opencv项目实践一(答题卡识别)
- 读入图片,做一些预处理工作。
- 进行轮廓检测,然后找到该图片最大的轮廓,就是答题卡部分。
- 进行透视变换,以去除除答题卡外的多于部分,并且可以对答题卡进行校正。
- 再次检测轮廓,定位每个选项。
- 对选项圆圈先按照竖坐标排序,再按照行坐标排序,这样就从左到右从上到下的获得了每个选项轮廓。
- 对每个选项轮廓进行检查,如果某个选项轮廓中的白色点多,说明该选项被选中,否则就是没被选上。
细节部分看过程:
1、预处理(去噪,灰度,二值化)
img = cv2.imread("1.png",1)
#高斯去噪
img_gs = cv2.GaussianBlur(img,[5,5],0)
# 转灰度
img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img_gs,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 自适应二值化
_,binary_img = cv2.threshold(img_gray,0,255,cv2.THRESH_OTSU|cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
注:cv2.THRESH_OTSU|cv2.THRESH_BINARY,该参数指的是自适应阈值+反二值化,做自适应阈值的时候阈值要设置为0
2、轮廓检测
# 找轮廓
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(binary_img,cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
# 按照轮廓的面积从大到小排序
cnts = sorted(contours,key = cv2.contourArea,reverse=True)
# 画轮廓
draw_img = cv2.drawContours(img.copy(),cnts[0],-1,(0,255,255),2)
注:findContours函数,传入的图像应该是二值图像,cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL指的是只检测外部轮廓,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE指的返回轮廓上的所有点。
# 轮廓近似
# 阈值,一般为轮廓长度的2%
alpha = 0.02*cv2.arcLength(cnts[0],True)
approxCurve = cv2.approxPolyDP(cnts[0],alpha,True)
draw_img = cv2.drawContours(img.copy(),[approxCurve],-1,(255,0,0),2)
这里做轮廓近似的目的是,之前检测到的轮廓看似是一个多边形,其实本质上是只是点集。
cv2.approxPolyDP(contour,epsilon,True),多边形逼近,第一个参数是点集,第二个参数是精度(原始轮廓的边界点与拟合多边形之间的最大距离),第三个参数指新产生的轮廓是否需要闭合,返回值approxCurve为多边形的点集(按照逆时针排序)。与该函数类似的函数还有cv2.boundingRect(矩形包围框)cv2.minAreaRect(最小包围矩形框),cv2.minEnclosingCircle(最小包围圆形)cv2.filtEllipse(最优拟合椭圆)cv2.filtLine(最优拟合直线),cv2.minEnclosingTriangle(最小外包三角形)
3、透视变换
#透视变换
# 矩形的四个顶点为approxCurve[0][0],approxCurve[1][0],approxCurve[2][0],approxCurve[3][0]
# 分别表示矩形的TL,BL,BR,TR四个点
a1 = list(approxCurve[0][0])
a2 = list(approxCurve[1][0])
a3 = list(approxCurve[2][0])
a4 = list(approxCurve[3][0])
# 原始矩阵
mat1 = np.array([a1,a2,a3,a4],dtype = np.float32)
# 计算矩形的w和h
w1 = int(np.sqrt((a1[0]-a4[0])**2+(a1[1]-a4[1])**2))
w2 = int(np.sqrt((a2[0]-a3[0])**2+(a2[1]-a3[1])**2))
h1 = int(np.sqrt((a1[0]-a2[0])**2+(a1[1]-a2[1])**2))
h2 = int(np.sqrt((a3[0]-a4[0])**2+(a3[1]-a4[1])**2))
w,h=max(w1,w2),max(h1,h2)
# 计算透视变换后的坐标
new_a1 = [0,0]
new_a2 = [0,h]
new_a3 = [w,h]
new_a4 = [w,0]
# 目标矩阵
mat2 = np.array([new_a1,new_a2,new_a3,new_a4],dtype = np.float32)
# 透视变换矩阵
mat = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(mat1,mat2)
# 进行透视变换
res = cv2.warpPerspective(img,mat,(w,h))
imshow((res))
- 首先获取原图多边形的四个顶点,注意顶点顺序。
- 然后构造原始顶点矩阵。
- 计算矩形长宽,构造变换后的目标矩阵。
- 获取原始矩阵到目标矩阵的透视变换矩阵
- 进行透视变换
4、轮廓检测,检测每个选项
res_gray = cv2.cvtColor(res,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
_,binary_res = cv2.threshold(res_gray,0,255,cv2.THRESH_OTSU|cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV)
contours = cv2.findContours(binary_res,cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)[0]
dst = cv2.drawContours(res.copy(),contours,-1,(0,0,255),1)
imshow(dst)
# 挑选合适的轮廓
def check(contours):
ans = []
for i in contours:
area = float(cv2.contourArea(i))
length = float(cv2.arcLength(i,True))
if area<=0 or length<=0:
continue
if area/length >7.05 and area/length<10.5:
ans.append(i)
return ans
ans_contours = check(contours)
dst_new = cv2.drawContours(res.copy(),ans_contours,-1,(0,255,255),3 )
imshow(dst_new)
# 遍历每一个圆形轮廓,画外接圆
circle = []
for i in ans_contours:
(x,y),r = cv2.minEnclosingCircle(i)
center = (int(x),int(y))
r = int(r)
circle.append((center,r))
# 按照外接圆的水平坐标排序center[1],也就是圆心的高度h,或者y坐标
circle.sort(key = lambda x:x[0][1])
A = []
for i in range(1,6):
now = circle[(i-1)*5:i*5]
now.sort(key = lambda x:x[0][0])
A.extend(now)
每个选项按照圆心从左到右,从上到下的顺序保存在了A中
6、选项检测
思路:对于A中的每个选项圆,计算它有所覆盖的坐标,然后判断这些坐标在二值图像中对应的值,统计白色点的个数,
如果白色点所占的比例比较大的话,说明该选项被选中。
def dots_distance(dot1,dot2):
#计算二维空间中两个点的距离
return ((dot1[0]-dot2[0])**2+(dot1[1]-dot2[1])**2)**0.5
def count_dots(center,radius):
#输入圆的中心点与半径,返回圆内所有的坐标
dots = []
for i in range(-radius,radius+1):
for j in range(-radius,radius+1):
dot2 = (center[0]+i,center[1]+j)
if dots_distance(center,dot2) <= radius:
dots.append(dot2)
return dots
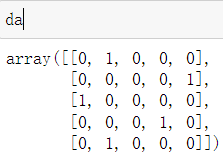
da = []
for i in A:
dots = count_dots(i[0],i[1])
all_dots = len(dots)
whilt_dots = 0
for j in dots:
if binary_res[j[1]][j[0]] == 255:
whilt_dots = whilt_dots+1
if whilt_dots/all_dots>=0.4:
da.append(1)
else:
da.append(0)
da = np.array(da)
da = np.reshape(da,(5,5))