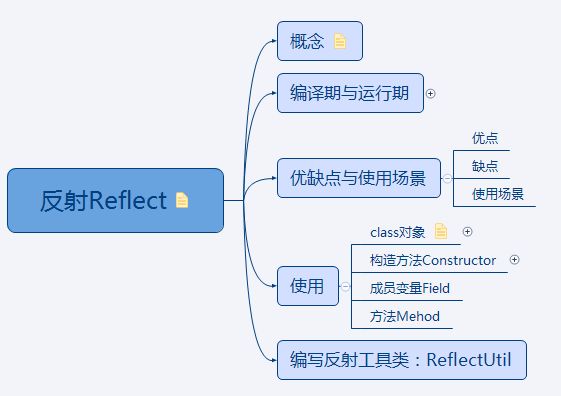
目录:
概念:
反射(Reflection)是Java程序开发语言的特征之一,它允许运行中的Java程序获取自身的信息,并且可以操作类或对象的内部属性。主要是指程序可以访问、检测和修改它本身状态或行为的一种能力,并能根据自身行为的状态和结果,调整或修改应用所描述行为的状态和相关的语义。
编译期与运行期:
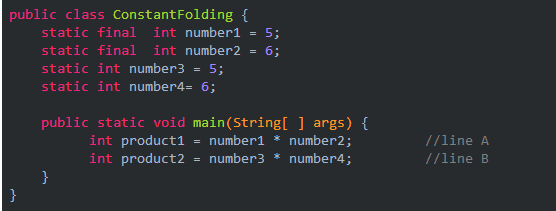
编译期:将java文件执行为class文件的过程,如通过new的方式创建对象是在编译期。方法重载,泛型均在编译期
运行期:将class文件执行到最终结果。如通过反射创建对象,方法重写,多态。
特点:
优点:
1,能够运行时动态获取类的实例,大大提高系统的灵活性和扩展性。(如:工厂设计模式)
2,android的开发中,反射可以获取系统未开发的属性,或修改系统类的private属性
3,反射在Android框架中的应用。如:https://juejin.im/post/5a2c1c5bf265da431956334c
缺点:
1,使用反射影响性能
2,破坏类的结果
3,存在安全隐患
使用场景:
1,修改系统的属性,获取系统的属性,如:状态栏的高度
2,动态代理的实现
3,Android中第三方框的使用
使用:
1, 获取类的对象(三种方式,基本数据类型如:boolean需要使用Boolean)
//1,使用类名.class
Class studentClass = Student.class;
//2,使用Class的forName方法
try {
Class forName = Class.forName("com.learn.study.bean.reflect.Student");
}catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//3,通过对象的getClass()方法获取
Student student =new Student();
Class aClass = student.getClass();
//获取父类的class对象
Class superclass = studentClass.getSuperclass();
2,获取构造方法与创建对象
//1,获取当前类的所有非private的构造方法,无则返回length=0的数组
Constructor[] constructors = studentClass.getConstructors();
//2,获取当前类指定参数的非private构造方法,无则异常:NoSuchMethodException
Constructor constructor = studentClass.getConstructor(String.class, Integer.class);
//3,获取当前类的所有构造方法,包含private
Constructor declaredConstructor = studentClass.getDeclaredConstructor();
//4,获取当前类指定参数的构造方法,包含private
Constructor declaredConstructor1 = studentClass.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class, Integer.class);
//1,使用class对象创建类的对象(注:只能针对非private的无参构造函数)
Student student = studentClass.newInstance();
//2,使用获取的构造方法创建对象
Constructor declaredConstructor = studentClass.getDeclaredConstructor();
declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true); //针对private的构造方法
Student student = declaredConstructor.newInstance(null);
declaredConstructor.setAccessible(false);
3,获取成员变量
//1,获取类下的所有非private成员变量
Field[] fields = studentClass.getFields();
//2,获取指定名称的非private成员变量
Field aa = studentClass.getField("aa");
//3,获取所有的成员变量
Field[] declaredFields = studentClass.getDeclaredFields();
//4,获取指定的成员变量
Field mName = studentClass.getDeclaredField("mName");
//获取成员变量的值
mName.setAccessible(true);
String aaStr = (String) mName.get(student);
Field mTest = studentClass.getDeclaredField("mTest");
mTest.setAccessible(true);
//静态的成员变量,参数可以为:null
String test = (String) mTest.get(null);
4,获取方法
//1,获取类下所有的非private方法
Method[] methods = studentClass.getMethods();
//2,获取类下指定的非private方法
Method doStudy = studentClass.getMethod("doStudy");
//3,获取类下的所有方法,包含private
Method[] declaredMethods = studentClass.getDeclaredMethods();
//4,获取类下指定的方法,包含private
Method setName = studentClass.getDeclaredMethod("setName", String.class);
//调用方法并获取值
Method getName = studentClass.getDeclaredMethod("getName");
getName.setAccessible(true);
String invoke = (String) getName.invoke(student);
Method setTest = studentClass.getDeclaredMethod("setTest", String.class);
setTest.setAccessible(true);
//静态方法调用时可以不传入对象
setTest.invoke(null, "mmmm");
String test2 = (String) mTest.get(null);
5,编写反射工具类时的注意点:
方法中的int类型在反射中需要传入int.class,但传入的具体值如:10,使用getClass()后变成了java.lang.Integer,故出现异常:NoSuchFieldException,此时需要获取所有的方法,进行参数匹配。
//反射操作带参数的方法
public ReflectUtil method(String methodName, Object... args) {
Class[] tem = argsToClass(args);
Method[] methods = type.getMethods();
if (methods != null && methods.length > 0) {
boolean hasMethod = false;
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < methods.length; i++) {
Method method = methods[i];
Class[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
if (methodName.equals(method.getName()) && parameterTypes.length == tem.length && match(parameterTypes, tem)) {
hasMethod = true;
index = i;
break;
}
}
if (hasMethod) {
try {
Method method = methods[index];
mValue = method.invoke(mObject, args);
return this;
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else {
Method[] declaredMethods = type.getDeclaredMethods();
if (declaredMethods != null && declaredMethods.length > 0) {
boolean hasMethod2 = false;
int index2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < declaredMethods.length; i++) {
Method declaredMethod = declaredMethods[i];
Class[] parameterTypes = declaredMethod.getParameterTypes();
if (methodName.equals(declaredMethod.getName()) && parameterTypes.length == tem.length && match(parameterTypes, tem)) {
hasMethod2 = true;
index2 = i;
break;
}
}
if (hasMethod2) {
try {
Method declaredMethod = declaredMethods[index2];
declaredMethod.setAccessible(true);
mValue = declaredMethod.invoke(mObject, args);
declaredMethod.setAccessible(false);
return this;
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
return this;
}
//进行方法的参数匹配
private boolean match(Class[] parameterTypes, Class[] tem) {
for (int i = 0; i < parameterTypes.length; i++) {
if (checkClass(parameterTypes[i]) != checkClass(tem[i])) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
//将基本数据类型的class转换为对应包装类的class
private Class checkClass(Class type) {
if (type == null) {
return null;
} else if (type == byte.class) {
return Byte.class;
} else if (type == short.class) {
return Short.class;
} else if (type == int.class) {
return Integer.class;
} else if (type == long.class) {
return Long.class;
} else if (type == boolean.class) {
return Boolean.class;
} else if (type == char.class) {
return Character.class;
} else if (type == float.class) {
return Float.class;
} else if (type == double.class) {
return Double.class;
}
return type;
}