ContentProvider的启动流程
一、概要
作为四大组件之一的ContentProvider,在日常开发工作中相对其他组件来说使用频率不是很高。的启动相对activity的启动来说比较简单。关于contentProvider的使用可以看看这个。结合Activity、service和BroadCastRevicer的启动流程,ContentProvider的启动也有着相似的流程。
1、涉及主要类
android.app.ContextImpl.java
android.app.ActivityThread.java
com.android.server.am.ActivityManagerService.java
com.android.server.am.ContentProviderRecord.java
android.app.ApplicationContentResolver.java
android.content.ContentProvider.java
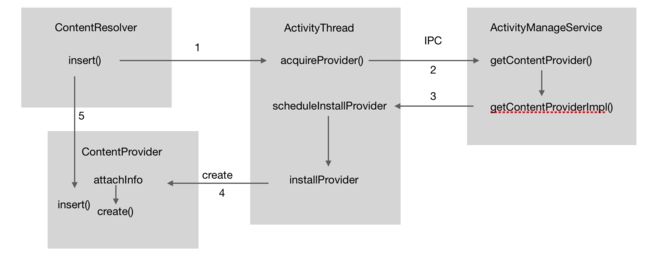
2、流程图
二、具体流程
1、ContentResolver.insert()
public final @Nullable Uri insert(@RequiresPermission.Write @NonNull Uri url,
@Nullable ContentValues values) {
Preconditions.checkNotNull(url, "url");
IContentProvider provider = acquireProvider(url);
if (provider == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown URL " + url);
}
try {
long startTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
Uri createdRow = provider.insert(mPackageName, url, values);
long durationMillis = SystemClock.uptimeMillis() - startTime;
maybeLogUpdateToEventLog(durationMillis, url, "insert", null /* where */);
return createdRow;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// Arbitrary and not worth documenting, as Activity
// Manager will kill this process shortly anyway.
return null;
} finally {
releaseProvider(provider);
}
}
从这里知道通过acquireProvider()方法返回了ContentProvider的实例;然后就可以直接调用insert()方法(这个过程也是IPC的过程),接下来看acquireProvider()方法的具体实现。也就是ContentResolver的实现类ApplicationContentResolver的acquireProvider()方法:
2、ApplicationContentResolver.acquireProvider()
@Override
protected IContentProvider acquireProvider(Context context, String auth) {
return mMainThread.acquireProvider(context,
ContentProvider.getAuthorityWithoutUserId(auth),
resolveUserIdFromAuthority(auth), true);
}
很简单直接调用了ActivityThread类的acquireProvider方法:
3、ActivityThread.acquireProvider()
public final IContentProvider acquireProvider(
Context c, String auth, int userId, boolean stable) {
final IContentProvider provider = acquireExistingProvider(c, auth, userId, stable);
if (provider != null) {
return provider;
}
ContentProviderHolder holder = null;
try {
holder = ActivityManager.getService().getContentProvider(
getApplicationThread(), auth, userId, stable);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
if (holder == null) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Failed to find provider info for " + auth);
return null;
}
holder = installProvider(c, holder, holder.info,
true /*noisy*/, holder.noReleaseNeeded, stable);
return holder.provider;
}
在这一步首先会通过AMS完成初始化ContentProvider的准备工作,包括判断contentProvider启动的权限及进程初始化,然后ActivityThread通过反射创建contentProvider实例。
4、ActivityManagegeService.getContentProvider()
最后会调用getContentProviderImpl()方法:
private ContentProviderHolder getContentProviderImpl(IApplicationThread caller,
String name, IBinder token, boolean stable, int userId) {
ContentProviderRecord cpr;
ContentProviderConnection conn = null;
ProviderInfo cpi = null;
synchronized(this) {
// 省略部分代码
//判断该contentProvider是否正在运行
boolean providerRunning = cpr != null && cpr.proc != null && !cpr.proc.killed;
if (providerRunning) {
cpi = cpr.info;
String msg;
checkTime(startTime, "getContentProviderImpl: before checkContentProviderPermission");
//检查contentProvider调用的权限
if ((msg = checkContentProviderPermissionLocked(cpi, r, userId, checkCrossUser))
!= null) {
throw new SecurityException(msg);
}
checkTime(startTime, "getContentProviderImpl: after checkContentProviderPermission");
//若存在则直接返回
if (r != null && cpr.canRunHere(r)) {
ContentProviderHolder holder = cpr.newHolder(null);
holder.provider = null;
return holder;
}
// Don't expose providers between normal apps and instant apps
try {
//检查相应的设置(setting里的)
if (AppGlobals.getPackageManager()
.resolveContentProvider(name, 0 /*flags*/, userId) == null) {
return null;
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
//省略部分代码
}
if (!providerRunning) {
try {
checkTime(startTime, "getContentProviderImpl: before resolveContentProvider");
cpi = AppGlobals.getPackageManager().
resolveContentProvider(name,
STOCK_PM_FLAGS | PackageManager.GET_URI_PERMISSION_PATTERNS, userId);
checkTime(startTime, "getContentProviderImpl: after resolveContentProvider");
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
}
//若没有符合注册条件的contentProvider 直接返回null
if (cpi == null) {
return null;
}
//系统contentProvider
boolean singleton = isSingleton(cpi.processName, cpi.applicationInfo,
cpi.name, cpi.flags)
&& isValidSingletonCall(r.uid, cpi.applicationInfo.uid);
if (singleton) {
userId = UserHandle.USER_SYSTEM;
}
//省略部分代码
// If the provider is not already being launched, then get it
// started.
if (i >= N) {
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
//省略部分代码
// Use existing process if already started
checkTime(startTime, "getContentProviderImpl: looking for process record");
ProcessRecord proc = getProcessRecordLocked(
cpi.processName, cpr.appInfo.uid, false);
//若contentProvider所在的进程已经启动了
if (proc != null && proc.thread != null && !proc.killed) {
if (!proc.pubProviders.containsKey(cpi.name)) {
checkTime(startTime, "getContentProviderImpl: scheduling install");
proc.pubProviders.put(cpi.name, cpr);
try {
//初始化contentProvider
proc.thread.scheduleInstallProvider(cpi);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
}
} else {
checkTime(startTime, "getContentProviderImpl: before start process");
//若contentProvider所在的进程没有启动,则启动该进程
proc = startProcessLocked(cpi.processName,
cpr.appInfo, false, 0, "content provider",
new ComponentName(cpi.applicationInfo.packageName,
cpi.name), false, false, false);
checkTime(startTime, "getContentProviderImpl: after start process");
if (proc == null) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Unable to launch app "
+ cpi.applicationInfo.packageName + "/"
+ cpi.applicationInfo.uid + " for provider "
+ name + ": process is bad");
return null;
}
}
cpr.launchingApp = proc;
mLaunchingProviders.add(cpr);
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
}
checkTime(startTime, "getContentProviderImpl: updating data structures");
// Make sure the provider is published (the same provider class
// may be published under multiple names).
if (firstClass) {
mProviderMap.putProviderByClass(comp, cpr);
}
mProviderMap.putProviderByName(name, cpr);
conn = incProviderCountLocked(r, cpr, token, stable);
if (conn != null) {
conn.waiting = true;
}
}
checkTime(startTime, "getContentProviderImpl: done!");
grantEphemeralAccessLocked(userId, null /*intent*/,
cpi.applicationInfo.uid, UserHandle.getAppId(Binder.getCallingUid()));
}
//阻塞等待contentProvider所在进程启动完成
synchronized (cpr) {
while (cpr.provider == null) {
if (cpr.launchingApp == null) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Unable to launch app "
+ cpi.applicationInfo.packageName + "/"
+ cpi.applicationInfo.uid + " for provider "
+ name + ": launching app became null");
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.AM_PROVIDER_LOST_PROCESS,
UserHandle.getUserId(cpi.applicationInfo.uid),
cpi.applicationInfo.packageName,
cpi.applicationInfo.uid, name);
return null;
}
try {
if (DEBUG_MU) Slog.v(TAG_MU,
"Waiting to start provider " + cpr
+ " launchingApp=" + cpr.launchingApp);
if (conn != null) {
conn.waiting = true;
}
cpr.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException ex) {
} finally {
if (conn != null) {
conn.waiting = false;
}
}
}
}
return cpr != null ? cpr.newHolder(conn) : null;
}
这里主要做的工作是判断该contentProvider所在的进程是否启动了,如果没有启动则启动该进程。
5、ActivityTHread.installProvider()
private ContentProviderHolder installProvider(Context context,
ContentProviderHolder holder, ProviderInfo info,
boolean noisy, boolean noReleaseNeeded, boolean stable) {
ContentProvider localProvider = null;
IContentProvider provider;
if (holder == null || holder.provider == null) {
//省略部分代码...
try {
final java.lang.ClassLoader cl = c.getClassLoader();
localProvider = (ContentProvider)cl.
loadClass(info.name).newInstance();
provider = localProvider.getIContentProvider();
if (provider == null) {
return null;
}
localProvider.attachInfo(c, info);
//省略部分代码...
return retHolder;
}
最后通过反射创建ContentProvider的实例,至此ContentProvider就已经启动了。
三、总结
ContentProvider的启动也是IPC的过程。通过ActivityThread和AMS之间的通信来完成ContentProvider的启动