JavaScript学习笔记(一)基础语法
JS基础语法
-
- 一,Output
- 二,数据类型
- 三,对象
- 四,函数
- 五,事件
- 六,流程控制
- 七,类型转换
一,Output
1,使用windows.alert()弹出警告框
window.alert(5 + 6);
2,使用document.write()方法将内容写到HTML文档中
document.write("这是一个标题
")
只能在 HTML 输出流中使用 document.write。 如果在文档已加载后使用它(比如在函数中),会覆盖整个文档。
3,使用innerHTML写入到HTML元素
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = "段落已修改";
4,使用console.log()写入到浏览器的控制台
console.log("six");
二,数据类型
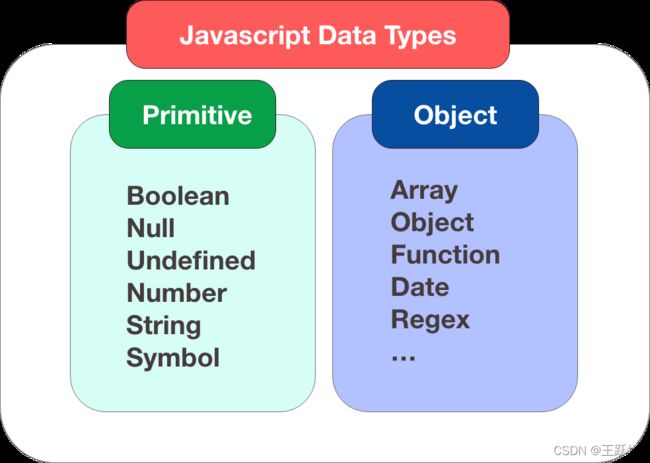
1,基本数据类型
字符串(String)、数字(Number)、布尔(Boolean)、对空(Null)、未定义(Undefined)、Symbol
Symbol 是 ES6 引入了一种新的原始数据类型,表示独一无二的值。
需要注意的是:
==:等于
===:绝对等于
2,引用数据类型
对象(Object)、数组(Array)、函数(Function),还有两个特殊的对象:正则(RegExp)和日期(Date)
3,JS拥有动态类型
JavaScript 拥有动态类型。这意味着相同的变量可用作不同的类型:
var x; // x 为 undefined
var x = 5; // 现在 x 为数字
var x = "John"; // 现在 x 为字符串
4,typeof关键字可以获取数据类型
typeof "John" // 返回 string
typeof 3.14 // 返回 number
typeof false // 返回 boolean
typeof [1,2,3,4] // 返回 object
typeof {name:'John', age:34} // 返回 object
5,JS的创建与访问
方法一:
var cars=new Array();
cars[0]="Saab";
cars[1]="Volvo";
cars[2]="BMW";
方法二:
var cars=new Array("Saab","Volvo","BMW");
方法三:
var cars=["Saab","Volvo","BMW"];
6,JS对象的创建与访问
对象由花括号分隔。在括号内部,对象的属性以名称和值对的形式 (name : value) 来定义。属性由逗号分隔:
//创建
var person={firstname:"John", lastname:"Doe", id:5566};
//访问
name=person.lastname;
name=person["lastname"];
7,Undefined和Null
Undefined 这个值表示变量不含有值。
可以通过将变量的值设置为 null 来清空变量。
var person;
var car="Volvo";
document.write(person + "
");
document.write(car + "
");
var car=null
document.write(car + "
");
null 和 undefined 的值相等,但类型不等:
typeof undefined // undefined
typeof null // object
null === undefined // false
null == undefined // true
在 JavaScript 中, null 用于对象, undefined 用于变量,属性和方法。
对象只有被定义才有可能为 null,否则为 undefined。
如果我们想测试对象是否存在,在对象还没定义时将会抛出一个错误。
错误的使用方式:
if (myObj !== null && typeof myObj !== "undefined")
正确的方式是我们需要先使用 typeof 来检测对象是否已定义:
if (typeof myObj !== "undefined" && myObj !== null)
8,声明变量类型
当您声明新变量时,可以使用关键词 “new” 来声明其类型:
JavaScript 变量均为对象。当您声明一个变量时,就创建了一个新的对象。
var carname=new String;
var x= new Number;
var y= new Boolean;
var cars= new Array;
var person= new Object;
三,对象
1,创建对象方法
methodName : function() {
// 代码
}
2,调用对象方法
objectName.methodName()
objectName.methodName
通常 fullName() 是作为 person 对象的一个方法, fullName 是作为一个属性。
如果使用 fullName 属性,不添加 (), 它会返回函数的定义:
如:
var person = {
firstName: "John",
lastName : "Doe",
id : 5566,
Name : function()
{
return this.firstName + "-----" + this.lastName;
}
};
document.getElementById("demo1").innerHTML = "不加括号输出函数表达式:" + person.Name;
document.getElementById("demo2").innerHTML = "加括号输出函数执行结果:" + person.Name();
四,函数
1,函数定义
函数就是包裹在花括号中的代码块,前面使用了关键词 function:
//无参函数
function functionname()
{
// 执行代码
}
//带参函数
function myFunction(var1,var2)
{
//代码
}
//带返回值的函数
function myFunction(a,b)
{
return a*b;
}
2,函数调用
五,事件
1,HTML事件的触发
2,常见的六种HTML时间
事件
描述
onchange
HTML元素改变
onclick
用户点击HTML元素
onmouseover
鼠标指针移动到指定的元素上时发生
onmouseout
用户从一个 HTML 元素上移开鼠标时发生
onkeydown
用户按下键盘按键
onload
浏览器已完成页面的加载
3,事件可以做什么?
通过事件触发JS函数,可以用于处理表单验证,用户输入,用户行为及浏览器动作。
六,流程控制
1,for/in
用于循环遍历未知大小的数据
语法结构
var person={fname:"Bill",lname:"Gates",age:56};
for (x in person) // x 为属性名
{
txt=txt + person[x];
}
举例说明:
点击下面的按钮,循环遍历对象 "person" 的属性。
function myFunction(){
var x;
var txt="";
var person={fname:"Bill",lname:"Gates",age:56};
for (x in person){
txt=txt + person[x];
}
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML=txt;
}
七,类型转换
1,constructor属性
constructor 属性返回所有 JavaScript 变量的构造函数。
"John".constructor // 返回函数 String() { [native code] }
(3.14).constructor // 返回函数 Number() { [native code] }
false.constructor // 返回函数 Boolean() { [native code] }
[1,2,3,4].constructor // 返回函数 Array() { [native code] }
{name:'John', age:34}.constructor // 返回函数 Object() { [native code] }
new Date().constructor // 返回函数 Date() { [native code] }
function () {}.constructor // 返回函数 Function(){ [native code] }
使用 constructor 属性来查看对象是否为数组 (包含字符串 “Array”):
function isArray(myArray) {
return myArray.constructor.toString().indexOf("Array") > -1;
}
你可以使用 constructor 属性来查看对象是否为日期 (包含字符串 “Date”):
function isDate(myDate) {
return myDate.constructor.toString().indexOf("Date") > -1;
}

