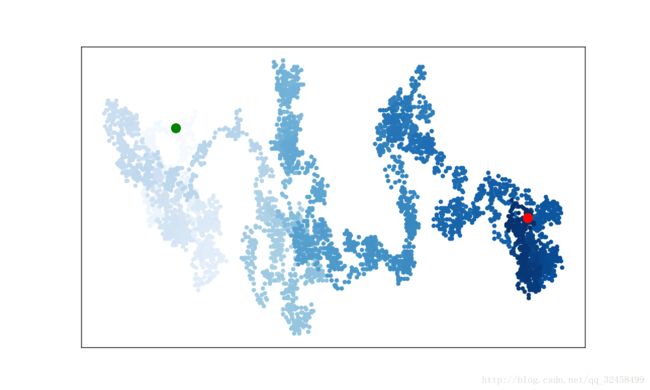
python数据可视化——散点图实例之随机漫步
随机漫步是这样行走得到的途径:每次行走都是完全随机的,没有明确的方向,结果是由一系列随机决策决定的。
#random_walk.py
from random import choice
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
class RandomWalk():
#一个生成随机漫步数据的类
def __init__(self,num_points=5000):
self.num_points=num_points
self.x_values=[0]
self.y_values=[0]
def fill_walk(self):
#计算随机漫步包含的所有点
while len(self.x_values)#决定前进方向以及沿这个方向前进的距离
x_direction=choice([-1,1])
x_distance=choice([0,1,2,3,4])
x_step=x_direction*x_distance
y_direction=choice([-1,1])
y_distance=choice([0,1,2,3,4])
y_step=y_direction*y_distance
#拒绝原地踏步
if x_step==0 and y_step==0:
continue
#计算下一个点的x和y值
next_x=self.x_values[-1]+x_step
next_y=self.y_values[-1]+y_step
self.x_values.append(next_x)
self.y_values.append(next_y)
#rw.py
# coding=gbk
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from random_walk import RandomWalk
while True:
rw=RandomWalk()
rw.fill_walk()
#设置绘图窗口的尺寸
plt.figure(dpi=128,figsize=(10,6))
point_numbers=list(range(rw.num_points))
plt.scatter(rw.x_values,rw.y_values,c=point_numbers,cmap=plt.cm.Blues,s=15)
#突出起点和终点
plt.scatter(0,0,c='green',s=100)
plt.scatter(rw.x_values[-1],rw.y_values[-1],c='red',s=100)
#隐藏坐标轴
plt.axes().get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
plt.axes().get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
plt.show()
keep_running=input("Make another walk?(y/n):")
if keep_running=='n':
break