PointPillars点云检测在OpenPCDet推理代码详解
在之前的文章中已经详细解析了PointPillars的论文和训练代码的实现和详解,可以参考之前的博客:PointPillars论文解析和OpenPCDet代码解析_NNNNNathan的博客-CSDN博客。
本篇博客将会详细解析PointPillars模型在OpenPCDet中推理代码,并测试推理的效果。
读者可以下载OpenPCDet后根据文章进行阅读和理解。
由于本人才疏学浅,解析中难免会出现不足之处,欢迎指正、讨论,有好的建议或意见都可以在评论区留言。谢谢大家!
PointPillars的论文地址为:
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1812.05784.pdf
解析参考代码:
https://github.com/open-mmlab/OpenPCDet
详细注释代码在已放到我的github仓库:
GitHub - Nathansong/OpenPCDdet-annotated: OpenPCDdet模型代码解析
一、PointPillars网络结构和数据预处理
![]()
网络结构已经在之前训练的结构中进行了详细的介绍。这里将跳过这部分内容直接续接到之前的检测头实现代码中解析推理实现。
在推理之前,需要对原始的点云数据进行预处理操作;需要把在指定范围之外的点云移除,同时还需要使用VoxelGeneratorWrapper将点云生成一个一个pillar。详情可以看训练博客介绍。
二、网络推理结果
在PointPillars的最终结果中,我们得到了特征图上的每个anchor和每个anchor预测7个回归参数、1一个类别、一个方向分类这三个结果。其中7回归参数 (x, y, z, w, l, h, θ);x, y, z预测了目标中心点到该anchor左上顶点的偏移数值, w,l,h预测了基于该anchor长宽高的调整系数,θ预测了box的旋转角度、方向类别预测了box的朝向,两个方向关系如下(与雷达坐标系下的x轴偏差45度,原因可以查看这个issue:https://github.com/open-mmlab/OpenPCDet/issues/80)。
下图来自FCOS3D:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2104.10956.pdf
代码在pcdet/models/dense_heads/anchor_head_single.py
import numpy as np
import torch.nn as nn
from .anchor_head_template import AnchorHeadTemplate
class AnchorHeadSingle(AnchorHeadTemplate):
"""
Args:
model_cfg: AnchorHeadSingle的配置
input_channels: 384 输入通道数
num_class: 3
class_names: ['Car','Pedestrian','Cyclist']
grid_size: (432, 496, 1)
point_cloud_range: (0, -39.68, -3, 69.12, 39.68, 1)
predict_boxes_when_training: False
"""
def __init__(self, model_cfg, input_channels, num_class, class_names, grid_size, point_cloud_range,
predict_boxes_when_training=True, **kwargs):
super().__init__(
model_cfg=model_cfg, num_class=num_class, class_names=class_names, grid_size=grid_size,
point_cloud_range=point_cloud_range,
predict_boxes_when_training=predict_boxes_when_training
)
# 每个点有3个尺度的个先验框 每个先验框都有两个方向(0度,90度) num_anchors_per_location:[2, 2, 2]
self.num_anchors_per_location = sum(self.num_anchors_per_location) # sum([2, 2, 2])
# Conv2d(512,18,kernel_size=(1,1),stride=(1,1))
self.conv_cls = nn.Conv2d(
input_channels, self.num_anchors_per_location * self.num_class,
kernel_size=1
)
# Conv2d(512,42,kernel_size=(1,1),stride=(1,1))
self.conv_box = nn.Conv2d(
input_channels, self.num_anchors_per_location * self.box_coder.code_size,
kernel_size=1
)
# 如果存在方向损失,则添加方向卷积层Conv2d(512,12,kernel_size=(1,1),stride=(1,1))
if self.model_cfg.get('USE_DIRECTION_CLASSIFIER', None) is not None:
self.conv_dir_cls = nn.Conv2d(
input_channels,
self.num_anchors_per_location * self.model_cfg.NUM_DIR_BINS,
kernel_size=1
)
else:
self.conv_dir_cls = None
self.init_weights()
# 初始化参数
def init_weights(self):
pi = 0.01
# 初始化分类卷积偏置
nn.init.constant_(self.conv_cls.bias, -np.log((1 - pi) / pi))
# 初始化分类卷积权重
nn.init.normal_(self.conv_box.weight, mean=0, std=0.001)
def forward(self, data_dict):
# 从字典中取出经过backbone处理过的信息
# spatial_features_2d 维度 (batch_size, 384, 248, 216)
spatial_features_2d = data_dict['spatial_features_2d']
# 每个坐标点上面6个先验框的类别预测 --> (batch_size, 18, 200, 176)
cls_preds = self.conv_cls(spatial_features_2d)
# 每个坐标点上面6个先验框的参数预测 --> (batch_size, 42, 200, 176) 其中每个先验框需要预测7个参数,分别是(x, y, z, w, l, h, θ)
box_preds = self.conv_box(spatial_features_2d)
# 维度调整,将类别放置在最后一维度 [N, H, W, C] --> (batch_size, 200, 176, 18)
cls_preds = cls_preds.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous()
# 维度调整,将先验框调整参数放置在最后一维度 [N, H, W, C] --> (batch_size ,200, 176, 42)
box_preds = box_preds.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous()
# 将类别和先验框调整预测结果放入前向传播字典中
self.forward_ret_dict['cls_preds'] = cls_preds
self.forward_ret_dict['box_preds'] = box_preds
# 进行方向分类预测
if self.conv_dir_cls is not None:
# # 每个先验框都要预测为两个方向中的其中一个方向 --> (batch_size, 12, 200, 176)
dir_cls_preds = self.conv_dir_cls(spatial_features_2d)
# 将类别和先验框方向预测结果放到最后一个维度中 [N, H, W, C] --> (batch_size, 248, 216, 12)
dir_cls_preds = dir_cls_preds.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous()
# 将方向预测结果放入前向传播字典中
self.forward_ret_dict['dir_cls_preds'] = dir_cls_preds
else:
dir_cls_preds = None
"""
如果是在训练模式的时候,需要对每个先验框分配GT来计算loss
"""
if self.training:
# targets_dict = {
# 'box_cls_labels': cls_labels, # (4,211200)
# 'box_reg_targets': bbox_targets, # (4,211200, 7)
# 'reg_weights': reg_weights # (4,211200)
# }
targets_dict = self.assign_targets(
gt_boxes=data_dict['gt_boxes'] # (4,39,8)
)
# 将GT分配结果放入前向传播字典中
self.forward_ret_dict.update(targets_dict)
# 如果不是训练模式,则直接生成进行box的预测
if not self.training or self.predict_boxes_when_training:
# 根据预测结果解码生成最终结果
batch_cls_preds, batch_box_preds = self.generate_predicted_boxes(
batch_size=data_dict['batch_size'],
cls_preds=cls_preds, box_preds=box_preds, dir_cls_preds=dir_cls_preds
)
data_dict['batch_cls_preds'] = batch_cls_preds # (1, 211200, 3) 70400*3=211200
data_dict['batch_box_preds'] = batch_box_preds # (1, 211200, 7)
data_dict['cls_preds_normalized'] = False
return data_dict经过头预测后,可以得到三个张量,分别是:
每个anchor的类别预测: (batch_size, 248, 216, 18)
每个anchor的7个回归参数预测: (batch_size ,248, 216, 42)
每个anchor的方向分类: (batch_size ,248, 216, 12)
其中18可以看成是6个anchor,每个anchor预测3个类别;
其中42可以看成是6个anchor,每个anchor预测7个回归参数;
其中12可以看成是6个anchor,每个anchor预测2个方向;
注:推理时,默认的batch_size为1。
接下来生成预测结果:
代码在:pcdet/models/dense_heads/anchor_head_template.py
def generate_predicted_boxes(self, batch_size, cls_preds, box_preds, dir_cls_preds=None):
"""
Args:
batch_size:
cls_preds: (N, H, W, C1)
box_preds: (N, H, W, C2)
dir_cls_preds: (N, H, W, C3)
Returns:
batch_cls_preds: (B, num_boxes, num_classes)
batch_box_preds: (B, num_boxes, 7+C)
"""
if isinstance(self.anchors, list):
# 是否使用多头预测,默认否
if self.use_multihead:
anchors = torch.cat([anchor.permute(3, 4, 0, 1, 2, 5).contiguous().view(-1, anchor.shape[-1])
for anchor in self.anchors], dim=0)
else:
"""
每个类别anchor的生成情况:
[(Z, Y, X, anchor尺度, 该尺度anchor方向, 7个回归参数)
(Z, Y, X, anchor尺度, 该尺度anchor方向, 7个回归参数)
(Z, Y, X, anchor尺度, 该尺度anchor方向, 7个回归参数)]
在倒数第三个维度拼接
anchors 维度 (Z, Y, X, 3个anchor尺度, 每个尺度两个方向, 7)
(1, 248, 216, 3, 2, 7)
"""
anchors = torch.cat(self.anchors, dim=-3)
else:
anchors = self.anchors
# 计算一共有多少个anchor Z*Y*X*num_of_anchor_scale*anchor_rot
num_anchors = anchors.view(-1, anchors.shape[-1]).shape[0]
# (batch_size, Z*Y*X*num_of_anchor_scale*anchor_rot, 7)
batch_anchors = anchors.view(1, -1, anchors.shape[-1]).repeat(batch_size, 1, 1)
# 将预测结果都flatten为一维的
# (batch_size, Z*Y*X*num_of_anchor_scale*anchor_rot, 3)
batch_cls_preds = cls_preds.view(batch_size, num_anchors, -1).float() \
if not isinstance(cls_preds,
list) else cls_preds
# (batch_size, Z*Y*X*num_of_anchor_scale*anchor_rot, 7)
batch_box_preds = box_preds.view(batch_size, num_anchors, -1) if not isinstance(box_preds, list) \
else torch.cat(box_preds, dim=1).view(batch_size, num_anchors, -1)
# 对7个预测的box参数进行解码操作
batch_box_preds = self.box_coder.decode_torch(batch_box_preds, batch_anchors)
# 每个anchor的方向预测
if dir_cls_preds is not None:
# 0.78539 方向偏移
dir_offset = self.model_cfg.DIR_OFFSET
# 0
dir_limit_offset = self.model_cfg.DIR_LIMIT_OFFSET # 0
# 将方向预测结果flatten为一维的 (batch_size, Z*Y*X*num_of_anchor_scale*anchor_rot, 2)
dir_cls_preds = dir_cls_preds.view(batch_size, num_anchors, -1) if not isinstance(dir_cls_preds, list) \
else torch.cat(dir_cls_preds, dim=1).view(batch_size, num_anchors, -1) # (1, 321408, 2)
# (batch_size, Z*Y*X*num_of_anchor_scale*anchor_rot)
# 取出所有anchor的方向分类 : 正向和反向
dir_labels = torch.max(dir_cls_preds, dim=-1)[1]
# pi
period = (2 * np.pi / self.model_cfg.NUM_DIR_BINS)
# 将角度在0到pi之间 在OpenPCDet中,坐标使用的是统一规范坐标,x向前,y向左,z向上
# 这里参考训练时候的原因,现将角度角度沿着x轴的逆时针旋转了45度得到dir_rot
dir_rot = common_utils.limit_period(
batch_box_preds[..., 6] - dir_offset, dir_limit_offset, period
)
"""
从新将角度旋转回到激光雷达坐标系中,所以需要加回来之前减去的45度,
如果dir_labels是1的话,说明方向在是180度的,因此需要将预测的角度信息加上180度,
否则预测角度即是所得角度
"""
batch_box_preds[..., 6] = dir_rot + dir_offset + period * dir_labels.to(batch_box_preds.dtype)
# PointPillars中无此项
if isinstance(self.box_coder, box_coder_utils.PreviousResidualDecoder):
batch_box_preds[..., 6] = common_utils.limit_period(
-(batch_box_preds[..., 6] + np.pi / 2), offset=0.5, period=np.pi * 2
)
return batch_cls_preds, batch_box_preds上述代码中的box解码操作,也就是编码的逆操作:
代码在:pcdet/utils/box_coder_utils.py
def decode_torch(self, box_encodings, anchors):
"""
Args:
box_encodings: (B, N, 7 + C) or (N, 7 + C) [x, y, z, dx, dy, dz, heading or *[cos, sin], ...]
anchors: (B, N, 7 + C) or (N, 7 + C) [x, y, z, dx, dy, dz, heading, ...]
Returns:
"""
# 这里指torch.split的第二个参数 torch.split(tensor, split_size, dim=) split_size是切分后每块的大小,不是切分为多少块!,多余的参数使用*cags接收
xa, ya, za, dxa, dya, dza, ra, *cas = torch.split(anchors, 1, dim=-1)
# 分割编码后的box PointPillar为False
if not self.encode_angle_by_sincos:
xt, yt, zt, dxt, dyt, dzt, rt, *cts = torch.split(box_encodings, 1, dim=-1)
else:
xt, yt, zt, dxt, dyt, dzt, cost, sint, *cts = torch.split(box_encodings, 1, dim=-1)
# 计算anchor对角线长度
diagonal = torch.sqrt(dxa ** 2 + dya ** 2) # (B, N, 1)-->(1, 321408, 1)
# loss计算中anchor与GT编码的运算:g表示gt,a表示anchor
# ∆x = (x^gt − xa^da)/diagonal --> x^gt = ∆x * diagonal + x^da
# 下同
xg = xt * diagonal + xa
yg = yt * diagonal + ya
zg = zt * dza + za
# ∆l = log(l^gt / l^a)的逆运算 --> l^gt = exp(∆l) * l^a
# 下同
dxg = torch.exp(dxt) * dxa
dyg = torch.exp(dyt) * dya
dzg = torch.exp(dzt) * dza
# 如果角度是cos和sin编码,采用新的解码方式 PointPillar为False
if self.encode_angle_by_sincos:
rg_cos = cost + torch.cos(ra)
rg_sin = sint + torch.sin(ra)
rg = torch.atan2(rg_sin, rg_cos)
else:
# rts = [rg - ra] 角度的逆运算
rg = rt + ra
# PointPillar无此项
cgs = [t + a for t, a in zip(cts, cas)]
return torch.cat([xg, yg, zg, dxg, dyg, dzg, rg, *cgs], dim=-1)三、推理结果后处理
此处对所有的预测结果进行了无类别的nms操作,得到了最终的预测结果。
代码在:pcdet/models/detectors/detector3d_template.py
def post_processing(self, batch_dict):
"""
Args:
batch_dict:
batch_size:
batch_cls_preds: (B, num_boxes, num_classes | 1) or (N1+N2+..., num_classes | 1)
or [(B, num_boxes, num_class1), (B, num_boxes, num_class2) ...]
multihead_label_mapping: [(num_class1), (num_class2), ...]
batch_box_preds: (B, num_boxes, 7+C) or (N1+N2+..., 7+C)
cls_preds_normalized: indicate whether batch_cls_preds is normalized
batch_index: optional (N1+N2+...)
has_class_labels: True/False
roi_labels: (B, num_rois) 1 .. num_classes
batch_pred_labels: (B, num_boxes, 1)
Returns:
"""
# post_process_cfg后处理参数,包含了nms类型、阈值、使用的设备、nms后最多保留的结果和输出的置信度等设置
post_process_cfg = self.model_cfg.POST_PROCESSING
# 推理默认为1
batch_size = batch_dict['batch_size']
# 保留计算recall的字典
recall_dict = {}
# 预测结果存放在此
pred_dicts = []
# 逐帧进行处理
for index in range(batch_size):
if batch_dict.get('batch_index', None) is not None:
assert batch_dict['batch_box_preds'].shape.__len__() == 2
batch_mask = (batch_dict['batch_index'] == index)
else:
assert batch_dict['batch_box_preds'].shape.__len__() == 3
# 得到当前处理的是第几帧
batch_mask = index
# box_preds shape (所有anchor的数量, 7)
box_preds = batch_dict['batch_box_preds'][batch_mask]
# 复制后,用于recall计算
src_box_preds = box_preds
if not isinstance(batch_dict['batch_cls_preds'], list):
# (所有anchor的数量, 3)
cls_preds = batch_dict['batch_cls_preds'][batch_mask]
# 同上
src_cls_preds = cls_preds
assert cls_preds.shape[1] in [1, self.num_class]
if not batch_dict['cls_preds_normalized']:
# 损失函数计算使用的BCE,所以这里使用sigmoid激活函数得到类别概率
cls_preds = torch.sigmoid(cls_preds)
else:
cls_preds = [x[batch_mask] for x in batch_dict['batch_cls_preds']]
src_cls_preds = cls_preds
if not batch_dict['cls_preds_normalized']:
cls_preds = [torch.sigmoid(x) for x in cls_preds]
# 是否使用多类别的NMS计算,否。
if post_process_cfg.NMS_CONFIG.MULTI_CLASSES_NMS:
if not isinstance(cls_preds, list):
cls_preds = [cls_preds]
multihead_label_mapping = [torch.arange(1, self.num_class, device=cls_preds[0].device)]
else:
multihead_label_mapping = batch_dict['multihead_label_mapping']
cur_start_idx = 0
pred_scores, pred_labels, pred_boxes = [], [], []
for cur_cls_preds, cur_label_mapping in zip(cls_preds, multihead_label_mapping):
assert cur_cls_preds.shape[1] == len(cur_label_mapping)
cur_box_preds = box_preds[cur_start_idx: cur_start_idx + cur_cls_preds.shape[0]]
cur_pred_scores, cur_pred_labels, cur_pred_boxes = model_nms_utils.multi_classes_nms(
cls_scores=cur_cls_preds, box_preds=cur_box_preds,
nms_config=post_process_cfg.NMS_CONFIG,
score_thresh=post_process_cfg.SCORE_THRESH
)
cur_pred_labels = cur_label_mapping[cur_pred_labels]
pred_scores.append(cur_pred_scores)
pred_labels.append(cur_pred_labels)
pred_boxes.append(cur_pred_boxes)
cur_start_idx += cur_cls_preds.shape[0]
final_scores = torch.cat(pred_scores, dim=0)
final_labels = torch.cat(pred_labels, dim=0)
final_boxes = torch.cat(pred_boxes, dim=0)
else:
# 得到类别预测的最大概率,和对应的索引值
cls_preds, label_preds = torch.max(cls_preds, dim=-1)
if batch_dict.get('has_class_labels', False):
label_key = 'roi_labels' if 'roi_labels' in batch_dict else 'batch_pred_labels'
label_preds = batch_dict[label_key][index]
else:
# 类别预测值加1
label_preds = label_preds + 1
# 无类别NMS操作
# selected : 返回了被留下来的anchor索引
# selected_scores : 返回了被留下来的anchor的置信度分数
selected, selected_scores = model_nms_utils.class_agnostic_nms(
# 每个anchor的类别预测概率和anchor回归参数
box_scores=cls_preds, box_preds=box_preds,
nms_config=post_process_cfg.NMS_CONFIG,
score_thresh=post_process_cfg.SCORE_THRESH
)
# 无此项
if post_process_cfg.OUTPUT_RAW_SCORE:
max_cls_preds, _ = torch.max(src_cls_preds, dim=-1)
selected_scores = max_cls_preds[selected]
# 得到最终类别预测的分数
final_scores = selected_scores
# 根据selected得到最终类别预测的结果
final_labels = label_preds[selected]
# 根据selected得到最终box回归的结果
final_boxes = box_preds[selected]
# 如果没有GT的标签在batch_dict中,就不会计算recall值
recall_dict = self.generate_recall_record(
box_preds=final_boxes if 'rois' not in batch_dict else src_box_preds,
recall_dict=recall_dict, batch_index=index, data_dict=batch_dict,
thresh_list=post_process_cfg.RECALL_THRESH_LIST
)
# 生成最终预测的结果字典
record_dict = {
'pred_boxes': final_boxes,
'pred_scores': final_scores,
'pred_labels': final_labels
}
pred_dicts.append(record_dict)
return pred_dicts, recall_dict无类别nms操作
代码在:pcdet/models/model_utils/model_nms_utils.py
def class_agnostic_nms(box_scores, box_preds, nms_config, score_thresh=None):
# 1.首先根据置信度阈值过滤掉部过滤掉大部分置信度低的box,加速后面的nms操作
src_box_scores = box_scores
if score_thresh is not None:
# 得到类别预测概率大于score_thresh的mask
scores_mask = (box_scores >= score_thresh)
# 根据mask得到哪些anchor的类别预测大于score_thresh-->anchor类别
box_scores = box_scores[scores_mask]
# 根据mask得到哪些anchor的类别预测大于score_thresh-->anchor回归的7个参数
box_preds = box_preds[scores_mask]
# 初始化空列表,用来存放经过nms后保留下来的anchor
selected = []
# 如果有anchor的类别预测大于score_thresh的话才进行nms,否则返回空
if box_scores.shape[0] > 0:
# 这里只保留最大的K个anchor置信度来进行nms操作,
# k取min(nms_config.NMS_PRE_MAXSIZE, box_scores.shape[0])的最小值
box_scores_nms, indices = torch.topk(box_scores, k=min(nms_config.NMS_PRE_MAXSIZE, box_scores.shape[0]))
# box_scores_nms只是得到了类别的更新结果;
# 此处更新box的预测结果 根据tokK重新选取并从大到小排序的结果 更新boxes的预测
boxes_for_nms = box_preds[indices]
# 调用iou3d_nms_utils的nms_gpu函数进行nms,
# 返回的是被保留下的box的索引,selected_scores = None
# 根据返回索引找出box索引值
keep_idx, selected_scores = getattr(iou3d_nms_utils, nms_config.NMS_TYPE)(
boxes_for_nms[:, 0:7], box_scores_nms, nms_config.NMS_THRESH, **nms_config
)
selected = indices[keep_idx[:nms_config.NMS_POST_MAXSIZE]]
if score_thresh is not None:
# 如果存在置信度阈值,scores_mask是box_scores在src_box_scores中的索引,即原始索引
original_idxs = scores_mask.nonzero().view(-1)
# selected表示的box_scores的选择索引,经过这次索引,
# selected表示的是src_box_scores被选择的box索引
selected = original_idxs[selected]
return selected, src_box_scores[selected]nms_gpu
代码在:pcdet/ops/iou3d_nms/iou3d_nms_utils.py
def nms_gpu(boxes, scores, thresh, pre_maxsize=None, **kwargs):
"""
:param boxes: 经过筛选的anchor的7个回归预测结果(N, 7) [x, y, z, dx, dy, dz, heading]
:param scores: 经过筛选的anchor的类别,与boxes一一对应(N)
:param thresh:
:return:
"""
assert boxes.shape[1] == 7
# 对分数按列降序排序(从大到小),并取出对应索引
# dim=0 按列排序,dim=1 按行排序,默认 dim=1
# 因为传入的scores已经在之前进行过排序,所以order就是[0 ,1, 2, 3, ...]
order = scores.sort(0, descending=True)[1]
# 如果存在NMS前的最大box数量(4096),则取出前4096个box索引
if pre_maxsize is not None:
order = order[:pre_maxsize]
# 取出NMS前的box, 之前已经有序,此处无变化
boxes = boxes[order].contiguous()
# 构造一个boxes.size维度的向量 PPP
keep = torch.LongTensor(boxes.size(0))
# 调用cuda函数进行加速
# keep:记录保留目标框的下标
# num_out:返回保留下来的个数
num_out = iou3d_nms_cuda.nms_gpu(boxes, keep, thresh)
# 经过iou3d_nms_cuda之后,之所以要取前num_out个数的原因是keep初始化的最大长度是4096
return order[keep[:num_out].cuda()].contiguous(), None四、可视化
可视化代码运行:
1、权重文件:https://drive.google.com/file/d/1wMxWTpU1qUoY3DsCH31WJmvJxcjFXKlm/view![]() https://drive.google.com/file/d/1wMxWTpU1qUoY3DsCH31WJmvJxcjFXKlm/view
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1wMxWTpU1qUoY3DsCH31WJmvJxcjFXKlm/view
2、kitti数据集:The KITTI Vision Benchmark Suite![]() http://www.cvlibs.net/datasets/kitti/eval_object.php?obj_benchmark=3d
http://www.cvlibs.net/datasets/kitti/eval_object.php?obj_benchmark=3d
代码在:tools/demo.py
import argparse
import glob
from pathlib import Path
try:
import open3d
from visual_utils import open3d_vis_utils as V
OPEN3D_FLAG = True
except:
import mayavi.mlab as mlab
from visual_utils import visualize_utils as V
OPEN3D_FLAG = False
import numpy as np
import torch
from pcdet.config import cfg, cfg_from_yaml_file
from pcdet.datasets import DatasetTemplate
from pcdet.models import build_network, load_data_to_gpu
from pcdet.utils import common_utils
class DemoDataset(DatasetTemplate):
def __init__(self, dataset_cfg, class_names, training=True, root_path=None, logger=None, ext='.bin'):
"""
Args:
root_path:
dataset_cfg:
class_names:
training:
logger:
"""
super().__init__(
dataset_cfg=dataset_cfg, class_names=class_names, training=training, root_path=root_path, logger=logger
)
self.root_path = root_path
self.ext = ext
data_file_list = glob.glob(str(root_path / f'*{self.ext}')) if self.root_path.is_dir() else [self.root_path]
data_file_list.sort()
self.sample_file_list = data_file_list
def __len__(self):
return len(self.sample_file_list)
def __getitem__(self, index):
if self.ext == '.bin':
points = np.fromfile(self.sample_file_list[index], dtype=np.float32).reshape(-1, 4)
elif self.ext == '.npy':
points = np.load(self.sample_file_list[index])
else:
raise NotImplementedError
input_dict = {
'points': points,
'frame_id': index,
}
data_dict = self.prepare_data(data_dict=input_dict)
return data_dict
def parse_config():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='arg parser')
parser.add_argument('--cfg_file', type=str, default='cfgs/kitti_models/pointpillar.yaml',
help='specify the config for demo')
parser.add_argument('--data_path', type=str, default='/home/nathan/OpenPCDet/data/kitti/training/velodyne',
help='specify the point cloud data file or directory')
parser.add_argument('--ckpt', type=str,
default="/home/nathan/OpenPCDet/output/kitti_models/pointpillar/default/ckpt/checkpoint_epoch_79.pth", help='specify the pretrained model')
parser.add_argument('--ext', type=str, default='.bin', help='specify the extension of your point cloud data file')
args = parser.parse_args()
cfg_from_yaml_file(args.cfg_file, cfg)
return args, cfg
def main():
args, cfg = parse_config()
logger = common_utils.create_logger()
logger.info('-----------------Quick Demo of OpenPCDet-------------------------')
demo_dataset = DemoDataset(
dataset_cfg=cfg.DATA_CONFIG, class_names=cfg.CLASS_NAMES, training=False,
root_path=Path(args.data_path), ext=args.ext, logger=logger
)
logger.info(f'Total number of samples: \t{len(demo_dataset)}')
model = build_network(model_cfg=cfg.MODEL, num_class=len(cfg.CLASS_NAMES), dataset=demo_dataset)
model.load_params_from_file(filename=args.ckpt, logger=logger, to_cpu=True)
model.cuda()
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
for idx, data_dict in enumerate(demo_dataset):
logger.info(f'Visualized sample index: \t{idx + 1}')
data_dict = demo_dataset.collate_batch([data_dict])
load_data_to_gpu(data_dict)
pred_dicts, _ = model.forward(data_dict)
V.draw_scenes(
points=data_dict['points'][:, 1:], ref_boxes=pred_dicts[0]['pred_boxes'],
ref_scores=pred_dicts[0]['pred_scores'], ref_labels=pred_dicts[0]['pred_labels']
)
if not OPEN3D_FLAG:
mlab.show(stop=True)
logger.info('Demo done.')
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
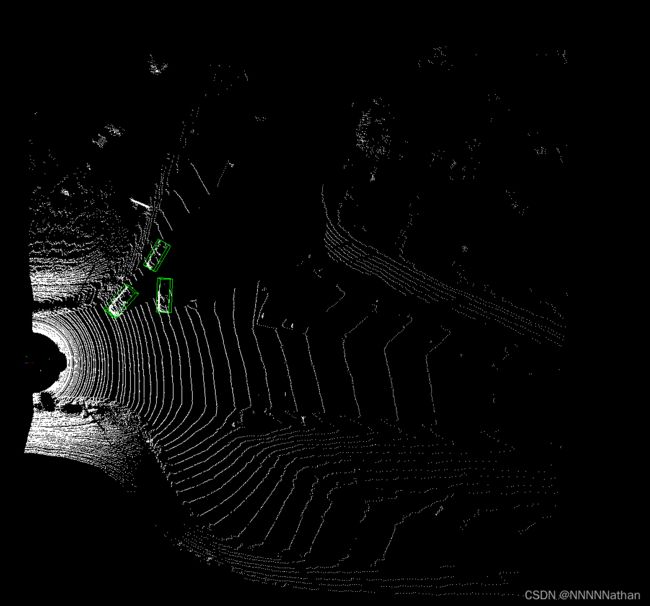
结果1:
二号彩色相机:
点云检测结果:
结果2
2号彩色相机
参考文章或文献:
1、https://github.com/open-mmlab/OpenPCDet/
2、https://github.com/jjw-DL/OpenPCDet-Noted
3、使用KITTI数据集实现坐标转换 - 知乎
4、【3D目标检测】PointPillars论文和代码解析 - 知乎
5、【3D目标检测】SECOND算法解析 - 知乎
6、https://arxiv.org/abs/1812.05784
7、Sensors | Free Full-Text | SECOND: Sparsely Embedded Convolutional Detection
8、https://arxiv.org/abs/1711.06396
9、https://arxiv.org/abs/1612.00593
10、【3D计算机视觉】从PointNet到PointNet++理论及pytorch代码_小执着的博客-CSDN博客_pointnet
11、【3D计算机视觉】PointNet++的pytorch实现代码阅读_小执着的博客-CSDN博客_pointnet pytorch
12、The KITTI Vision Benchmark Suite
13、KITTI数据集--参数_cuichuanchen3307的博客-CSDN博客_kitti
14、https://arxiv.org/pdf/2104.10956.pdf