用python实现自动化办公------Excel操作
用python实现自动化办公------Excel操作
用python实现自动化办公------Excel操作
-
- 用python实现自动化办公------Excel操作
- 摘要
- 一 matplotlib和pandas的安装
- 二 matplotlib和pandas的实例
- 三 代码中用到的方法总结
摘要
不得不说,Excel是一款功能强大的数据存储、分析软件,但是并不是一款功能完整的数据分析软件。对于数据分析师来说,使用Excel是很难得出结论的,就拿简简单单的密度图来说,Excel完成密度图的工作量是非常大的,所以,在日常的数据分析工作中,能够使用其它辅助软件配合Excel来完成日常工作是事半功倍的。
今天的内容除了基本的使用python来实现和Exce同样功能l的操作,还有配合Excel中的数据进行各种图表的绘制工作,包括柱形图、折线图、散点图、密度图、堆积图等。对于读者来说,使用本文中的代码不用去自己填充Excel数据,所有需要用到的数据已经在各程序代码中自动生成。
本文在第二节会将所有代码罗列出来,但是对代码没有任何解释(除了注释),读者可以通过代码在本文第三节查找各函数的使用方法。
以下是今天用matplot和pandas绘制出的图表。








一 matplotlib和pandas的安装
①matplot的安装
windows:pip install matplotlib
读者可以在matplotlib官网进行深度学习。
②pandas的安装
windows:pip install pandas
读者可以在pandas官网进行深度学习。
二 matplotlib和pandas的实例
下面读者可以根据我的代码一步一步学习matplotlib和pandas的使用。考虑到很多读者在学习过程中遇到无法获取到实例所使用的数据表,在下面的python的文件中,对于#create random data下面注释的数据是用来建立模拟数据的,读者可以将此后段代码注释后运行代码得到各程序需要的数据表。
1 learn_1.py
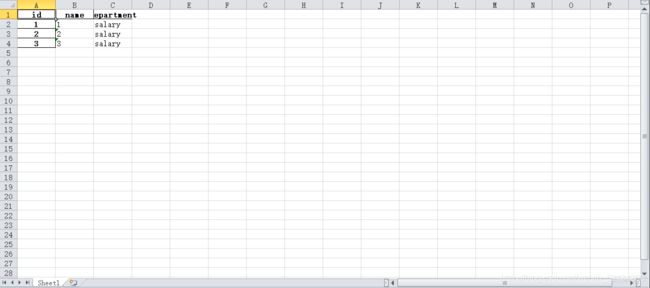
import pandas as pd
df=pd.DataFrame({
"id":[1,2,3],
"name":["1","2","3"],
"department":"salary"
})
df=df.set_index('id')
print(df)
df.to_excel('./dataframe/learn1.xlsx')
此段代码可以搭建一个最简单的Excel表格。运行这段代码后可以得到learn1.xlsx的文档如下所示。
2 learn_2.py
import pandas as pd
# df=pd.read_excel('./dataframe/example.xlsx',header=None)#读取文件,从headers=1第excel第二行开始读
# print(df.shape)#行和列数
# print(df.columns)#列名
# df.columns=['date','socer1','socer2','socer3','socer4']
# df=df.set_index('date')
# print(df.head(3))
# print(df.tail(3))
# print(df.columns)
# df.to_excel('./dataframe/learn1.xlsx')
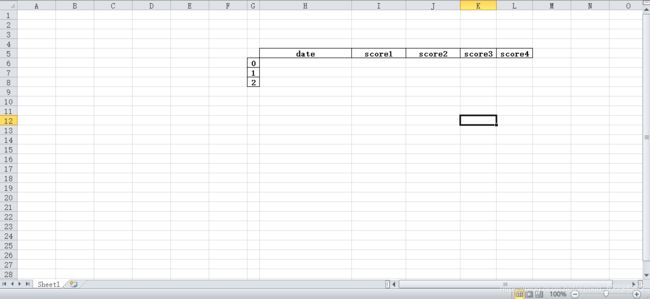
df=pd.read_excel('./dataframe/example.xlsx')#读取文件,从headers=1第excel第二行开始读
print(df.head())#行和列数
df.columns=['index','date','socer1','socer2','socer3','socer4']
print(df[0])
df.to_excel('./dataframe/example.xlsx')
3 learn_3.py
import pandas as pd
s1=pd.Series([1,2,3],index=[1,2,3],name='A')
s2=pd.Series([10,20,30],index=[1,2,3],name='B')
s3=pd.Series([100,200,300],index=[1,2,3],name='C')
df=pd.DataFrame({
s1.name:s1,
s2.name:s2,
s3.name:s3
})
print(df)
df['D']=pd.Series([100,200,300],index=[1,2,3],name='D')
print(df)
4 learn_4.py
import pandas as pd
from datetime import date,timedelta
def add_month(d,md):
yd=md%12
m=d.month+md%12
if m!=12:
yd+=m//12
m=m%12
return date(d.year+yd,m,d.day)
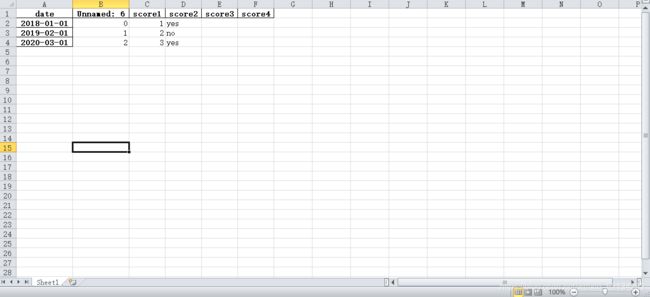
df=pd.read_excel('./dataframe/example.xlsx',skiprows=4,usecols='G:L',index_col=None,
dtype={'date':str,'score1':str,'score2':str,'score3':str,'score4':str})
#df['date'].at[0]='2021-01-05 00:00:00'
#print(df['date'])
start=date(2018,1,1)
print(df)
print(df.index)
for i in df.index:
df['score1'].at[i]=i+1
df['score2'].at[i]='yes' if i%2==0 else 'no'
#df['date'].at[i]=date(start.year+i,start.month+i,start.day+i)
#df['date'].at[i]=start+timedelta(days=i)
df['date'].at[i]=add_month(start,i)
df.set_index('date',inplace=True)
print(df)
df.to_excel('./dataframe/auto_increase_data.xlsx')
auto_increasw_data.xlsx
5 learn_5.py
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import random
#create random data
# word=[chr(i) for i in range(97,123)]
# word_select_list=[]
# for i in range(10):
# word_select=''
# for i in range(5):
# word_select+=random.choice(word)
# word_select_list.append(word_select.title())
# number_select=[ random.choice(range(100,1000)) for i in range(10)]
# discount_select=[round(random.random(),1) for i in range(10)]
# print(number_select)
# id=pd.Series(range(1,11))
# book_name=pd.Series(word_select_list)
# salary=pd.Series(range(100,200,10))
# number=pd.Series(number_select)
# discount=pd.Series(discount_select)
# df=pd.DataFrame({
# 'id':id,
# 'book_name':book_name,
# 'salary':salary,
# 'number':number,
# 'discount':discount,
# 'money':None,
# })
# df.set_index('id',inplace=True)
# print(df)
# df.to_excel('./dataframe/random_data.xlsx')
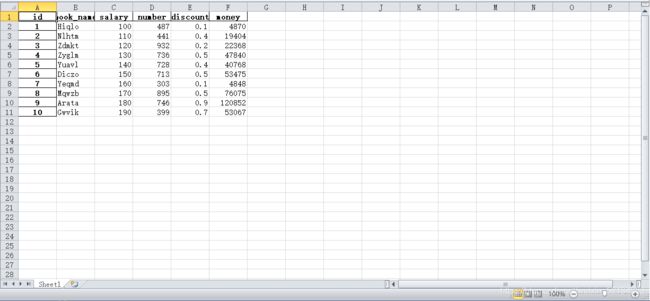
def add_2(x):
return x+2
df=pd.read_excel('./dataframe/random_data.xlsx')
print(df.columns)
# print(len(df['salary']))
#加价一
# for i in range(len(df['salary'])):
# df['salary'].at[i]+=2
#加价二
# df['salary']+=2
#加价三
# df['salary']=df['salary'].apply(add_2)
df['salary']=df['salary'].apply(lambda x:x+2)
print(df)
# df['money']=df['salary']*df['number']*df['discount']#公式
# df.set_index('id',inplace=True)
# df.to_excel('./dataframe/random_data.xlsx')
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import random
#create random data
# word=[chr(i) for i in range(97,123)]
# word_select_list=[]
# for i in range(10):
# word_select=''
# for i in range(5):
# word_select+=random.choice(word)
# word_select_list.append(word_select.title())
# discount_select=[round(random.random(),1) for i in range(10)]
# width_select=[random.choice(['yes','no']) for i in range(10)]
# id=pd.Series(range(1,11))
# book_name=pd.Series(word_select_list)
# salary=pd.Series(range(100,200,10))
# width=pd.Series(width_select,dtype=str)
# discount=pd.Series(discount_select)
# df=pd.DataFrame({
# 'id':id,
# 'book_name':book_name,
# 'salary':salary,
# 'width':width,
# })
# df.set_index('id',inplace=True)
# print(df)
# df.to_excel('./dataframe/learn_6.xlsx')
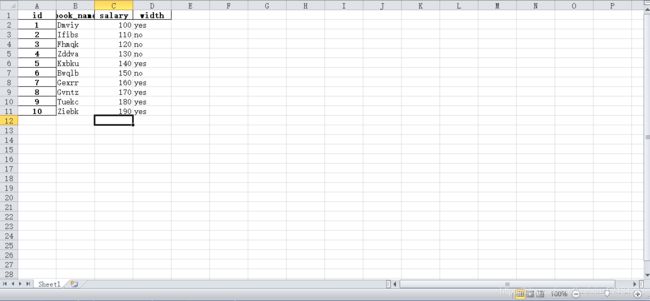
#排序
df=pd.read_excel('./dataframe/learn_6.xlsx',index_col='id')
df.sort_values(by=["width","salary"],inplace=True,ascending=[True,False])
print(df)
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import random
# create random data
# word=[chr(i) for i in range(97,123)]
# word_select_list=[]
# for i in range(10):
# word_select=''
# for i in range(5):
# word_select+=random.choice(word)
# word_select_list.append(word_select.title())
# discount_select=[round(random.random(),1) for i in range(10)]
# width_select=[random.choice(['yes','no']) for i in range(10)]
# id=pd.Series(range(1,11))
# name=pd.Series(word_select_list)
# age_select=[random.choice(range(10,13)) for i in range(10)]
# salary=pd.Series(range(100,200,10))
# age=pd.Series(age_select)
# width=pd.Series(width_select,dtype=str)
# score=pd.Series([random.choice(range(50,100)) for i in range(10)])
# discount=pd.Series(discount_select)
# df=pd.DataFrame({
# 'id':id,
# 'name':name,
# 'age':age,
# 'score':score,
# })
# df.set_index('id',inplace=True)
# print(df)
# df.to_excel('./dataframe/learn_7.xlsx')
def age_11_to_12(a):
return 11<=a<=12
def level_a(s):
return s>=90
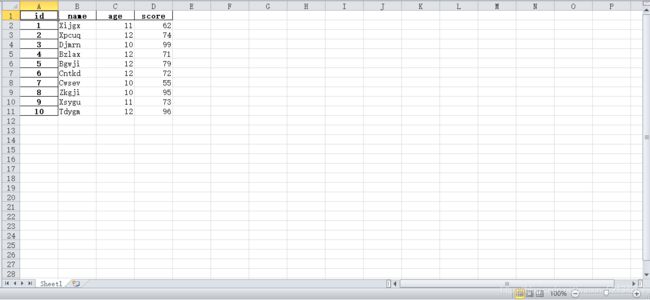
#筛选数据
df=pd.read_excel('./dataframe/learn_7.xlsx',index_col='id')
print(df)
#筛选方法
# df=df.loc[df['age'].apply(age_11_to_12)].loc[df['score'].apply(level_a)]
# df=df.loc[df.age.apply(age_11_to_12)].loc[df.score.apply(level_a)]
df=df.loc[df.age.apply(lambda a: 11<=a<=12)].loc[df.score.apply(lambda s:s>=90)]
print(df)
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#create random data
# word=[chr(i) for i in range(97,123)]
# word_select_list=[]
# for i in range(10):
# word_select=''
# for i in range(5):
# word_select+=random.choice(word)
# word_select_list.append(word_select.title())
# discount_select=[round(random.random(),1) for i in range(10)]
# width_select=[random.choice(['yes','no']) for i in range(10)]
# id=pd.Series(range(1,11))
# name=pd.Series(word_select_list)
# age_select=[random.choice(range(10,13)) for i in range(10)]
# salary=pd.Series(range(100,200,10))
# age=pd.Series(age_select)
# width=pd.Series(width_select,dtype=str)
# score=pd.Series([random.choice(range(50,100)) for i in range(10)])
# discount=pd.Series(discount_select)
# df=pd.DataFrame({
# 'name':name,
# 'number':score
# })
# df.set_index('name',inplace=True)
# print(df)
# df.to_excel('./dataframe/learn_8.xlsx')
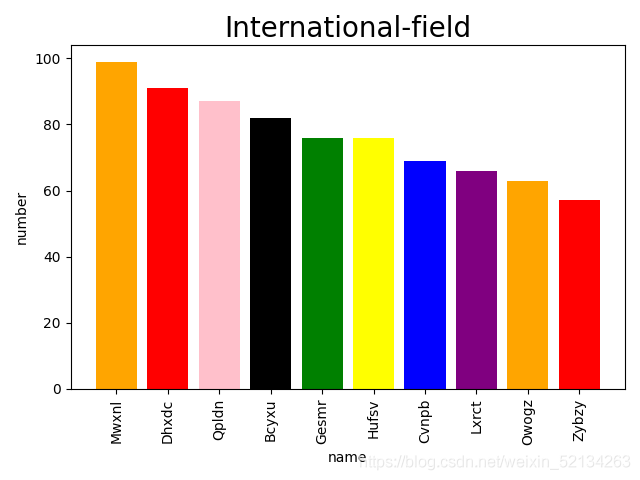
df=pd.read_excel('./dataframe/learn_8.xlsx')
df.sort_values(by="number",inplace=True,ascending=False)
print(df)
# df.plot.bar(x='name',y='number',color=['orange','red'],title='international-field')
plt.bar(df.name,df.number,color=['orange','red','pink','black','green','yellow','blue','purple'])
plt.xticks(df.name,rotation=90)#rotation为翻转角度
plt.xlabel("name")
plt.ylabel("number")
plt.title("International-field",fontsize=20)
plt.tight_layout()#紧凑型
plt.show()
9 learn_9.py
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#create random data
# word=[chr(i) for i in range(97,123)]
# word_select_list=[]
# for i in range(10):
# word_select=''
# for i in range(5):
# word_select+=random.choice(word)
# word_select_list.append(word_select.title())
# discount_select=[round(random.random(),1) for i in range(10)]
# width_select=[random.choice(['yes','no']) for i in range(10)]
# id=pd.Series(range(1,11))
# name=pd.Series(word_select_list)
# age_select=[random.choice(range(10,13)) for i in range(10)]
# salary=pd.Series(range(100,200,10))
# age=pd.Series(age_select)
# width=pd.Series(width_select,dtype=str)
# score1=pd.Series([random.choice(range(50,100)) for i in range(10)])
# score2=pd.Series([random.choice(range(50,100)) for i in range(10)])
# discount=pd.Series(discount_select)
# df=pd.DataFrame({
# 'name':name,
# '2016':score1,
# '2017':score2
# })
# df.set_index('name',inplace=True)
# print(df)
# df.to_excel('./dataframe/learn_9.xlsx')
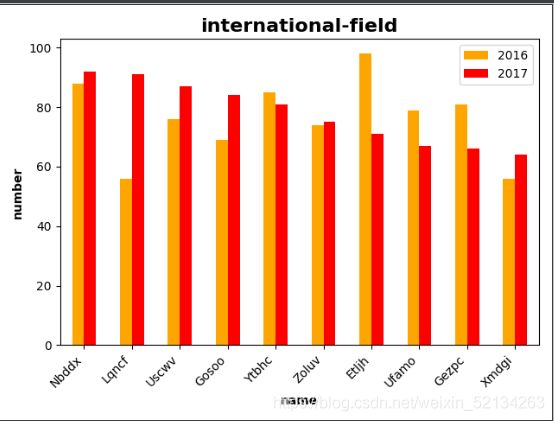
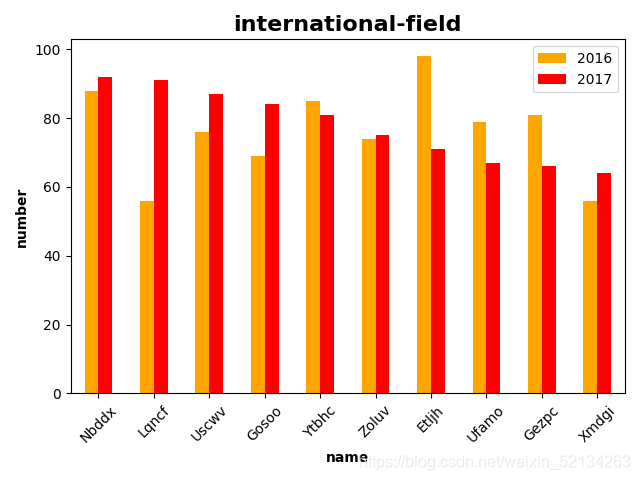
df=pd.read_excel('./dataframe/learn_9.xlsx')
print(df)
df.sort_values(by="2017",inplace=True,ascending=False)
df.plot.bar(x='name',y=['2016','2017'],color=["orange","red"])
plt.title("international-field",fontsize=16,fontweight="bold")
plt.xlabel("name",fontweight="bold")
plt.ylabel("number",fontweight="bold")
ax=plt.gca()#getcutaccent
ax.set_xticklabels(df['name'],rotation=45,ha="right")
# f=plt.gcf()
# f.subplots_adjust(left=0.2,bottom=0.42)
plt.tight_layout()#紧凑型
plt.show()
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# create random data
# word=[chr(i) for i in range(97,123)]
# word_select_list=[]
# for i in range(10):
# word_select=''
# for i in range(5):
# word_select+=random.choice(word)
# word_select_list.append(word_select.title())
# discount_select=[round(random.random(),1) for i in range(10)]
# width_select=[random.choice(['yes','no']) for i in range(10)]
# id=pd.Series(range(1,11))
# name=pd.Series(word_select_list)
# age_select=[random.choice(range(100,300)) for i in range(10)]
# salary=pd.Series(range(100,200,10))
# age=pd.Series(age_select)
# width=pd.Series(width_select,dtype=str)
# score=pd.Series([random.choice(range(100,300)) for i in range(10)])
# discount=pd.Series(discount_select)
# df=pd.DataFrame({
# 'id':id,
# 'name':name,
# '10月':score,
# '11月':age,
# '12月':score,
# })
# df.set_index('id',inplace=True)
# print(df)
# df.to_excel('./dataframe/learn_10.xlsx')
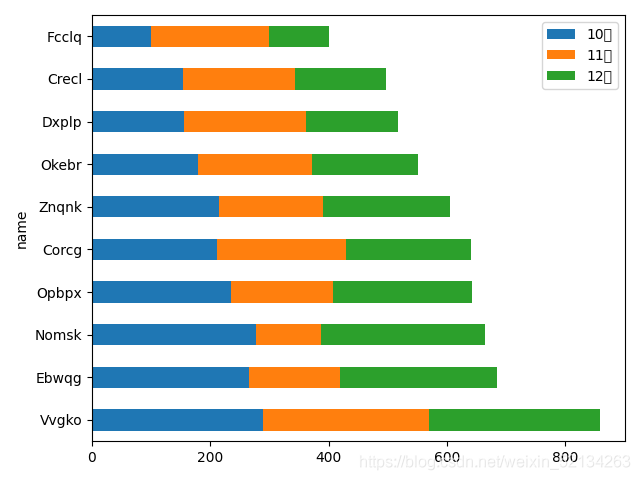
df=pd.read_excel('./dataframe/learn_10.xlsx')
print(df)
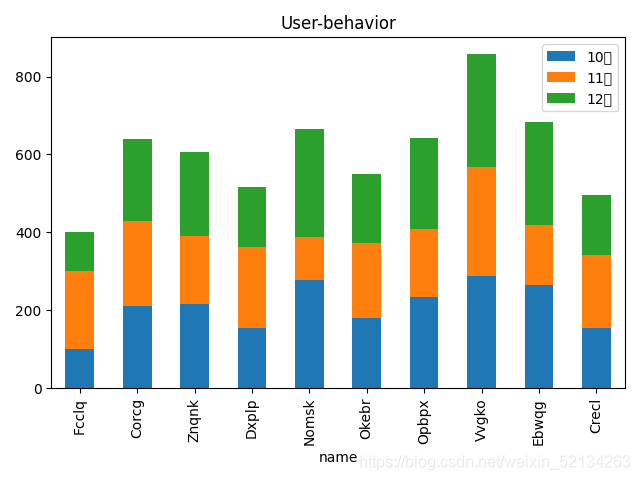
df['total']=df['10月']+df['11月']+df['12月']
df.sort_values(by='total',inplace=True,ascending=False)
print(df)
#水平
#df.plot.bar(x='name',y=['10月','11月','12月'],stacked=True)#叠加图
#df.plot.bar(x='name',y=['10月','11月','12月'],stacked=True)#叠加图
#垂直
df.plot.barh(x='name',y=['10月','11月','12月'],stacked=True)#叠加图
#plt.title("User-behavior")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#create random data
# word=[chr(i) for i in range(97,123)]
# word_select_list=[]
# for i in range(10):
# word_select=''
# for i in range(5):
# word_select+=random.choice(word)
# word_select_list.append(word_select.title())
# discount_select=[round(random.random(),1) for i in range(10)]
# width_select=[random.choice(['yes','no']) for i in range(10)]
# name=pd.Series(word_select_list)
# age_select=[random.choice(range(10,13)) for i in range(10)]
# salary=pd.Series(range(100,200,10))
# age=pd.Series(age_select)
# width=pd.Series(width_select,dtype=str)
# id=pd.Series(range(1,11))
# score1=pd.Series([random.choice(range(50,100)) for i in range(10)])
# score2=pd.Series([random.choice(range(50,100)) for i in range(10)])
# # discount=pd.Series(discount_select)
# df=pd.DataFrame({
# 'Id':id,
# 'From':pd.Series(['China','Canada','US','UK','Japan','French','German','India','England','Austria']),
# '2016_year':score1,
# '2017_year':score2
# })
# df.set_index('Id',inplace=True)
# print(df)
# df.to_excel('./dataframe/learn_11.xlsx')
df=pd.read_excel('./dataframe/learn_11.xlsx',index_col='From')
print(df)
#顺时针方法一
#df['2017_year'].sort_values(ascending=True).plot.pie(fontsize=8,startangle=-270)#顺时针
#顺势正方法二
df['2017_year'].plot.pie(fontsize=8,counterclock=False,startangle=-270)
plt.title("Source of International Student",fontsize=16,fontweight="bold")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.ylabel("2017",fontsize=12,fontweight="bold")
plt.show()
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#create random data
# id=pd.Series(range(1,51))
# df=pd.DataFrame({
# 'Week':id,
# 'lingjian_1':pd.Series([random.choice(range(340,1500)) for i in range(50)]),
# 'lingjian_2':pd.Series([random.choice(range(100,15000)) for i in range(50)]),
# 'lingjian_3':pd.Series([random.choice(range(234,98730)) for i in range(50)]),
# 'lingjian_4':pd.Series([random.choice(range(100,15000)) for i in range(50)]),
# 'lingjian_5':pd.Series([random.choice(range(2340,35000)) for i in range(50)])
# })
# df.set_index('Week',inplace=True)
# print(df)
# df.to_excel('./dataframe/learn_12.xlsx')
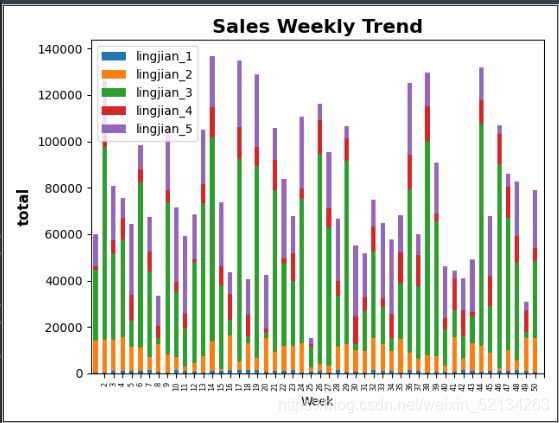
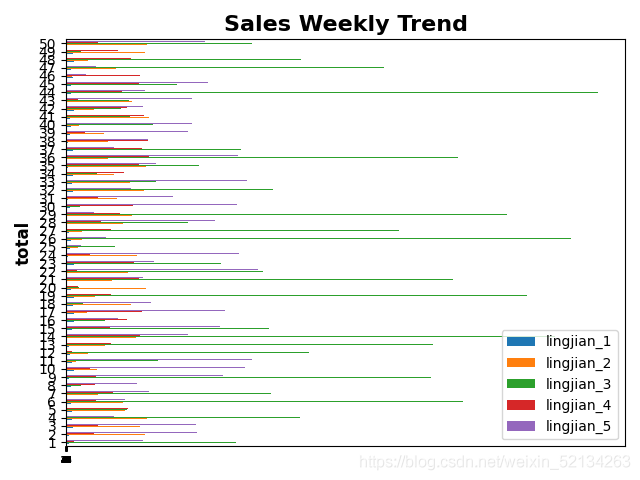
df=pd.read_excel('./dataframe/learn_12.xlsx',index_col='Week')
df['total']=df['lingjian_1']+df['lingjian_2']+df['lingjian_3']+df['lingjian_4']+df['lingjian_5']
# print(df.columns)
#叠加图
#df.plot.area(y=['lingjian_1', 'lingjian_2', 'lingjian_3', 'lingjian_4', 'lingjian_5'])
#折线图
#df.plot(y=['lingjian_1', 'lingjian_2', 'lingjian_3', 'lingjian_4', 'lingjian_5'])
#柱状图
#df.plot.bar(y=['lingjian_1', 'lingjian_2', 'lingjian_3', 'lingjian_4', 'lingjian_5'])
#叠加Y柱状图
#df.plot.barh(y=['lingjian_1', 'lingjian_2', 'lingjian_3', 'lingjian_4', 'lingjian_5'])
#叠加X柱状图
df.plot.bar(y=['lingjian_1', 'lingjian_2', 'lingjian_3', 'lingjian_4', 'lingjian_5'],stacked=True)
plt.title("Sales Weekly Trend",fontsize=16,fontweight="bold")
plt.ylabel("total",fontsize=12,fontweight='bold')
plt.xticks(df.index,fontsize=6)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#create random data
# id=pd.Series(range(1,51))
# df=pd.DataFrame({
# 'City':pd.Series(['Beijing','Shanghai','Tianjin','Guangzhou','Shenzhen','Taiwan','Hangzhou','Xian','Taiyuan','Chengdu','Lanzhou',
# 'Xining','Nanning','Guilin','Huizhou','Dongguan','Fuzhou','Xiamen','Putian','Wenzhou','Lishui','Taizhou','Ningbo',
# 'Jiaxing','Wuxi','Suzhou','Nanjing','Changzhou','Panzhihua','Jinan']
# ),
# 'Sales':pd.Series([random.choice(range(34000,150000)) for i in range(30)]),
# 'Bedroom':pd.Series([random.choice(range(1,5)) for i in range(30)]),
# 'Bathroom':pd.Series([random.choice(range(1,5)) for i in range(30)]),
# 'Area':pd.Series([random.choice(range(100,250)) for i in range(30)]),
# 'Dixiashi':pd.Series([random.choice(range(0,350)) for i in range(30)]),
# 'Yield':pd.Series([random.choice(range(0,350)) for i in range(30)]),
# 'Floors':pd.Series([random.choice(range(1,5)) for i in range(30)]),
# 'Built-year':pd.Series([random.choice(range(1998,2021)) for i in range(30)])
# })
# df.set_index('City',inplace=True)
# print(df)
# df.to_excel('./dataframe/learn_13.xlsx')
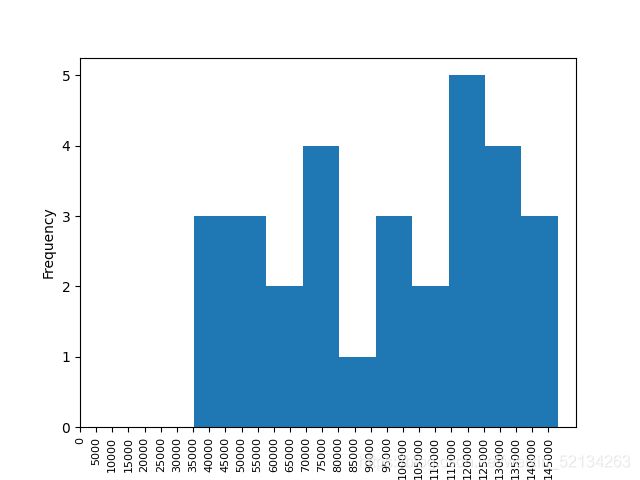
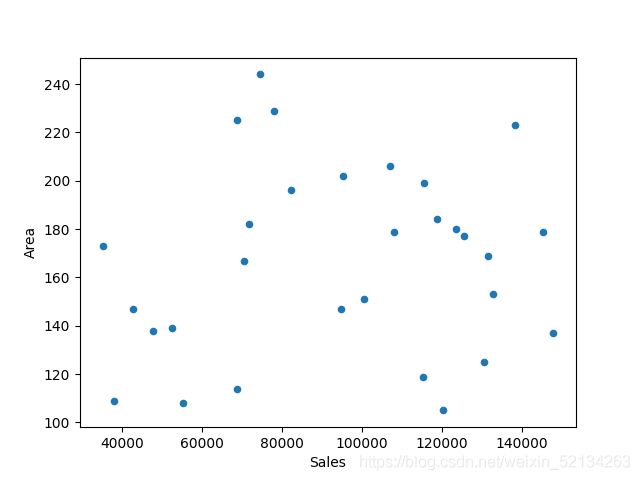
df=pd.read_excel('./dataframe/learn_13.xlsx')
pd.options.display.max_columns=555
print(df)
#散点图
#df.plot.scatter(y='Area',x='Sales')
#分布图
# df.Sales.plot.hist(bins=10)
# plt.xticks(range(0,max(df.Sales),5000),fontsize=8,rotation=90)
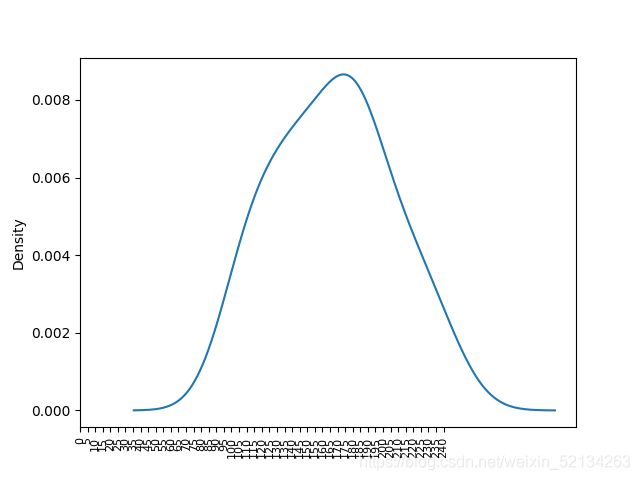
#密度图
# df.Area.plot.kde()
# plt.xticks(range(0,max(df.Area),8),fontsize=8,rotation=90)
# plt.show()
print(df.corr())
三 代码中用到的方法总结
对于第二节中的代码,我没有做更多解释,读者只需要看懂本小节就会很容易理解上述的代码。第二小结中的带create random data注释的代码都是用于实例所需要的数据表所要自动生成的代码,后段代码运行需要先将前段代码注释掉,对于后段代码一些图的绘制方法都有注释,读者只需要注释其它,运行一个就可以实现画图功能。下面总结本文使用到的pandas和matplot的知识点。
①Excel操作
对于上文中列出的代码,将一部分方法进行解释
df=pd.read_excel(’./dataframe/learn1.xlsx’):将learn_1.xlsx文件读出做为df实例
pd.DataFrame():建表
df.set_index():将设置df中的索引列
df.to_excel(’./dataframe/learn1.xlsx’):将df生成xlsx文件保存
df.head(3):df前三行的数据
df.tail(3):df后三行的数据
df.columns=[‘date’,‘socer1’,‘socer2’,‘socer3’,‘socer4’]:给df赋值列名
df.columns:返回df包含列名的列表
df.shape:返回df共有的行数和列数
s1=pd.Series([1,2,3],index=[1,2,3],name=‘A’):生成一个名为’A’的列,索引为[1,2,3]
df.set_index(‘date’,inplace=True):将df中的’date’列设置为索引
df[‘salary’]=df[‘salary’].apply(lambda x:x+2):将df中的’salary’列每行数据加2
df.sort_values(by=[“width”,“salary”],inplace=True,ascending=[True,False]):以’width’和’salary’列为df排序,前者为顺序,后者为逆序
df=df.loc[df.age.apply(lambda a: 11<=a<=12)].loc[df.score.apply(lambda s:s>=90)]:筛选
plt.bar(df.name,df.number,color=[‘orange’,‘red’,‘pink’,‘black’,‘green’,‘yellow’,‘blue’,‘purple’]):条形图
plt.xticks(df.name,rotation=90)#rotation为翻转角度
plt.xlabel(“name”):为x轴标注轴名
plt.ylabel(“number”):为y轴标住轴名
plt.title(“International-field”,fontsize=20):标住图的标题名以及字体大小
plt.tight_layout()#紧凑型
plt.show():将图表展示出来
df.plot.bar(x=‘name’,y=[‘2016’,‘2017’],color=[“orange”,“red”])#比较柱形图
df.plot.barh(x=‘name’,y=[‘10月’,‘11月’,‘12月’],stacked=True)#叠加图
df.plot.bar(x=‘name’,y=[‘10月’,‘11月’,‘12月’],stacked=True)#叠加图
df.plot.bar(x=‘name’,y=[‘10月’,‘11月’,‘12月’],stacked=True)#叠加图
df.plot.area(y=[‘lingjian_1’, ‘lingjian_2’, ‘lingjian_3’, ‘lingjian_4’, ‘lingjian_5’])#叠加图
df.plot(y=[‘lingjian_1’, ‘lingjian_2’, ‘lingjian_3’, ‘lingjian_4’, ‘lingjian_5’]):折线图
df.plot.bar(y=[‘lingjian_1’, ‘lingjian_2’, ‘lingjian_3’, ‘lingjian_4’, ‘lingjian_5’]):柱状图
df.plot.barh(y=[‘lingjian_1’, ‘lingjian_2’, ‘lingjian_3’, ‘lingjian_4’, ‘lingjian_5’]):叠加Y柱状图
df.corr():返回相关性
pd.options.display.max_columns=555:控制台打印出最多555列的数据
如果对我的文章感兴趣,请为我点一个赞,如果有python的知识需要了解或探讨,可以加本人微信cuiliang1666457052