【java】 如何自己写一把多线程锁 中 重写lock,trylock,unlok方法
4.拿到unsafe
import sun.misc.Unsafe;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.AbstractQueuedSynchronizer;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
/**
* @author sz
* @DATE 2022/3/16 20:30
*/
public class MyReentrantLock implements Lock {
//记录锁状态 0 -> 锁可用 1-> 锁被占 >1 -> 锁重入
private int status = 0;
private long offset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset(MyLock.class.getDeclaredField("status"));
private static Unsafe unsafe;
static {
try {
unsafe = getUnsafe();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public MyReentrantLock() throws NoSuchFieldException {
}
public static Unsafe getUnsafe() throws Exception {
//利用反射
Field theUnsafe = Unsafe.class.getDeclaredField("theUnsafe");
theUnsafe.setAccessible(true); // 设置为可见
Unsafe unsafe = (Unsafe) theUnsafe.get(null); // 获取Unsafe对象
return unsafe;
}
@Override
public void lock() {
new ReentrantLock().lock();
}
@Override
public void unlock() {
}
@Override
public boolean tryLock() {
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean tryLock(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
return false;
}
@Override
public void lockInterruptibly() throws InterruptedException {
}
@Override
public Condition newCondition() {
return null;
}
}
接下来就能为所欲为了 哈哈
5.搞定 trylock 方法
整个流程如上 代码怎么写呢
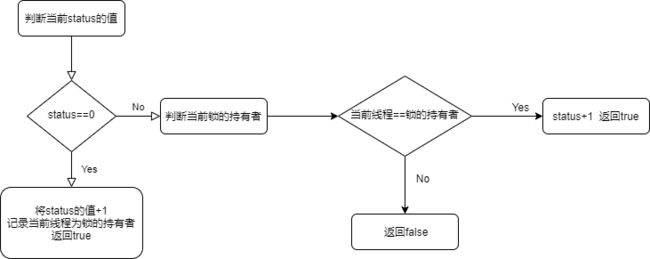
首先 if判断 尝试修改 status的值
if (unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(this,offset,0,1))
offset ==> status 在内存中的偏移量
如果status的值是0,就改成1 并且 返回 true 否则返回false
返回true 记录下当前锁是那个线程持有的 以后解锁要用 谁家的锁谁来开
//将当前锁的主人设置为当前线程
master_thred = Thread.currentThread();
return true;
如果 尝试修改status的值 失败 判断是不是锁重入 如果是锁重入 将status的值 +1 并且返回true
//判断是否锁重入
if (Thread.currentThread()==master_thred){
//如果是锁重入 状态值 +1
unsafe.getAndAddInt(this,offset,1);
//锁重入成功
return true;
如果上面条件都不满足 直接返回 false
于是tryLock 方法重写后就是这个样子
@Override
public boolean tryLock() {
//如果 status的值是 0 没有人用锁 改成1
if (unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(this,offset,0,1)){
//将当前锁的主人设置为当前线程
master_thred = Thread.currentThread();
return true;
}else {
//判断是否锁重入
if (Thread.currentThread()==master_thred){
//如果是锁重入 状态值 +1
unsafe.getAndAddInt(this,offset,1);
//锁重入成功
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
我们来测试一下 一个线程尝试加锁三次 试试锁重入
第一次调用trylock方法 status的值正好是0 修改成功 并且记录当前线程为锁的持有者 第二次循环尝试修改值失败 进入判断语句
当前线程正好是锁的持有者 于是把 status的值 +1 第三次循环依然如此
至此 trylock方法 搞定
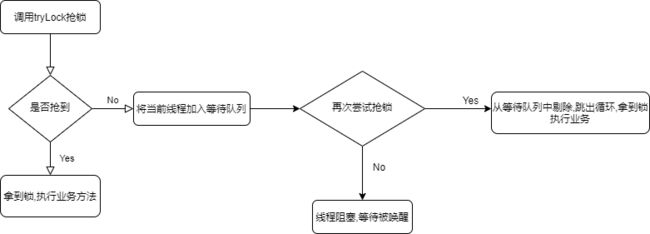
6.搞定lock方法
lock方法和trylock方法的区别在于 trylock方法是尝试一下 获取到锁了就返回true 没有就返回false 不会阻塞在这等
而lock 方法获取到锁了就立即返回 没有获取到锁就一直等待 等待别唤醒后 继续抢锁 没有抢到继续等待
首先创建一个等待队列 没抢到锁的线程进入等待队列等待
//获取锁失败的线程的等待队列
LinkedBlockingQueue waitQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>();
@Override
public void lock() {
//如果没有获取到锁
if (!tryLock()){
//将当前线程加入等待队列
waitQueue.add(Thread.currentThread());
//循环不停抢锁
while (true){
//不停尝试抢锁
if (tryLock()){
//抢到了 从队列中剔除
//poll() 检索并删除此队列的头部,如果此队列为空,则返回 null 。
waitQueue.poll();
//跳出循环
break;
}else {
//没有抢到 阻塞等待 等待被唤醒
unsafe.park(false,0);
}
}
}
}
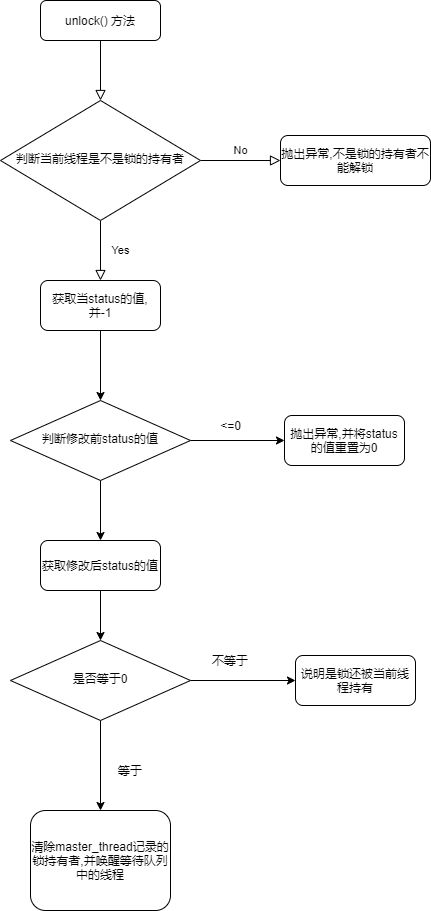
7.搞定unlock方法
首先我们要搞清楚这个两个问题
- 谁去解锁?
- 解锁将产生什么变化呢?
谁去解锁 当然是锁的主人 也就是 master_thred 记录的线程
解锁将产生什么变化 锁说到底就是判断一个标记位 它的不同状态代表着锁的不同状态 也就是改变 status的值 然后看下等待队列中是否有其他等待的线程 唤醒它们
搞清楚这两点后 开始写代码
@Override
public void unlock() {
//首先判断锁的持有者是不是当前线程
if (Thread.currentThread() != master_thred) {
//前朝的剑怎么斩本朝的官
throw new RuntimeException("释放锁失败,当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread() + "未持有锁");
}
//能过前面的if判断 说明当前锁是被人占用的 且是当前线程占有的
//修改status的值
if (unsafe.getAndAddInt(this, offset, -1) > 0) {
if (unsafe.getInt(this, offset) == 0) {
//如果当前status==0也就是没有线程持有锁了
master_thred = null;
//再从等待队列中拿出等待线程
if (waitQueue.size()!=0) {
//注意这个 peek 方法 不会把线程从队列中删除 因为即时唤醒也有可能拿不到锁
//真正从队列中删除要等到 抢到锁了 调用 poll 方法
Thread peek = waitQueue.peek();
//唤醒线程
if (peek != null) {
unsafe.unpark(peek);
}
}
}
} else {
//重置锁
unsafe.putInt(this, offset, 0);
//锁已经被释放了 抛出异常
throw new RuntimeException("释放锁失败,锁已经被释放");
}
}
到此 重写了 lock接口的 trylock方法 lock方法 与unlock 方法 是不是就没问题呢?
留着大家测试 欢迎评论区留言