- set 和 sorted set
- 前言
- set
- 常见命令
- set 的使用场景
- 看下源码实现
- insert
- dict
- sorted set
- 常见的命令
- 使用场景
- 分析下源码实现
- ZADD
- ZRANGE
- 总结
- 参考
set 和 sorted set
前言
前面在几个文章聊到了 list,string,hash 等结构的实现,这次来聊一下 set 和 sorted set 的细节。
set
Redis 的 Set 是 String 类型的无序集合,集合成员是唯一的。
底层实现主要用到了两种数据结构 hashtable 和 inset(整数集合)。
集合中最大的成员数为2的32次方-1 (4294967295, 每个集合可存储40多亿个成员)。
常见命令
来看下几个常用的命令
# 向集合添加一个或多个成员
SADD key member1 [member2]
# 获取集合的成员数
SCARD key
# 返回第一个集合与其他集合之间的差异。
SDIFF key1 [key2]
# 返回给定所有集合的差集并存储在 destination 中
SDIFFSTORE destination key1 [key2]
# 返回给定所有集合的交集
SINTER key1 [key2]
# 返回给定所有集合的交集并存储在 destination 中
SINTERSTORE destination key1 [key2]
# 判断 member 元素是否是集合 key 的成员
SISMEMBER key member
# 返回集合中的所有成员
SMEMBERS key
# 将 member 元素从 source 集合移动到 destination 集合
SMOVE source destination member
# 移除并返回集合中的一个随机元素
SPOP key
# 返回集合中一个或多个随机数
SRANDMEMBER key [count]
# 移除集合中一个或多个成员
SREM key member1 [member2]
# 返回所有给定集合的并集
SUNION key1 [key2]
# 所有给定集合的并集存储在 destination 集合中
SUNIONSTORE destination key1 [key2]
# 迭代集合中的元素
SSCAN key cursor [MATCH pattern] [COUNT count]
来个栗子
127.0.0.1:6379> SADD set-test xiaoming
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> SADD set-test xiaoming
(integer) 0
127.0.0.1:6379> SADD set-test xiaoming1
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> SADD set-test xiaoming2
127.0.0.1:6379> SMEMBERS set-test
1) "xiaoming2"
2) "xiaoming"
3) "xiaoming1"
上面重复值的插入,只有第一次可以插入成功
set 的使用场景
比较适用于聚合分类
1、标签:比如我们博客网站常常使用到的兴趣标签,把一个个有着相同爱好,关注类似内容的用户利用一个标签把他们进行归并。
2、共同好友功能,共同喜好,或者可以引申到二度好友之类的扩展应用。
3、统计网站的独立IP。利用set集合当中元素不唯一性,可以快速实时统计访问网站的独立IP。
不过对于 set 中的命令要合理的应用,不然很容易造成慢查询
1、使用高效的命令,比如说,如果你需要返回一个 SET 中的所有成员时,不要使用 SMEMBERS 命令,而是要使用 SSCAN 多次迭代返回,避免一次返回大量数据,造成线程阻塞。
2、当你需要执行排序、交集、并集操作时,可以在客户端完成,而不要用SORT、SUNION、SINTER这些命令,以免拖慢 Redis 实例。
看下源码实现
这里来看下 set 中主要用到的数据类型
代码路径https://github.com/redis/redis/blob/6.2/src/t_set.c
void saddCommand(client *c) {
robj *set;
int j, added = 0;
set = lookupKeyWrite(c->db,c->argv[1]);
if (checkType(c,set,OBJ_SET)) return;
if (set == NULL) {
set = setTypeCreate(c->argv[2]->ptr);
dbAdd(c->db,c->argv[1],set);
}
for (j = 2; j < c->argc; j++) {
if (setTypeAdd(set,c->argv[j]->ptr)) added++;
}
if (added) {
signalModifiedKey(c,c->db,c->argv[1]);
notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_SET,"sadd",c->argv[1],c->db->id);
}
server.dirty += added;
addReplyLongLong(c,added);
}
// 当 value 是整数类型使用 intset
// 否则使用哈希表
robj *setTypeCreate(sds value) {
if (isSdsRepresentableAsLongLong(value,NULL) == C_OK)
return createIntsetObject();
return createSetObject();
}
/* Add the specified value into a set.
*
* If the value was already member of the set, nothing is done and 0 is
* returned, otherwise the new element is added and 1 is returned. */
int setTypeAdd(robj *subject, sds value) {
long long llval;
// 如果是 OBJ_ENCODING_HT 说明是哈希类型
if (subject->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_HT) {
dict *ht = subject->ptr;
dictEntry *de = dictAddRaw(ht,value,NULL);
if (de) {
// 设置key ,value 设置成null
dictSetKey(ht,de,sdsdup(value));
dictSetVal(ht,de,NULL);
return 1;
}
// OBJ_ENCODING_INTSET 代表是 inset
} else if (subject->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_INTSET) {
if (isSdsRepresentableAsLongLong(value,&llval) == C_OK) {
uint8_t success = 0;
subject->ptr = intsetAdd(subject->ptr,llval,&success);
if (success) {
/* Convert to regular set when the intset contains
* too many entries. */
// 如果条目过多将会转换成集合
size_t max_entries = server.set_max_intset_entries;
/* limit to 1G entries due to intset internals. */
if (max_entries >= 1<<30) max_entries = 1<<30;
if (intsetLen(subject->ptr) > max_entries)
setTypeConvert(subject,OBJ_ENCODING_HT);
return 1;
}
} else {
/* Failed to get integer from object, convert to regular set. */
setTypeConvert(subject,OBJ_ENCODING_HT);
/* The set *was* an intset and this value is not integer
* encodable, so dictAdd should always work. */
serverAssert(dictAdd(subject->ptr,sdsdup(value),NULL) == DICT_OK);
return 1;
}
} else {
serverPanic("Unknown set encoding");
}
return 0;
}
通过上面的源码分析,可以看到
1、set 中主要用到了 hashtable 和 inset;
2、如果存储的类型是整数类型就会使用 inset,否则使用 hashtable;
3、使用 inset 有一个最大的限制,达到了最大的限制,也是会使用 hashtable;
再来看下 inset 数据结构
代码地址https://github.com/redis/redis/blob/6.2/src/intset.h
typedef struct intset {
// 编码方法,指定当前存储的是 16 位,32 位,还是 64 位的整数
uint32_t encoding;
uint32_t length;
// 实际保存元素的数组
int8_t contents[];
} intset;
insert
来看下 intset 的数据插入
/* Insert an integer in the intset */
intset *intsetAdd(intset *is, int64_t value, uint8_t *success) {
// 计算value的编码长度
uint8_t valenc = _intsetValueEncoding(value);
uint32_t pos;
if (success) *success = 1;
/* Upgrade encoding if necessary. If we need to upgrade, we know that
* this value should be either appended (if > 0) or prepended (if < 0),
* because it lies outside the range of existing values. */
// 如果value的编码长度大于当前的编码位数,进行升级
if (valenc > intrev32ifbe(is->encoding)) {
/* This always succeeds, so we don't need to curry *success. */
return intsetUpgradeAndAdd(is,value);
} else {
/* Abort if the value is already present in the set.
* This call will populate "pos" with the right position to insert
* the value when it cannot be found. */
// 当前值不存在的时候才进行插入
if (intsetSearch(is,value,&pos)) {
if (success) *success = 0;
return is;
}
is = intsetResize(is,intrev32ifbe(is->length)+1);
if (pos < intrev32ifbe(is->length)) intsetMoveTail(is,pos,pos+1);
}
// 数据插入
_intsetSet(is,pos,value);
is->length = intrev32ifbe(intrev32ifbe(is->length)+1);
return is;
}
intset 的数据插入有一个数据升级的过程,当一个整数被添加到整数集合时,首先需要判断下 新元素的类型和集合中现有元素类型的长短,如果新元素是一个32位的数字,现有集合类型是16位的,那么就需要将整数集合进行升级,然后才能将新的元素加入进来。
这样做的优点:
1、提升整数集合的灵活性,可以随意的添加整数,而不用关心整数的类型;
2、可以尽可能的节约内存。
了解完数据的插入再来看下 intset 中是如何来快速的搜索里面的数据
/* Search for the position of "value". Return 1 when the value was found and
* sets "pos" to the position of the value within the intset. Return 0 when
* the value is not present in the intset and sets "pos" to the position
* where "value" can be inserted. */
// 如果找到了对应的数据,返回 1 将 pos 设置为对应的位置
// 如果找不到,返回0,设置 pos 为可以为数据可以插入的位置
// intset 中的数据是排好序的,所以使用二分查找来寻找对应的元素
static uint8_t intsetSearch(intset *is, int64_t value, uint32_t *pos) {
int min = 0, max = intrev32ifbe(is->length)-1, mid = -1;
int64_t cur = -1;
/* The value can never be found when the set is empty */
if (intrev32ifbe(is->length) == 0) {
if (pos) *pos = 0;
return 0;
} else {
/* Check for the case where we know we cannot find the value,
* but do know the insert position. */
if (value > _intsetGet(is,max)) {
if (pos) *pos = intrev32ifbe(is->length);
return 0;
} else if (value < _intsetGet(is,0)) {
if (pos) *pos = 0;
return 0;
}
}
// 使用二分查找
while(max >= min) {
mid = ((unsigned int)min + (unsigned int)max) >> 1;
cur = _intsetGet(is,mid);
if (value > cur) {
min = mid+1;
} else if (value < cur) {
max = mid-1;
} else {
break;
}
}
if (value == cur) {
if (pos) *pos = mid;
return 1;
} else {
if (pos) *pos = min;
return 0;
}
}
可以看到这里用到的是二分查找,intset 中的数据本身也就是排好序的
dict
来看下 dict 的数据结构
typedef struct dict {
dictType *type;
void *privdata;
// 哈希表数组,长度为2,一个正常存储数据,一个用来扩容
dictht ht[2];
long rehashidx; /* rehashing not in progress if rehashidx == -1 */
int16_t pauserehash; /* If >0 rehashing is paused (<0 indicates coding error) */
} dict;
// 哈希表结构,通过两个哈希表使用,实现增量的 rehash
typedef struct dictht {
dictEntry **table;
// hash 容量大小
unsigned long size;
// 总是等于 size - 1,用于计算索引值
unsigned long sizemask;
// 实际存储的 dictEntry 数量
unsigned long used;
} dictht;
// k/v 键值对节点,是实际存储数据的节点
typedef struct dictEntry {
// 键对象,总是一个字符串类型的对象
void *key;
union {
// void指针,这意味着它可以指向任何类型
void *val;
uint64_t u64;
int64_t s64;
double d;
} v;
// 指向下一个节点
struct dictEntry *next;
} dictEntry;
可以看到 dict 中,是预留了两个哈希表,来处理渐进式的 rehash
rehash 细节参加 redis 中的字典
再来看下 dict 数据的插入
dictEntry *dictAddRaw(dict *d, void *key, dictEntry **existing)
{
long index;
dictEntry *entry;
dictht *ht;
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) _dictRehashStep(d);
/* Get the index of the new element, or -1 if
* the element already exists. */
if ((index = _dictKeyIndex(d, key, dictHashKey(d,key), existing)) == -1)
return NULL;
/* Allocate the memory and store the new entry.
* Insert the element in top, with the assumption that in a database
* system it is more likely that recently added entries are accessed
* more frequently. */
// 这里来判断是否正在 Rehash 中
ht = dictIsRehashing(d) ? &d->ht[1] : &d->ht[0];
entry = zmalloc(sizeof(*entry));
entry->next = ht->table[index];
ht->table[index] = entry;
ht->used++;
/* Set the hash entry fields. */
// 插入具体的数据
dictSetKey(d, entry, key);
return entry;
}
这里重点来分析下 Rehash 的过程
int dictRehash(dict *d, int n) {
int empty_visits = n*10; /* Max number of empty buckets to visit. */
// 这里来判断是否正在 Rehash 中
if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) return 0;
// used 实际存储的 dictEntry 数量
// 如果有数据进行下面的迁移
while(n-- && d->ht[0].used != 0) {
dictEntry *de, *nextde;
/* Note that rehashidx can't overflow as we are sure there are more
* elements because ht[0].used != 0 */
assert(d->ht[0].size > (unsigned long)d->rehashidx);
while(d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx] == NULL) {
d->rehashidx++;
if (--empty_visits == 0) return 1;
}
// 获取老数据中的数据
de = d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx];
/* Move all the keys in this bucket from the old to the new hash HT */
while(de) {
uint64_t h;
nextde = de->next;
/* Get the index in the new hash table */
// 获取新哈希表的索引
h = dictHashKey(d, de->key) & d->ht[1].sizemask;
de->next = d->ht[1].table[h];
// 将数据放入到新的 dity 中
d->ht[1].table[h] = de;
d->ht[0].used--;
d->ht[1].used++;
de = nextde;
}
d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx] = NULL;
d->rehashidx++;
}
/* Check if we already rehashed the whole table... */
// 这里来检测是否完成了整个的 rehash 操作
if (d->ht[0].used == 0) {
zfree(d->ht[0].table);
// 将 ht[1] 的内容放入到 ht[0] 中,ht[1] 作为备用,下次 rehash 使用
d->ht[0] = d->ht[1];
_dictReset(&d->ht[1]);
d->rehashidx = -1;
return 0;
}
/* More to rehash... */
return 1;
}
// 使用增量的方式 rehash
// 当然数据很大的话,一次迁移所有的数据,显然是不合理的,会造成Redis线程阻塞,无法服务其他请求。这里 Redis 使用的是渐进式 rehash。
// 在 rehash 期间,每次执行添加,删除,查找或者更新操作时,除了对命令本身的处理,还会顺带将哈希表1中的数据拷贝到哈希表2中。从索引0开始,每执行一次操作命令,拷贝一个索引位置的数据。
// 如果没有读入和写入操作,这时候就不能进行 rehash
// 所以会定时执行一定数量的 rehash 操作
int incrementallyRehash(int dbid) {
/* Keys dictionary */
if (dictIsRehashing(server.db[dbid].dict)) {
dictRehashMilliseconds(server.db[dbid].dict,1);
return 1; /* already used our millisecond for this loop... */
}
/* Expires */
if (dictIsRehashing(server.db[dbid].expires)) {
dictRehashMilliseconds(server.db[dbid].expires,1);
return 1; /* already used our millisecond for this loop... */
}
return 0;
}
1、rehash 的过程 Redis 默认使用了两个全局哈希表;
2、rehash 的过程是渐进式的,因为如果数据量很大的话,一次迁移所有的数据,会造成Redis线程阻塞,无法服务其他请求;
3、在进行 rehash 期间,删除,查找或者更新操作都会在两个哈希表中执行,添加操作就直接添加到哈希表2中了。查找会把两个哈希表都找一遍,直到找到或者两个都找不到;
4、如果在 reash 期间,如果没有读写操作,这时候,就不能迁移工作了,所以后台定时执行一定数量的数据迁移。
sorted set
sorted set有序集合和集合一样也是 string 类型元素的集合,同时也不允许有重复的成员。
不同的是sorted set中的每个元素都会关联一个 double 类型的分数,sorted set通过这个分数给集合中的成员进行从小到大的排序。有序集合中的成员是唯一的,关联的 score 可以重复。
常见的命令
下面看下有序集合中常见的命令
# 向有序集合添加一个或多个成员,或者更新已存在成员的分数
ZADD key score1 member1 [score2 member2]
# 获取有序集合的成员数
ZCARD key
# 计算在有序集合中指定区间分数的成员数
ZCOUNT key min max
# 有序集合中对指定成员的分数加上增量 increment
ZINCRBY key increment member
# 计算给定的一个或多个有序集的交集并将结果集存储在新的有序集合 destination 中
ZINTERSTORE destination numkeys key [key ...]
# 在有序集合中计算指定字典区间内成员数量
ZLEXCOUNT key min max
# 通过索引区间返回有序集合指定区间内的成员
ZRANGE key start stop [WITHSCORES]
# 通过字典区间返回有序集合的成员
ZRANGEBYLEX key min max [LIMIT offset count]
# 通过分数返回有序集合指定区间内的成员
ZRANGEBYSCORE key min max [WITHSCORES] [LIMIT]
# 返回有序集合中指定成员的索引
ZRANK key member
# 移除有序集合中的一个或多个成员
ZREM key member [member ...]
# 移除有序集合中给定的字典区间的所有成员
ZREMRANGEBYLEX key min max
# 移除有序集合中给定的排名区间的所有成员
ZREMRANGEBYRANK key start stop
# 移除有序集合中给定的分数区间的所有成员
ZREMRANGEBYSCORE key min max
# 返回有序集中指定区间内的成员,通过索引,分数从高到低
ZREVRANGE key start stop [WITHSCORES]
# 返回有序集中指定分数区间内的成员,分数从高到低排序
ZREVRANGEBYSCORE key max min [WITHSCORES]
# 返回有序集合中指定成员的排名,有序集成员按分数值递减(从大到小)排序
ZREVRANK key member
# 返回有序集中,成员的分数值
ZSCORE key member
# 计算给定的一个或多个有序集的并集,并存储在新的 key 中
ZUNIONSTORE destination numkeys key [key ...]
# 迭代有序集合中的元素(包括元素成员和元素分值)
ZSCAN key cursor [MATCH pattern] [COUNT count]
来个栗子
127.0.0.1:6379> ZADD test-sset 1 member1
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> ZADD test-sset 2 member2
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> ZADD test-sset 3 member3
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> ZADD test-sset 3 member3
(integer) 0
127.0.0.1:6379> ZADD test-sset 4 member3
(integer) 0
127.0.0.1:6379> ZADD test-sset 5 member5
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> ZRANGE test-sset 0 10 WITHSCORES
1) "member1"
2) "1"
3) "member2"
4) "2"
5) "member3"
6) "4"
7) "member5"
8) "5"
使用场景
来看下sorted set的使用场景
1、通过 score 的排序功能,可以实现类似排行榜,学习成绩的排序功能;
2、也可以实现带权重队列,比如普通消息的 score 为1,重要消息的 score 为2,然后工作线程可以选择按 score 的倒序来获取工作任务。让重要的任务优先执行;
3、也可以实现一个延迟队列,将 score 存储过期时间,从小到大排序,最靠前的就是最先过期的。
分析下源码实现
sorted set 中的代码主要在下面的两个文件中
结构定义:server.h
实现:t_zset.c
先来看下sorted set的数据结构
typedef struct zset {
dict *dict;
zskiplist *zsl;
} zset;
typedef struct zskiplist {
// 头,尾节点
struct zskiplistNode *header, *tail;
// 节点数量
unsigned long length;
// 目前表内节点的最大层数
int level;
} zskiplist;
/* ZSETs use a specialized version of Skiplists */
// ZSETs 使用的是特定版的 Skiplists
typedef struct zskiplistNode {
// 这里使用 sds 存储具体的元素
sds ele;
// 元素的权重
double score;
// 后向指针(为了便于从跳表的尾节点倒序查找)
struct zskiplistNode *backward;
// 层
// 保存着指向其他元素的指针。高层的指针越过的元素数量大于等于低层的指针,为了提高查找的效率,程序总是从高层先开始访问,然后随着元素值范围的缩小,慢慢降低层次。
struct zskiplistLevel {
// 节点上的前向指针
struct zskiplistNode *forward;
// 跨度
// 用于记录两个节点之间的距离
unsigned long span;
} level[];
} zskiplistNode;
看上面的数据结构可以发现sorted set的实现主要使用了 dict 和 zskiplist 两种数据结构。不过sorted set在元素较少的情况下使用的压缩列表,具体细节参见下文的 zsetAdd 函数。
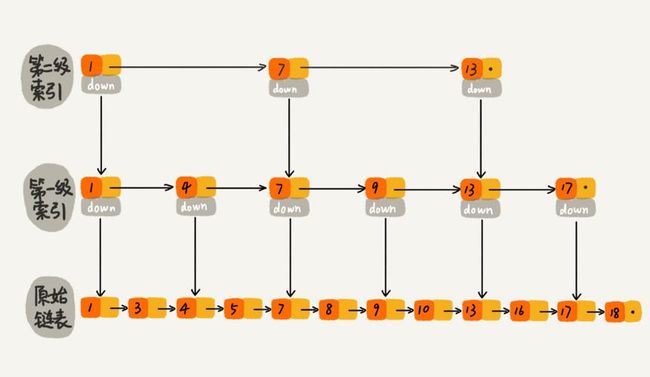
ZADD
来看下 ZADD 的插入
// 代码地址 https://github.com/redis/redis/blob/6.2/src/t_zset.c
// ZADD 命令
void zaddCommand(client *c) {
zaddGenericCommand(c,ZADD_IN_NONE);
}
/* This generic command implements both ZADD and ZINCRBY. */
void zaddGenericCommand(client *c, int flags) {
...
/* Lookup the key and create the sorted set if does not exist. */
zobj = lookupKeyWrite(c->db,key);
if (checkType(c,zobj,OBJ_ZSET)) goto cleanup;
if (zobj == NULL) {
if (xx) goto reply_to_client; /* No key + XX option: nothing to do. */
// 超过阈值(zset-max-ziplist-entries、zset-max-ziplist-value)后,使用 hashtable + skiplist 存储
if (server.zset_max_ziplist_entries == 0 ||
server.zset_max_ziplist_value < sdslen(c->argv[scoreidx+1]->ptr))
{
zobj = createZsetObject();
} else {
zobj = createZsetZiplistObject();
}
dbAdd(c->db,key,zobj);
}
...
}
// 代码地址 https://github.com/redis/redis/blob/6.2/src/t_zset.c
// 看下具体的插入过程
int zsetAdd(robj *zobj, double score, sds ele, int in_flags, int *out_flags, double *newscore) {
/* Turn options into simple to check vars. */
int incr = (in_flags & ZADD_IN_INCR) != 0;
int nx = (in_flags & ZADD_IN_NX) != 0;
int xx = (in_flags & ZADD_IN_XX) != 0;
int gt = (in_flags & ZADD_IN_GT) != 0;
int lt = (in_flags & ZADD_IN_LT) != 0;
...
/* Update the sorted set according to its encoding. */
// 如果类型是 ZIPLIST
if (zobj->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST) {
unsigned char *eptr;
if ((eptr = zzlFind(zobj->ptr,ele,&curscore)) != NULL) {
...
/* Remove and re-insert when score changed. */
// 当分数改变时移除并重新插入
if (score != curscore) {
zobj->ptr = zzlDelete(zobj->ptr,eptr);
zobj->ptr = zzlInsert(zobj->ptr,ele,score);
*out_flags |= ZADD_OUT_UPDATED;
}
return 1;
// 新元素
} else if (!xx) {
/* check if the element is too large or the list
* becomes too long *before* executing zzlInsert. */
// 如果元素过大就使用跳表
if (zzlLength(zobj->ptr)+1 > server.zset_max_ziplist_entries ||
sdslen(ele) > server.zset_max_ziplist_value ||
!ziplistSafeToAdd(zobj->ptr, sdslen(ele)))
{
zsetConvert(zobj,OBJ_ENCODING_SKIPLIST);
} else {
zobj->ptr = zzlInsert(zobj->ptr,ele,score);
if (newscore) *newscore = score;
*out_flags |= ZADD_OUT_ADDED;
return 1;
}
} else {
*out_flags |= ZADD_OUT_NOP;
return 1;
}
}
/* Note that the above block handling ziplist would have either returned or
* converted the key to skiplist. */
// 表示使用的类型是跳表
if (zobj->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_SKIPLIST) {
zset *zs = zobj->ptr;
zskiplistNode *znode;
dictEntry *de;
// 在哈希表中查找元素
de = dictFind(zs->dict,ele);
if (de != NULL) {
/* NX? Return, same element already exists. */
if (nx) {
*out_flags |= ZADD_OUT_NOP;
return 1;
}
// 哈希表中获取元素的权重
curscore = *(double*)dictGetVal(de);
/* Prepare the score for the increment if needed. */
// 更新权重值
if (incr) {
score += curscore;
if (isnan(score)) {
*out_flags |= ZADD_OUT_NAN;
return 0;
}
}
/* GT/LT? Only update if score is greater/less than current. */
if ((lt && score >= curscore) || (gt && score <= curscore)) {
*out_flags |= ZADD_OUT_NOP;
return 1;
}
if (newscore) *newscore = score;
/* Remove and re-insert when score changes. */
// 如果权重发生变化了
if (score != curscore) {
znode = zslUpdateScore(zs->zsl,curscore,ele,score);
/* Note that we did not removed the original element from
* the hash table representing the sorted set, so we just
* update the score. */
dictGetVal(de) = &znode->score; /* Update score ptr. */
*out_flags |= ZADD_OUT_UPDATED;
}
return 1;
// 如果新元素不存在
} else if (!xx) {
ele = sdsdup(ele);
// 插入到跳表节点
znode = zslInsert(zs->zsl,score,ele);
// 在哈希表中插入
serverAssert(dictAdd(zs->dict,ele,&znode->score) == DICT_OK);
*out_flags |= ZADD_OUT_ADDED;
if (newscore) *newscore = score;
return 1;
} else {
*out_flags |= ZADD_OUT_NOP;
return 1;
}
} else {
serverPanic("Unknown sorted set encoding");
}
return 0; /* Never reached. */
}
sorted set 的插入使用了两种策略
1、如果插入的数据量和长度没有达到阀值,就使用压缩列表进行保存,反之就使用跳表加哈希表的组合方式进行保存;
2、压缩列表本身是就不适合保存过多的元素,所以达到阀值使用跳表加哈希表的组合方式进行保存;
3、这里跳表加哈希表的组合方式也是很巧妙的,跳表用来进行范围的查询,通过哈希表来实现单个元素权重值的查询,组合的方式提高了查询的效率;

ZRANGE
看完了插入函数,这里再来分析下 ZRANGE
// 获取有序集合中, 指定数据的排名.
// 若reverse==0, 排名以得分升序排列. 否则排名以得分降序排列.
// 第一个数据的排名为0, 而不是1
// 使用压缩列表或者跳表,里面的数据都是排好序的
long zsetRank(robj *zobj, sds ele, int reverse) {
unsigned long llen;
unsigned long rank;
llen = zsetLength(zobj);
// 压缩列表
if (zobj->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST) {
unsigned char *zl = zobj->ptr;
unsigned char *eptr, *sptr;
eptr = ziplistIndex(zl,0);
serverAssert(eptr != NULL);
sptr = ziplistNext(zl,eptr);
serverAssert(sptr != NULL);
rank = 1;
while(eptr != NULL) {
if (ziplistCompare(eptr,(unsigned char*)ele,sdslen(ele)))
break;
rank++;
zzlNext(zl,&eptr,&sptr);
}
if (eptr != NULL) {
// 逆向取rank
// 返回后面的数据
if (reverse)
return llen-rank;
else
return rank-1;
} else {
return -1;
}
// 跳表
} else if (zobj->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_SKIPLIST) {
zset *zs = zobj->ptr;
zskiplist *zsl = zs->zsl;
dictEntry *de;
double score;
de = dictFind(zs->dict,ele);
if (de != NULL) {
score = *(double*)dictGetVal(de);
// 查找包含给定分值和成员对象的节点在跳跃表中的排位
rank = zslGetRank(zsl,score,ele);
/* Existing elements always have a rank. */
serverAssert(rank != 0);
// 逆向取rank
if (reverse)
return llen-rank;
else
return rank-1;
} else {
return -1;
}
} else {
serverPanic("Unknown sorted set encoding");
}
}
/*
* 查找包含给定分值和成员对象的节点在跳跃表中的排位。
*
* 如果没有包含给定分值和成员对象的节点,返回 0 ,否则返回排位。
* 注意,因为跳跃表的表头也被计算在内,所以返回的排位以 1 为起始值。
* T_wrost = O(N), T_avg = O(log N)
*/
unsigned long zslGetRank(zskiplist *zsl, double score, sds ele) {
zskiplistNode *x;
unsigned long rank = 0;
int i;
x = zsl->header;
for (i = zsl->level-1; i >= 0; i--) {
// 遍历所有对比的节点
while (x->level[i].forward &&
(x->level[i].forward->score < score ||
(x->level[i].forward->score == score &&
sdscmp(x->level[i].forward->ele,ele) <= 0))) {
rank += x->level[i].span;
// 沿着前进指针遍历跳跃表
x = x->level[i].forward;
}
/* x might be equal to zsl->header, so test if obj is non-NULL */
if (x->ele && sdscmp(x->ele,ele) == 0) {
return rank;
}
}
return 0;
}
通过索引区间返回有序集合指定区间内的成员,因为数据在插入的时候,已经按照从小到大进行了,排序,所以返回指定区间的成员,遍历对应的数据即可。
总结
1、Redis 的 Set 是 String 类型的无序集合,集合成员是唯一的;
2、sorted set有序集合和集合一样也是 string 类型元素的集合,同时也不允许有重复的成员。不同的是sorted set中的每个元素都会关联一个 double 类型的分数;
3、set 底层实现主要用到了两种数据结构 hashtable 和 inset(整数集合);
4、sorted set在元素较少的情况下使用的压缩列表存储数据,数据量超过阀值的时候 使用 dict 加 zskiplist 来存储数据;
4、跳表加哈希表的组合方式也是很巧妙的,跳表用来进行范围的查询,通过哈希表来实现单个元素权重值的查询,组合的方式提高了查询的效率。
参考
【Redis核心技术与实战】https://time.geekbang.org/column/intro/100056701
【Redis设计与实现】https://book.douban.com/subject/25900156/
【redis 集合(set)类型的使用和应用场景】https://www.oraclejsq.com/redisjc/040101720.html
【跳跃表】https://redisbook.readthedocs.io/en/latest/internal-datastruct/skiplist.html
【Redis学习笔记】https://github.com/boilingfrog/Go-POINT/tree/master/redis
【Redis 中的 set 和 sorted set 如何使用】https://boilingfrog.github.io/2022/03/21/Redis中的set和sortedset/