【CSAPP随笔】CH2:A Tour of Computer Systems | 计算机系统漫游
![]()
前言:
《深入理解操作系统》个人用学习笔记。
目录
前言:
0x00 Journey of Hello.c in Computer Systems - 计算机系统漫游
0x01 ASCII - 美国信息交换标准代码
0x02 Compilation System - 编译系统
0x03 Compilation Overview - 汇编概览
0x04 Executable Object Program - 可执行目标程序
0x05 Hardware Organization of a System - 系统的硬件组成
0x06 Running “hello” Program - 跑一下 "hello" 程序
0x07 Shell Program
0x08 Reading hello command from keyboard - 从键盘上读取 hello 指令
0x09 Loading executable from disk into memory - 将可执行文件从磁盘加载到内存中
0x0A Running "hello" program - 运行 hello 程序
0x0B Writing “hello, world” from memory to display - 将 "hello, world" 从内存中整到显示器上
0x0C Caches matters - 缓存问题
0x0D Memory hierarchy - 存储器层次结构
0x0E The operating system manages the hardware - 操作系统管理硬件
0x0F Abstractions?
0x10 The operating system manages the hardware - 操作系统管理硬件
0x11 Systems communicate with other systems using net works - 利用网络系统和其他系统通信
0x00 Journey of Hello.c in Computer Systems - 计算机系统漫游
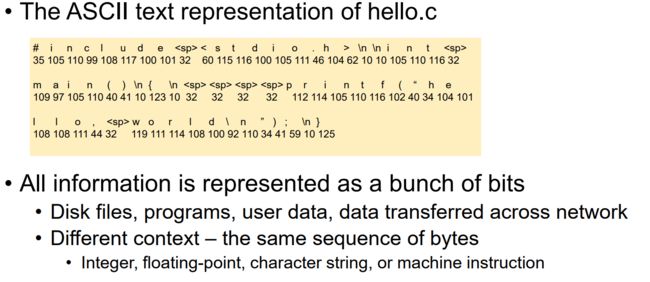
hello.c
#include
int main()
{
printf("hello, world\n");
} 转换为 ASCII 码表示:
所有信息都以一堆 bits 来表示:
- 磁盘文件、程序、用户数据、网络上传输的数据
- 不同的背景 - 相同的字节序列
- 整数、浮点、字符串或机器指令
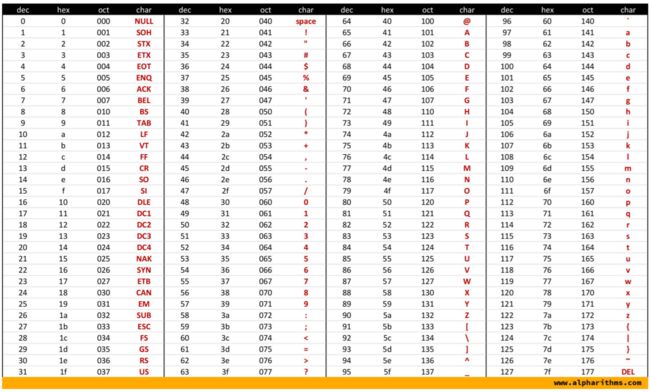
0x01 ASCII - 美国信息交换标准代码
American Standard Code for Information Interchange
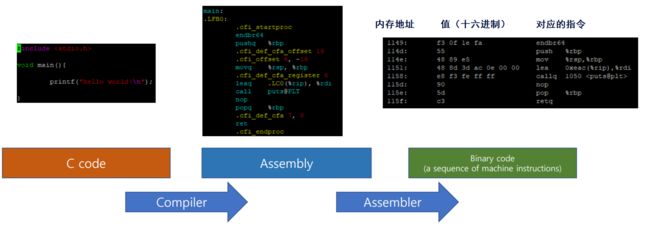
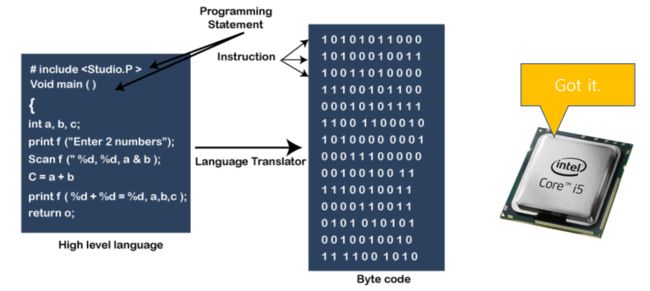
0x02 Compilation System - 编译系统
Translate a high-level C program into the binary code that is read and operated by the processor.
将高级C语言程序翻译成处理器读取和操作的二进制代码。
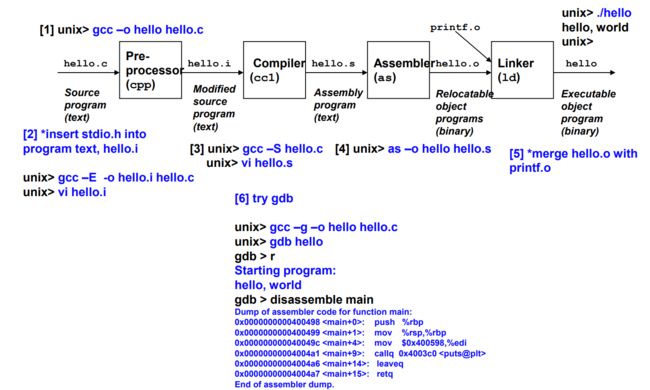
0x03 Compilation Overview - 汇编概览
1. The preprocessor modifies the original C program according to directives that begin with the # character, and deletes the comments. The result is another C program with the .i suffix.
2. The compiler translates the text file hello.i into the text file hello.s, which contains an assembly-language program. Each statement in an assembly-language program exactly describes one low-level machine-language instruction.
3. The assembler translates hello.s into machine-language instructions, packages them in a form known as a relocatable object program. The result is stored as object file hello.o.
4. A program can call a function resides in a separate precompiled object file. The linker handles this merging, and the executable object file hello is the final output.
预处理阶段:
预处理器(cpp)根据字符#开头的命令(directives),修改原始的C程序。比如 hello.c 中的第一行 #inlclude
编译阶段:
编译器(cc1)将文本文件 stdio.i 翻译成文本文件 hello.c,它包含一个汇编语言程序。汇编语言程序中的每条语句都以一种标准的文本格式确切的描述了一条地基机械语言指令。
汇编阶段:
接下来,汇编器(as)将hello.s 翻译成机器语言指令,把这些指令打包成为一种叫做可重定位(relocatable )目标程序的格式,并将结果保存在目标文件hello.o 中。hello.o文件是一个二进制文件,它的字节编码是机器语言指令而不是字符。如果我们在文本编辑器中打开hello.o文件,呈现的将是一堆乱码。
链接阶段:
请注意,我们的 hello程序调用了printf 函数,它是标准C库中的一个函数,每个C编译器都提供。printf函数存在于一个名为 printf.o的单独的预编译目标文件中,而这个文件必须以某种方式并入到我们的hello.o程序中。链接器(ld)就负责处理这种并入,结果就得到hello文件,它是一个可执行目标文件(或者简称为可执行文件)。可执行文件加载到存储器后,由系统负责执行。
0x04 Executable Object Program - 可执行目标程序
A program that is ready to be loaded into memory and executed by the computer system.
一个准备装入内存并由计算机系统执行的程序:
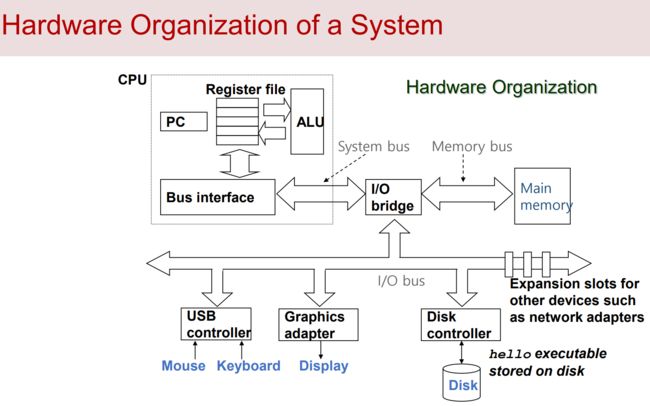
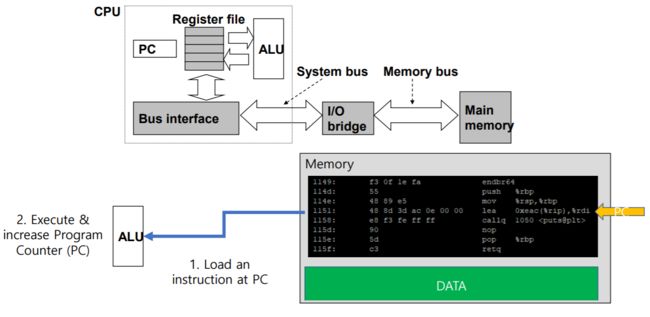
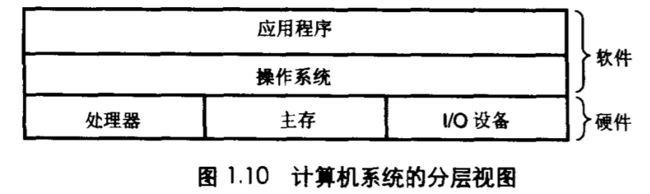
0x05 Hardware Organization of a System - 系统的硬件组成
BUS(总线)
a collection of electrical wires that carry bytes of information back and forth between the components.
一组电线,携带信息字节并负责在各个部件值间传递。
IO devices(IO 设备)
the system’s connection to the external world. ex: display, mouse, disk, and network adapter.
IO 设备是系统与外界联系的通道。比如,显示器,鼠标,磁盘和网络适配器。
Main memory(主存)
a temporary storage device that holds both a program and the data it manipulates while the processor is executing the program.
主存是一个临时存储设备,在处理器执行程序时,他被用来存放程序和程序处理的数据。
Processor or central processing unit (处理器)
an engine that interprets or executes program instructions stored in main memory.
• Register file: small storage
• Arithmetic/logic unit: computing unit
• Program counter: line indicator
中央处理单元(CPU)简称处理器,是解释或执行存储在主存中指令的引擎。
寄存器文件(register file):小型存储器
算数逻辑元(ALU):计算单元
程序计数器(PC):线路指示器
CPU:中央处理单元
ALU:算数/逻辑单员
PC:程序计数器
USB: 通用串行总线
0x06 Running “hello” Program - 跑一下 "hello" 程序
1. Get a command executing “hello” program in the shell program.
2. The operating system loads “hello” executable program stored in the disk to the memory and start running the program.
3. A processor executes the instructions of loaded “hello” program.
4. After termination, switch back to the shell program.
1. 在shell程序中获得一个执行 "hello "程序的命令。
2. 操作系统将存储在磁盘中的 "hello "可执行程序加载到内存中并开始运行该程序。
3. 一个处理器执行加载的 "hello "程序的指令。
4. 终止后,切换回shell程序。
0x07 Shell Program
基于文本的用户界面
基于命令行的解释器
① 直接运行命令
② 探索文件系统
③ 删除和创建文件
④ 浏览路径
⑤ 运行程序
⑥ 打印文本
0x08 Reading hello command from keyboard - 从键盘上读取 hello 指令
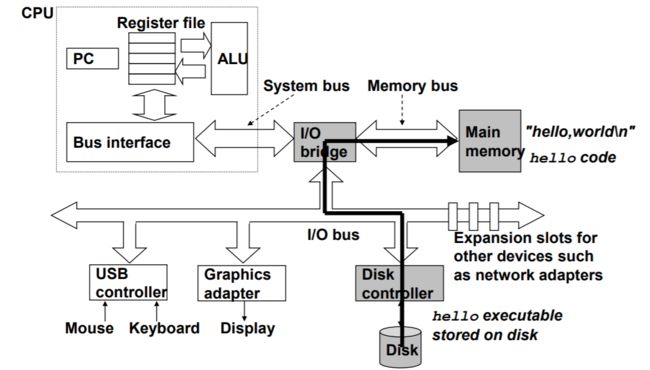
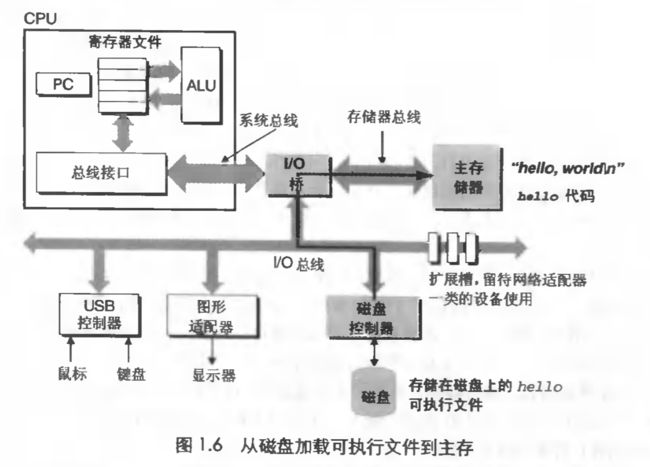
我们在键盘上输入字符串 ./hello 后,shell 程序就逐一读取字符到寄存器,再把它存放到寄存器中。当我们在键盘上敲回车键时,shell就知道我们已经输完了,然后 shell 会执行一系列指令,这些指令将 hello 目标文件中大哥代码和数据从磁盘拷贝到主存,从而加载 hello 文件。数据包括最终会被输出的字符串 "hello, world\n" 。
0x09 Loading executable from disk into memory - 将可执行文件从磁盘加载到内存中
这里利用了 DMA技术 (直接存储器存器),使得数据可以不通过处理器,直接从磁盘到达主存。
0x0A Running "hello" program - 运行 hello 程序
0x0B Writing “hello, world” from memory to display - 将 "hello, world" 从内存中整到显示器上
hello 目标文件中的代码和数据被加载到了处理器后,处理器就开始执行 hello 程序的主程序中的机器语言指令,这些指令将 "hello,world\n" 串中的字节从存储器中拷贝到寄存器文件,再从寄存器中 文件拷贝到 显示设备,最终显示在屏幕上。
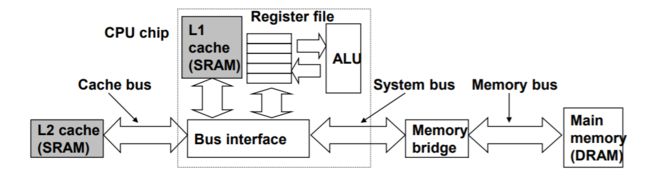
0x0C Caches matters - 缓存问题
Processor memory gap increases
a few hundreds bytes of register file / millions of bytes in main memory (but 100 times faster than main memory)
Programmer can exploit caches to improve the performance of their programs
处理器内存差距不断增大
几百字节的寄存器文件/数百万字节的主内存(但比主内存快100倍)。
为了解决处理器与主存之间的差异,系统设计者采用了更小更快的存储设备 —— 高速缓存存储器(cache memories)。
程序员可以利用缓存来提高其程序的性能。
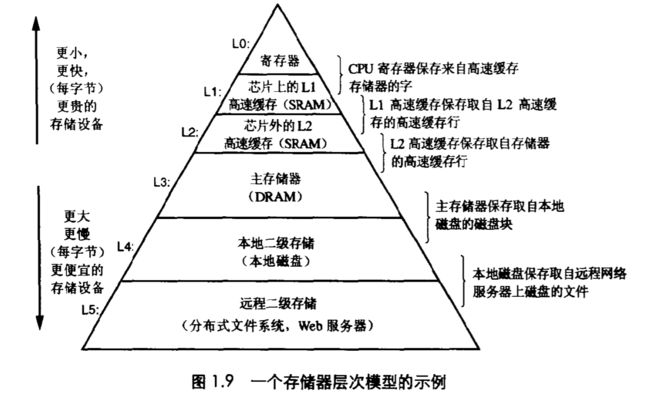
0x0D Memory hierarchy - 存储器层次结构
a) Explain the role of the registers:
Registers are a type of computer memory used to quickly accept, store, and transfer data and instructions that are being used immediately by the CPU
b) Explain the role of the main memory.
The main memory is a temporary storage device that holds both a program and the data it manipulates while the processor is executing the program.
c) Caches are located between main memory and registers. What is the advantage of using caches?
The L1 and L2 caches serve as temporary staging areas for information that the processor is likely to need in the near future. So, the processor can read data faster.
a) 解释一下寄存器的作用:
寄存器是一种计算机存储器,用于快速接受和传输数据和指令,供CPU立即使用。
b) 解释一下主存储器的作用。
主存储器是一种临时存储设备,在处理器执行程序时,它既能保存程序,又能保存它所操作的数据。
c) 缓存位于主存储器和寄存器之间。使用缓存的好处是什么?
L1和L2缓存作为处理器在不久的将来可能需要的信息的临时暂存区。所以,处理器可以更快地读取数据。
(就像程序员可以运用 L1 和 L2 的知识来提高程序性能一样,程序员同样可以利用对整个存储器层次模型的理解来提高程序性能)
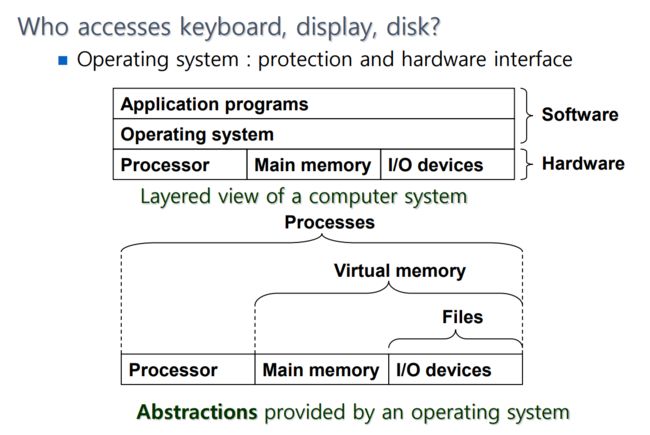
0x0E The operating system manages the hardware - 操作系统管理硬件
Who accesses keyboard, display, disk?
Operating system : protection and hardware interface
谁来访问键盘、显示器、磁盘?
操作系统:保护和硬件接口
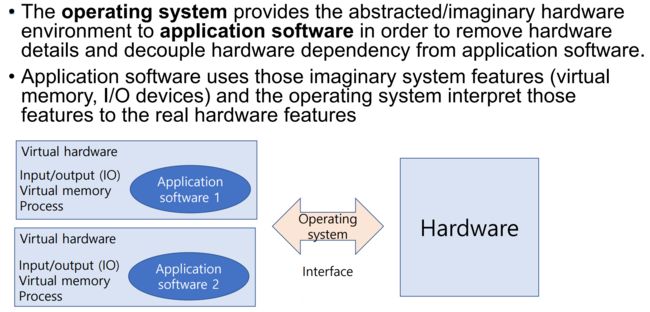
操作系统为应用软件提供抽象的/假想的硬件环境,以消除硬件细节,并将硬件依赖性与应用软件解耦。应用软件使用这些假想的系统特性(虚拟内存、I/O设备),而操作系统则将这些特性解释为真实的硬件特性。
0x0F Abstractions?
操作系统为应用软件提供抽象的/假想的硬件环境,以消除硬件细节,并将硬件依赖性与应用软件解耦。
应用软件使用这些假想的系统特性(虚拟内存、I/O设备),而操作系统则将这些特性解释为真实的硬件特性。
0x10 The operating system manages the hardware - 操作系统管理硬件
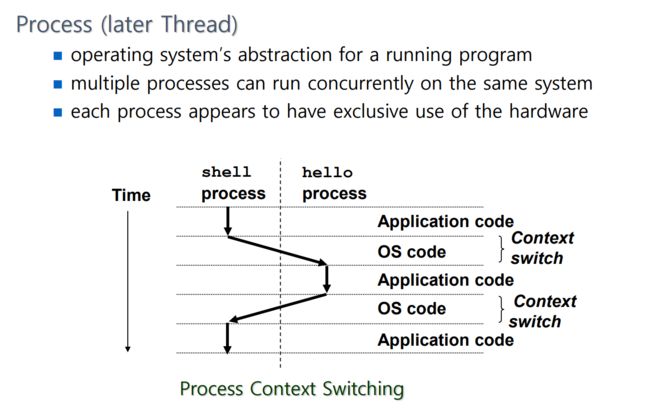
进程(后来的线程):
① 操作系统对正在运行的程序的抽象
② 多个进程可以在同一个系统上同时运行
③ 每个进程似乎都有对硬件的独家使用权
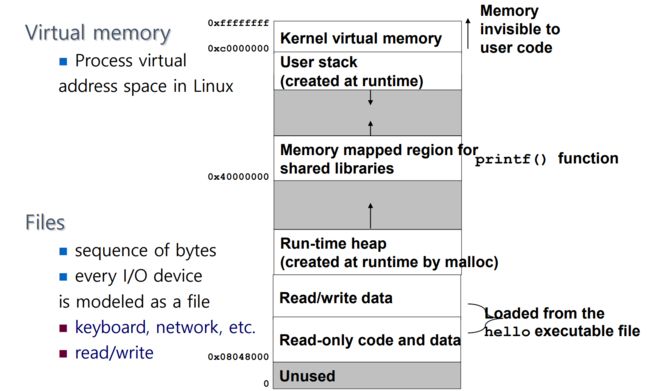
虚拟存储器(Virtual memory):Linux 中的进程虚拟地址空间
文件(Files):字节序列,每个I/O设备都被建模为文件键盘、网络等。 读/写。
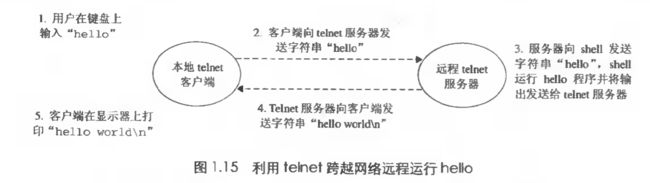
0x11 Systems communicate with other systems using net works - 利用网络系统和其他系统通信
网络也是一种 I/O 设备。
参考资料
Computer Systems: A Programmer's Perspective (3rd Edition)