lmplot
lmplot 是一种集合基础绘图与基于数据建立回归模型的绘图方法。旨在创建一个方便拟合数据集回归模型的绘图方法,利用'hue'、'col'、'row'参数来控制绘图变量。
同时可以使用模型参数来调节需要拟合的模型:order、logistic、lowess、robust、logx。
seaborn.lmplot(x, y, data, hue=None, col=None, row=None, palette=None, col_wrap=None, size=5, aspect=1, markers='o', sharex=True, sharey=True, hue_order=None, col_order=None, row_order=None, legend=True, legend_out=True, x_estimator=None, x_bins=None, x_ci='ci', scatter=True, fit_reg=True, ci=95, n_boot=1000, units=None, order=1, logistic=False, lowess=False, robust=False, logx=False, x_partial=None, y_partial=None, truncate=False, x_jitter=None, y_jitter=None, scatter_kws=None, line_kws=None)
Common Parameters:
hue, col, row: strings #定义数据子集的变量,并在不同的图像子集中绘制
Variables that define subsets of the data, which will be drawn on separate facets in the grid. See the *_order parameters to control the order of levels of this variable.
size: scalar, optional #定义子图的高度
Height (in inches) of each facet. See also: aspect.
markers: matplotlib marker code or list of marker codes, optional #定义散点的图标
Markers for the scatterplot. If a list, each marker in the list will be used for each level of the hue variable.
col_wrap: int, optional #设置每行子图数量
“Wrap” the column variable at this width, so that the column facets span multiple rows. Incompatible with a row facet.
order: int, optional #多项式回归,设定指数
If order is greater than 1, use numpy.polyfit to estimate a polynomial regression.
logistic: bool, optional #逻辑回归
If True, assume that y is a binary variable and use statsmodels to estimate a logistic regression model. Note that this is substantially more computationally intensive than linear regression, so you may wish to decrease the number of bootstrap resamples (n_boot) or set ci to None.
logx: bool, optional #转化为 log(x)
If True, estimate a linear regression of the form y ~ log(x), but plot the scatterplot and regression model in the input space. Note that x must be positive for this to work.
Senior Example Ⅰ for Practice
importseabornassnssns.set_style("whitegrid")
tips=sns.load_dataset("tips")
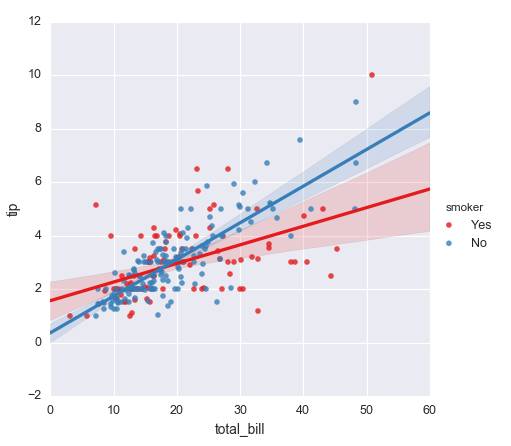
#载入自带数据集#研究小费tips与总消费金额total_bill在吸烟与不吸烟人之间的关系
g=sns.lmplot(x="total_bill",y="tip",hue="smoker",data=tips,palette="Set1")
通过回归模型发现 total_bill=20 为分界点,不吸烟者的小费高于吸烟者
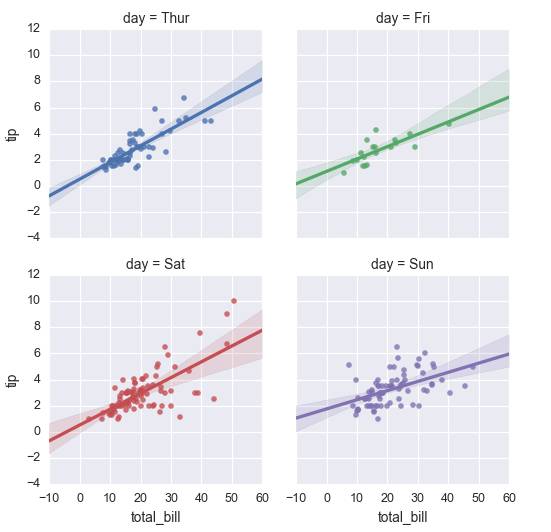
#研究在不同星期下,消费总额与消费的回归关系,col|hue控制子图不同的变量day,col_wrap控制每行子图数量,size控制子图高度g=sns.lmplot(x="total_bill",y="tip",col="day",hue="day",data=tips,col_wrap=2,size=3)
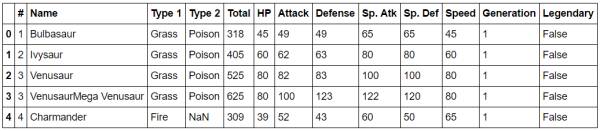
#继续研究pokemon数据集importpandasaspd
importseabornassns
pokemon=pd.read_csv('H:/zhihu/Pokemon.csv')
pokemon.head()
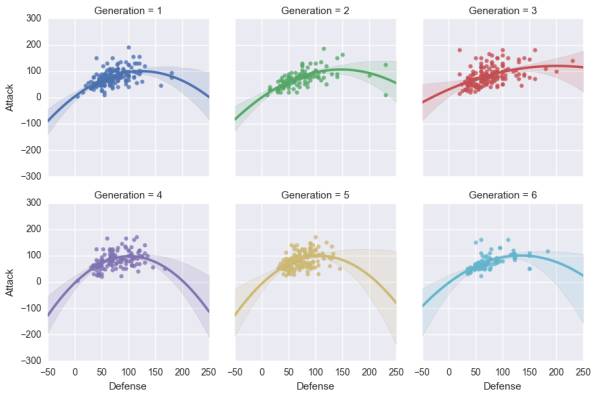
#观察每一代攻击与防御的分布,利用二次多项式逼近sns.lmplot(x="Defense",y="Attack",data=pokemon,col="Generation",hue="Generation",col_wrap=3,size=3,order=2)
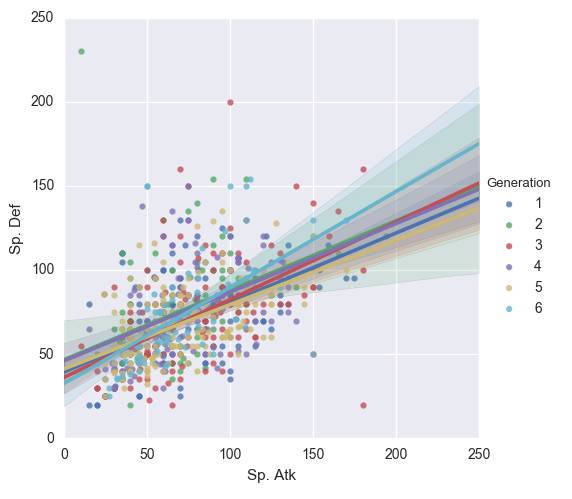
#继续在同一图中观察不同代的sp.Atk,Sp.Def线性关系sns.lmplot(x="Sp. Atk",y="Sp. Def",data=pokemon,hue='Generation',size=5,order=1)
sp.Atk,Sp.Def线性相关性不高导致图像有点浮夸模糊
pokemon 数据集
https://pan.baidu.com/s/1hsDn0mK#list/path=%2F
密码:4zma
如需转载请联系EasyCharts团队!
微信后台回复“转载”即可!
送福利啦!
【书籍推荐】
【必备插件】
【网易云课堂】
欢迎加入 图表绘制之魔方学院QQ群 交流探讨
责任编辑: