所有异常
1.2 捕获异常
try
{
//包含容易产生异常的代码
}
catch
{
//异常处理代码
}
用户不能获得对异常对象的访问,而对该对象含有重要的出错信息,也就不能得到出错的信息
try
{
//包含容易产生异常的代码
}
catch(异常类,异常实例对象)
{
//异常处理代码
}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace _1_捕获异常
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//利用try catch语句捕获数组的越界问题
int[] myint = { 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20 };
try
{
for (int i = 0; i <= myint.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(myint[i]);
}
}
//词条语句虽然可以捕获异常,并给出提示,但并不能很只能的秒数异常的原因
//catch
//{
// Console.Write("异常已经发生");
//}
catch (Exception myex)
{
Console.WriteLine(myex.Message.ToString()); //Message是获取秒数当前异常信息
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
2、清除、处理所有异常
如果客户对产生的错误不进行处理,而消除产生的错误分配的资源
try
{
//包含容易产生异常的代码
}
finally
{
//用于消除try块中分配的任何资源以及运行任何即使在发生异常时,也必须执行的代码
//无论是否发生异常都会执行finally块中的语句
}
最好的组合,合并两种错误处理技术,即捕获错误、消除并继续执行应用程序
try
{
//包含容易产生异常的代码
}
catch(异常类,异常实例对象)
{
//异常处理代码
}
finally
{
//用于消除try块中分配的任何资源以及运行任何即使在发生异常时,也必须执行的代码
//无论是否发生异常都会执行finally块中的语句
}
- 处理异常会大大地降低性能,不要将它用在控制撑场程序流程中,如有可能检测到代码中可能导致异常的状态,请执行这种操作。不要在处理该状态之前捕获异常本身,如除一个数时,可通过if先判断除数数据不等0,然后在进行相除
3、引发异常
在编写程序时,有时可能要引发异常,以便捕获异常
引发异常的格式 throw new 异常类(异常信息);
异常类:系统预定义的或自定义的
异常信息:类型是字符串 例如 “格式转换错误”
实例:为Program类定义一个将字符串转换成整数的私有静态方法ConvertStringToInt;它含有一个字符串类型参数,返回一个整数,然后通过这个使用方法将一个不能转换成整数的字符串转换成整数,故引发异常。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace _3_引发异常
{
class Program
{
private static int ConvertStringToInt(string mystr)
{
int outnum;
try
{
outnum = Convert.ToInt32(mystr);
return outnum;
}
catch
{
//只有这里抛出异常,在调用时才能按照抛出异常的内容显示异常信息
//此处抛出异常,也相当于将异常信息当做结果返回调用.
//此处不抛出异常信息,作为有返回值的方法会报错
throw new FormatException("格式转换不正确(自定义内容)");
}
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string mystr = "123darly";
try
{
int myint = Program.ConvertStringToInt(mystr);
Console.WriteLine(myint);
}
catch (FormatException exf)
{
Console.WriteLine(exf.Message.ToString()); ;
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
4、预定义异常类(1)
Exception:所有异常对象的基类
SystemException:运行时产生的所有错误的基类
IndexOutOfRangeException:当一个数组的下标超出范围时运行时引发
NullReferenceException:当一个空对象被引用时运行时引发
ArgumentException:所有参数异常的基类
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace _4_预定义异常类
{
class Program
{
static int DivideByTwo(int num)
{
if (num % 2 == 1) throw new ArgumentException("此处参数必须是偶数","num"); //第一个参数是提示,第二个参数是出错的参数
return num / 2;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//IndexOutOfRangeException
int[] myint = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0 };
try
{
for (int i = 0; i < myint.Length + 1; i++) Console.WriteLine(myint[i]);
}
catch (IndexOutOfRangeException exIOR)
{
Console.WriteLine(exIOR.Message.ToString());
}
//NullReferenceException
string mystr = null;
try
{
Console.WriteLine(mystr.ToString());
}
catch (NullReferenceException exNull)
{
Console.WriteLine(exNull.Message.ToString());
}
//ArgumentException
try
{
Console.WriteLine(DivideByTwo(9));
}
catch (ArgumentException exArg)
{
Console.WriteLine("9不能被2整除");
Console.WriteLine(exArg.Message.ToString());
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
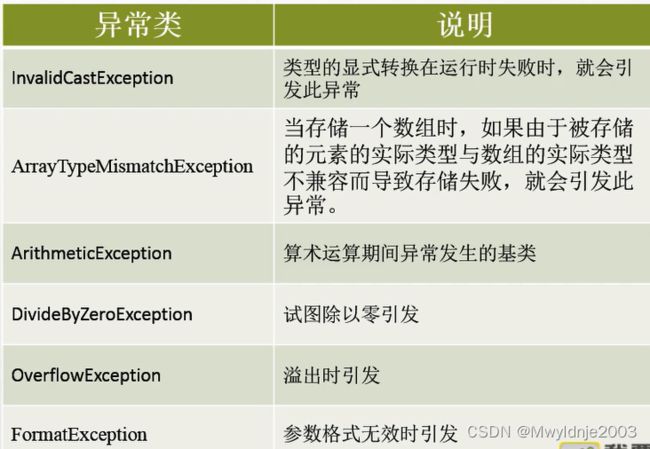
5、预定义异常类(2)
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace _5_预定义异常类_2_
{
class Program
{
//InvalidCastException
static void Main(string[] args)
{
bool myboll = true;
try
{
char mychar = Convert.ToChar(myboll);
Console.WriteLine(mychar);
}
catch (InvalidCastException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message.ToString());
}
//ArrayTypeMismatchException
string[] mystrArry = { "cat", "dog", "pig", };
Object[] myobj = mystrArry;
foreach (Object outobj in myobj)
{
Console.WriteLine(outobj);
Console.WriteLine(outobj.GetType());
}
try
{
myobj[2] = 13;
}
catch (ArrayTypeMismatchException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message.ToString());
}
//ArithmeticException
try
{
int num = 10;
Console.WriteLine(num/0);
}
catch (ArithmeticException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message.ToString());
}
//DivideByZeroException
try
{
int num = 10;
Console.WriteLine(num / 0);
}
catch (DivideByZeroException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message.ToString());
}
//OverflowException
try
{
byte mybyte = Convert.ToByte(Console.ReadLine());
}
catch (OverflowException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message.ToString());
}
//FormatException见第3节
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
6、自定义异常类
- C#语言虽然预定义了许多异常类,但是,在有一些场合,创建自己的异常类可能会更方便。自定义异常类是通过继承system.Excepiton类来创建自己的异常类
- 声明异常格式:class 自定义的异常类名:Exception{}
- 引发异常格式:throw(自定义的异常类名);
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace _6_自定义异常类
{
class MyException:Exception
{
public MyException(string message):base(message)
{
}
}
}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace _6_自定义异常类
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
Console.WriteLine("这行代码在引发异常前被执行");
string mystr = "这是我自己定义的异常";
throw new MyException(mystr);
Console.WriteLine("由于引发了异常,这行代码不会被执行");
}
catch (MyException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message.ToString());
//Console.WriteLine("这是我自己定义的异常");
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
任务实施
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 实例
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("请输入一个整数");
try
{
while (true)
{
int myint = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
double mydouble = 1.0 / myint;
Console.WriteLine("该数{0}的倒数是{1}", myint, mydouble);
}
}
catch (DivideByZeroException)
{
Console.WriteLine("产生除零异常");
}
catch (OverflowException)
{
Console.WriteLine("溢出异常");
}
catch (FormatException)
{
Console.WriteLine("转换异常");
}
catch (Exception)
{
Console.WriteLine("其他异常");
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}