十分钟手撕栈与队列——栈与队列实现详解
目录
-
- 传统艺能
- 栈
- “栈”与“栈”的区别
- 后进先出
- 栈的实现
- 队列
- 队列实现
传统艺能
小编是双非本科大一菜鸟不赘述,欢迎大佬指点江山(QQ:1319365055)
此前博客点我!点我!请搜索博主 【知晓天空之蓝】
乔乔的gitee代码库(打灰人 )欢迎访问,点我!
非科班转码社区诚邀您入驻
小伙伴们,打码路上一路向北,背后烟火,彼岸之前皆是疾苦
一个人的单打独斗不如一群人的砥砺前行
这是我和梦想合伙人组建的社区,诚邀各位有志之士的加入!!
社区用户好文均加精(“标兵”文章字数2000+加精,“达人”文章字数1500+加精)
直达: 社区链接点我
栈
首先应该搞清楚的是什么的是栈,栈是一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。进行数据插入和删除操作的一端称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出 LIFO(Last In First Out)的原则。
压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈、压栈,入栈,入数据在栈顶。
出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈,出数据也在栈顶。
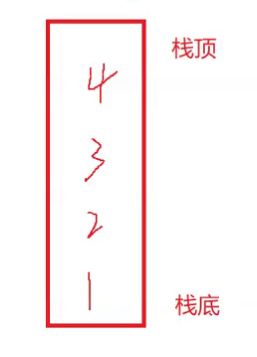
栈的应用场景也很多,比如解决括号匹配问题,逆波兰表达式求解,递归改非递归。
“栈”与“栈”的区别
我们熟知的栈有两种,一个是数据结构的栈,人如其名他是个数据结构,另一个是操作系统中内存划分的一个区域,叫作栈,存放局部变量或在调用函数时建立栈帧。

后进先出
栈的这个特性可以生动形象的类比为给弹夹上子弹与弹子弹的过程,也不一定是要全进再从尾全出,可以进一个出一个,进出时机都是随机的,比如 1,2,3,4依次进栈,进栈过程中可以出栈,则他的序列的可能情况可以有:4,3,2,1
1,4,3,2
2,3,4,1
3,4,2,1
等等
栈的实现
要实现栈其实思路上很简单,底层结构无非还是数组或者链表,我们就要考虑哪个结构更优,相比之下因为动态栈涉及扩容必然链表结构更佳
Stack.h
#pragma once
#includeStack.c
# define _CRTSECURE_NO_WARNINGS
# include"stack.h"
void init(stack* p)
{
assert(p);
p->a = NULL;
p->capacity = 0;
p->top = 0;
}//初始化
void destroy(stack* p)
{
assert(p);
free(p->a);
p->a = 0;
p->capacity = 0;
p->top = 0;
}//销毁
void push(stack* p, Stacktype* x)
{
assert(p);
if (p->capacity == p->top)
{
int newcapa = p->capacity == 0 ? 4 : p->capacity * 2;
p->a = realloc(p->a, newcapa * sizeof(stack));
if (p->a == NULL)
{
printf("fail!\n");
exit(-1);
}
p->capacity = newcapa;
}
p->a[p->top] = x;
p->top++;
}//压栈
void pop(stack* p)
{
assert(p);
assert(p->top > 0);
p->top--;
}//出栈
bool empty(stack* p)
{
assert(p);
/*if (p->capacity == 0)
{
return false;
}
return true;*/
return p->capacity == 0;
}//测空
Stacktype* stacktop(stack* p)
{
assert(p);
return p->top;
}
test.c
# define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
# include"stack.h"
void test()
{
stack p;
init(&p);
push(&p, 1);
push(&p, 2);
push(&p, 3);
pop(&p);
printf("%d ", stacktop(&p));
destroy(&p);
}
int main()
{
test();
return 0;
}
队列
队列和栈是差不多的概念,但二者的实现是完全相反的,栈是只允许在一端进行插入删除的结构,而队列是在一端插入在另一端删除的结构,队列的特点的叫先进先出
入队列:进行插入操作的一端叫做队尾
出队列:进行删除操作的一端叫做队头
队列常用来解决公平排队问题,广度优先遍历等问题。
队列实现
不难想象,队列实现适合用链式结构,毕竟不涉及中间的插入删除,而且数组结构会面临数据挪动问题,大不方便,因此这里用单链表结构就恰到好处。
因为实现简单就不赘述,直接上代码:
Queue.h
#pragma once
#includeQueue.c
# define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
# include"pq.h"
void init(queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->head = NULL;
pq->tail = NULL;
}//初始化
void destroy(queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
qnode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
qnode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->head =pq->tail=NULL;
}//销毁
void push(queue* pq,Queuetype x)
{
assert(pq);
qnode* newnode = (qnode*)malloc(sizeof(qnode));
assert(newnode);
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
if (pq->head == NULL)
{
pq->tail = pq->head = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->tail->next = newnode;
pq->tail = newnode;
}
}//入队
void pop(queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
if (pq->head == pq->tail)
{
free(pq);
pq = NULL;
}
else
{
qnode* cur = pq->head;
qnode* next = cur->next;
free(pq->head);
cur = next;
pq->head = cur;
}
}
bool empty(queue * pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->head == NULL;
}//出队
size_t size(queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
qnode* cur = pq->head;
size_t size = 0;
while (cur)
{
cur = cur->next;
size++;
}
return size;
}
Queuetype front(queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head);
return pq->head->data;
}
Queuetype tail(queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->tail);
return pq->tail->data;
}
test.c
# define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
# include"pq.h"
void test()
{
………
}
int main()
{
test();
return 0;
}