mysql官方的HA中间件
mysql官方的HA中间件
http://www.innomysql.net/article/4417.html
http://www.mysql.com/products/enterprise/fabric.html
MySQL Fabric is an extensible framework for managing farms of MySQL Servers. Two features have been implemented - High Availability (HA) and scaling out using data sharding. These features can be used in isolation or in combination.
Both features are implemented in two layers:
- The mysqlfabric process which processes any management requests. When using the HA feature, this process can also be made responsible for monitoring the master server and initiating failover to promote a slave to be the new master should it fail.
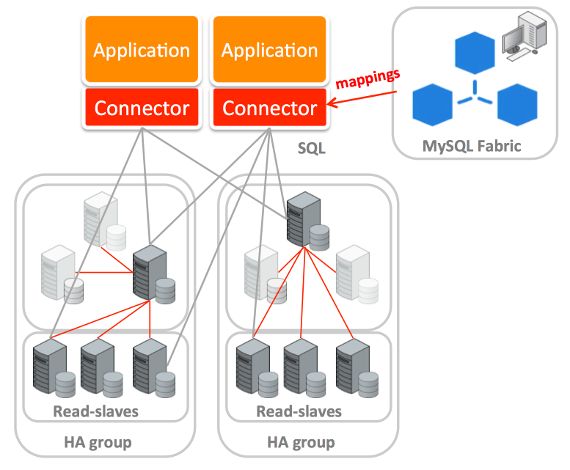
- MySQL Fabric-aware connectors store a cache of the routing information that it has fetched from MySQL Fabric and then uses that information to send transactions or queries to the correct MySQL Server.
MySQL Fabric provides high availability and database sharding for MySQL Servers
High Availability
HA Groups are formed from pools of two or more MySQL Servers; at any point in time, one of those servers is the Primary (MySQL Replication master) and the others are Secondaries (MySQL Replication slaves). The role of a HA Group is to ensure that access to the data held within that group is always available.
While MySQL Replication allows the data to be made safe by duplicating it, for a HA solution two extra components are needed and MySQL Fabric provides these:
- Failure detection and promotion - MySQL Fabric monitors the Primary within the HA group and should that server fail then it selects one of the Secondaries and promotes it to be the Primary
- Routing of database requests - The routing of writes to the Primary and load balancing reads across the slaves is transparent to the application, even when the topology changes during failover
Sharding - Scaling out
When nearing the capacity or write performance limit of a single MySQL Server (or HA group), MySQL Fabric can be used to scale-out the database servers by partitioning the data across multiple MySQL Server "groups". Note that a group could contain a single MySQL Server or it could be a HA group.
The administrator defines how data should be sharded between these servers; indicating which table columns should be used as shard keys and whether HASH or RANGE mappings should be used to map from those keys to the correct shard.
If further shards are needed then MySQL Fabric can split existing shards; it is also possible to relocate shards.
MySQL Fabric-Aware Connectors
MySQL Fabric-Aware connectors are currently available for Java, PHP and Python. These connectors automatically fetch routing information from MySQL Fabric and then cache it in order to route queries and transactions directly to the correct MySQL Server. The application simply provides the sharding key - with no knowledge of the topology of the server farm or the state of any server.
Proxy-Free Operation
As transactions and queries are routed directly to the correct MySQL Server, there is no need for a proxy function - saving latency and complexity. In addition, there is no need for agents to be run on any of the target machines.