Mybatis源码解读
1 源码下载
学习源码之前需要先将源码下载下来,这里需要下载mybatis源码和mybatis-parent源码,下载地址如下:
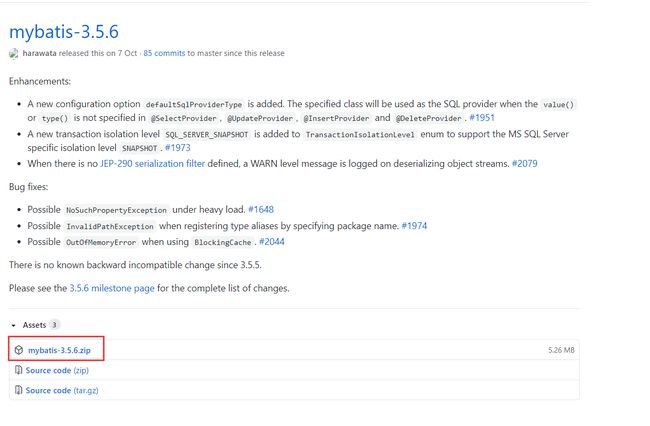
下载mybatis源码时选择对应的Release版本:
下载完mybatis源码之后,将其导入到IDEA中,注意pom.xml中的依赖版本
org.mybatis
mybatis-parent
32
../parent-mybatis-parent-32/pom.xml
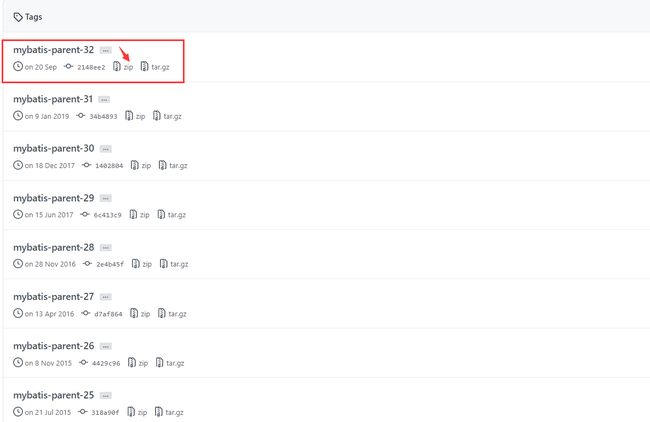
其中关注version为32,relativePath为编译后的mybatis-parent中pom.xml文件的相对路径。从https://github.com/mybatis/parent下载对应版本的依赖
下载之后,解压先编译mybatis-parent-32在编译mybatis
编译mybatis-parent-32:进入目录执行
mvn clean install -Dmaven.test.skip
编译mybatis:进入目录执行
mvn clean install -Dmaven.test.skip
显示BUILD SUCCESS表示导入成功,就可以阅读源码了。
2 源码解读
我们知道mybatis是一款在持久层使用的框架,其内部封装了JDBC的操作,首先看看JDBC操作数据库的过程
package cn.jdbc;
import java.sql.*;
public class jdbcTest { //定义测试类
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
String driver = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";//1.定义driverClass
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test"; //2.定义url
String username = "root"; //3.定义用户名,写你想要连接到的用户。
String password = "123456"; //4.用户密码。
String sql = "select * from user"; //5.你想要查找的表名。
Class.forName(driver);//6.注册驱动程序
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);//7.获取数据库连接
//Statement stmt=conn.createStatement(); //8.构造一个statement对象来执行sql语句
pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//CallableStatement cstmt = conn.prepareCall("{CALL demoSp(? , ?)}") ;
rs = pstmt.executeQuery();//9.执行sql
while (rs.next()) { //10.遍历结果集
//do something...
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (rs != null) {//11.关闭记录集
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (pstmt != null) {//12.关闭声明的对象
try {
pstmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null) {//13.关闭连接
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
以上流程大致分为四步分别是获取连接对象、执行sql语句、处理结果集、关闭连接
mybatis源码也为我们封装了这四步
2.1 获取连接对象
首先看看mybatis官方入门文档,需要创建一个xml文件,并且定义数据源DataSource以及事务管理器TransactionFactory,然后通过加载解析xml文件生成Configuration,下面给出xml文件的简单示例:
其中environment包含数据源和事务管理器,mapper有三个属性分别是resource、class、url
resource表示Mapper.xml文件的资源路径
class表示Mapper接口的路径,这里搜索Mapper.xml文件默认从Mapper接口下查找
url路径对应的是网络上了某个文件,注意file:// 前缀 +路径+文件名
当然也可以使用package表示指定包下的所有Mapper
mybatis主要通过SqlSession操作数据的,对于SqlSession的获取首先需要构建一个SqlSessionFactory工厂,其代码如下:
String resource = "org/mybatis/example/mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
跟踪build方法发现最终执行
//最终执行此方法 reader输入流,environment环境,properties配置文件
public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader, String environment, Properties properties) {
try {
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(reader, environment, properties); return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.
}
}
}
其中XMLConfigBuilder中的parser方法跟踪如下:
//解析Configuration文件
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
try {
// issue #117 read properties first
//配置文件
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));
Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings"));
loadCustomVfs(settings);
loadCustomLogImpl(settings);
//配置别名
typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
//插件
pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));
objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory"));
settingsElement(settings);
// read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631
//环境 1.DataSource 2.TransactionFactory
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
//解析mapper
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
这里重点注意的是解析mapper,在Configuration中的MapperRegistry中添加mapper具体如下:
//在MapperRegistry中添加一个Mapper
public void addMapper(Class type) {
if (type.isInterface()) {
if (hasMapper(type)) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<>(type));
// It's important that the type is added before the parser is run
// otherwise the binding may automatically be attempted by the
// mapper parser. If the type is already known, it won't try.
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}
其中knownMappers的定义如下:
private final Map, MapperProxyFactory> knownMappers = new HashMap<>();
是一个map,map的key是Mapper的类型,value是Mapper的代理工厂MapperProxyFactory,使用该工厂动态代理出Mapper,MapperProxyFactory定义一个map:
private final Map methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
key是Method,value是MapperMethodInvoker,它是MapperProxy类的内部接口。
使用MapperAnnotationBuilder解析Mapper
//解析mapper
public void parse() {
String resource = type.toString();
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
//加载xml文件
loadXmlResource();
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
assistant.setCurrentNamespace(type.getName());
parseCache();
parseCacheRef();
for (Method method : type.getMethods()) {
if (!canHaveStatement(method)) {
continue;
}
if (getAnnotationWrapper(method, false, Select.class, SelectProvider.class).isPresent()
&& method.getAnnotation(ResultMap.class) == null) {
//构建resultMap
parseResultMap(method);
}
try {
//构建sql
parseStatement(method);
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteMethod(new MethodResolver(this, method));
}
}
}
parsePendingMethods();
}
这里主要关心构建sql过程,跟踪parseStatement方法
void parseStatement(Method method) {
final Class parameterTypeClass = getParameterType(method);
final LanguageDriver languageDriver = getLanguageDriver(method);
getAnnotationWrapper(method, true, statementAnnotationTypes).ifPresent(statementAnnotation -> {
//构建SqlSource
final SqlSource sqlSource = buildSqlSource(statementAnnotation.getAnnotation(), parameterTypeClass, languageDriver, method);
final SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = statementAnnotation.getSqlCommandType();
final Options options = getAnnotationWrapper(method, false, Options.class).map(x -> (Options)x.getAnnotation()).orElse(null);
final String mappedStatementId = type.getName() + "." + method.getName();
final KeyGenerator keyGenerator;
String keyProperty = null;
String keyColumn = null;
if (SqlCommandType.INSERT.equals(sqlCommandType) || SqlCommandType.UPDATE.equals(sqlCommandType)) {
// first check for SelectKey annotation - that overrides everything else
SelectKey selectKey = getAnnotationWrapper(method, false, SelectKey.class).map(x -> (SelectKey)x.getAnnotation()).orElse(null);
if (selectKey != null) {
keyGenerator = handleSelectKeyAnnotation(selectKey, mappedStatementId, getParameterType(method), languageDriver);
keyProperty = selectKey.keyProperty();
} else if (options == null) {
keyGenerator = configuration.isUseGeneratedKeys() ? Jdbc3KeyGenerator.INSTANCE : NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;
} else {
keyGenerator = options.useGeneratedKeys() ? Jdbc3KeyGenerator.INSTANCE : NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;
keyProperty = options.keyProperty();
keyColumn = options.keyColumn();
}
} else {
keyGenerator = NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;
}
Integer fetchSize = null;
Integer timeout = null;
StatementType statementType = StatementType.PREPARED;
ResultSetType resultSetType = configuration.getDefaultResultSetType();
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
boolean flushCache = !isSelect;
boolean useCache = isSelect;
if (options != null) {
if (FlushCachePolicy.TRUE.equals(options.flushCache())) {
flushCache = true;
} else if (FlushCachePolicy.FALSE.equals(options.flushCache())) {
flushCache = false;
}
useCache = options.useCache();
fetchSize = options.fetchSize() > -1 || options.fetchSize() == Integer.MIN_VALUE ? options.fetchSize() : null; //issue #348
timeout = options.timeout() > -1 ? options.timeout() : null;
statementType = options.statementType();
if (options.resultSetType() != ResultSetType.DEFAULT) {
resultSetType = options.resultSetType();
}
}
String resultMapId = null;
if (isSelect) {
ResultMap resultMapAnnotation = method.getAnnotation(ResultMap.class);
if (resultMapAnnotation != null) {
resultMapId = String.join(",", resultMapAnnotation.value());
} else {
resultMapId = generateResultMapName(method);
}
}
//构建MappedStatement
assistant.addMappedStatement(
mappedStatementId,
sqlSource,
statementType,
sqlCommandType,
fetchSize,
timeout,
// ParameterMapID
null,
parameterTypeClass,
resultMapId,
getReturnType(method),
resultSetType,
flushCache,
useCache,
// TODO gcode issue #577
false,
keyGenerator,
keyProperty,
keyColumn,
statementAnnotation.getDatabaseId(),
languageDriver,
// ResultSets
options != null ? nullOrEmpty(options.resultSets()) : null);
});
}
进入buildSqlSource方法查看解析sql的过程
//主要解析sql的方法
public String parse(String text) {
if (text == null || text.isEmpty()) {
return "";
}
// search open token
int start = text.indexOf(openToken);
if (start == -1) {
//找不到说明没有参数
return text;
}
//有参数,将字符串转化为数组进行操作
char[] src = text.toCharArray();
int offset = 0;
//保留字符串构建器
final StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
//表达式这里存储#{}或者${}括号中间的
StringBuilder expression = null;
do {
if (start > 0 && src[start - 1] == '\\') {
// this open token is escaped. remove the backslash and continue.
// \\${}或者\\#{}这时表示字符串"\${}"或者"\#{}"
// select * from user where id=\\#{id} => select * from user where id=#{id}
builder.append(src, offset, start - offset - 1).append(openToken);
offset = start + openToken.length();
} else {
// found open token. let's search close token.
if (expression == null) {
expression = new StringBuilder();
} else {
expression.setLength(0);
}
//将openToken之间的拷贝到builder中
builder.append(src, offset, start - offset);
//偏移openToken.length个长度
offset = start + openToken.length();
//从偏移开始找closeToken位置
int end = text.indexOf(closeToken, offset);
while (end > -1) {
if (end > offset && src[end - 1] == '\\') {
// this close token is escaped. remove the backslash and continue.
// 若是\\}情况则跳过,继续找下一个}
expression.append(src, offset, end - offset - 1).append(closeToken);
offset = end + closeToken.length();
end = text.indexOf(closeToken, offset);
} else {
//expression存储openToken和closeToken之间的字符
//找到了closeToken直接跳出循环
expression.append(src, offset, end - offset);
break;
}
}
//走到这里 1.找不到closeToken 这里end=-1 后面的全部填上
if (end == -1) {
// close token was not found.
builder.append(src, start, src.length - start);
offset = src.length;
} else {
//有openToken和closeToken 将其替换成? 并且将参数设置到Handler中
builder.append(handler.handleToken(expression.toString()));
offset = end + closeToken.length();
}
}
start = text.indexOf(openToken, offset);
} while (start > -1);
if (offset < src.length) {
builder.append(src, offset, src.length - offset);
}
return builder.toString();
}
执行完毕后Configuration对象构造成功,返回DefaultSqlSessionFactory,通过openSession方法获得SqlSession对象。
2.2 执行sql语句
生成Mapper代理对象过程如下
DefaultSqlSession--->Configuration--->MapperRegistry--->MapperProxyFactory
获取代理对象之后执行方法时会自动调用MapperProxy中的invoke方法,跟踪
//执行主入口,根据sql类型执行相应的分支
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
switch (command.getType()) {
//新增逻辑
case INSERT: {
//将args对象数组,转换成sql参数
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case DELETE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case SELECT:
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
//返回值是list
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
if (method.returnsOptional()
&& (result == null || !method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) {
result = Optional.ofNullable(result);
}
}
break;
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}
其中Insert、Update、Delete的返回结果都是int或者long 其表示操作影响行数,而Select的返回结果有
Void、many、one、map、cursor,下面分析Select过程
public List query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
//queryStack缓存栈指针为0 且可以清空缓存 则清空缓存
clearLocalCache();
}
List list;
try {
queryStack++;
list = resultHandler == null ? (List) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
//从数据库查数据
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
queryStack--;
}
if (queryStack == 0) {
for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) {
deferredLoad.load();
}
// issue #601
deferredLoads.clear();
if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
// issue #482
clearLocalCache();
}
}
return list;
}
其中有缓存直接从缓存中拿,没有缓存则从数据库查
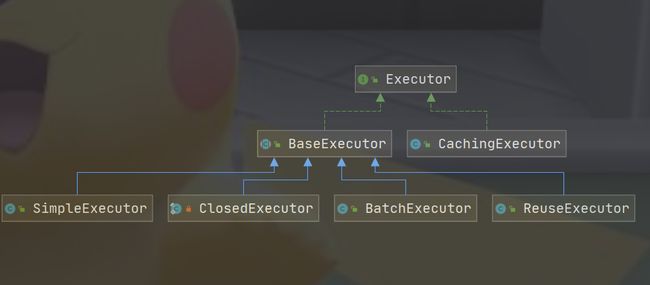
执行器的继承结构如下:
最终在相应的Executor执行相应的逻辑,以query为例
public List doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
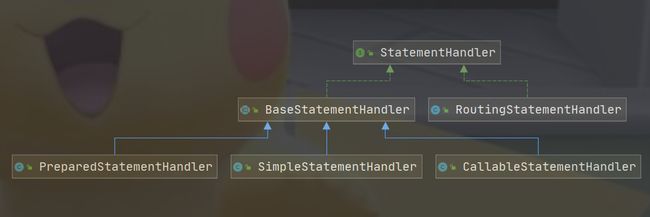
下面是StatementHandler的继承结构
其中PreparedStatementHandler、SimpleStatementHandler、CallableStatementhandler分别对应Statement接口中的PreparedStatement、Statement、CallableStatement
2.3 处理结果集
进入query方法处理结果集
//处理结果集
@Override
public List