无约束优化问题之梯度下降法、牛顿法原理
无约束优化问题是机器学习中最普遍、最简单的优化问题
x ∗ = m i n x f ( x ) , x ∈ R n x^{*}=\mathop{min}\limits_{x}f_{(x)},x\in R^{n} x∗=xminf(x),x∈Rn
梯度下降法推导
对于只有两个维度的函数 f ( x , y ) f_{(x,y)} f(x,y),如下图所示。
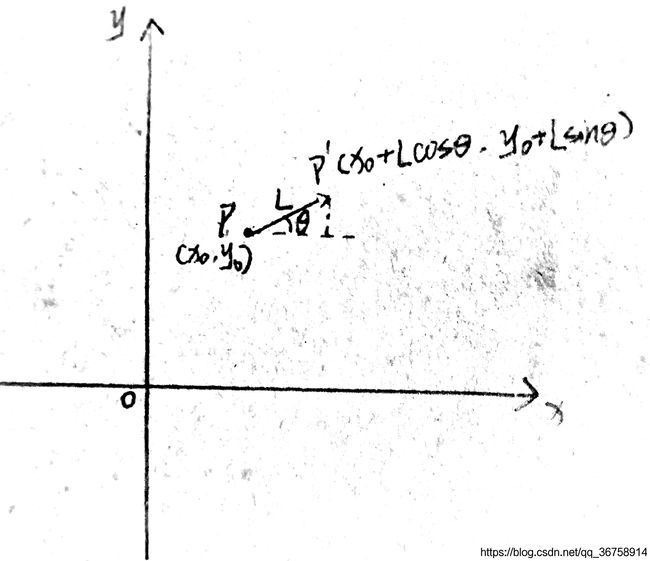
如果现在在 P P P点,假设 ∣ P P ′ ∣ = L , ∠ P ′ P x = θ |PP'|=L,\angle P'Px=\theta ∣PP′∣=L,∠P′Px=θ,则由 P P P到 P ′ P' P′,函数的单位长度变化量为:
f ( x 0 + L cos θ , y 0 + L sin θ ) − f ( x 0 , y 0 ) L \frac{f_{(x_{0}+L\cos{\theta}, y_{0}+L\sin{\theta})}-f_{(x_{0}, y_{0})}}{L} Lf(x0+Lcosθ,y0+Lsinθ)−f(x0,y0)
= f ( x 0 + L cos θ , y 0 + L sin θ ) − f ( x 0 + L cos θ , y 0 ) L + f ( x 0 + L cos θ , y 0 ) − f ( x 0 , y 0 ) L =\frac{f_{(x_{0}+L\cos{\theta}, y_{0}+L\sin{\theta})}-f_{(x_{0}+L\cos{\theta}, y_{0})}}{L}+\frac{f_{(x_{0}+L\cos{\theta}, y_{0})}-f_{(x_{0}, y_{0})}}{L} =Lf(x0+Lcosθ,y0+Lsinθ)−f(x0+Lcosθ,y0)+Lf(x0+Lcosθ,y0)−f(x0,y0)
= sin θ f ( x 0 + L cos θ , y 0 + L sin θ ) − f ( x 0 + L cos θ , y 0 ) L sin θ + cos θ f ( x 0 + L cos θ , y 0 ) − f ( x 0 , y 0 ) L cos θ =\sin{\theta}\frac{f_{(x_{0}+L\cos{\theta}, y_{0}+L\sin{\theta})}-f_{(x_{0}+L\cos{\theta}, y_{0})}}{L\sin{\theta}}+\cos{\theta}\frac{f_{(x_{0}+L\cos{\theta}, y_{0})}-f_{(x_{0}, y_{0})}}{L\cos{\theta}} =sinθLsinθf(x0+Lcosθ,y0+Lsinθ)−f(x0+Lcosθ,y0)+cosθLcosθf(x0+Lcosθ,y0)−f(x0,y0)
= sin θ f y ( x 0 , y 0 ) + cos θ f x ( x 0 , y 0 ) ( L → 0 ) =\sin{\theta}f_{y(x_{0},y_{0})}+\cos{\theta}f_{x(x_{0},y_{0})}\quad(\mathop{L\rightarrow0}) =sinθfy(x0,y0)+cosθfx(x0,y0)(L→0)
由柯西不等式:
< m , n > = ∣ ∣ m ∣ ∣ ⋅ ∣ ∣ n ∣ ∣ ⋅ c o s θ
< m , n > 2 = ∣ ∣ m ∣ ∣ 2 ⋅ ∣ ∣ n ∣ ∣ 2 ⋅ c o s 2 θ ≤ ∣ ∣ m ∣ ∣ 2 ⋅ ∣ ∣ n ∣ ∣ 2
且只有当 θ = 0 \theta =0 θ=0即两向量共线时等号成立。
令 m = ( sin θ , cos θ ) , n = ( f y , f x ) m=(\sin{\theta},\cos{\theta}),n=(f_{y},f_{x}) m=(sinθ,cosθ),n=(fy,fx),则
( sin θ ⋅ f y + cos θ ⋅ f x ) 2 ≤ ( sin 2 θ + cos 2 θ ) ( f y 2 + f x 2 ) = f y 2 + f x 2 (\sin{\theta}\cdot f_{y}+\cos{\theta}\cdot f_{x})^{2}\leq(\sin^{2}{\theta}+\cos^{2}{\theta})(f_{y}^{2}+f_{x}^{2})=f_{y}^{2}+f_{x}^{2} (sinθ⋅fy+cosθ⋅fx)2≤(sin2θ+cos2θ)(fy2+fx2)=fy2+fx2
" = " "=" "="成立的条件是两向量共线,即
sin θ cos θ = f y f x \frac{\sin{\theta}}{\cos{\theta}}=\frac{f_{y}}{f_{x}} cosθsinθ=fxfy
此时函数的单位长度变化量最大。
而 sin θ cos θ = f y f x \frac{\sin{\theta}}{\cos{\theta}}=\frac{f_{y}}{f_{x}} cosθsinθ=fxfy意味着单位长度变化量最大的方向为梯度方向。
类比于有 n n n个自变量的函数 f ( x 1 , x 2 … … x n ) f_{(x_{1},x_{2}……x_{n})} f(x1,x2……xn),其梯度为 ( ∂ f ∂ x 1 , ∂ f ∂ x 2 … … ∂ f ∂ x n ) (\frac{\partial f}{\partial x_{1}},\frac{\partial f}{\partial x_{2}}……\frac{\partial f}{\partial x_{n}}) (∂x1∂f,∂x2∂f……∂xn∂f),则延梯度方向函数增长最快。
基于此原理,梯度下降法取梯度的反方向作为移动方向,延此方向函数下降最快。
牛顿法推导
初级版本
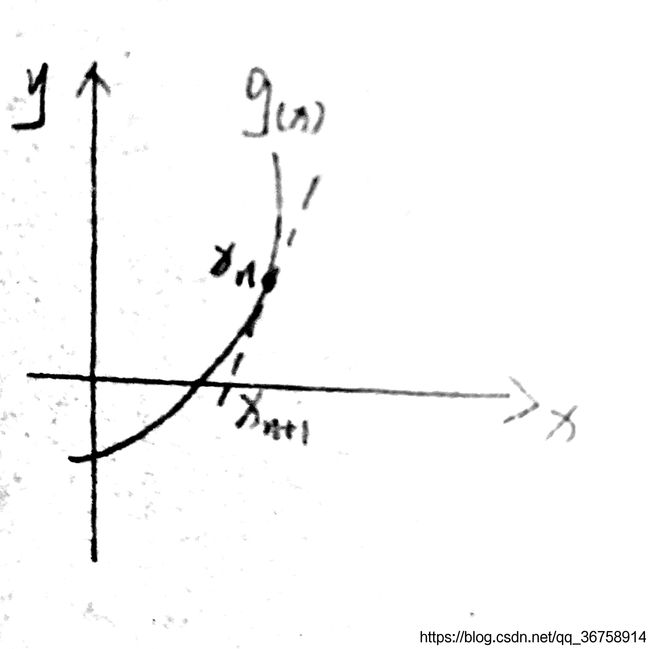
对于 m i n f ( x ) minf_{(x)} minf(x)来说,需要 g ( x ) = f ( x ) ′ = 0 g_{(x)}=f_{(x)}^{'}=0 g(x)=f(x)′=0。
x n x_{n} xn是第 n n n个点的横坐标,我们需要求出 g ( x ) = 0 g_{(x)}=0 g(x)=0时的横坐标。
首先对第 n n n个点求切线为:
y − g ( x n ) = g ( x n ) ′ ( x − x n ) y-g_{(x_{n})}=g_{(x_{n})}^{'}(x-x_{n}) y−g(xn)=g(xn)′(x−xn)
令 y = 0 y=0 y=0得到 x = x n − g ( x n ) g ( x n ) ′ x=x_{n}-\frac{g_{(x_{n})}}{g_{(x_{n})}^{'}} x=xn−g(xn)′g(xn)
用 f ( x ) ′ f_{(x)}^{'} f(x)′代替 g ( x ) g_{(x)} g(x),得:
x n + 1 = x n − f ( x n ) ′ f ( x n ) ′ ′ x_{n+1}=x_{n}-\frac{f_{(x_{n})}^{'}}{f_{(x_{n})}^{''}} xn+1=xn−f(xn)′′f(xn)′
高级版本

要求 m i n f ( x ) minf_{(x)} minf(x),
先将 f ( x ) f_{(x)} f(x)进行泰勒公式展开,得:
f ( x ) = f ( x n ) + f ( x n ) ′ ( x − x n ) + f ( x n ) ′ ′ 2 ! ( x − x n ) 2 + … … f_{(x)}=f_{(x_{n})}+f_{(x_{n})}^{'}(x-x_{n})+\frac{f_{(x_{n})}^{''}}{2!}(x-x_{n})^{2}+…… f(x)=f(xn)+f(xn)′(x−xn)+2!f(xn)′′(x−xn)2+……
将只保留有关 x x x的项,得:
f ( x ) = f ( x n ) ′ ′ 2 x 2 + ( f ( x n ) ′ − x n f ( x n ) ′ ′ ) x + … … f_{(x)}=\frac{f_{(x_{n})}^{''}}{2}x^{2}+(f_{(x_{n})}^{'}-x_{n}f_{(x_{n})}^{''})x+…… f(x)=2f(xn)′′x2+(f(xn)′−xnf(xn)′′)x+……
此时已将 f ( x ) f_{(x)} f(x)化为一个一元二次函数。
所以当此函数取最小值时的横坐标为:
x n + 1 = − b 2 a = − f ( x n ) ′ − x n f ( x n ) ′ ′ f ( x n ) ′ ′ = x n − f ( x n ) ′ f ( x n ) ′ ′ x_{n+1}=-\frac{b}{2a}=-\frac{f_{(x_{n})}^{'}-x_{n}f_{(x_{n})}^{''}}{f_{(x_{n})}^{''}}=x_{n}-\frac{f_{(x_{n})}^{'}}{f_{(x_{n})}^{''}} xn+1=−2ab=−f(xn)′′f(xn)′−xnf(xn)′′=xn−f(xn)′′f(xn)′