一、为什么使用移动面积算法
解:常规波峰判定是采用高低阈值的方法进行筛除,但会出现如图情况。左边噪声高于实际波峰(绿色)高度,甚至高于阈值(红色),会造成波峰高度的误判等。
二、移动面积算法的雏形与原理
选定矩形(mask),此处我设其宽为波峰的1/2,高为波峰最高,面积为S2。通过mask在I-V图中,从左到右移动,计算出每一次移动后mask捕捉到的波峰面积(黄色),黄色面积为S1。
通过ratio = S1 / S2,将得到每一个 mask 位置不一样的黄色面积占比,我称之为 ratio。如图,明显可见最右边的 mask 中,黄色占比大于50%(或0.5)。则阈值考量可以设置为0.5~1之间,具体须看实际数据。
ratio > 0.5 时,则 mask 捕捉到了波峰位置。
而且值得注意的是,图二和图一的峰的横坐标位置不一致,由此可见移动面积算法存在高灵活性的巨大优势。
三、代码注释0~7的细解:
0. 限制范围0.1V~1.1V (排除0.1V附近的干扰噪声)
1. 计算峰最高点位置,坐标(V, Imax)
2. 确定移动矩形(称之为mask) 的长和宽,delta_I 和delta_V
3. 确定 mask 移动的初始电压位置(X轴)为0.1V, 限制范围:0A
area = (Vn - Vn-1) * (In + In-1)/2 ;
比值: # mask从横坐标左往右移动,分别计算并保存每次的ratio值
ratio = 峰波形在mask 所占面积 / mask 总面积 ;
4. 从保存的所有ratio 值,求最大ratio(最大ratio值大于0.5,则可说明波峰存在)
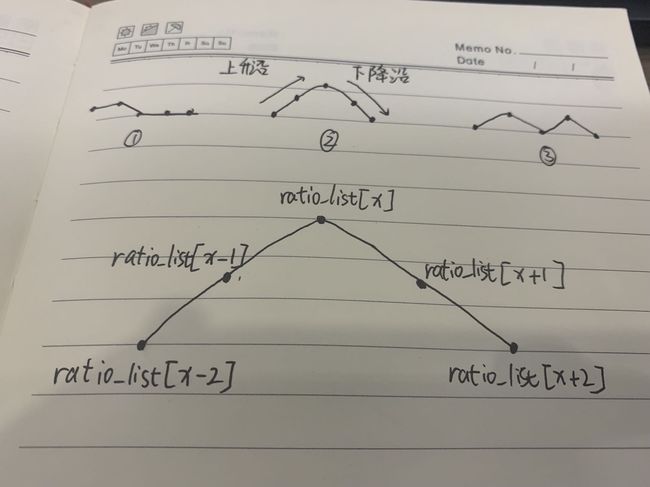
5.五点法确定峰顶点位置
(1)从保存的所有ratio 值,求ratio>0.7 的数量 # 标准峰型通常为30个,此数量体现峰的宽度,筛除脉冲形状的峰
(2)五点法,前三点上升沿与后三点下降沿,判断峰是否为峰,代码中满足①②时皆为波峰顶点,③存在情况过多且不符。
6. 计算单峰面积(不包括其余噪声,即从峰宽两侧算起) # 面积算法(包括噪声)
此计算公式存在些许不足,有一定偏差,可忽视不用。
7. fitter 滤波。
拟合波形,多项式拟合法。作参考。 # 目前屏蔽,暂时不用
四、全篇代码:
def get_moverectangleratiovalue(volts, diffcrnts, weno, movevspos=0.1, detwidth=0.1, noise_line=0, ratiothreshold=0.40, ratiocntlimit=0): #--Mei """Get moving rectangle mask ratio value.(Area of interest is called mask.) The area occupancy ratio Args: volts (list) -- List of voltages (float) in volts diffcrnts (list) -- List of hybrid-to-base current differences (float) in amps weno(int) -- we number detwidth (float) -- The width of the interval used to detect the calculated mask voltage range(Usually 0~0.2V) movevspos (float) -- The starting voltage value used to move the mask (Usually 0~0.5V) noise_line (float) -- Below the apparent noise line is noise, and the ampere value of the noise line is used as the baseline for mask calculation ratiothreshold (float) -- In the mask, the threshold of the ratio of the waveform area to the total area of the mask rectangle (threshold size: 0~1) If there is a peak, usually 0.5~1 ratiocntlimit (int) -- Determines the peak width.If the ratio count(>0.5)is greater than the limit, Returns: result (bool) -- Determine whether there is a peak by this ratio and return the result. If the ratio is higher than "ratiothreshold" return True, and lower than "ratiothreshold" return False. ratio (float*1.00) -- The ratio of the area of the waveform to the area of the mask ampere_max (float) -- Maximum current value peakmainarea (float) -- Peak area except for noise range(not the peak range) """ # init parameter result = False result_code = 0 # Tracing the cause of NEG results (0 ~ 5) 0 means POS result. Other means NEG. limit_volts = [] # V>0 limit_amps = [] # when V>0 peak_pos = (0, 0) # max peak pos (V, A) mask_wavearea = 0 mask_waveareamovelist = [] ratio_list = [] list_area = [] ratio_cnt = 0 peakposlis = [] def find_cmax(volts, diffcrnts, detv1=0.1, detv2=1.0): # Find max diff current value maxcrnt = -1e20 maxv = 9 # Impossibly large value for x, volt in enumerate(volts): if volt < detv1: continue if volt > detv2: break if diffcrnts[x] > maxcrnt: maxcrnt = diffcrnts[x] maxv = volts[x] return (maxcrnt, maxv) # Normally we will set the noise to 0 or to 2.5e-8 A(real noise) in order to count. for index, volt in enumerate(volts): if volt >= movevspos: # Usually the point before 0.1V is not used as a reference. limit_volts.append(volt) limit_amps.append(diffcrnts[index]) if len(limit_amps) <= 0: limit_amps.append(0) # current_max = max(limit_amps) # current_max = get_peakdetectionvalue # 0. Ensure that 'limit_volts' and 'ratio_list' list have the same number of indexes current_max, volt_max = find_cmax(volts, diffcrnts) if current_max < noise_line: # noise line is 0 to 2.5e-8(A) print("return False: Max ampere is lower than noise line") result_code = 1 return False, 0.05, 0, 0 # print("===================================================================") # 1.The first "for" loop is for finding the peak pos for x, volt in enumerate(volts): # Now I limit the first voltage start value (volt > 0). if diffcrnts[x] == current_max and volt >= 0: # find max peak point pos (volt, ampere) peak_volt = volts[x] peak_pos = (peak_volt, current_max) # 2.The second "for" loop is for finding the valley pos. # Now that the valley pos is not used, if there is a better way to judge the valley pos ?? for x, volt in enumerate(volts): if volt > 0 and volt < peak_pos[0] and diffcrnts[x-1] < noise_line and diffcrnts[x] >= noise_line: valley_pos = (volt, diffcrnts[x]) # Mask is the valley pos(x_min, y_min) between peak pos(x_max,y_max) of rectangle area. delta_V = detwidth #(peak_pos[0] - valley_pos[0]) # Don't pay attention to the impact of noise line for now.(Reserved for subsequent development.) delta_A = (peak_pos[1] - noise_line) # eliminate noise about 0.25e-7 or lower. mask_totalarea = delta_V * delta_A # print("mask total area = %s" % mask_totalarea) # 3. The third "for" loop is for calculating every moving wave area on mask. def mask_algorithm(volts, diffcrnts, noise_line, movevspos): for x, volt in enumerate(volts): # Determine the starting point pos of the mask # checking mask range mask_Vmax = volt + delta_V # new range from max volt of mask mask_rect = (volt, noise_line, mask_Vmax, peak_pos[1]) # (Vmin,Amin,Vmax,Amax) if volt >= movevspos: # movevspos or the first volt.This is defined mask moving start pos. # count the wave area on mask mask_wavearea = 0 # reset new wave area is 0 for index, v in enumerate(volts): # Use this FOR loop to count waveform surface base in rectangular area. # Only count the waveform area of the rectangular area. if v >= volt and v <= mask_Vmax: # Each cycle calculates a slice in the mask, # and each slice is determined by two adjacent points of VOLT. ampere2 = diffcrnts[index] ampere1 = diffcrnts[index - 1] # Ensure that diffcrnts are larger than the noise line.Otherwise equal to the noise line. if diffcrnts[index] < noise_line: ampere2 = noise_line if diffcrnts[index - 1] < noise_line: ampere1 = noise_line if diffcrnts[index] > peak_pos[1]: ampere2 = peak_pos[1] if diffcrnts[index - 1] > peak_pos[1]: ampere1 = peak_pos[1] # Only count ampere more than noise_line 0.25(e-7) # area = (V1-V2)*(A2+A1-3*A0)/2; A0 = 0 area = (v - volts[index - 1]) * (ampere2 + ampere1 - (3 * noise_line)) / 2 # print("area = (%s - %s) * (%s + %s -3(%s)) / 2 = %s" % (volts[index], volts[index-1], ampere2, ampere1, noise_line, area)) mask_wavearea += area list_area.append(area) # print("every mask area = %s" % mask_wavearea) # print("********************* every wave area is equaled all slice area ************************") mask_waveareamovelist.append(mask_wavearea) # print("mask wave area = %s" % mask_wavearea) # 3.1 Save the waveform to the mask area ratio for singlearea in mask_waveareamovelist: ratio_list.append(round(singlearea / mask_totalarea, 5)) # print(ratio_list) # print("++++++++++++++++++++++++++ all for loop end +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ ") # 3. Calculating every moving wave area on mask. mask_algorithm(volts, diffcrnts, noise_line, movevspos) # 4.When there is more than one peak or no peak, the judgment result is False. ratio = max(ratio_list) def multipeaks_screen(ratio, ratio_cnt, result, result_code): maxratio = 0 if ratio >= ratiothreshold: # if someone scale more than ratio threshold(usually 0.5) 计数:比值大于阈值的情况 for rat in ratio_list: if rat >= ratiothreshold: ratio_cnt += 1 if ratio_cnt > 30: # ratio_cnt 体现的是峰的宽度,ratio_cnt 越大峰越宽。 result_code = 3 result = False maxratio = 0 # print("weno = %s, ratio count = %s, max-ratio = %s" % (weno, ratio_cnt, ratio)) # Normally it is 30. You can also use the PRINT above to check the ratio count of the normal peak shape. if ratio_cnt > ratiocntlimit and ratio_cnt <= 30: # If the ratio count is greater than the limit, the waveform is too wide. result = False maxratio = ratio # If the waveform is too wide, we need confirm the waveform is whether the waveform is multiple peaks. if ratio_cnt <= 25 and ratio_cnt > 0: peak_cnt = 0 volts_xlist = [] for i, v in enumerate(volts): volts_xlist.append(i) for x, ratio_x in enumerate(ratio_list): # If there is not noly one peak(maybe more), I set a limit for cheaking a thing called'AS A PEAK'. if ratio_x > ratiothreshold: # 五点法确定峰顶点位置 if x > 2 and x+2 <= len(ratio_list)-1 :#and x % 2 == 0: if (ratio_x - ratio_list[x-1]) >= 0 and (ratio_x - ratio_list[x+1]) >= 0: if (ratio_list[x-2] - ratio_list[x-1]) < 0 and (ratio_list[x+1] - ratio_list[x+2]) > 0: # Limit the peak appearing before 0.2V, which is regarded as invalid. if limit_volts[x] > 0.4 and limit_volts[x] < 1.1: peak_cnt += 1 maxratio = ratio_x # peakposlis.append((volts[x], diffcrnts[x])) # log peak pos(Shaped like a peak) # print("Peak pos = (%s, %s); index = %s" % (volts[x], diffcrnts[x], x)) # print("Peak volt pos= %s" % (limit_volts[x])) # print("peak cnt = %s" % peak_cnt) if peak_cnt > 1 or peak_cnt == 0: result = False maxratio = 0 result_code = 4 if peak_cnt == 1: result = True # else: # result = True else: result_code = 2 return maxratio, ratio_cnt, result, result_code # 5. Multi peaks screening ratio, ratio_cnt, result, result_code = multipeaks_screen(ratio, ratio_cnt, result, result_code) def calculate_area(x, noiseline, volts): # Area calculation formula a2 = diffcrnts[x] a1 = diffcrnts[x - 1] area = (volts[x] - volts[x - 1]) * (a2 + a1 - (3 * noiseline)) / 2 return area # 6. Calculate the only one peak area if result: # 多峰筛除之后,Ture结果进行 # calculate peak area 计算单峰面积 peakposlis.append(peak_pos) # print(peak_pos) peakarealis = [] temp_min = peak_pos[1]/2 log_index = 0 if peakposlis != []: for m, (x, y) in enumerate(peakposlis): for n, volt in enumerate(volts): if volt > 0.3: value = abs(diffcrnts[n] - (y/2)) # half peak high 半峰高度与 if value <= temp_min: temp_min = value log_index = n # print(peakposlis[m][0]) # print(volts[log_index]) min_halfwidth = round(abs(peakposlis[m][0] - volts[log_index]), 4) # print("min_halfwidth=%s" % min_halfwidth) x_min = peakposlis[m][0] - (min_halfwidth * 2) x_max = peakposlis[m][0] + (min_halfwidth * 2) # print("x_min=%s, x_max=%s" % (x_min,x_max)) peakarea = 0 for index, v in enumerate(volts): if v >= x_min and v <= x_max: peakarea += calculate_area(index, noise_line, volts) # print("peak area = %s" % peakarea) peakarealis.append(peakarea) peakmainarea = 0 maxv = 0 for peakarea in peakarealis: if maxv < peakarea: maxv = peakarea peakmainarea = maxv if peakmainarea == 0: result = False result_code = 4 ra_index = ratio_list.index(max(ratio_list, key=abs)) # print("ratio max index = %s " % ra_index) # print("===========================================================================") else: peakmainarea = 0 # 7. if not result and dglobs.fiter_enable and False: # debug fitting and sum res # Before fitting debug befo_maxratio = ratio befo_res = result calculate_y = fitter.polynomial_fittodraw(volts, diffcrnts, 12, weno) # only a fiter and draw to show # Fit the original data and output fitted current data diffs_fited = fitter.polynomial_fitting(volts, diffcrnts, 15) # complex degree = 15 mask_algorithm(volts, diffs_fited, noise_line, movevspos) after_maxratio = max(ratio_list) after_res = None if after_maxratio > ratiothreshold: after_res = True else: after_res = False result_code = 5 result = after_res # print("enable fitter and adjust result") # getamps_leastsquarefitting(volts, diffcrnts) # print("-----------------Area-Mei----------------") # print("we: %s, res: %s, ratio: %s, A max: %s, peak area: %s" # % (weno, result, ratio, current_max, peakmainarea)) # debug+ # calculate_y = fitter.polynomial_fittodraw(volts, diffcrnts, 12, weno) # only a fiter and draw to show # time.sleep(1) # Save volt (value/pos) of the max ampere # for index, volt in enumerate(volts): # if diffcrnts[index] == current_max: # dglobs.allwes_peakpos.append(volt) # debug+ # print("weno = %s, ratio count = %s, max-ratio = %s" % (weno, ratio_cnt, ratio)) # print("result code = %s" % result_code) return result, ratio, current_max, peakmainarea, result_code