Class
类:拥有相同属性的对象。
自有属性
每个class都有一个constructor构造函数,用来创建自有属性
class Person{
constructor(name,age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
共有属性
写在contrustor外的属性为共有属性。
class Person{
constructor(name,age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
walk(){
console.log('我在走路');
}
}
new,参数传递,this
- 当声明一个对象的时候,必须使用
new。
var p1 = new Person('frank',18)
- 当向Person()括号内传递参数的时候,默认会传递给构造函数
constructor。 -
this就是指对象实例,上面this就是指p1.
继承
- 动物类
class Animal{
constructor(){
this.body = "身体";
}
move(){
console.log('动物可以行走');
}
}
- 人类继承动物
class Person extends Animal{
constructor(name){
super(); //执行所继承类的constructor
this.name = name;
}
walk(){
console.log('人类可以行走')
}
}
-
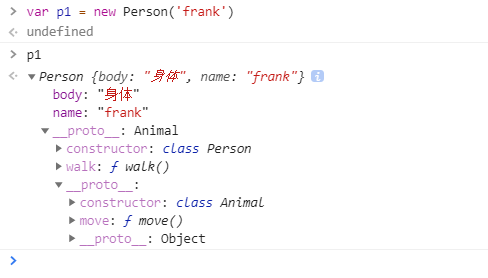
相关截图:
因为p1是person的类,所以有walk和name 属性,又因为Person继承Animal,所以p1有move()属性。
-
extends:继承,其中Person叫做类,Animal叫做基类或者超类。 -
super():执行所继承的类的constructor。在调用this之前先调用super(),有顺序问题。
属性封装:get和set
在Class中,共有属性不能是非函数。
在一个函数属性前面加get,在调用函数的时候,不需要加()就可以执行这个函数。
class Animal{
constructor(){
this.body = "身体";
}
move(){
console.log('动物可以行走');
}
get race(){
return "种族"
}
}
//调用
p1.race //即可
但是在,这种方式存在一个Bug,即race的返回结果无法更改。因为它始终都是在调用race。
race的返回值无法更改.jpg
如果使用get将函数更改为类似非函数,想更改这个非函数的值,使用 set。
class Animal{
constructor(){
this.body = "身体"
this._race = "运物" //隐藏属性
}
move(){
console.log('动物可以行走');
}
get race(){
return this._race
}
set race(value){
return this._race = value
}
}
p1.race = "动物"实际上调用的就是set race(value){}这个函数,所以race的值可以被更改。
set可以更改race的值.jpg
get的好处
可以使某些属性,无法被更改,用来控制只读属性.
class Person extends Animal{
constructor(name){
super(); //执行所继承类的constructor
this.name = name;
this._age = 18;
}
walk(){
console.log('人类可以行走')
}
get age(){
return this._age;
}
}
以上代码,年龄不能被修改了,只能是18。
get用来控制只读属性.jpg
set的作用:
set 用开控制属性值的写入,可以进行判断,来确定是否要更改属性值。
class Person extends Animal{
constructor(name){
super(); //执行所继承类的constructor
this._name = name;
this._age = 18;
}
walk(){
console.log('人类可以行走')
}
get name(){
return this._name;
}
set name(value){
if(value.length > 4){
console.log('拒绝')
}else if(value.length < 2){
console.log('拒绝')
}else {
return this._name = value
}
}
}
静态方法,只能通过类名来访问,不能通过类(即实例)来访问。
class Person{
constructor(name){
this.name = name
}
//静态方法
static die(){
console.log('地球炸了')
}
}
//访问静态方法
Person.die()
静态方法的访问.jpg
在原型上,是实例能访问的方法写在prototype上,使函数自己能访问的代码,直接写在函数上。
Person.die() //等价于上述的static die()
Person.prototype.walk() //等价于上述的walk()