神经网络实践一 · 利用PyTorch进行气温预测
利用NN进行简单的气温预测,数据集已上传。数据集主要字段介绍:
- year,moth,day,week:表示的具体的时间,因为为字符格式需要进行独热编码处理
- temp_2:前天的最高温度值
- temp_1:昨天的最高温度值
- average:历史中每年这一天的平均最高温度
- actual:标签值,表示当天的真实最高温度
- friend:用不到,暂不用管
原始数据维度: (348, 9), 数据:
year month day week temp_2 temp_1 average actual friend
0 2016 1 1 Fri 45 45 45.6 45 29
1 2016 1 2 Sat 44 45 45.7 44 61
2 2016 1 3 Sun 45 44 45.8 41 56
3 2016 1 4 Mon 44 41 45.9 40 53
4 2016 1 5 Tues 41 40 46.0 44 41 我们现在需要根据训练集中,除了actual作为标签的这一列以外的数据进行训练,得出NN预测模型的所有参数。可以看到训练集的数据中,week这一列包含字符串而不是如同其他列中的数字,无法在训练中进行数值计算,因此需要把week进行额外处理。这里可以利用sklearn对week独热编码从而标准化特性。处理后的训练数据如下:
标准化原始数据,维度:(348, 14) 具体数据:
[[ 0. -1.5678393 -1.65682171 ... -0.40482045 -0.41913682
-0.40482045]
[ 0. -1.5678393 -1.54267126 ... -0.40482045 -0.41913682
-0.40482045]
[ 0. -1.5678393 -1.4285208 ... -0.40482045 -0.41913682
-0.40482045]
...
[ 0. 1.5810006 1.53939107 ... 2.47023092 -0.41913682
-0.40482045]
[ 0. 1.5810006 1.65354153 ... -0.40482045 -0.41913682
-0.40482045]
[ 0. 1.5810006 1.76769198 ... -0.40482045 -0.41913682
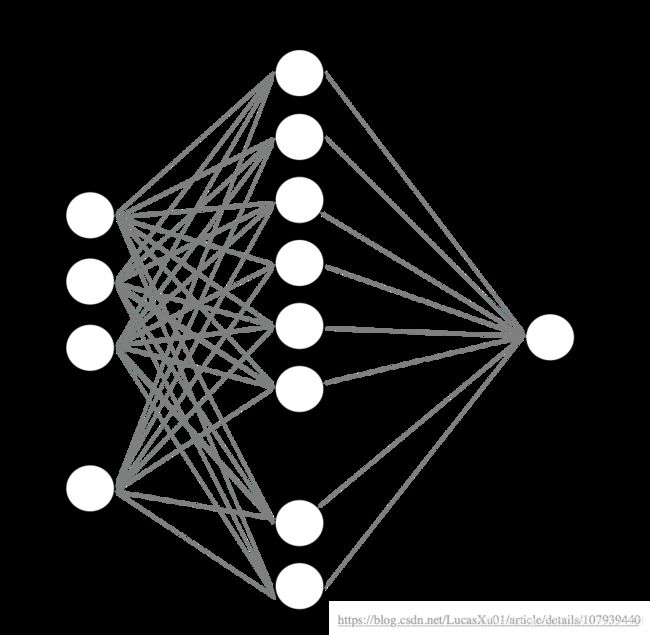
-0.40482045]]这里我们采用一个隐藏层,隐藏层大小设为128,Batch Size大小设为16(Batch就是每次送入网络中训练的一部分数据,而Batch Size就是每个batch中训练样本的数量)。设计的神经网络会意图如下:
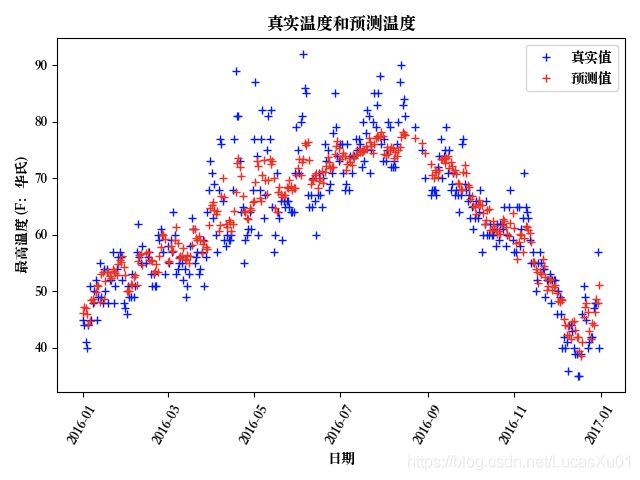
编写代码并运行,得到的气温预测图如下:(我们还可以自行更改Batch Size的大小或隐藏层大小并以此观察对预测结果的影响,如过拟合等现象)
代码如下:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torch
import datetime
from sklearn import preprocessing
import matplotlib
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
features = pd.read_csv('temps.csv')
# 看看数据长什么样子,head()默认展示前五个
print('原始数据维度: {0}, 数据: \n{1} '.format(features.shape, features.head()))
# 独热编码 将week中的Fri、Sun等编码而不是String格式
features = pd.get_dummies(features)
features.head(5)
# 标签 也就要预测的温度的真实值
labels = np.array(features['actual'])
# 在特征中去掉标签
features = features.drop('actual', axis=1)
# 训练集每列名字单独保存,留备用
feature_list = list(features.columns)
# 转换成合适的格式
features = np.array(features)
input_features = preprocessing.StandardScaler().fit_transform(features)
print("\n标准化原始数据,维度:{0} 具体数据:\n{1}".format(input_features.shape, input_features))
# 构建网络模型
input_size = input_features.shape[1]
hidden_size = 128
output_size = 1
batch_size = 16
my_nn = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Linear(input_size, hidden_size),
torch.nn.Sigmoid(),
torch.nn.Linear(hidden_size, output_size),
)
cost = torch.nn.MSELoss(reduction='mean') # 计算损失函数(均方误差)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(my_nn.parameters(), lr=0.001) # 优化器
# 训练网络
losses = []
for i in range(500):
batch_loss = []
# MINI-Batch方法来进行训练
for start in range(0, len(input_features), batch_size):
end = start + batch_size if start + batch_size < len(input_features) else len(input_features)
xx = torch.tensor(input_features[start:end], dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True)
yy = torch.tensor(labels[start:end], dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True)
prediction = my_nn(xx)
loss = cost(prediction, yy)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward(retain_graph=True)
# 所有optimizer都实现了step()方法,它会更新所有的参数。
# 一旦梯度被如backward()之类的函数计算好后,我们就可以调用这个函数。
optimizer.step()
batch_loss.append(loss.data.numpy())
# 打印损失 每100轮打印一次
if i % 100 == 0:
losses.append(np.mean(batch_loss))
print(i, np.mean(batch_loss), batch_loss)
# 预测训练结果
x = torch.tensor(input_features, dtype=torch.float)
predict = my_nn(x).data.numpy()
# 转换日期格式
months = features[:, feature_list.index('month')]
days = features[:, feature_list.index('day')]
years = features[:, feature_list.index('year')]
dates = [str(int(year)) + '-' + str(int(month)) + '-' + str(int(day)) for year, month, day in zip(years, months, days)]
dates = [datetime.datetime.strptime(date, '%Y-%m-%d') for date in dates]
# 创建一个表格来存日期和其对应的标签数值
true_data = pd.DataFrame(data={'date': dates, 'actual': labels})
# 同理,再创建一个来存日期和其对应的模型预测值
test_dates = [str(int(year)) + '-' + str(int(month)) + '-' + str(int(day)) for year, month, day in
zip(years, months, days)]
test_dates = [datetime.datetime.strptime(date, '%Y-%m-%d') for date in test_dates]
predictions_data = pd.DataFrame(data={'date': test_dates, 'prediction': predict.reshape(-1)})
# 开始画图
# matplotlib添加本地的支持中文的字体库,默认是英文的无法显示中文
matplotlib.rc("font", family='Songti SC')
# 真实值
plt.plot(true_data['date'], true_data['actual'], 'b+', label='真实值')
# 预测值
plt.plot(predictions_data['date'], predictions_data['prediction'], 'r+', label='预测值')
plt.xticks(rotation='60')
plt.legend()
# 图名
plt.xlabel('日期')
plt.ylabel('最高温度 (F:华氏)')
plt.title('真实温度和预测温度')
plt.show()