一.内存布局
如上图,内存布局共分为如下几个区:
-
内核:由系统控制处理的,大概有占有1个GB -
栈:函数、方法、局部变量等会储存在这里面 -
堆:通过alloc分配对象、block copy... -
bss:未初始化的全局变量、静态变量... -
data:已初始化的全局变量、静态变量... -
text: 程序代码 -
保留:由系统控制处理
(0xC0000000 = 3221225472 = 3GB),所以从栈区到保留区占有3GB
栈区从高地址向低地址延伸,堆区从低地址向高地址攀升
bss和data区在不区分是否初始化时,一般统称全局区
栈区内存地址:⼀般为:0x7开头
堆区内存地址:⼀般为:0x6开头
数据段,BSS内存地址:⼀般为:0x1开头
二.内存管理方案
iOS提供三种内存管理方案,TaggedPointer,NONPOINTER_ISA,散列表.
1.TaggedPointer:
- ⼩对象-NSNumber,NSDate等
- 不再是一个简单的地址,而是真正的值,里面包含值,类型等等。它不再是一个对象,内存不存储在堆中,也不需要
malloc/free - 读取速度快3倍,创建速度提升106倍。
位运算知识补充
- (1)对同一个数值异或()两次,能回到原来的值(ab^b=a)。
1010 1101 a
^ 0000 1100 b
---------
1010 0001
^ 0000 1100 b
---------
1010 1101 a
- (2)按位取反(~)
~100001
-------
011110
- (3)左移(<<)右移(>>)操作
10000111 << 3 = 10000111000
10000111 >> 3 = 10000
- (4)位与(&)位或(|), (a | b ^ b = b)
1000 1100 a
| 1010 1010 b
------------
1010 1110
& 1010 1010 b
-------------
1010 1010 b
源码分析
-
TaggedPointer生成:
#if __has_feature(objc_fixed_enum) || __cplusplus >= 201103L
enum objc_tag_index_t : uint16_t
#else
typedef uint16_t objc_tag_index_t;
enum
#endif
{
// 60-bit payloads
OBJC_TAG_NSAtom = 0,
OBJC_TAG_1 = 1,
OBJC_TAG_NSString = 2,
OBJC_TAG_NSNumber = 3,
OBJC_TAG_NSIndexPath = 4,
OBJC_TAG_NSManagedObjectID = 5,
OBJC_TAG_NSDate = 6,
// 60-bit reserved
OBJC_TAG_RESERVED_7 = 7,
// 52-bit payloads
OBJC_TAG_Photos_1 = 8,
OBJC_TAG_Photos_2 = 9,
OBJC_TAG_Photos_3 = 10,
OBJC_TAG_Photos_4 = 11,
OBJC_TAG_XPC_1 = 12,
OBJC_TAG_XPC_2 = 13,
OBJC_TAG_XPC_3 = 14,
OBJC_TAG_XPC_4 = 15,
OBJC_TAG_First60BitPayload = 0,
OBJC_TAG_Last60BitPayload = 6,
OBJC_TAG_First52BitPayload = 8,
OBJC_TAG_Last52BitPayload = 263,
OBJC_TAG_RESERVED_264 = 264
};
#if __has_feature(objc_fixed_enum) && !defined(__cplusplus)
typedef enum objc_tag_index_t objc_tag_index_t;
#endif
static inline void * _Nonnull
_objc_makeTaggedPointer(objc_tag_index_t tag, uintptr_t value)
{
// PAYLOAD_LSHIFT and PAYLOAD_RSHIFT are the payload extraction shifts.
// They are reversed here for payload insertion.
// assert(_objc_taggedPointersEnabled());
if (tag <= OBJC_TAG_Last60BitPayload) {
// assert(((value << _OBJC_TAG_PAYLOAD_RSHIFT) >> _OBJC_TAG_PAYLOAD_LSHIFT) == value);
uintptr_t result =
(_OBJC_TAG_MASK |
((uintptr_t)tag << _OBJC_TAG_INDEX_SHIFT) |
((value << _OBJC_TAG_PAYLOAD_RSHIFT) >> _OBJC_TAG_PAYLOAD_LSHIFT));
return _objc_encodeTaggedPointer(result);
} else {
// assert(tag >= OBJC_TAG_First52BitPayload);
// assert(tag <= OBJC_TAG_Last52BitPayload);
// assert(((value << _OBJC_TAG_EXT_PAYLOAD_RSHIFT) >> _OBJC_TAG_EXT_PAYLOAD_LSHIFT) == value);
uintptr_t result =
(_OBJC_TAG_EXT_MASK |
((uintptr_t)(tag - OBJC_TAG_First52BitPayload) << _OBJC_TAG_EXT_INDEX_SHIFT) |
((value << _OBJC_TAG_EXT_PAYLOAD_RSHIFT) >> _OBJC_TAG_EXT_PAYLOAD_LSHIFT));
return _objc_encodeTaggedPointer(result);
}
}
源码中通过对类型tag和value进行一些列位运算
tag << _OBJC_TAG_INDEX_SHIFT说明最后一位是用来存储类型,
(value << _OBJC_TAG_PAYLOAD_RSHIFT) >> _OBJC_TAG_PAYLOAD_LSHIFT)存储value,
_OBJC_TAG_MASK用来快速标记这是一个TaggedPointer类型
然后调用_objc_encodeTaggedPointer进行混淆,这也是为什么直接打印地址无法看出这是一个特殊地址的原因。
- 编码,解码
_objc_encodeTaggedPointer和_objc_decodeTaggedPointer使用的就是a^b^b=a这个原理.
static inline void * _Nonnull
_objc_encodeTaggedPointer(uintptr_t ptr)
{
return (void *)(objc_debug_taggedpointer_obfuscator ^ ptr);
}
static inline uintptr_t
_objc_decodeTaggedPointer(const void * _Nullable ptr)
{
return (uintptr_t)ptr ^ objc_debug_taggedpointer_obfuscator;
}
static void
initializeTaggedPointerObfuscator(void)
{
if (sdkIsOlderThan(10_14, 12_0, 12_0, 5_0, 3_0) ||
// Set the obfuscator to zero for apps linked against older SDKs,
// in case they're relying on the tagged pointer representation.
DisableTaggedPointerObfuscation) {
objc_debug_taggedpointer_obfuscator = 0;
} else {
// Pull random data into the variable, then shift away all non-payload bits.
arc4random_buf(&objc_debug_taggedpointer_obfuscator,
sizeof(objc_debug_taggedpointer_obfuscator));
objc_debug_taggedpointer_obfuscator &= ~_OBJC_TAG_MASK;
}
}
在sdkIsOlderThan(10_14, 12_0, 12_0, 5_0, 3_0说明在这之前的版本objc_debug_taggedpointer_obfuscator为0,可以直接看出地址的特殊性。单只之后的版本就无法看出了,需要手动_objc_decodeTaggedPointer才能看到.
- 判断是否为
TaggedPointer类型
static inline bool
_objc_isTaggedPointer(const void * _Nullable ptr)
{
return ((uintptr_t)ptr & _OBJC_TAG_MASK) == _OBJC_TAG_MASK;
}
通过位运算补充中的(4)a|b&b=b可快速判断是否为TaggedPointer
-
TaggedPointer取值
static inline uintptr_t
_objc_getTaggedPointerValue(const void * _Nullable ptr)
{
// assert(_objc_isTaggedPointer(ptr));
uintptr_t value = _objc_decodeTaggedPointer(ptr);
uintptr_t basicTag = (value >> _OBJC_TAG_INDEX_SHIFT) & _OBJC_TAG_INDEX_MASK;
if (basicTag == _OBJC_TAG_INDEX_MASK) {
return (value << _OBJC_TAG_EXT_PAYLOAD_LSHIFT) >> _OBJC_TAG_EXT_PAYLOAD_RSHIFT;
} else {
return (value << _OBJC_TAG_PAYLOAD_LSHIFT) >> _OBJC_TAG_PAYLOAD_RSHIFT;
}
}
首先进行_objc_decodeTaggedPointer解密
然后使用和TaggedPointer生成算法相反方式取出值.
实践
extern uintptr_t objc_debug_taggedpointer_obfuscator;
int a = 10;
NSString * t = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"jensen"];
NSNumber *aNum = @(a);// 64
NSLog(@"%s %p %@ 0x%lx",object_getClassName(aNum),aNum,aNum,_objc_encodeTaggedPointer(aNum));
NSLog(@"%s %p %@
0x%lx",object_getClassName(t),t,t,_objc_encodeTaggedPointer(t));
uintptr_t _objc_encodeTaggedPointer(uintptr_t ptr)
{
return (objc_debug_taggedpointer_obfuscator ^ ptr);
}
打印结果:
__NSCFNumber 0xa39a2c1af54f3585 10 0xb0000000000000a3
NSTaggedPointerString 0xb39cca4dc3a96380 jensen 0xa006e65736e656a6
总结
TaggedPointer是通过对值和类型进行一系列位运算生成数值。通过这个数据可以快速判断类型,和获取对应的值。对小类型(NSNumber,NSDate等)将不需要在使用64位来存储,大大节省占用的内存,提高创建和访问效率。
面试题
- (void)taggedPointer_1 {
dispatch_queue_t queue = dispatch_queue_create("jensen", DISPATCH_QUEUE_CONCURRENT);
for (int i = 0; i<10000; i++) {
dispatch_async(queue, ^{
self.nameStr = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"jensen"];
NSLog(@"%@",self.nameStr);
});
}
}
- (void)taggedPointer_2 {
dispatch_queue_t queue = dispatch_queue_create("jensen2", DISPATCH_QUEUE_CONCURRENT);
for (int i = 0; i<10000; i++) {
dispatch_async(queue, ^{
self.nameStr = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"大家一起搞起来"];
NSLog(@"%@",self.nameStr);
});
}
}
测试结果:taggedPointer_1运行正常,taggedPointer_2却崩溃,什么原因?
从崩溃信息中,我们知道是释放过度导致的。
代码中self.nameStr = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"大家一起搞起来"];,调用属性的set方法。
static inline void reallySetProperty(id self, SEL _cmd, id newValue, ptrdiff_t offset, bool atomic, bool copy, bool mutableCopy)
{
if (offset == 0) {
object_setClass(self, newValue);
return;
}
id oldValue;
id *slot = (id*) ((char*)self + offset);
if (copy) {
newValue = [newValue copyWithZone:nil];
} else if (mutableCopy) {
newValue = [newValue mutableCopyWithZone:nil];
} else {
if (*slot == newValue) return;
newValue = objc_retain(newValue);
}
if (!atomic) {
oldValue = *slot;
*slot = newValue;
} else {
spinlock_t& slotlock = PropertyLocks[slot];
slotlock.lock();
oldValue = *slot;
*slot = newValue;
slotlock.unlock();
}
objc_release(oldValue);
}
从上述代码,我们知道对象赋值(set)实际上是retain/copy新值,释放(release)旧值。由于多线程操作不断的retain/release,这种情况下是不安全的。会造成对象过度释放的情况。
__attribute__((aligned(16), flatten, noinline))
id
objc_retain(id obj) {
if (!obj) return obj;
if (obj->isTaggedPointer()) return obj;
return obj->retain();
}
__attribute__((aligned(16), flatten, noinline))
void
objc_release(id obj) {
if (!obj) return;
if (obj->isTaggedPointer()) return;
return obj->release();
}
如果是TaggedPointer类型,在retain/release会直接retuan,不会真正的调用对象的retain/release。当对象赋值为jensen属于TaggedPointer类型,当字符串中包含有中文,或者长度比较长,TaggedPointer无法存储,那就不是TaggedPointer了。
2.NONPOINTER_ISA:⾮指针型isa
什么是NONPOINTER_ISA?
我们知道在OC中,万物皆对象objc_object。
struct objc_object {
Class _Nonnull isa OBJC_ISA_AVAILABILITY;
};
在此之前,我一直认为isa就是仅仅只是一个指针,实例对象的isa指向类,类对象的指针指向元类。但其实isa除包含指针外还包含其他信息,例如对象的引用计数、是否包含C++析构、是否被弱引用等等...这时这个isa就是NONPOINTER_ISA。isa是isa_t类型的联合体,其内部通过位域技术储存很多了对象的信息。
union isa_t
{
isa_t() { }
isa_t(uintptr_t value) : bits(value) { }
Class cls;
uintptr_t bits;
# if __arm64__
# define ISA_MASK 0x0000000ffffffff8ULL
# define ISA_MAGIC_MASK 0x000003f000000001ULL
# define ISA_MAGIC_VALUE 0x000001a000000001ULL
struct {
uintptr_t nonpointer : 1;
uintptr_t has_assoc : 1;
uintptr_t has_cxx_dtor : 1;
uintptr_t shiftcls : 33; // MACH_VM_MAX_ADDRESS 0x1000000000
uintptr_t magic : 6;
uintptr_t weakly_referenced : 1;
uintptr_t deallocating : 1;
uintptr_t has_sidetable_rc : 1;
uintptr_t extra_rc : 19;
# define RC_ONE (1ULL<<45)
# define RC_HALF (1ULL<<18)
};
}
-
nonpointer:表示是否对 isa 指针开启指针优化
0:纯isa指针,1:不⽌是类对象地址,isa 中包含了类信息、对象的引⽤计数等 -
has_assoc:关联对象标志位,0没有,1存在 -
has_cxx_dtor:该对象是否有 C++ 或者 Objc 的析构器,如果有析构函数,则需要做析构逻辑,
如果没有,则可以更快的释放对象 -
shiftcls:
存储类指针的值。开启指针优化的情况下,在 arm64 架构中有 33 位⽤来存储类指针。 -
magic:⽤于调试器判断当前对象是真的对象还是没有初始化的空间 -
weakly_referenced:标识对象是否被指向或者曾经指向⼀个 ARC 的弱变量,
没有弱引⽤的对象可以更快释放。 -
deallocating:标志对象是否正在释放内存 -
has_sidetable_rc:当对象引⽤技术⼤于 10 时,则需要借⽤该变量存储进位 -
extra_rc:表示该对象的引⽤计数值,实际上是引⽤计数值减 1,
例如,如果对象的引⽤计数为 10,那么 extra_rc 为 9。如果引⽤计数⼤于 10,
则需要使⽤到下⾯的 has_sidetable_rc。
注:当对象重写过retain,release,allocWithZone(rr/awz),那就不再是一个NONPOINTER_ISA
3.散列表:引⽤计数表,弱引⽤表
SideTables是系统维护的哈希表,内部存储了一张张散列表SideTable.每一张散列表主要用来记录对象的引用计数,弱引用对象存储等。
SideTables
SideTables数据结构:
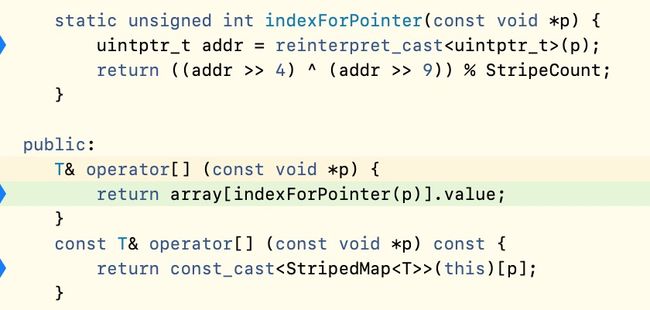
class StripedMap {
#if TARGET_OS_IPHONE && !TARGET_OS_SIMULATOR
enum { StripeCount = 8 };
#else
enum { StripeCount = 64 };
#endif
struct PaddedT {
T value alignas(CacheLineSize);
};
PaddedT array[StripeCount];
static unsigned int indexForPointer(const void *p) {
uintptr_t addr = reinterpret_cast(p);
return ((addr >> 4) ^ (addr >> 9)) % StripeCount;
}
public:
T& operator[] (const void *p) {
return array[indexForPointer(p)].value;
}
const T& operator[] (const void *p) const {
return const_cast>(this)[p];
}
// Shortcuts for StripedMaps of locks.
void lockAll() {
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < StripeCount; i++) {
array[i].value.lock();
}
}
void unlockAll() {
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < StripeCount; i++) {
array[i].value.unlock();
}
}
void forceResetAll() {
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < StripeCount; i++) {
array[i].value.forceReset();
}
}
void defineLockOrder() {
for (unsigned int i = 1; i < StripeCount; i++) {
lockdebug_lock_precedes_lock(&array[i-1].value, &array[i].value);
}
}
void precedeLock(const void *newlock) {
// assumes defineLockOrder is also called
lockdebug_lock_precedes_lock(&array[StripeCount-1].value, newlock);
}
void succeedLock(const void *oldlock) {
// assumes defineLockOrder is also called
lockdebug_lock_precedes_lock(oldlock, &array[0].value);
}
const void *getLock(int i) {
if (i < StripeCount) return &array[i].value;
else return nil;
}
#if DEBUG
StripedMap() {
// Verify alignment expectations.
uintptr_t base = (uintptr_t)&array[0].value;
uintptr_t delta = (uintptr_t)&array[1].value - base;
assert(delta % CacheLineSize == 0);
assert(base % CacheLineSize == 0);
}
#else
constexpr StripedMap() {}
#endif
};
-
static unsigned int indexForPointer(const void *p)对象指针通过哈希算法计算出对应的下标序号。 -
T& operator[] (const void *p)重写[]操作符,可通过,&SideTables()[oldObj]方式获取这个对象指针对应的SideTable。 -
lldb调试,在SideTables结构中获取一张SideTable
(lldb) p indexForPointer(p)
(unsigned int) $4 = 4
(lldb) p array[indexForPointer(p)].value
((anonymous namespace)::SideTable) $5 = {
slock = {
mLock = (_os_unfair_lock_opaque = 0)
}
refcnts = {
Buckets = 0x0000000000000000
NumEntries = 0
NumTombstones = 0
NumBuckets = 0
}
weak_table = {
weak_entries = 0x0000000000000000
num_entries = 0
mask = 0
max_hash_displacement = 0
}
}
SideTable
SideTable内部数据结构:
struct SideTable {
spinlock_t slock;
RefcountMap refcnts;
weak_table_t weak_table;
...
};
spinlock_t slock自旋锁,用于控制SideTable的访问安全.
refcnts引用计数表,是一个Map,用于存储引用计数,具体下面会展开讲解。
weak_table弱引用表.
疑问
1.SidleTables是一张哈希表,内部存了多张散列表。为什么需要使用多张?
答:对SidleTable操作时,需要进行加锁、解锁。频繁操作,会降低性能。多张表可以分开加锁,提高效率。
2.为什么不是一个类对应一个SidleTable?
创建SidleTable和管理SidleTable都需要耗费性能,所以几个类共用一个SidleTable
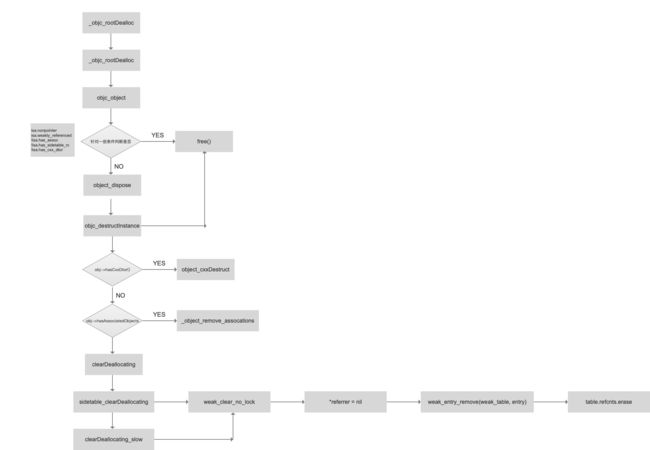
三.引用计数
1.alloc出来的引用技术是多少?
2.对象在什么时候会调用Dealloc?
3.引用计数在什么时候会加,减?
4.引用计数存在哪?
5.dealloc底层,应该做一些什么事情?
带着上面几个问题,我们展开对源码的分析。引用计数的核心就是对象的retain、release,因此首先从这2个函数入手分析:
retain
-(id) retain
{
return _objc_rootRetain(self);
}
id
_objc_rootRetain(id obj)
{
assert(obj);
return obj->rootRetain();
}
objc_object::rootRetain()
{
return rootRetain(false, false);
}
objc_object::rootRetain(bool tryRetain, bool handleOverflow)
{
//1. isTaggedPointer 直接返回
if (isTaggedPointer()) return (id)this;
//2.用于标记锁的状态
bool sideTableLocked = false;
//3.标记是否需要装到到
bool transcribeToSideTable = false;
isa_t oldisa;
isa_t newisa;
do {
transcribeToSideTable = false;
oldisa = LoadExclusive(&isa.bits);
newisa = oldisa;
//4.不是nonpointer
if (slowpath(!newisa.nonpointer)) {
ClearExclusive(&isa.bits);
if (!tryRetain && sideTableLocked) sidetable_unlock();
if (tryRetain) return sidetable_tryRetain() ? (id)this : nil;
//5.不是nonpointer类型,跳转nonpointer
else return sidetable_retain();
}
// don't check newisa.fast_rr; we already called any RR overrides
//6.析构,返回nil
if (slowpath(tryRetain && newisa.deallocating)) {
ClearExclusive(&isa.bits);
if (!tryRetain && sideTableLocked) sidetable_unlock();
return nil;
}
//7.进位标记
uintptr_t carry;
//8.extra_rc++
newisa.bits = addc(newisa.bits, RC_ONE, 0, &carry); // extra_rc++
if (slowpath(carry)) {
//9. newisa.extra_rc++ overflowed
if (!handleOverflow) {
ClearExclusive(&isa.bits);
return rootRetain_overflow(tryRetain);
}
// Leave half of the retain counts inline and
// prepare to copy the other half to the side table.
if (!tryRetain && !sideTableLocked) sidetable_lock();
sideTableLocked = true;
transcribeToSideTable = true;
//10.溢出时extra_rc保存一把
newisa.extra_rc = RC_HALF;
newisa.has_sidetable_rc = true;
}
} while (slowpath(!StoreExclusive(&isa.bits, oldisa.bits, newisa.bits)));
if (slowpath(transcribeToSideTable)) {
// Copy the other half of the retain counts to the side table.
sidetable_addExtraRC_nolock(RC_HALF);
}
if (slowpath(!tryRetain && sideTableLocked)) sidetable_unlock();
return (id)this;
}
id
objc_object::sidetable_retain()
{
#if SUPPORT_NONPOINTER_ISA
assert(!isa.nonpointer);
#endif
SideTable& table = SideTables()[this];
table.lock();
size_t& refcntStorage = table.refcnts[this];
if (! (refcntStorage & SIDE_TABLE_RC_PINNED)) {
refcntStorage += SIDE_TABLE_RC_ONE;
}
table.unlock();
return (id)this;
}
- 1.
TaggedPointer类型,直接return - 2.不是
nonpointer类型,调用sidetable_retain,对引用计数表数值+1 - 3.
nonpointer类型,extra_rc++,判断是否溢出,溢出时,extra_rc存储RC_HALF(RC_HALF)的引用计数,另一半存储值散列表的引用技术表。
release
和retain类似,此处就不再贴源码.
- 1.
TaggedPointer类型,直接return - 2.不是
nonpointer类型,调用sidetable_retain,对引用计数表数值-1 - 3.
nonpointer类型,extra_rc--,判断是否下溢出 - 4.当下溢出时,判断散列表是否还有值,如果有就从散列表借,extra_rc存储
RC_HALF(RC_HALF)引用计数. - 如果散列表也没有了,那就标记
deallocating为true,并发送dealloc消息.
retainCount()
inline uintptr_t
objc_object::rootRetainCount()
{
if (isTaggedPointer()) return (uintptr_t)this;
sidetable_lock();
isa_t bits = LoadExclusive(&isa.bits);
ClearExclusive(&isa.bits);
if (bits.nonpointer) {
uintptr_t rc = 1 + bits.extra_rc;
if (bits.has_sidetable_rc) {
rc += sidetable_getExtraRC_nolock();
}
sidetable_unlock();
return rc;
}
sidetable_unlock();
return sidetable_retainCount();
}
- 1.
TaggedPointer返回的是(uintptr_t)this -
-
nonpointer返回的是1 + bits.extra_rc,如果引用计数表有值,还需要加上引用计数表的存储值
-
-
- 非
nonpointer,返回计数表的存储值
- 非
dealloc
if (isTaggedPointer()) return; // fixme necessary?
if (fastpath(isa.nonpointer &&
!isa.weakly_referenced &&
!isa.has_assoc &&
!isa.has_cxx_dtor &&
!isa.has_sidetable_rc))
{
assert(!sidetable_present());
free(this);
}
else {
object_dispose((id)this);
}
- 1.TaggedPointer,直接return
- 2.
isa.nonpointer && !isa.weakly_referenced && !isa.has_assoc && !isa.has_cxx_dtor && !isa.has_sidetable_rc,直接释放 - 3.存在析构函数、关联对象,都需要移除
- 4.在引用计数表中檫除对象,弱引用表设置为Nil
-
5.释放
总结:通过对retain,release,retainCount,dealloc源码分析,上述5个问题均可以在里面找到答案。此处就不在赘述。
四.弱引用weak
1.弱引用对象是如何加入弱引用计数?
2.对象析构时,对象弱引用表中的对象如何设置为nil?
NSObject * n = [[NSObject alloc] init];
__weak NSObject *weakN = n;
lldb调试得出,声明以为
weak变量首先会执行objc_initWeak函数,因此我们从此处入手进行分析。
id
objc_initWeak(id *location, id newObj)
{
if (!newObj) {
*location = nil;
return nil;
}
return storeWeak
(location, (objc_object*)newObj);
}
-
newObj不存在,直接return,否则调用storeWeak
static id
storeWeak(id *location, objc_object *newObj)
{
assert(haveOld || haveNew);
if (!haveNew) assert(newObj == nil);
Class previouslyInitializedClass = nil;
id oldObj;
SideTable *oldTable;
SideTable *newTable;
// Acquire locks for old and new values.
// Order by lock address to prevent lock ordering problems.
// Retry if the old value changes underneath us.
retry:
if (haveOld) {
oldObj = *location;
oldTable = &SideTables()[oldObj];
} else {
oldTable = nil;
}
if (haveNew) {
newTable = &SideTables()[newObj];
} else {
newTable = nil;
}
SideTable::lockTwo(oldTable, newTable);
if (haveOld && *location != oldObj) {
SideTable::unlockTwo(oldTable, newTable);
goto retry;
}
// Prevent a deadlock between the weak reference machinery
// and the +initialize machinery by ensuring that no
// weakly-referenced object has an un-+initialized isa.
if (haveNew && newObj) {
Class cls = newObj->getIsa();
if (cls != previouslyInitializedClass &&
!((objc_class *)cls)->isInitialized())
{
SideTable::unlockTwo(oldTable, newTable);
class_initialize(cls, (id)newObj);
// If this class is finished with +initialize then we're good.
// If this class is still running +initialize on this thread
// (i.e. +initialize called storeWeak on an instance of itself)
// then we may proceed but it will appear initializing and
// not yet initialized to the check above.
// Instead set previouslyInitializedClass to recognize it on retry.
previouslyInitializedClass = cls;
goto retry;
}
}
// Clean up old value, if any.
if (haveOld) {
weak_unregister_no_lock(&oldTable->weak_table, oldObj, location);
}
// Assign new value, if any.
if (haveNew) {
newObj = (objc_object *)
weak_register_no_lock(&newTable->weak_table, (id)newObj, location,
crashIfDeallocating);
// weak_register_no_lock returns nil if weak store should be rejected
// Set is-weakly-referenced bit in refcount table.
if (newObj && !newObj->isTaggedPointer()) {
newObj->setWeaklyReferenced_nolock();
}
// Do not set *location anywhere else. That would introduce a race.
*location = (id)newObj;
}
else {
// No new value. The storage is not changed.
}
SideTable::unlockTwo(oldTable, newTable);
return (id)newObj;
}
- 如果存在旧值,调用
weak_unregister_no_lock处理。
void
weak_unregister_no_lock(weak_table_t *weak_table, id referent_id,
id *referrer_id)
{
objc_object *referent = (objc_object *)referent_id;
objc_object **referrer = (objc_object **)referrer_id;
weak_entry_t *entry;
if (!referent) return;
if ((entry = weak_entry_for_referent(weak_table, referent))) {
remove_referrer(entry, referrer);
bool empty = true;
if (entry->out_of_line() && entry->num_refs != 0) {
empty = false;
}
else {
for (size_t i = 0; i < WEAK_INLINE_COUNT; i++) {
if (entry->inline_referrers[i]) {
empty = false;
break;
}
}
}
if (empty) {
weak_entry_remove(weak_table, entry);
}
}
// Do not set *referrer = nil. objc_storeWeak() requires that the
// value not change.
}
- 首先调用
weak_entry_for_referent从waek_table中获取entry - 然后调用
remove_referrer,在entry的referrers中找到地址的索引,entry->referrers[index] = nil;entry->num_refs--;设置为nil,并将num_refs减1 - 判断
entry是否还有值,没有就在weak_table移除这个entry
- 如果不存在旧值,调用
weak_register_no_lock
// now remember it and where it is being stored
weak_entry_t *entry;
if ((entry = weak_entry_for_referent(weak_table, referent))) {
append_referrer(entry, referrer);
}
else {
weak_entry_t new_entry(referent, referrer);
weak_grow_maybe(weak_table);
weak_entry_insert(weak_table, &new_entry);
(entry = weak_entry_for_referent(weak_table, referent))获取entry
(1)entry存在,调用append_referrer,将new_referrer添加到entry->referrers
将new_referrer先赋值到entry->inline_referrers[i]
然后将entry->inline_referrers循环对应拷贝到new_referrers
将new_referrers赋值给entry->referrers = new_referrers;
(2)entry不存在,
创建⼀个weak_entry_t
把referent加⼊到weak_entry_t的数组inline_referrers,``
把weak_table扩容,weak_grow_maybe(weak_table)
把new_entry加⼊到weak_table中.weak_entry_insert(weak_table, &new_entry);
在三.引用计数的dealloc中,我们知道,对象在析构(deealloc)时,如果存在弱引用对象:
...
SideTable& table = SideTables()[this];
table.lock();
if (isa.weakly_referenced) {
weak_clear_no_lock(&table.weak_table, (id)this);
}
//在引用技术标中,移除这个对象。
if (isa.has_sidetable_rc) {
table.refcnts.erase(this);
}
table.unlock()
...
存在弱引用对象,调用weak_clear_no_lock
void
weak_clear_no_lock(weak_table_t *weak_table, id referent_id)
{
objc_object *referent = (objc_object *)referent_id;
weak_entry_t *entry = weak_entry_for_referent(weak_table, referent);
if (entry == nil) {
/// XXX shouldn't happen, but does with mismatched CF/objc
//printf("XXX no entry for clear deallocating %p\n", referent);
return;
}
// zero out references
weak_referrer_t *referrers;
size_t count;
if (entry->out_of_line()) {
referrers = entry->referrers;
count = TABLE_SIZE(entry);
}
else {
referrers = entry->inline_referrers;
count = WEAK_INLINE_COUNT;
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < count; ++i) {
objc_object **referrer = referrers[i];
if (referrer) {
if (*referrer == referent) {
*referrer = nil;
}
else if (*referrer) {
_objc_inform("__weak variable at %p holds %p instead of %p. "
"This is probably incorrect use of "
"objc_storeWeak() and objc_loadWeak(). "
"Break on objc_weak_error to debug.\n",
referrer, (void*)*referrer, (void*)referent);
objc_weak_error();
}
}
}
weak_entry_remove(weak_table, entry);
}
- 在
weak_table获取对象的entry - 循环
entry下的referrers,将其指向设置为nil,*referrer = nil; -
weak_table中移除entry
五.变量修饰符
变量修饰符有一下几种情况:
typedef enum {
objc_ivar_memoryUnknown, // unknown / unknown
objc_ivar_memoryStrong, // direct access / objc_storeStrong
objc_ivar_memoryWeak, // objc_loadWeak[Retained] / objc_storeWeak
objc_ivar_memoryUnretained // direct access / direct access
} objc_ivar_memory_management_t;
通过源码分析变量不同修饰符的setter方法的处理:
void _object_setIvar(id obj, Ivar ivar, id value, bool assumeStrong)
{
if (!obj || !ivar || obj->isTaggedPointer()) return;
ptrdiff_t offset;
objc_ivar_memory_management_t memoryManagement;
_class_lookUpIvar(obj->ISA(), ivar, offset, memoryManagement);
if (memoryManagement == objc_ivar_memoryUnknown) {
if (assumeStrong) memoryManagement = objc_ivar_memoryStrong;
else memoryManagement = objc_ivar_memoryUnretained;
}
id *location = (id *)((char *)obj + offset);
switch (memoryManagement) {
case objc_ivar_memoryWeak: objc_storeWeak(location, value); break;
case objc_ivar_memoryStrong: objc_storeStrong(location, value); break;
case objc_ivar_memoryUnretained: *location = value; break;
case objc_ivar_memoryUnknown: _objc_fatal("impossible");
}
}
-
TaggedPointer类型,直接return - 获取内存修饰符
objc_ivar_memory_management_t._class_lookUpIvar(obj->ISA(), ivar, offset, memoryManagement)
(1)objc_ivar_memoryWeak,调用objc_storeWeak操作弱引用表,上述已经分析过.
(2)objc_ivar_memoryStrong,调用objc_storeStrong,retain新值,释放旧值
(3)objc_ivar_memoryUnretained,直接将value存储至*location。这也说明为什么Unretained是不安全的。
六.自动释放池AutoReleasePool
自动释放池介绍
AutoReleasePool 是ARC引入的,用于管理对象的引用计数。
以下是AutoReleasePool的几个要点:
- 一个线程的自动释放池是一种栈形式的指针集合,先进后出;
- 每个指针要么是要释放的对象,要么是池的边界,即自动释放池边界;
- 池token是指向该池边界的指针。当池被弹出时,所有比哨兵还热的对象都被释放;
- 这个栈是一个双向链表的页面列表。根据需要添加和删除页面。
- 线程本地存储指向热页,其中存储新的自动释放的对象。
AutoReleasePool结构图:
[图片上传失败...(image-5bbdcf-1585145402449)]
AutoReleasePool数据结构:
class AutoreleasePoolPage;
struct AutoreleasePoolPageData {
magic_t const magic; // 16
__unsafe_unretained id *next; //8
pthread_t const thread; // 8
//证明了双向链表结构
AutoreleasePoolPage * const parent; //8
AutoreleasePoolPage *child; //8
uint32_t const depth; // 4
uint32_t hiwat; // 4
AutoreleasePoolPageData(__unsafe_unretained id* _next, pthread_t _thread, AutoreleasePoolPage* _parent, uint32_t _depth, uint32_t _hiwat)
: magic(), next(_next), thread(_thread),
parent(_parent), child(nil),
depth(_depth), hiwat(_hiwat)
{
}
};
-
AutoreleasePoolPage是个继承于AutoreleasePoolPageData结构体的类,objc4-779.1版本开始独立出AutoreleasePoolPageData结构体,之前变量是直接在AutoreleasePoolPage中。 -
magic_t const magic:用来校验AutoreleasePoolPage的结构是否完整 -
__unsafe_unretained id *next: 指向最新添加的autorelease对象的下一个位置,初始化时指向begin() -
pthread_t const thread:当前线程 -
AutoreleasePoolPage * const parent:指向父节点,第一个parent节点为nil -
AutoreleasePoolPage *child:指向子节点,最后一个child节点为nil -
uint32_t const depth:代表深度,从0开始,递增+1 -
uint32_t hiwat:代表 high water Mark 最大入栈数量标记
自动释放池探索
使用clang -rewrite-objc main.m -o main.cpp编译如下代码:
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
@autoreleasepool {
NSLog(@"Jensen");
}
return 0;
}
编译结果:
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
/* @autoreleasepool */ { __AtAutoreleasePool __autoreleasepool;
NSLog((NSString *)&__NSConstantStringImpl__var_folders_v7_6tlrq64x5w5gqg17582f4p500000gn_T_main_3f39be_mi_0);
}
return 0;
}
struct __AtAutoreleasePool {
__AtAutoreleasePool() {atautoreleasepoolobj = objc_autoreleasePoolPush();}
~__AtAutoreleasePool() {objc_autoreleasePoolPop(atautoreleasepoolobj);}
void * atautoreleasepoolobj;
};
@autoreleasepool{}实际上是实例化__AtAutoreleasePool,在构造方法中调用objc_autoreleasePoolPush
atautoreleasepoolobj = objc_autoreleasePoolPush();
static inline void *push()
{
id *dest;
if (slowpath(DebugPoolAllocation)) {
// Each autorelease pool starts on a new pool page.
dest = autoreleaseNewPage(POOL_BOUNDARY);
} else {
dest = autoreleaseFast(POOL_BOUNDARY);
}
ASSERT(dest == EMPTY_POOL_PLACEHOLDER || *dest == POOL_BOUNDARY);
return dest;
}
- 通过环境变量
OBJC_DEBUG_POOL_ALLOCATION判断自动释放池是否被允许跟踪调试,如果允许调用autoreleaseNewPage,否则进入autoreleaseFast.此处,我们分析autoreleaseFast。 - 自动释放池初始化,会调用
objc_autoreleasePoolPush
static inline id *autoreleaseFast(id obj)
{
AutoreleasePoolPage *page = hotPage();
if (page && !page->full()) {
return page->add(obj);
} else if (page) {
return autoreleaseFullPage(obj, page);
} else {
return autoreleaseNoPage(obj);
}
}
- 获取当前
AutoreleasePoolPage的hotPage - 存在
hotPage,并且未满,直接调用page->add(obj)将对象添加到AutoreleasePoolPage - 存在
hotPage,但是已满,调用autoreleaseFullPage - 没有
hotPage,说明是第一次加入,调用autoreleaseNoPage
id *add(id obj)
{
ASSERT(!full());
unprotect();
id *ret = next; // faster than `return next-1` because of aliasing
*next++ = obj;
protect();
return ret;
}
将对象加入到hotPage中.
static __attribute__((noinline))
id *autoreleaseFullPage(id obj, AutoreleasePoolPage *page)
{
// The hot page is full.
// Step to the next non-full page, adding a new page if necessary.
// Then add the object to that page.
ASSERT(page == hotPage());
ASSERT(page->full() || DebugPoolAllocation);
do {
if (page->child) page = page->child;
else page = new AutoreleasePoolPage(page);
} while (page->full());
setHotPage(page);
return page->add(obj);
}
循环找到最后一页,当前page作为父page创建一个新的AutoreleasePoolPage,将新创建的page设置为hotPage,调用add将对象加入到新page中.
static __attribute__((noinline))
id *autoreleaseNoPage(id obj)
{
// "No page" could mean no pool has been pushed
// or an empty placeholder pool has been pushed and has no contents yet
ASSERT(!hotPage());
bool pushExtraBoundary = false;
if (haveEmptyPoolPlaceholder()) {
// We are pushing a second pool over the empty placeholder pool
// or pushing the first object into the empty placeholder pool.
// Before doing that, push a pool boundary on behalf of the pool
// that is currently represented by the empty placeholder.
pushExtraBoundary = true;
}
else if (obj != POOL_BOUNDARY && DebugMissingPools) {
// We are pushing an object with no pool in place,
// and no-pool debugging was requested by environment.
_objc_inform("MISSING POOLS: (%p) Object %p of class %s "
"autoreleased with no pool in place - "
"just leaking - break on "
"objc_autoreleaseNoPool() to debug",
objc_thread_self(), (void*)obj, object_getClassName(obj));
objc_autoreleaseNoPool(obj);
return nil;
}
else if (obj == POOL_BOUNDARY && !DebugPoolAllocation) {
// We are pushing a pool with no pool in place,
// and alloc-per-pool debugging was not requested.
// Install and return the empty pool placeholder.
return setEmptyPoolPlaceholder();
}
// We are pushing an object or a non-placeholder'd pool.
// Install the first page.
AutoreleasePoolPage *page = new AutoreleasePoolPage(nil);
setHotPage(page);
// Push a boundary on behalf of the previously-placeholder'd pool.
if (pushExtraBoundary) {
page->add(POOL_BOUNDARY);
}
// Push the requested object or pool.
return page->add(obj);
}
会直接创建第一个page,并将这个page设置为hotPage,然后加入边界符POOL_BOUNDARY
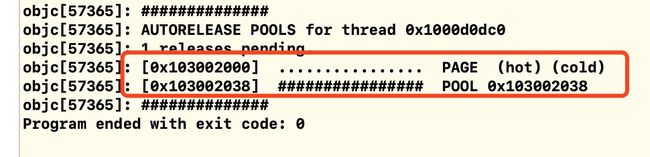
用_objc_autoreleasePoolPrint();打印一个空的自动释放池:
一张page占用4096字节,从图中我们知道page属性占用56(3 * 16 + 8)字节,一个page能容纳505((4096 - 56)/8 = 505)个对象,第一页包含POOL的特殊边界符,占用1个对象,因此第一页能容纳504个对象和1个特殊标记符,其他页面能容纳505个对象。
objc_autoreleasePoolPop
void
_objc_autoreleasePoolPop(void *ctxt)
{
objc_autoreleasePoolPop(ctxt);
}
void
objc_autoreleasePoolPop(void *ctxt)
{
AutoreleasePoolPage::pop(ctxt);
}
static inline void
pop(void *token)
{
AutoreleasePoolPage *page;
id *stop;
if (token == (void*)EMPTY_POOL_PLACEHOLDER) {
// Popping the top-level placeholder pool.
page = hotPage();
if (!page) {
// Pool was never used. Clear the placeholder.
return setHotPage(nil);
}
// Pool was used. Pop its contents normally.
// Pool pages remain allocated for re-use as usual.
page = coldPage();
token = page->begin();
} else {
page = pageForPointer(token);
}
stop = (id *)token;
if (*stop != POOL_BOUNDARY) {
if (stop == page->begin() && !page->parent) {
// Start of coldest page may correctly not be POOL_BOUNDARY:
// 1. top-level pool is popped, leaving the cold page in place
// 2. an object is autoreleased with no pool
} else {
// Error. For bincompat purposes this is not
// fatal in executables built with old SDKs.
return badPop(token);
}
}
if (slowpath(PrintPoolHiwat || DebugPoolAllocation || DebugMissingPools)) {
return popPageDebug(token, page, stop);
}
return popPage(token, page, stop);
}
- 自动释放池析构时,调用
_objc_autoreleasePoolPop -
token指定需要释放到的位置 - 找到
token对应的page -
popPage开始pop(token, page, stop);
template
static void
popPage(void *token, AutoreleasePoolPage *page, id *stop)
{
if (allowDebug && PrintPoolHiwat) printHiwat();
page->releaseUntil(stop);
// memory: delete empty children
if (allowDebug && DebugPoolAllocation && page->empty()) {
// special case: delete everything during page-per-pool debugging
AutoreleasePoolPage *parent = page->parent;
page->kill();
setHotPage(parent);
} else if (allowDebug && DebugMissingPools && page->empty() && !page->parent) {
// special case: delete everything for pop(top)
// when debugging missing autorelease pools
page->kill();
setHotPage(nil);
} else if (page->child) {
// hysteresis: keep one empty child if page is more than half full
if (page->lessThanHalfFull()) {
page->child->kill();
}
else if (page->child->child) {
page->child->child->kill();
}
}
}
-
page->releaseUntil(stop);释放对象 - page为空,直接释放这个page,如果有child,将child也kill
void releaseUntil(id *stop)
{
// Not recursive: we don't want to blow out the stack
// if a thread accumulates a stupendous amount of garbage
while (this->next != stop) {
// Restart from hotPage() every time, in case -release
// autoreleased more objects
AutoreleasePoolPage *page = hotPage();
// fixme I think this `while` can be `if`, but I can't prove it
while (page->empty()) {
page = page->parent;
setHotPage(page);
}
page->unprotect();
id obj = *--page->next;
memset((void*)page->next, SCRIBBLE, sizeof(*page->next));
page->protect();
if (obj != POOL_BOUNDARY) {
objc_release(obj);
}
}
setHotPage(this);
#if DEBUG
// we expect any children to be completely empty
for (AutoreleasePoolPage *page = child; page; page = page->child) {
ASSERT(page->empty());
}
#endif
}
- 循环遍历,取出对象,并释放。
总结:
当要pop对象的时候,系统给一个token对象指针,这个指针用于指定释放的程度
找到token对象所在的page,并生成一个stop停止对象,然后开始pop操作
page->releaseUntil(stop),内部循环遍历执行对象的release,直到stop对象,并将当前page设为hotpage
将已经释放对象所属的page杀了,即删除空的child page.
autorelease
前面已经介绍了objc_autoreleasePoolPush和objc_autoreleasePoolPop,接下来我们看看autorelease又做了什么.
static inline id autorelease(id obj)
{
ASSERT(obj);
ASSERT(!obj->isTaggedPointer());
id *dest __unused = autoreleaseFast(obj);
ASSERT(!dest || dest == EMPTY_POOL_PLACEHOLDER || *dest == obj);
return obj;
}
static inline id *autoreleaseFast(id obj)
{
AutoreleasePoolPage *page = hotPage();
if (page && !page->full()) {
return page->add(obj);
} else if (page) {
return autoreleaseFullPage(obj, page);
} else {
return autoreleaseNoPage(obj);
}
}
autorelease的实现和objc_autoreleasePoolPush类似,这里就不在赘述了。
自动释放池、RunLoop
App启动后,苹果在主线程
RunLoop里注册了两个Observer,其回调都是_wrapRunLoopWithAutoreleasePoolHandler()。第一个
Observer监视的事件是 Entry(即将进入Loop),其回调内会调用_objc_autoreleasePoolPush()创建自动释放池。其 order 是-2147483647,优先级最高,保证创建释放池发生在其他所有回调之前。第二个
Observer监视了两个事件:BeforeWaiting(准备进入休眠)时调用_objc_autoreleasePoolPop()和_objc_autoreleasePoolPush()释放旧的池并创建新池;Exit(即将退出Loop)时调用_objc_autoreleasePoolPop()来释放自动释放池。这个 Observer 的 order 是 2147483647,优先级最低,保证其释放池子发生在其他所有回调之后。在主线程执行的代码,通常是写在诸如事件回调、Timer回调内的。这些回调会被 RunLoop 创建好的 AutoreleasePool 环绕着,所以不会出现内存泄漏,开发者也不必显示创建 Pool了。
一个线程只有一个
autoreleasePoolautoreleasePool嵌套时,只会创建一个page,但是有两个池边界
observers = (
"{valid = Yes, activities = 0x1, repeats = Yes, order = -2147483647, callout = _wrapRunLoopWithAutoreleasePoolHandler (0x10dd891b1), context = {type = mutable-small, count = 0, values = ()}}",
"{valid = Yes, activities = 0x20, repeats = Yes, order = 0, callout = _UIGestureRecognizerUpdateObserver (0x10d95b473), context = }",
"{valid = Yes, activities = 0xa0, repeats = Yes, order = 1999000, callout = _beforeCACommitHandler (0x10ddb8dfc), context = }",
"{valid = Yes, activities = 0xa0, repeats = Yes, order = 2001000, callout = _afterCACommitHandler (0x10ddb8e75), context = }",
"{valid = Yes, activities = 0xa0, repeats = Yes, order = 2147483647, callout = _wrapRunLoopWithAutoreleasePoolHandler (0x10dd891b1), context = {type = mutable-small, count = 0, values = ()}}"
),