pytorch 导出 onnx 模型 ;onnxruntime在线推理
参考:
https://github.com/microsoft/onnxruntime-inference-examples/blob/main/python/OpenVINO_EP/yolov4_object_detection/yolov4.py
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/413992538
ww.cnblogs.com/sddai/p/14537381.html
https://www.guyuehome.com/37123
1、pytorch模型保存onnx
# coding=gbk
#_*_ coding=utf-8 _*_
import torch
import torchvision
import torch.nn as nn
from torchvision import models
import time
import torch.utils.model_zoo as model_zoo
import torch.nn.init as init
class SuperResolutionNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, upscale_factor, inplace=False):
super(SuperResolutionNet, self).__init__()
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=inplace)
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 64, (5, 5), (1, 1), (2, 2))
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(64, 64, (3, 3), (1, 1), (1, 1))
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(64, 32, (3, 3), (1, 1), (1, 1))
self.conv4 = nn.Conv2d(32, upscale_factor ** 2, (3, 3), (1, 1), (1, 1))
self.pixel_shuffle = nn.PixelShuffle(upscale_factor)
self._initialize_weights()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.relu(self.conv1(x))
x = self.relu(self.conv2(x))
x = self.relu(self.conv3(x))
x = self.pixel_shuffle(self.conv4(x))
return x
def _initialize_weights(self):
init.orthogonal_(self.conv1.weight, init.calculate_gain('relu'))
init.orthogonal_(self.conv2.weight, init.calculate_gain('relu'))
init.orthogonal_(self.conv3.weight, init.calculate_gain('relu'))
init.orthogonal_(self.conv4.weight)
# Create the super-resolution model by using the above model definition.
torch_model = SuperResolutionNet(upscale_factor=3)
# Load pretrained model weights
model_url = 'https://s3.amazonaws.com/pytorch/test_data/export/superres_epoch100-44c6958e.pth'
batch_size = 1 # just a random number
# Initialize model with the pretrained weights
map_location = lambda storage, loc: storage
if torch.cuda.is_available():
map_location = None
torch_model.load_state_dict(model_zoo.load_url(model_url, map_location=map_location))
# set the model to inference mode
torch_model.eval()
# Input to the model
x = torch.randn(batch_size, 1, 224, 224, requires_grad=True)
torch_out = torch_model(x)
# Export the model
torch.onnx.export(torch_model, # model being run
x, # model input (or a tuple for multiple inputs)
"super_resolution.onnx", # where to save the model (can be a file or file-like object)
export_params=True, # store the trained parameter weights inside the model file
opset_version=10, # the ONNX version to export the model to
do_constant_folding=True, # whether to execute constant folding for optimization
input_names = ['input'], # the model's input names
output_names = ['output'], # the model's output names
dynamic_axes={'input' : {0 : 'batch_size'}, # variable lenght axes
'output' : {0 : 'batch_size'}})
2、验证onnx及查看结构
import onnx
onnx_model = onnx.load("super_resolution.onnx")
onnx.checker.check_model(onnx_model)
##查看结构
print(onnx.helper.printable_graph(onnx_model.graph))
**拖拉上传onnx用https://netron.app/在线查看
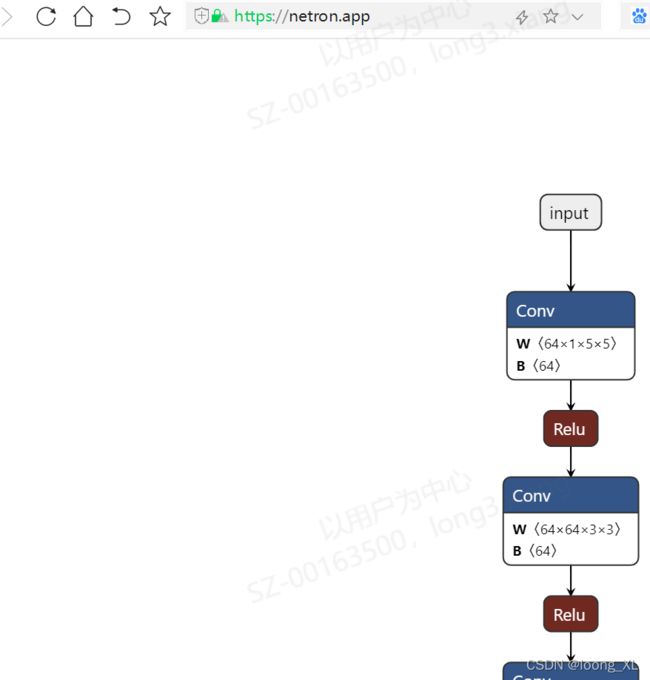
3、onnxruntime在线推理
import onnxruntime
import numpy as np
ort_session = onnxruntime.InferenceSession("super_resolution.onnx")
def to_numpy(tensor):
return tensor.detach().cpu().numpy() if tensor.requires_grad else tensor.cpu().numpy()
# compute ONNX Runtime output prediction
ort_inputs = {ort_session.get_inputs()[0].name: to_numpy(x)}
ort_outs = ort_session.run(None, ort_inputs)
# compare ONNX Runtime and PyTorch results
np.testing.assert_allclose(to_numpy(torch_out), ort_outs[0], rtol=1e-03, atol=1e-05)
print("Exported model has been tested with ONNXRuntime, and the result looks good!")

