1.单变量线性回归练习
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
data=[[230.1,37.8,69.2,22.1],[44.5,39.3,45.1,10.4],[17.2,45.9,69.3,9.3],
[151.5,41.3,58.5,18.5],[180.8,10.8,58.4,12.9],[8.7,48.9,75,7.2],
[57.5,32.8,23.5,11.8],[120.2,19.6,11.6,13.2],[8.6,2.1,1,4.8],
[199.8,2.6,21.2,10.6],[66.1,5.8,24.2,8.6],[214.7,24,4,17.4],
[23.8,35.1,65.9,9.2],[97.5,7.6,7.2,9.7]]
index=np.arange(1,15)
columns=['TV','Radio','Newspaper','Sales']
df=pd.DataFrame(data,index,columns)
x1=df['TV']
x1=np.c_[x1]
x2=df['Radio']
x2=np.c_[x2]
x3=df['Newspaper']
x3=np.c_[x3]
y=df['Sales']
y=np.c_[y]
y=y.reshape((1,len(x1)))
y=y[0]
print(y)
m=x1.shape[0]
print(m)
a=np.ones(m)
def suofang(x):
xmin=np.min(x,axis=0)
xmax=np.max(x,axis=0)
s=(x-xmin)/(xmax-xmin)
return s
x1=suofang(x1)
x11=np.c_[a,x1]
x22=np.c_[a,x2]
x33=np.c_[a,x3]
print(x11)
def model(x,theta):
h=x.dot(theta)
return h
def cost(h,y):
m=h.shape[0]
j=1/(2*m)*np.sum((h-y)**2)
return j
def gradeDecline(xx,y,alpha,nums):
m,n=xx.shape
theta=np.zeros(n)
j=np.ones(nums)
for i in range(nums):
h=model(xx,theta)
j[i]=cost(h,y)
dieta=(1/m)*xx.T.dot(h-y)
theta=theta-alpha*dieta
return theta,j,h
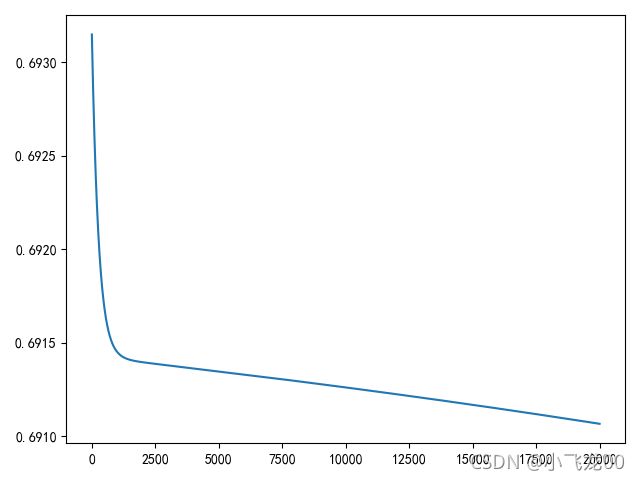
theta,j,h=gradeDecline(x11,y,0.000051,50000)
plt.subplot(321)
plt.scatter(x1,y)
plt.plot(x1,h)
plt.subplot(322)
plt.plot(j)
theta1,j,h=gradeDecline(x22,y,0.000045,50000)
print(j)
plt.subplot(323)
plt.scatter(x2,y)
plt.plot(x2,h)
plt.subplot(324)
plt.plot(j)
print('h=',h)
theta2,j,h=gradeDecline(x3,y,0.0000034,500000)
print(j)
plt.subplot(325)
plt.scatter(x3,y)
plt.plot(x3,h)
plt.subplot(326)
plt.plot(j)
plt.show()
2. 多变量线性回归
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
def model(x,theta):
h=x.dot(theta)
return h
def cost(h,y):
j=1/(2*m)*np.sum((h-y)**2)
return j
def gradeDecline(xx,y,alpha,nums):
m,n=xx.shape
theta=np.zeros((n,1))
j=np.zeros(nums)
for i in range(nums):
h=model(xx,theta)
j[i]=cost(h,y)
dieta=(1/m)*xx.T.dot(h-y)
theta=theta-alpha*dieta
return theta,j,h
def score(x,y,theta):
h=model(x,theta)
u=np.sum((h-y)**2)
v=np.sum((y-np.mean(y))**2)
return 1-u/v
def suofang(x):
xmin=np.min(x,axis=0)
xmax=np.max(x,axis=0)
x=(x-xmin)/(xmax-xmin)
return x
if __name__ == '__main__':
data=np.loadtxt('data1.txt',delimiter=',')
x=data[:,:-1]
y=data[:,-1:]
np.random.seed(4)
m,n=data.shape
order=np.random.permutation(m)
x=x[order]
y=y[order]
x=suofang(x)
xx=np.c_[np.ones(len(x)),x]
print(xx)
trunnum=int(len(x)*0.7)
trainx=xx[:trunnum,:]
testx=xx[trunnum:,:]
trainy=y[:trunnum,:]
testy=y[trunnum:,:]
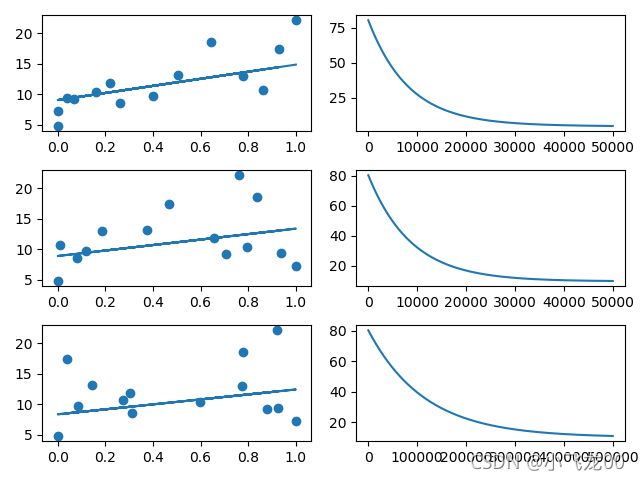
theta,j,h=gradeDecline(trainx,trainy,0.001,500000)
print(theta)
plt.subplot(121)
plt.scatter(trainy,trainy)
plt.scatter(testy,model(testx,theta))
plt.subplot(122)
plt.plot(j)
plt.show()
s=score(trainx,trainy,theta)
print('训练集精度',s)
s1=score(testx,testy,theta)
print('测试集精度',s1)
3. 逻辑回归
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
data=np.loadtxt(r'E:\机器学习\机器学习1\机器\线性回归\ex2data2.txt',delimiter=',')
print(data)
x=data[:,:-1]
y=data[:,-1]
def suofang(x):
miu=np.mean(x)
sigma=np.std(x)
s=(x-miu)/sigma
return s
x=suofang(x)
m,n=x.shape
np.random.seed(4)
order=np.random.permutation(m)
x=x[order]
y=y[order]
xx=np.c_[np.ones((m,1)),x]
print(xx)
trun=int(m*0.7)
trainx=xx[:trun,:]
testx=xx[trun:,:]
trainy=y[:trun]
testy=y[trun:]
tx=x[:trun,:]
print(tx)
def sigmoid(x,theta):
z=x.dot(theta)
h=1/(1+np.exp(-z))
return h
def cost(h,y):
j=-(1/m)*np.sum(y*np.log(h)+(1-y)*np.log(1-h))
return j
def gradeDecline(x,y,alpha,nums):
m,n=x.shape
theta=np.zeros(n)
j=np.zeros(nums)
for i in range(nums):
h=sigmoid(x,theta)
j[i]=cost(h,y)
dietatheta=1/m*x.T.dot(h-y)
theta=theta-alpha*dietatheta
return theta,h,j
def score(x,theta):
count=0
h=sigmoid(x,theta)
for i in range(m):
if (np.where(h[i]>0.5,1,0)==y[i]):
count+=1
accurancy=count/m
return count,accurancy
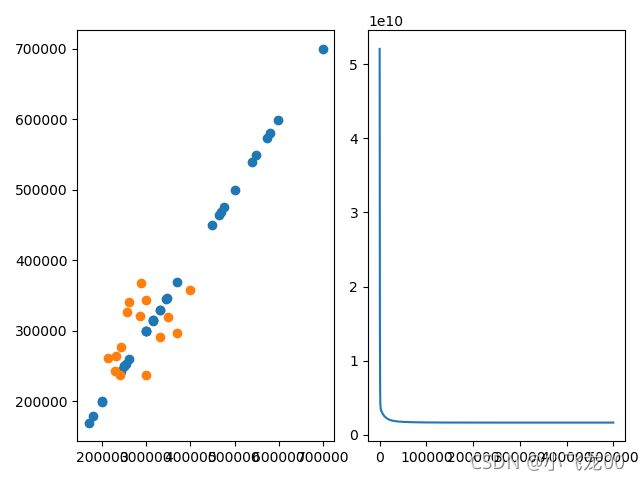
theta,h,j=gradeDecline(xx,y,0.01,10000)
plt.plot(j)
plt.show()
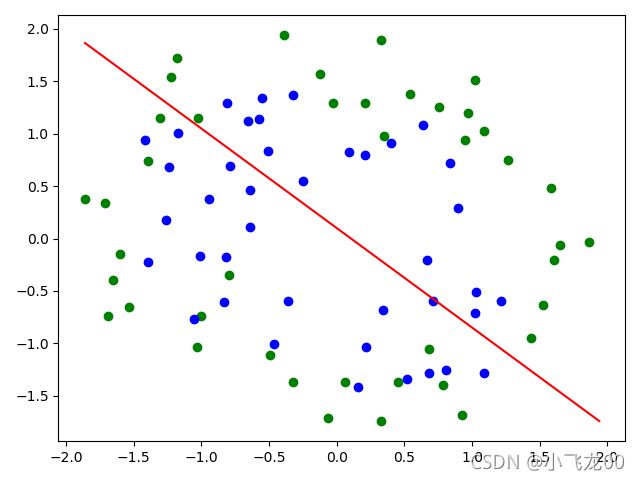
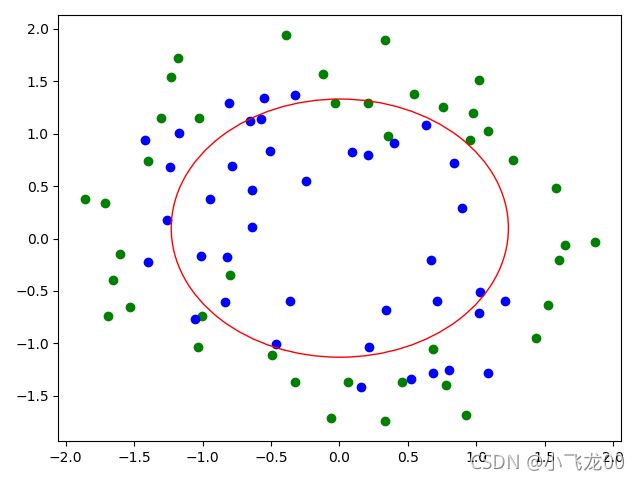
plt.scatter(tx[trainy==0,0],tx[trainy==0,1],c='green')
plt.scatter(tx[trainy==1,0],tx[trainy==1,1],c='blue')
def huaquan(x):
x1min=np.min(x[:,0])
x1max=np.max(x[:,0])
x2min=np.min(x[:,1])
x2max=np.max(x[:,1])
xa=(x1max+x1min)/2
ya=(x2min+x2max)/2
r=np.mean([x-x1min,x1max-x,x-x2min,x2max-x])
circle=plt.Circle((xa,ya),r-0.62,color='red',fill=False)
plt.gcf().gca().add_artist(circle)
huaquan(x)
def zhixian(trainx):
x1min=trainx[:,1].min()
x1max=trainx[:,1].max()
x2min=trainx[:,2].min()
x2max=trainx[:,2].max()
plt.plot([x1min,x1max],[x2max,x2min],c='red')
zhixian(trainx)
plt.show()
print(score(xx,theta))
4. 神经网络
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=['SimHei']
x1 = [0.697,0.774,0.634,0.608,0.556,0.403,0.481,0.437,0.666,0.243,0.245,0.343,0.639,0.657,0.360,0.593,0.719]
x2 = [0.460,0.376,0.264,0.318,0.215,0.237,0.149,0.211,0.091,0.267,0.057,0.099,0.161,0.198,0.370,0.042,0.103]
y = [1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0]
xx=np.c_[np.ones(len(x1)),x1,x2]
yy=np.c_[y]
order=np.random.permutation(len(xx))
xxx=xx[order]
yyy=yy[order]
m,n=xx.shape
print(xxx)
def model(x,theta):
return x.dot(theta)
def sigmoid(z,grad=False):
if grad==True:
return z*(1-z)
return 1/(1+np.exp(-z))
def frontp(a1,theta1,theta2):
z2=model(a1,theta1)
a2=sigmoid(z2)
z3=model(a2,theta2)
a3=sigmoid(z3)
return a2,a3
def cost(a3,y):
return -np.mean(y*np.log(a3)+(1-y)*np.log(1-a3))
def backp(y,a1,a2,a3,theta2,theta1,alpha=0.01):
sigma3=a3-y
sigma2=sigma3.dot(theta2.T)*sigmoid(a2,grad=True)
dt3=1/m*a2.T.dot(sigma3)
dt2=1/m*a1.T.dot(sigma2)
theta1=theta1-alpha*dt2
theta2=theta2-alpha*dt3
return theta1,theta2
def gradeDecline(a1,y,nums):
m,n=a1.shape
j=np.zeros(nums)
theta1=np.zeros((n,3))
theta2=np.zeros((3,1))
for i in range(nums):
a2,a3=frontp(a1,theta1,theta2)
j[i]=cost(a3,y)
theta1,theta2=backp(y,a1,a2,a3,theta2,theta1)
return theta1,theta2,j
def score(a3,y):
m,n=xxx.shape
count=0
for i in range(m):
if np.where(a3[i]>0.5,1,0)==y[i]:
count+=1
acc=count/m
return acc
theta1,theta2,j=gradeDecline(xxx,yyy,200000)
print(theta1)
print(theta2)
print(j)
plt.plot(j)
plt.show()
print('精度为:',score(a3,yyy)*100,'%')