数组模拟栈与队列
文章目录
- 数组模拟栈与队列
-
- 一、 数组模拟栈
-
- 模板
- 栈顶指针指向栈顶元素(**)
- 栈顶指针指向栈顶元素的后一个位置
- 二、数组模拟队列
-
- 模板
- 1.普通队列
- 2.循环队列
数组模拟栈与队列
一、 数组模拟栈
栈特点:后进先出
模板
// tt表示栈顶
int stk[N], tt = 0;
// 向栈顶插入一个数
stk[ ++ tt] = x;
// 从栈顶弹出一个数
tt -- ;
// 栈顶的值
stk[tt];
// 判断栈是否为空
if (tt > 0)
{
}
栈顶指针指向栈顶元素(**)
tt 栈顶指针指向栈顶元素
stk[0]不会进行赋值
先栈顶指针++, 后赋值 stk[tt++]=x
输出栈顶元素 cout<
弹出栈顶元素 t --
【参考代码】
#include【改成函数】
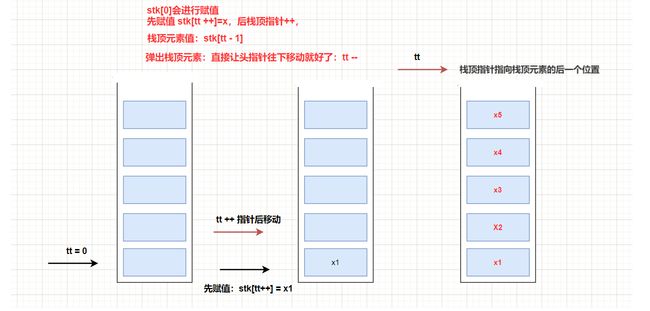
#include栈顶指针指向栈顶元素的后一个位置
tt 栈顶指针指向栈顶元素的后一个位置
stk[0]会进行赋值
先栈顶赋值stk[k++] = x, 后栈顶指针++
输出栈顶元素 cout<
弹出栈顶元素 t --
【参考代码】
#include总结:
以上两种实现方式,用其中一种即可!
【判断回文串】
#include
if(str == s) cout<<"是回文串"<<endl;
else cout<<"NO"<<endl;
return 0;
}
【 进制转换】
#include二、数组模拟队列
队列特点:先进先出
模板
1.普通队列
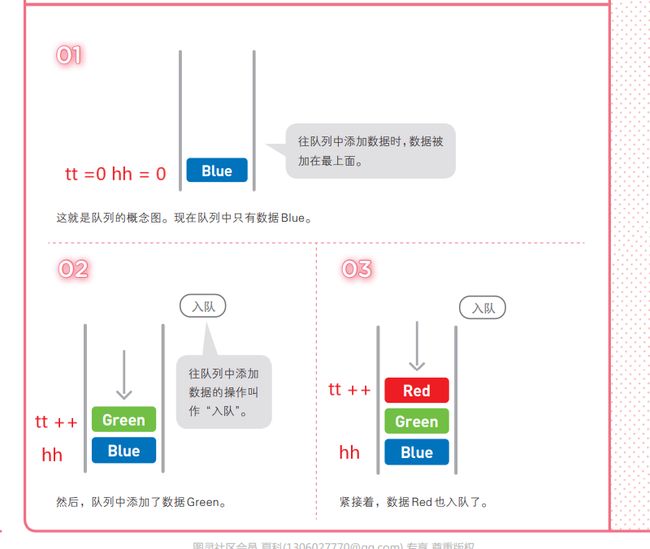
// hh 表示队头,tt表示队尾
int q[N], hh = 0, tt = -1; // 因为hh从0开始且入队时++tt所有tt从-1开始(q[0]赋值)
// 向队尾插入一个数
q[ ++ tt] = x;
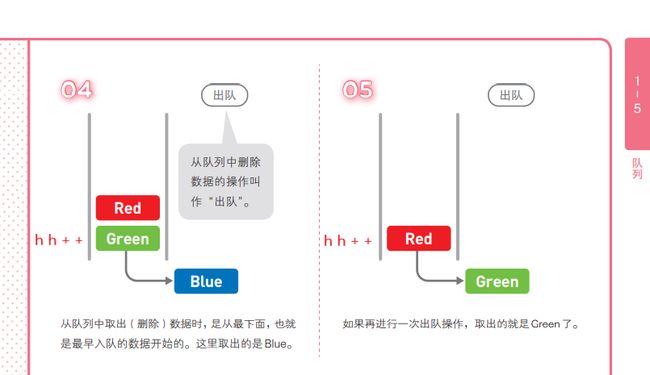
// 从队头弹出一个数
hh ++ ;
// 队头的值
q[hh];
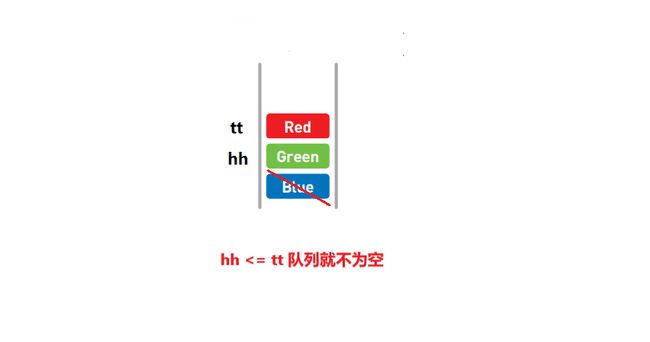
// 判断队列是否为空
if (hh <= tt)
{
}
实现一个队列,队列初始为空,支持四种操作:
push x– 向队尾插入一个数 xx;pop– 从队头弹出一个数;empty– 判断队列是否为空;query– 查询队头元素。现在要对队列进行 M 个操作,其中的每个操作 3 和操作 4 都要输出相应的结果。
输入格式
第一行包含整数 M,表示操作次数。
接下来 M 行,每行包含一个操作命令,操作命令为
push x,pop,empty,query中的一种。输出格式
对于每个
empty和query操作都要输出一个查询结果,每个结果占一行。其中,
empty操作的查询结果为YES或NO,query操作的查询结果为一个整数,表示队头元素的值。数据范围
1≤M≤100000,
1≤x≤109,
所有操作保证合法。输入样例:
10
push 6
empty
query
pop
empty
push 3
push 4
pop
query
push 6输出样例:
NO
6
YES
4
#include2.循环队列
// hh 表示队头,tt表示队尾的后一个位置
int q[N], hh = 0, tt = 0;
// 向队尾插入一个数
q[tt ++ ] = x;
if (tt == N) tt = 0;
// 从队头弹出一个数
hh ++ ;
if (hh == N) hh = 0;
// 队头的值
q[hh];
// 判断队列是否为空
if (hh != tt)
{
}
“先来的数据先处理”是一种很常见的思路,所以队列的应用范围非常广泛。往后学习的
广度优先搜索算法,通常就会从搜索候补中选择最早的数据作为下 一个顶点。此时,在候补顶点的管理上就可以使用队列。