BYOL(Bootstrap your own latent A new approach to self-supervised Learning)算法笔记
Bootstrap your own latent A new approach to self-supervised Learning
引导你自己潜在的自我监督学习的新方法
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.07733
复现代码:https://github.com/HibikiJie/BYOL
\
为什么使用自监督学习
网络更加庞大,难以训练,需要大量的标记数据来监督训练,成本过高。所以需要一种自监督学习,来训练网络,使网络更加泛化。
网络没有预训练,直接使用在自己的标签数据上时,效果可能不会太好,并且收敛也较慢。如果网络能在大规模的数据集上完成自监督训练,只需要训练出它的强特征提取能力,无论是在后续的任务中,是冻结网络权重,还是不冻结权重继续学习有标签数据,网络都是能够提供极强的特征提取能力,并且极大提高网络收敛速度。该方法更多是为网络的迁移学习做准备的,特别是在应对数据量非常少的情况下,如果网络没有一个事先的强特征提取能力,对后续特定学习效果将不会太好,并且也将影响网络泛化性。
\
方法
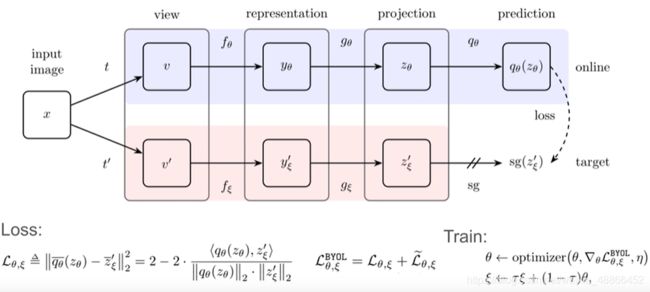
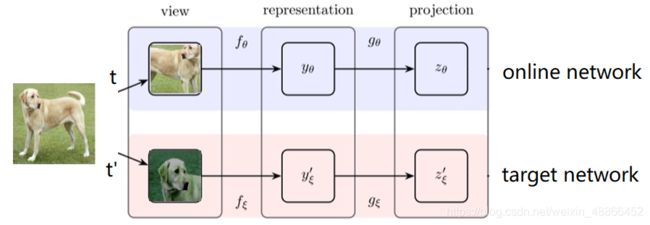
输入一张图片(input image),记作 x x x ,通过两种随机的图像增强策略(记作: t t t, t ′ t^{'} t′),得到两种不同的图片(记作: v v v, v ′ v^{'} v′),但语义内容相同的图片。
再将图片 v v v 输入网络( 网络记作 f θ f_{\theta} fθ,其中网络参数为 θ \theta θ )中,得到这张图片对于网络 f θ f_{\theta} fθ 的一个表示(representation, y θ y_{\theta} yθ ),也就是说是,图片输入网络后,得到的特征图(feature map)为 y θ y_{\theta} yθ 。之后将 y θ y_{\theta} yθ 输入 后续网络(记作 g θ g_{\theta} gθ ),将 y θ y_{\theta} yθ 的特征图投射至一个更加高维的潜在空间,得到输出特征向量 z θ z_{\theta} zθ ;
相同的图片 v ′ v^{'} v′ 输入另一和网络 f θ f_{\theta} fθ 相同的,但参数不同的网络(记作 f ξ f_{\xi} fξ ,参数为 ξ \xi ξ ),得到输出 y ξ ′ y_{\xi}^{'} yξ′ ,再输入网络 g ξ g_{\xi} gξ (与 g θ g_{\theta} gθ 相同,但参数不同),得到输出特征向量 z ξ ′ z_{\xi}^{'} zξ′;
将参数为 θ \theta θ 的网络称为在线网络( online network ),参数为 ξ \xi ξ 的网络称为目标网络(target network)
我们想要网络projection空间中的, z θ z_{\theta} zθ 和 z ξ ′ z_{\xi}^{'} zξ′ 相同,但是这两个输出来源于同一幅图片的随机图像增强,而且输入结构相同参数不同的网络,得到投影(projection)的特征向量必然是不同的,如果强制学习到相同输出,网络可能就直接输出常数了。所以再加上一层网络 q θ q_{\theta} qθ,将 z θ z_{\theta} zθ 再一次变换,使得变换后的输出 q θ ( z θ ) q_{\theta}(z_{\theta}) qθ(zθ) 与 z ξ ′ z_{\xi}^{'} zξ′ 比较距离,做损失。
由此优化在线网络( online network )的参数 θ \theta θ ;
而目标网络(target network)的参数 ξ \xi ξ 更新,根据旧的 ξ \xi ξ 和更新后的 θ \theta θ,按照以下公式更新
![]()
系数 τ \tau τ 的 大小选择,在 τ = 1 \tau = 1 τ=1 的时候表示,目标网络(target network)的参数一直都不变,就是一个学习随机网络的输出的结果,为18.8。而 τ = 0 \tau = 0 τ=0 时,表示目标网络完全由在线网络(online network)的参数替换,相当于每次都更新网络参数,这时候,效果非常差,相当于训练崩塌。而中间的3种取值悬着,让目标网络权重更新不会太快,而不会太慢。可以看出在 τ = 0.99 \tau =0.99 τ=0.99时,效果最优

这篇论文的motivation来源于一个有趣的实验,首先有一个网络参数随机初始化且固定的target network,target network的top1准确率只有1.4%,target network输出feature作为另一个叫online network的训练目标,等这个online network训练好之后,online network的top1准确率可以达到18.8%,这就非常有意思了,假如将target network替换为效果更好的网络参数(比如此时的online network),然后再迭代一次,也就是再训练一轮online network,去学习新的target network输出的feature,那效果应该是不断上升的,类似左右脚踩楼梯不断上升一样。BYOL基本上就是这样做的,并且取得了非常好的效果。
类似于梯云纵的功法。在线网络向目标网络学习一点后,将自己的参数更新一部分给目标网络,然后继续像目标网络学习。这样,完成了一个,在线网络学习一个参数随机初始化的目标网络的输出feature,当在线网络学习好后,将目标网络更换为效果更换的网络参数,也就是此时的在线网络。也就这样不断替换,完成学习。
\
代码
在线网络,和目标网络,使用resnet18
\
online_net = ResNet18() # 实例化online(在线网络)
target_net = ResNet18() # 实例化target(目标网络)
投射网络 q θ q_{\theta} qθ 为:
\
from torch import nn
class MLP(nn.Module):
"""
预测网络, 将在在线网络的输出投射至另一空间来预测目标网络的输出
"""
def __init__(self, in_features, hidden_features, projection_features):
"""
预测网络
:param in_features: 输入特征数
:param hidden_features: 隐藏特征数
:param projection_features: 投影特征数
"""
super(MLP, self).__init__()
self.layer = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(in_features, hidden_features),
nn.BatchNorm1d(hidden_features),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Linear(hidden_features, projection_features),
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.layer(x)
数据集使用CIFAR10
对图像的数据增强方式
\
class TransformsSimCLR:
"""
一种随机数据扩充模块,它对任意给定的数据实例进行随机转换,
得到同一实例的两个相关视图,
记为x̃i和x̃j,我们认为这是一个正对。
"""
def __init__(self, size, train=True):
"""
:param size:图片尺寸
"""
s = 1
color_jitter = torchvision.transforms.ColorJitter(
0.8 * s, 0.8 * s, 0.8 * s, 0.2 * s
)
self.train_transform = torchvision.transforms.Compose(
[
torchvision.transforms.RandomResizedCrop(size=size),
torchvision.transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(), # with 0.5 probability
torchvision.transforms.RandomApply([color_jitter], p=0.8),
torchvision.transforms.RandomGrayscale(p=0.2),
torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
]
)
self.test_transform = torchvision.transforms.Compose(
[
torchvision.transforms.Resize(size=size),
torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
]
)
self.train = train
def __call__(self, x):
"""
:param x: 图片
:return: x̃i和x̃j,即 v、v'
"""
if self.train:
return self.train_transform(x), self.train_transform(x)
else:
return self.test_transform(x)
训练过程中,将同一张图片,经过随机数据增强得到两张不同的图片,分别输入在线网络和目标网络,得到各自得projection,同时,对于目标网络,不追踪梯度。
online_projection_one = online_net(x_i)
with torch.no_grad():
target_projection_one = target_net(x_j)
然后将在线网络输出得projection,经过prediton的变换,与目标网络的projection做损失:
prediction = MLP(in_features=1000, hidden_features=2048, projection_features=1000)
loss_one = loss_function(prediction(online_projection_one), target_projection_one.detach())
损失函数为:
def loss_function(predict, target):
"""
损失函数,比较余弦相似度。归一化的欧氏距离等价于余弦相似度
:param predict: online net输出的prediction
:param target: target网络输出的projection
:return: loss(损失)
"""
return 2-2*torch.cosine_similarity(predict, target, dim=-1)
由此,优化参数 θ \theta θ
而目标网络参数的更新,根据在线网络更新:
for target_parameter, online_parameter in zip(target_net.parameters(), online_net.parameters()):
old_weight = target_parameter.data
update = online_parameter.data
target_parameter.data = old_weight * tau + (1 - tau) * update
完整训练代码
# coding=UTF-8
from torchvision.datasets import CIFAR10
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from utiles.transformations import TransformsSimCLR
from models.resnet50 import ResNet50
from models.resnet18 import ResNet18
from models.mlp import MLP
from utiles.loss_function import loss_function
import torch
import time
if __name__ == '__main__':
image_size = 112 # 图片尺寸
batch_size = 6 # 批次大小
num_epochs = 3000 # 要训练的迭代次数
learn_rate = 0.001 # 学习率
tau = 0.99 # 目标网络更新系数
device = torch.device('cuda:0' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu') # 选择训练设备
"""实例化数据集和数据集加载器"""
train_dataset = CIFAR10(
root='dataset',
train=True,
transform=TransformsSimCLR(size=image_size),
download=True
) # 训练数据集
train_loader = DataLoader(
dataset=train_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
drop_last=True,
num_workers=4,
) # 训练数据加载器
online_net = ResNet18().to(device) # 实例化online(在线网络)
target_net = ResNet18().to(device) # 实例化target(目标网络)
"""实例化prediction(预测网络)"""
prediction = MLP(in_features=1000, hidden_features=2048, projection_features=1000).to(device)
"""实例化优化器,放入在线网络(online_net),和预测网络(prediction)的参数优化;目标网络(target_net)采用其他方式更新参数"""
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam([{'params': online_net.parameters()}, {'params': prediction.parameters()}], lr=learn_rate)
"""训练train"""
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
for step, ((x_i, x_j), label) in enumerate(train_loader):
"""加载数据至GPU"""
x_i = x_i.to(device)
x_j = x_j.to(device)
"""计算在线网络和目标网络的输出,同时对目标网络不更新梯度"""
online_projection_one = online_net(x_i)
with torch.no_grad():
target_projection_one = target_net(x_j)
loss_one = loss_function(prediction(online_projection_one), target_projection_one.detach())
online_projection_two = online_net(x_j) # 交换x_i与x_j,再计算损失;此步是为了高效利用数据,也可以不用
with torch.no_grad():
target_projection_two = target_net(x_i)
loss_two = loss_function(prediction(online_projection_two), target_projection_two.detach())
loss = (loss_one + loss_two).mean() # 合计计算损失
"""update online parameters(更新在线网络的参数)"""
optimizer.zero_grad() # 清空梯度
loss.backward() # 反向传播
optimizer.step() # 优化在线网络参数
if step % 5 == 0: # 打印训练中的情况
print(f"Epoch {epoch}; Step [{step}/{len(train_loader)}]:\tLoss: {loss.item()}")
"""
update target parameters(更新目标网络的参数)
target_parameter <=== target_parameter * beta + (1 - beta) * online_parameter
"""
for target_parameter, online_parameter in zip(target_net.parameters(), online_net.parameters()):
old_weight = target_parameter.data
update = online_parameter.data
target_parameter.data = old_weight * tau + (1 - tau) * update
time.sleep(0.1) # 训练太快,防止显卡过热,掉驱动
"""save net weights"""
torch.save(online_net.state_dict(), 'net.pt')