以“冬奥之光,多彩冰灯”为主题的第四十一届全国专业冰雕比赛在冰城哈尔滨市进入第二天,60名冰雕高手在哈尔滨冰灯艺术游园会园区展开激烈的竞技比拼。
冰雕艺术
1. 概述
Bean的销毁是Bean的生命周期中最后一步,比如在Tomcat等容器关闭的时候会调用Bean的销毁方法,下面逐步分析。
2. 源码分析
在bean创建完成后,就会对这个bean注册一个销毁的Adapter对象,
protected Object doCreateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
......
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
//创建对象实例
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance();
Class beanType = instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass();
if (beanType != NullBean.class) {
mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType;
}
......
try {
// 属性赋值
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
// 初始化bean
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) {
throw (BeanCreationException) ex;
}
else {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex);
}
}
......
// Register bean as disposable.
try {
// 注册销毁的bean
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex);
}
return exposedObject;
}
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary方法中disposableBeans集合负责收集需要销毁的bean。
protected void registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(String beanName, Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
AccessControlContext acc = (System.getSecurityManager() != null ? getAccessControlContext() : null);
if (!mbd.isPrototype() && requiresDestruction(bean, mbd)) {
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
// Register a DisposableBean implementation that performs all destruction
// work for the given bean: DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessors,
// DisposableBean interface, custom destroy method.
// 注册销毁bean的DisposableBeanAdapter对象
registerDisposableBean(beanName,
new DisposableBeanAdapter(bean, beanName, mbd, getBeanPostProcessors(), acc));
}
......
public void registerDisposableBean(String beanName, DisposableBean bean) {
synchronized (this.disposableBeans) {
this.disposableBeans.put(beanName, bean);
}
}
DisposableBeanAdapter 对象就是负责 bean 销毁的类,这个类中收集 bean是否实现了 DisposableBean 接口
class DisposableBeanAdapter implements DisposableBean, Runnable, Serializable
是否配置 destroy-method 属性,过滤了 DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor 类型的接口,如下图所示:
public DisposableBeanAdapter(Object bean, String beanName, RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition,
List postProcessors, @Nullable AccessControlContext acc) {
......
this.beanPostProcessors = filterPostProcessors(postProcessors, bean);
}
private List filterPostProcessors(List processors, Object bean) {
List filteredPostProcessors = null;
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(processors)) {
filteredPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(processors.size());
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : processors) {
if (processor instanceof DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor dabpp = (DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor) processor;
if (dabpp.requiresDestruction(bean)) {
filteredPostProcessors.add(dabpp);
}
}
}
}
return filteredPostProcessors;
然后 bean 是在什么时候被销毁呢,在 tomcat 关闭的时候就会调用到 servlet 中的销毁方法,具体是通过类ContextLoaderListener.java 中的contextDestroyed 方法,通过 closeWebApplicationContext 方法一直往下找此为 servlet 规范的使用,一路往下调用。


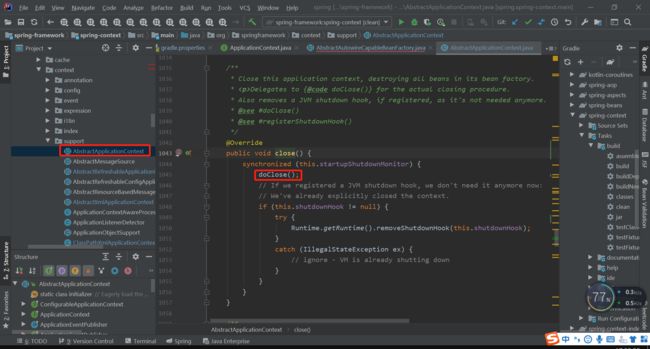
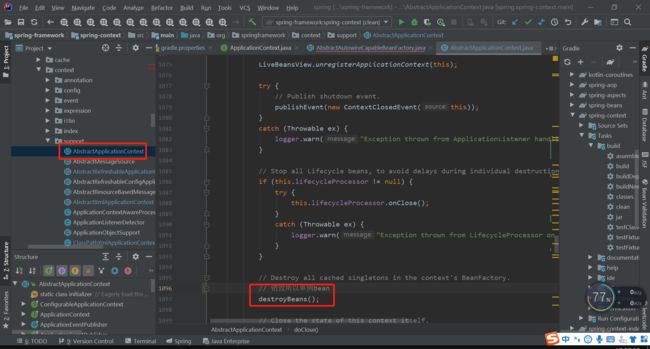

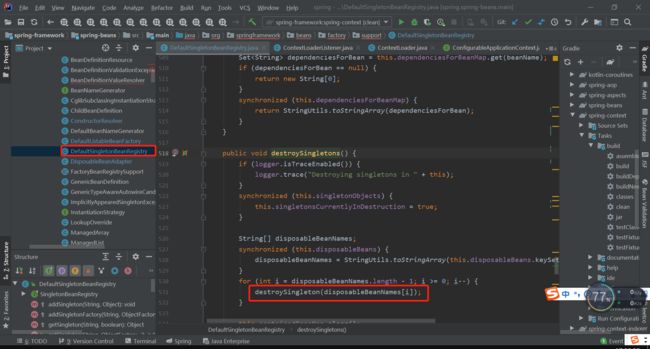


最终会进入DisposableBeanAdapter类中的destroy,方法该方法就会根据前面的收集进行调用。
public void destroy() {
// 处理@PreDestroy注解的beanpostProcessor实现类: InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.beanPostProcessors)) {
for (DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor processor : this.beanPostProcessors) {
processor.postProcessBeforeDestruction(this.bean, this.beanName);
}
}
// 处理实现DisposableBean接口的bean的销毁
if (this.invokeDisposableBean) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Invoking destroy() on bean with name '" + this.beanName + "'");
}
try {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction销毁bean的顺序是如下:
1)判断是否需要处理@PreDestroy注解的bean,如果需要,则通过beanpostProcessor实现类 InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor处理;
2)判断是否需要处理实现DisposableBean接口的bean的销毁;
3)判断是否需要处理配置文件中的bean配置了destroy-method的bean的销毁。
3. 案例演示
定义Bean,同时加入销毁对应的三种方法;
/**
* @Author: wzj
* @Date: 2021/7/2 11:32
* @Desc:
*/
public class Wzj implements DisposableBean {
public static Wzj factoryMethod() {
CQ cq = new CQ();
SC sc = new SC();
return new Wzj(sc, cq);
}
@PreDestroy
public void close() {
System.out.println("通过 @PreDestroy:销毁实例wzj");
}
public void destroyMethod() {
System.out.println("通过配置文件配置destroy-method:销毁实例wzj");
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("通过DisposableBean接口:销毁实例wzj");
}
配置文件如下:
测试类:
/**
* @Author: wzj
* @Date: 2021/3/30 15:08
* @Desc: 测试类
*/
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations = {"classpath:spring.xml"})
public class TestSpring {
@Autowired
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Test
public void testDestroy() {
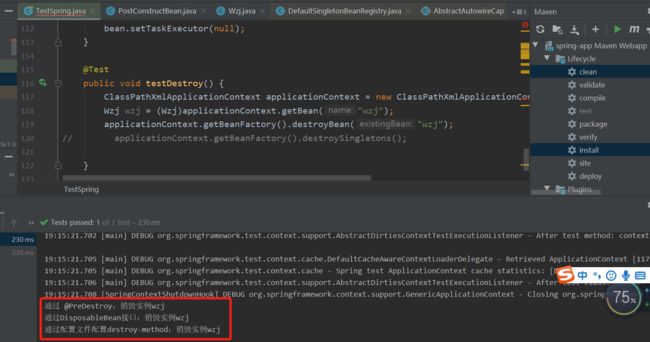
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
Wzj wzj = (Wzj)applicationContext.getBean("wzj");
applicationContext.getBeanFactory().destroyBean("wzj");
}
有人可能会问,为何Bean可以多次销毁,其实Bean的销毁并不是真正意义上的销毁Bean,而是在销毁前执行销毁方法,可能包含关闭数据库连接、关闭网络请求等逻辑操作,而后真正的销毁是由Spring容器执行关闭,其内部Bean也就自然而然消失了,Bean销毁是发生在Spring容器关闭过程中的。