第八章 条件生成对抗网络 CGAN
写在前面:最近看了《GAN实战》,由于本人忘性大,所以仅是笔记而已,方便回忆,如果能帮助大家就更好了。
目录
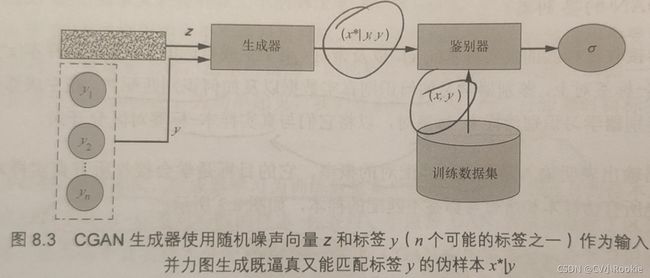
CGAN架构图
CGAN的生成器
CGAN的鉴别器
CGAN的MNIST实现
导入声明
模型输入维度
CGAN生成器
CGAN鉴别器
构建并编译CGAN的鉴别器和生成器模型
CGAN训练
输出样本图像
训练模型
与前面讲的所有GAN都不同,CGAN(Conditional GAN)使用标签来训练生成器和鉴别器
生成器学习为训练数据集中的每个标签生成逼真样本,而鉴别器学习区分真的样本-标签对与假的样本-标签对
CGAN架构图
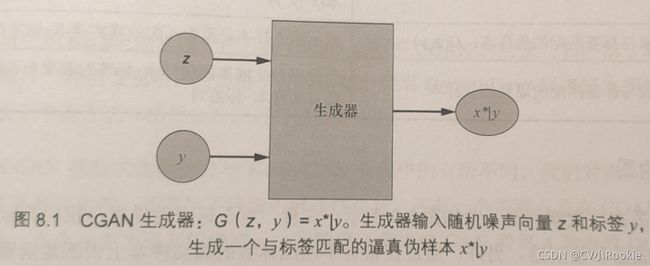
CGAN的生成器
生成器使用噪声向量z和标签y合成一个伪样本![]() (在以y为条件时的x*)。这个伪样本的目的是让鉴别器尽可能以为是给定标签的真实样本。
(在以y为条件时的x*)。这个伪样本的目的是让鉴别器尽可能以为是给定标签的真实样本。
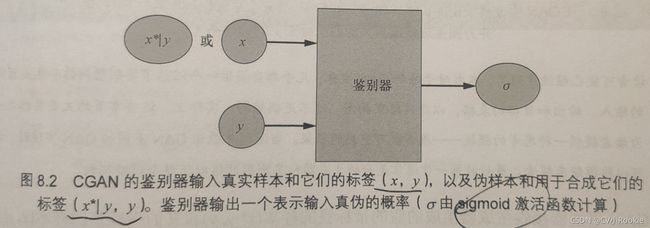
CGAN的鉴别器
鉴别器接受带标签的真实样本(x,y)或者带标签的伪样本(x*|y,y)。鉴别器学习如何识别真实数据以及如何识别匹配对,还要学习识别伪样本-标签对以及将它们与真实样本-标签对区分开
鉴别器的输出是真实匹配对的概率
CGAN的MNIST实现
导入声明
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from keras.datasets import mnist
from keras.layers import (Activation, BatchNormalization, Concatenate, Dense,
Embedding, Flatten, Input, Multiply, Reshape)
from keras.layers.advanced_activations import LeakyReLU
from keras.layers.convolutional import Conv2D, Conv2DTranspose
from keras.models import Model, Sequential
from keras.optimizers import Adam模型输入维度
img_rows = 28
img_cols = 28
channels = 1
# Input image dimensions
img_shape = (img_rows, img_cols, channels)
# Size of the noise vector, used as input to the Generator
z_dim = 100
# Number of classes in the dataset
num_classes = 10CGAN生成器
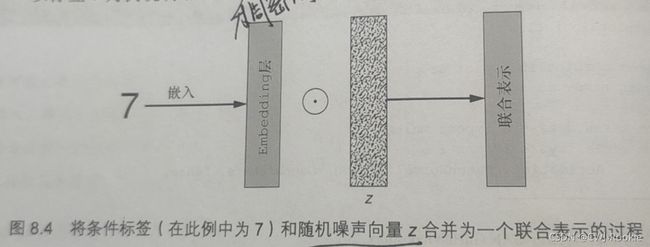
(1)使用Keras的Embedding层将标签y转换为大小为z_dim(随机向量的长度)的稠密向量
(2)使用Keras的Multipy层将标签与噪声向量z嵌入联合表示。(两个向量对应项相乘然后输出这个结果的向量)
(3)将得到的向量作为输入,保留CGAN生成器网络的其余部分以合成图像
def build_generator(z_dim):
model = Sequential()
# Reshape input into 7x7x256 tensor via a fully connected layer
model.add(Dense(256 * 7 * 7, input_dim=z_dim))
model.add(Reshape((7, 7, 256)))
# Transposed convolution layer, from 7x7x256 into 14x14x128 tensor
model.add(Conv2DTranspose(128, kernel_size=3, strides=2, padding='same'))
# Batch normalization
model.add(BatchNormalization())
# Leaky ReLU activation
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.01))
# Transposed convolution layer, from 14x14x128 to 14x14x64 tensor
model.add(Conv2DTranspose(64, kernel_size=3, strides=1, padding='same'))
# Batch normalization
model.add(BatchNormalization())
# Leaky ReLU activation
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.01))
# Transposed convolution layer, from 14x14x64 to 28x28x1 tensor
model.add(Conv2DTranspose(1, kernel_size=3, strides=2, padding='same'))
# Output layer with tanh activation
model.add(Activation('tanh'))
return model
def build_cgan_generator(z_dim):
# Random noise vector z
z = Input(shape=(z_dim, ))
# Conditioning label: integer 0-9 specifying the number G should generate
label = Input(shape=(1, ), dtype='int32')
# Label embedding:
# ----------------
# Turns labels into dense vectors of size z_dim
# Produces 3D tensor with shape (batch_size, 1, z_dim)
label_embedding = Embedding(num_classes, z_dim, input_length=1)(label)
# Flatten the embedding 3D tensor into 2D tensor with shape (batch_size, z_dim)
label_embedding = Flatten()(label_embedding)
# Element-wise product of the vectors z and the label embeddings
joined_representation = Multiply()([z, label_embedding])
generator = build_generator(z_dim)
# Generate image for the given label
conditioned_img = generator(joined_representation)
return Model([z, label], conditioned_img)CGAN鉴别器
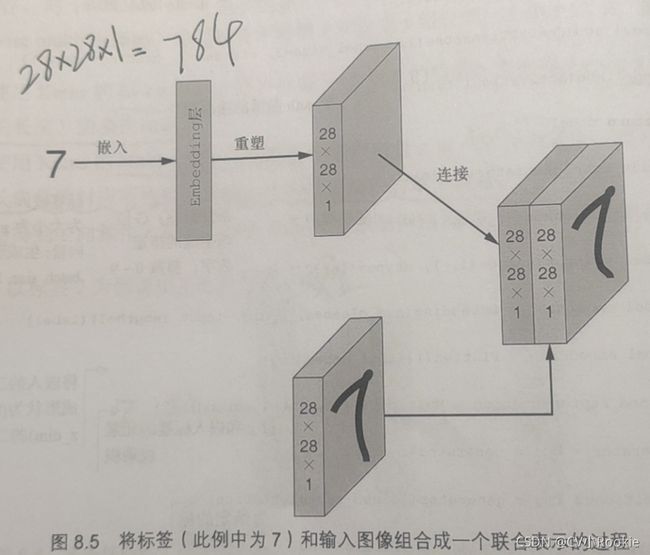
(1)取一个标签,使用Keras的Embedding层将标签变成扁平化图像长度的稠密向量
(2)将嵌入标签调整为图像尺寸
(3)将重塑后的嵌入标签连接到对应图像上,生成形状的联合
(4)将图像-标签的联合输入CGAN的鉴别器网络中。
def build_discriminator(img_shape):
model = Sequential()
# Convolutional layer, from 28x28x2 into 14x14x64 tensor
model.add(
Conv2D(64,
kernel_size=3,
strides=2,
input_shape=(img_shape[0], img_shape[1], img_shape[2] + 1),
padding='same'))
# Leaky ReLU activation
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.01))
# Convolutional layer, from 14x14x64 into 7x7x64 tensor
model.add(
Conv2D(64,
kernel_size=3,
strides=2,
input_shape=img_shape,
padding='same'))
# Batch normalization
model.add(BatchNormalization())
# Leaky ReLU activation
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.01))
# Convolutional layer, from 7x7x64 tensor into 3x3x128 tensor
model.add(
Conv2D(128,
kernel_size=3,
strides=2,
input_shape=img_shape,
padding='same'))
# Batch normalization
model.add(BatchNormalization())
# Leaky ReLU
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.01))
# Output layer with sigmoid activation
model.add(Flatten())
model.add(Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))
return model
def build_cgan_discriminator(img_shape):
# Input image
img = Input(shape=img_shape)
# Label for the input image
label = Input(shape=(1, ), dtype='int32')
# Label embedding:
# ----------------
# Turns labels into dense vectors of size z_dim
# Produces 3D tensor with shape (batch_size, 1, 28*28*1)
label_embedding = Embedding(num_classes,
np.prod(img_shape),
input_length=1)(label)
# Flatten the embedding 3D tensor into 2D tensor with shape (batch_size, 28*28*1)
label_embedding = Flatten()(label_embedding)
# Reshape label embeddings to have same dimensions as input images
label_embedding = Reshape(img_shape)(label_embedding)
# Concatenate images with their label embeddings
concatenated = Concatenate(axis=-1)([img, label_embedding])
discriminator = build_discriminator(img_shape)
# Classify the image-label pair
classification = discriminator(concatenated)
return Model([img, label], classification)构建并编译CGAN的鉴别器和生成器模型
def build_cgan(generator, discriminator):
# Random noise vector z
z = Input(shape=(z_dim, ))
# Image label
label = Input(shape=(1, ))
# Generated image for that label
img = generator([z, label])
classification = discriminator([img, label])
# Combined Generator -> Discriminator model
# G([z, lablel]) = x*
# D(x*) = classification
model = Model([z, label], classification)
return model
# Build and compile the Discriminator
discriminator = build_cgan_discriminator(img_shape)
discriminator.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy',
optimizer=Adam(),
metrics=['accuracy'])
# Build the Generator
generator = build_cgan_generator(z_dim)
# Keep Discriminator’s parameters constant for Generator training
discriminator.trainable = False
# Build and compile CGAN model with fixed Discriminator to train the Generator
cgan = build_cgan(generator, discriminator)
cgan.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer=Adam())CGAN训练
(1)训练鉴别器
a.随机取小批量有标签的真实样本及其标签(x,y)
b.计算给定小批量的D((x,y))并反向传播二分类损失更新![]() ,以使损失最小化
,以使损失最小化
c.随机取小批量的随机噪声向量和类别标签(z,y)并生成小批量伪样本:![]()
d.计算小批量的![]() 并反向传播二分类损失更新
并反向传播二分类损失更新![]() ,以使损失最小化
,以使损失最小化
(2)训练生成器
a. 随机取小批量的随机噪声和类别标签(z,y)生成小批量伪样本:![]()
b. 计算给定小批量的![]() 并反向传播二分类损失更新
并反向传播二分类损失更新![]() ,以使损失最大化
,以使损失最大化
accuracies = []
losses = []
def train(iterations, batch_size, sample_interval):
# Load the MNIST dataset
(X_train, y_train), (_, _) = mnist.load_data()
# Rescale [0, 255] grayscale pixel values to [-1, 1]
X_train = X_train / 127.5 - 1.
X_train = np.expand_dims(X_train, axis=3)
# Labels for real images: all ones
real = np.ones((batch_size, 1))
# Labels for fake images: all zeros
fake = np.zeros((batch_size, 1))
for iteration in range(iterations):
# -------------------------
# Train the Discriminator
# -------------------------
# Get a random batch of real images and their labels
idx = np.random.randint(0, X_train.shape[0], batch_size)
imgs, labels = X_train[idx], y_train[idx]
# Generate a batch of fake images
z = np.random.normal(0, 1, (batch_size, z_dim))
gen_imgs = generator.predict([z, labels])
# Train the Discriminator
d_loss_real = discriminator.train_on_batch([imgs, labels], real)
d_loss_fake = discriminator.train_on_batch([gen_imgs, labels], fake)
d_loss = 0.5 * np.add(d_loss_real, d_loss_fake)
# ---------------------
# Train the Generator
# ---------------------
# Generate a batch of noise vectors
z = np.random.normal(0, 1, (batch_size, z_dim))
# Get a batch of random labels
labels = np.random.randint(0, num_classes, batch_size).reshape(-1, 1)
# Train the Generator
g_loss = cgan.train_on_batch([z, labels], real)
if (iteration + 1) % sample_interval == 0:
# Output training progress
print("%d [D loss: %f, acc.: %.2f%%] [G loss: %f]" %
(iteration + 1, d_loss[0], 100 * d_loss[1], g_loss))
# Save losses and accuracies so they can be plotted after training
losses.append((d_loss[0], g_loss))
accuracies.append(100 * d_loss[1])
# Output sample of generated images
sample_images()输出样本图像
def sample_images(image_grid_rows=2, image_grid_columns=5):
# Sample random noise
z = np.random.normal(0, 1, (image_grid_rows * image_grid_columns, z_dim))
# Get image labels 0-9
labels = np.arange(0, 10).reshape(-1, 1)
# Generate images from random noise
gen_imgs = generator.predict([z, labels])
# Rescale image pixel values to [0, 1]
gen_imgs = 0.5 * gen_imgs + 0.5
# Set image grid
fig, axs = plt.subplots(image_grid_rows,
image_grid_columns,
figsize=(10, 4),
sharey=True,
sharex=True)
cnt = 0
for i in range(image_grid_rows):
for j in range(image_grid_columns):
# Output a grid of images
axs[i, j].imshow(gen_imgs[cnt, :, :, 0], cmap='gray')
axs[i, j].axis('off')
axs[i, j].set_title("Digit: %d" % labels[cnt])
cnt += 1训练模型
# Set hyperparameters
iterations = 12000
batch_size = 32
sample_interval = 1000
# Train the CGAN for the specified number of iterations
train(iterations, batch_size, sample_interval)