【Java知识体系】SpringMVC底层原理探究,源码解读
大家好!我是未来村村长,就是那个“请你跟我这样做,我就跟你这样做!”的村长!
||To Up||
未来村村长正推出一系列【To Up】文章,该系列文章重要是对Java开发知识体系的梳理,关注底层原理和知识重点。”天下苦八股文久矣?吾甚哀,若学而作苦,此门无缘,望去之。“该系列与八股文不同,重点在于对知识体系的构建和原理的探究。
文章目录
-
- ||To Up||
- 一、SpringMVC框架介绍
-
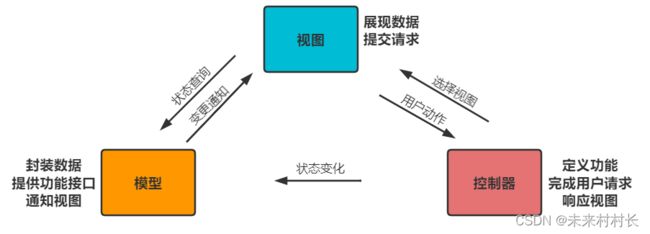
- 1、MVC
- 2、Spring MVC
-
- (1)概念
- (2)工作原理
- 3、SpringMVC的简单实现
-
- (1)一个Spring+SpringMVC的项目
-
- ① applicationContexe.xml
- ② dispatcher-servlet.xml
- ③ web.xml
- (2)简单实现流程
-
- ① 导入相关jar包
- ② 在Web.xml文件部署DispatcherServlet
- ③ 在beans文件配置视图解析器(ViewResolver)
- ④ 创建Controller类
- ⑥ 在IoC文件配置Controller映射信息
- ⑦ 要跳转的页面
- ⑧ 启动Tomcat进行测试
- 二、SpringMVC的设计和实现
-
- 1、SpringMVC与IoC
-
- (1)再读Web.xml
-
- ① DisapatcherServlet
- ② applicationContext
- ③ ContextLoaderListener
- (2)IoC容器的启动
- (3)ContextLoaderListener源码
- 2、DispatcherServlet设计概览
-
- (1)初始化工作
- (2)响应工作
- 3、DispatcherServlet的启动和初始化
-
- (1)Servlet初始化
- (2)IoC容器初始化
- (3)MVC框架初始化
- 4、HTTP分发请求的处理
- 三、总结
一、SpringMVC框架介绍
1、MVC
2、Spring MVC
(1)概念
Spring MVC是Spring 提供的一个基于MVC设计模式的轻量级Web开发框架,本质上相当于Servlet。
(2)工作原理
第一个阶段:客户端请求→Model&View
-
用户点击某个请求路径,发起一个 HTTPrequest 请求,该请求会被提交到DispatcherServlet(前端控制器);
-
由DispatcherServlet请求一个或多个HandlerMapping(处理器映射器),并返回一个执行链(HandlerExecutionChain)。
-
DispatcherServlet将执行链返回的Handler信息发送给HandlerAdapter(处理器适配器);
-
HandlerAdapter根据Handler信息找到并执行相应的Handler(常称为Controller);
-
Handler执行完毕后会返回给HandlerAdapter一个ModelAndView对象(Spring MVC的底层对象,包括 Model 数据模型和 View 视图信息);
第二个阶段:Model&View[解析]→客户端
- HandlerAdapter 接收到 ModelAndView 对象后,将其返回给 DispatcherServlet ;
- DispatcherServlet 接收到 ModelAndView 对象后,会请求 ViewResolver(视图解析器)对视图进行解析;
- ViewResolver 根据 View 信息匹配到相应的视图结果,并返回给 DispatcherServlet;
- DispatcherServlet 接收到具体的 View 视图后,进行视图渲染,将Model中的模型数据填充到View视图中的request 域,生成最终的View(视图);
- 视图负责将结果显示到浏览器(客户端)。
3、SpringMVC的简单实现
(1)一个Spring+SpringMVC的项目
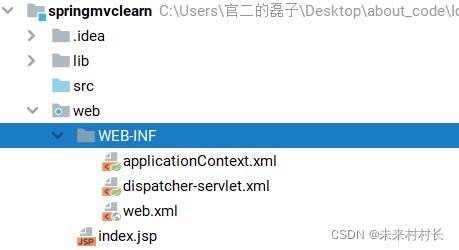
我们通过IDEA创建一个带有springMVC依赖的Spring项目。首先来看文件目录:
我们可以看到目录保留了WEB-INF和web.xml,符合Servlet(Tomcat)规范。我们具体来看文件内容和作用。
① applicationContexe.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
beans>
我们可以看到这是一个beans文件,可以用来定义bean,作为BeanDifinition的xml映射文件,ApplicationContext通过Resource定位、BeanDifinition载入、BeanDifiniton的注册进行初始化。在Resource定位过程中,就会读取beans.xml文件解析生成Resource对象。后续又经过加载解析为Document对象、BeanDifinitionHolder对象,最终实现Beandifinition注册(对象建立)。
② dispatcher-servlet.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
beans>
我们发现该文件还是一个beans文件,但是上一个文件的名称为applicationContexe,说明这是针对应用上下文进行bean注册的文件,而该文件名为dispatcher-servlet,说明该文件是用于配置dispatcher相关bean的文件。
③ web.xml
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0">
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocationparam-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xmlparam-value>
context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListenerlistener-class>
listener>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>dispatcherservlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServletservlet-class>
<load-on-startup>1load-on-startup>
servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>dispatcherservlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.formurl-pattern>
servlet-mapping>
web-app>
在之前的Servlet使用中,我们一般在web.xml中注册我们编写的实现的servlet。在初始化文件中,IDEA已经帮我们配置号了DispatcherServlet,也就是在前面提到的前端控制器,可以看到是读取默认文件org.springframework.web.servlet中的DispatcherServlet。
除此还注册了ContextLoaderListener,用于在WEB应用程序启动时载入IoC容器,ContextLoaderListener通过使用ContextLoader来完成IoC的初始化工作。
(2)简单实现流程
① 导入相关jar包
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-contextartifactId>
<version>5.0.5.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvcartifactId>
<version>5.0.5.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servletgroupId>
<artifactId>servlet-apiartifactId>
<version>2.5version>
dependency>
② 在Web.xml文件部署DispatcherServlet
<servlet>
<servlet-name>springmvcservlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServletservlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocationparam-name>
<param-value>classpath:springmvc-servlet.xmlparam-value>
init-param>
<load-on-startup>1load-on-startup>
servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>springmvcservlet-name>
<url-pattern>/url-pattern>
servlet-mapping>
③ 在beans文件配置视图解析器(ViewResolver)
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping"/>
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter"/>
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver" id="InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/jsp/"/>
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp"/>
bean>
beans>
④ 创建Controller类
package controller;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.Controller;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
//注意:这里我们先导入Controller接口
public class HelloController implements Controller {
public ModelAndView handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
//ModelAndView 模型和视图
ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView();
//封装对象,放在ModelAndView中。Model
mv.addObject("msg","HelloSpringMVC!");
//封装要跳转的视图,放在ModelAndView中
mv.setViewName("hello"); //: /WEB-INF/jsp/hello.jsp
return mv;
}
}
⑥ 在IoC文件配置Controller映射信息
<bean id="/hello" class="controller.HelloController"/>
⑦ 要跳转的页面
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
Title
${msg}
⑧ 启动Tomcat进行测试
打包项目配置到Tomcat中启动。
二、SpringMVC的设计和实现
1、SpringMVC与IoC
(1)再读Web.xml
在Web环境下,SpringMVC是建立在IoC容器的基础上的,我们再来看Web.xml的内容。从Web我们可以知道,SpringMVC两个核心类DispatcherServlet和ContextLoaderListener【实现了ServletContextListener】都是属于Servlet体系。
Servlet的创建由Web容器(Servlet容器)管理,当Web容器启动或终止Web应用时,会触发ServletContextEvent 事件,该事件由ServletContextListener 来处理。在 ServletContextListener 接口中定义了处理ServletContextEvent 事件的两个方法:contextInitialized()和contextDestroyed()。
① DisapatcherServlet
<servlet>
<servlet-name>dispatcherservlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServletservlet-class>
<load-on-startup>1load-on-startup>
servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>dispatcherservlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.formurl-pattern>
servlet-mapping>
DisapatcherServlet起着分发请求的作用,在部署中为DispatcherServlet定义了对应的url-pattern,这些url映射为这个Servlet指定了需要处理的HTTP请求。
② applicationContext
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocationparam-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xmlparam-value>
context-param>
context-param参数的配置用来指定SpringIoC容器读取Bean定义的XML文件路径,也就是说我们要将定义的Beans文件在该参数中进行注册,这里定义的文件名为applicationContext.xml。
③ ContextLoaderListener
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListenerlistener-class>
listener>
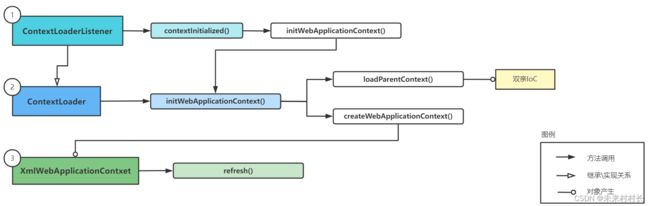
ContextLoaderListener是SpringMVC的启动类,被定义为一个监听器,由ContextLoaderListener监听器负责完成IoC容器在Web环境中的启动工作。
(2)IoC容器的启动
- ContextLoaderListener:ContextLoaderIistener通过实现ServletContextListener接口完成监听任务,通过继承ContextLoader类,完成IoC容器的载入
- ContextLoader:ContextLoader在调用initWebApplicationContext时会进行两个IoC容器的创建,一是双亲IoC容器,二是生成相应的WebApplicationContext
- XmlWebApplicationContext:XmlWebApplicationContext在继承ApplicationContext的基础上,增加了对Web环境和XML配置定义的处理。在XmlWebApplicationContext的启动过程中,也是通过refresh,在Resource资源定位的过程中通过调用loadBeanDifinition()默认读取/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml文件。
(3)ContextLoaderListener源码
public class ContextLoaderListener extends ContextLoader implements ServletContextListener {
public ContextLoaderListener() {
}
public ContextLoaderListener(WebApplicationContext context) {
super(context);
}
/**
* Initialize the root web application context.
*/
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}
/**
* Close the root web application context.
*/
@Override
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent event) {
closeWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
ContextCleanupListener.cleanupAttributes(event.getServletContext());
}
}
我们可以看到有两个方法:
- contextInitialized:用来启动根Web应用上下文,也就是根IoC容器,但IoC初始化的具体过程由ContextLoader实现
- contextDestroyed:关闭根Web应用上下文
所以我们可以知道ContextLoaderListener的作用就是通过监听控制IoC容器的开启和关闭。
2、DispatcherServlet设计概览
在完成对ContextLoaderListener的初始化后,Web容器开始初始化DispatcherServlet,DispatcherServlet底层就是Servlet。
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet
public abstract class FrameworkServlet extends HttpServletBean implements ApplicationContextAware
public abstract class HttpServletBean extends HttpServlet implements EnvironmentCapable, EnvironmentAware
public abstract class HttpServlet extends GenericServlet implements Serializable
public abstract class GenericServlet implements Servlet, ServletConfig, Serializable
我们可以看到,DispatcherServlet通过继承FrameworkServlet,从而继承了HttpServlet。我们接着看DispatcherServlet源码。
DispatcherServlet的工作主要为两个部分,一是初始化,二是对Http请求进行响应。我们先来看初始化部分。
(1)初始化工作
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
this.initStrategies(context);
}
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
this.initMultipartResolver(context);
this.initLocaleResolver(context);
this.initThemeResolver(context);
this.initHandlerMappings(context);
this.initHandlerAdapters(context);
this.initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
this.initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
this.initViewResolvers(context);
this.initFlashMapManager(context);
}
主要通过onRefresh开启初始化,我们可以看到通过调用initStrategies方法,初始化了HandlerMappings、ViewResolvers等模块。
(2)响应工作
在对Http请求进行响应的部分,Web容器会通过调用Servlet的doGet和doPost方法,在经过FrameworkServlet的processRequest简单处理后,调用DispathcherServlet的doService方法,在该方法中封装了doDispatch方法。
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
this.logRequest(request);
Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot = null;
if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) {
attributesSnapshot = new HashMap();
Enumeration attrNames = request.getAttributeNames();
label95:
while(true) {
String attrName;
do {
if (!attrNames.hasMoreElements()) {
break label95;
}
attrName = (String)attrNames.nextElement();
} while(!this.cleanupAfterInclude && !attrName.startsWith("org.springframework.web.servlet"));
attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName));
}
}
request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.getWebApplicationContext());
request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, this.getThemeSource());
if (this.flashMapManager != null) {
FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response);
if (inputFlashMap != null) {
request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap));
}
request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap());
request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager);
}
try {
//doDisapatch
this.doDispatch(request, response);
} finally {
if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted() && attributesSnapshot != null) {
this.restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot);
}
}
}
//doDisapatch是Dispatcher实现MVC模式的主要部分
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Object dispatchException = null;
try {
processedRequest = this.checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = processedRequest != request;
mappedHandler = this.getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
this.noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
HandlerAdapter ha = this.getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if ((new ServletWebRequest(request, response)).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
this.applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
} catch (Exception var20) {
dispatchException = var20;
} catch (Throwable var21) {
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", var21);
}
this.processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, (Exception)dispatchException);
} catch (Exception var22) {
this.triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, var22);
} catch (Throwable var23) {
this.triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", var23));
}
} finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
} else if (multipartRequestParsed) {
this.cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}
3、DispatcherServlet的启动和初始化
DispatcherServlet的初始化分为三步,一是初始化Servlet,二是初始化IoC容器,三是初始化MVC框架。我们来逐个解析源码。我们知道DispatcherServlet继承了FrameworkServlet,后者又继承了HttpServletBean,HttpServletBean继承了HttpServlet。
我们可以得知,DispatcherServlet,是一个具有HttpServlet功能的Bean,在此基础上进行了MVC框架的实现。
(1)Servlet初始化
public abstract class HttpServletBean extends HttpServlet implements EnvironmentCapable, EnvironmentAware {
@Override
public final void init() throws ServletException {
// Set bean properties from init parameters.
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
try {
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));
initBeanWrapper(bw);
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
// Let subclasses do whatever initialization they like.
initServletBean();
}
}
DispatcherServlet的初始化工作是在HttpServletBean中完成的,该类重写了init方法,也就是我们之前探究过的Servlet的初始化方法,这里有两个关键方法:initBeanWrapper和setPropertyValues。
调用initBeanWrapper初始化了BeanWrapper,通过setPropertyValues为Bean属性赋值:我们在之前的Spring文章中解析过,依赖注入的实际执行就是在BeanWrapper中的setPropertyValue实现的,所以在这里初始化了BeanWrapper,目的就是调用setPropertyValues方法为Bean赋值。
最后会调用initServletBean()方法,该方法具体是在FrameworkServlet中完成的。
public abstract class FrameworkServlet extends HttpServletBean implements ApplicationContextAware {
@Override
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring " + getClass().getSimpleName() + " '" + getServletName() + "'");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Initializing Servlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
initFrameworkServlet();
}
catch (ServletException | RuntimeException ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String value = this.enableLoggingRequestDetails ?
"shown which may lead to unsafe logging of potentially sensitive data" :
"masked to prevent unsafe logging of potentially sensitive data";
logger.debug("enableLoggingRequestDetails='" + this.enableLoggingRequestDetails +
"': request parameters and headers will be " + value);
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Completed initialization in " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) + " ms");
}
}
}
该方法主要完成的工作就是initWebApplicationContext(),进行IoC容器的初始化。
(2)IoC容器初始化
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set
// the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one
// has been registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it is assumed
// that the parent context (if any) has already been set and that the
// user has performed any initialization such as setting the context id
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
// Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh
// support or the context injected at construction time had already been
// refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here.
synchronized (this.onRefreshMonitor) {
onRefresh(wac);
}
}
if (this.publishContext) {
// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
}
return wac;
}
从该方法我们可知,该方法通过createWebApplicationContext使DispatchSerrvlet建立一个自己的Servlet名称命名的IoC容器,这个IoC容器是一个WebApplicationContext对象。
在该方法中,还有一个重要的方法onRefresh,该方法的具体实现是在其子类DispatcherServlet中,该方法调用了initStrategies进行MVC框架的初始化。
(3)MVC框架初始化
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
@Override
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
initStrategies(context);
}
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context);
initLocaleResolver(context);
initThemeResolver(context);
initHandlerMappings(context);
initHandlerAdapters(context);
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
initViewResolvers(context);
initFlashMapManager(context);
}
}
该方法通过调用initxxxx(context)初始化了相关对象,例如HandlerMappings、HandlerAdapters、ViewResolvers等,这里的对象都是一个个Bean对象,可以在DispatcherServlet的IoC容器或其双亲上下文中获取,我们具体来看initHandlerMappings的过程。
private void initHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext context) {
this.handlerMappings = null;
if (this.detectAllHandlerMappings) {
// Find all HandlerMappings in the ApplicationContext, including ancestor contexts.
Map<String, HandlerMapping> matchingBeans =
BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false);
if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
this.handlerMappings = new ArrayList<>(matchingBeans.values());
// We keep HandlerMappings in sorted order.
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerMappings);
}
}
else {
try {
HandlerMapping hm = context.getBean(HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME, HandlerMapping.class);
this.handlerMappings = Collections.singletonList(hm);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Ignore, we'll add a default HandlerMapping later.
}
}
// Ensure we have at least one HandlerMapping, by registering
// a default HandlerMapping if no other mappings are found.
if (this.handlerMappings == null) {
this.handlerMappings = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerMapping.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No HandlerMappings declared for servlet '" + getServletName() +
"': using default strategies from DispatcherServlet.properties");
}
}
}
从这句HandlerMapping hm = context.getBean(HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME, HandlerMapping.class);我们看到HandlerMapping的初始化是通过getBean获取的,此处的context是DispatcherServlet的IoC容器或其双亲上下文。其它相关对象也是通过getBean进行获取。
并且该HandlerMapping会存放在List中:this.handlerMappings = Collections.singletonList(hm);
4、HTTP分发请求的处理
DispatcherServlet不仅持有自己的IoC容器用于MVC框架的初始化和管理,还承担着请求分发处理的责任。对HTTP的请求处理是在doService()方法完成的。
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
@Override
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
logRequest(request);
// Keep a snapshot of the request attributes in case of an include,
// to be able to restore the original attributes after the include.
Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot = null;
if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) {
attributesSnapshot = new HashMap<>();
Enumeration<?> attrNames = request.getAttributeNames();
while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement();
if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PREFIX)) {
attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName));
}
}
}
// Make framework objects available to handlers and view objects.
request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext());
request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource());
if (this.flashMapManager != null) {
FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response);
if (inputFlashMap != null) {
request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap));
}
request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap());
request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager);
}
try {
doDispatch(request, response);
}
finally {
if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include.
if (attributesSnapshot != null) {
restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot);
}
}
}
}
}
该方法会对Request进行简单处理,再将Request对象传入doDispatch进行进一步处理。
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// Determine handler for the current request.
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// Actually invoke the handler.
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}
}
该方法串联了整个MVC的架构,通过调用getHandler响应HTTP请求,然后通过执行Handler的处理来得到返回的ModelAndView结果,最终将该结果交给相应的视图对象取呈现,具体的调用过程参照下面的时序图。
此处有几个关键的方法
- getHandler:通过HandlerMapptig去取相应的Handler,该过程会遍历当前持有的所有handlerMapping,直到找到一个需要的Handler,如果找不到,则会在handlerMapping中生成一个Handler。找到Handler后,会通过Handler返回一个HandlerExecutionChain对象,该对象中包含了最终的Controller(没错,你终于看到Controller了)和定义的拦截器链。
- getHandlerAdapter:会返回一个HandlerAdapter对象,这里传入的参数是mappedHandler.getHandler(),通过该对象调用handle方法[mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());]可以获取到ModelAndView。
- render:对视图呈现的处理是在render方法中调用完成的,传入的参数是ModelAndView、HttpServletRequest、HttpServletReponse。该方法会通过对视图名进行解析或直接getView的方法获取视图对象,通过HttpResponse把视图呈现给HTPT客户端。
三、总结
我们再来看这张图:
DispathcerServlet初始化:完成两个工作,一是建立自己的IoC容器,二是通过IoC容器初始化具体的MVC框架,在HandlerMapping的初始化过程中完成了Controller控制器和HTTP请求的映射关系的建立,并存入HandlerMap中。
Controller控制器和HTTP请求的映射关系建立:通过HandlerMapping封装的HandlerExecutionChain对象来完成,对Controller控制器和HTTP请求的映射关系是在Bean中定义的,在IoC容器初始化时,通过初始化HandlerMapping来完成,这些会载入到HandlerMap中使用。
HTTP请求处理:在MVC框架接收到HTTP请求时,DispatcherServlet会根据具体的URL请求信息,在HandlerMapping中进行查询得到对应的Handler,Handler返回HandlerExecutionChain对象,HandlerExecutionChain中封装了配置的Controller,请求对应的Controller会完成请求的响应动作,生成需要的ModelAndView对象。
视图的对象的呈现:DispatcherServlet会将ModelAndView交给特点的视图对象ViewResolver,视图对象会调用render方法来完成数据的视图呈现工作。
——————————————————
作者:未来村村长
参考:《Spring技术内幕》——计文柯
个人网站:www.76pl.com
点个关注,在未来村不会迷路
——————————————————