工业缺陷检测项目实战(二)——基于深度学习框架yolov5的钢铁表面缺陷检测
基于深度学习框架yolov5-6.0的钢铁表面缺陷检测
首先说明:
我做这个的主要目的,是利用opencv4.5.0的C++代码,加载深度学习模型框架进行检测识别。也就是说,在yolov5训练完后,用C++部署训练好的权重和网络模型,然后进行检测。这个过程,遇到特别多的坑,这里要给大家一一列出来,也防止我以后自己忘记哈哈哈哈。。。。
注意,方法适用于版本是最新的6.0版本
一. yolov5的模型学习
这里直接参考大佬们讲解,向大佬学习:
Yolov5 系列1— Yolo发展史以及Yolov5模型详解.
Yolov5 模型详解.
二. yolov5的训练过程
1.yolov5下载
https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5
文件内容:
2. 安装环境
pip install -r requirements.txt
3.数据集整理
使用yolov5的模型进行训练,首先要配置好数据集,数据的格式如下:
其中必须的是:train,valid,data.yaml
一个是训练集,一个是验证集,一个是加载数据集(训练+验证)的配置文件,其实就是写个路径进去。我们分别看看里面的样子:
(1) train:

images就不用说了,都是.jpg文件,我们这里都是钢材表面带有缺陷的图片:
labels标签是txt文件,这是yolov5特定的:
注意的是,每个标签文件的名字一定要根图片的名字对应上。我的data文件夹里配置有xml文件转txt文件的py文件,即xml2yolo,py。我们看txt文件的内容:
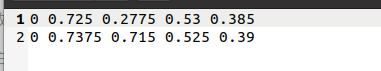
第一列为类别,剩余的四个列分别为x,y,w,h。
每一行表示缺陷个数。
(2) valid:

和train一样。
(3) data.yaml:
内容:
train: /home/cg/机器视觉与机器学习/工业缺陷检测项目/钢材表面缺陷检测/NEU-DET/train/images
val: /home/cg/机器视觉与机器学习/工业缺陷检测项目/钢材表面缺陷检测/NEU-DET/valid/images
nc: 6
names: ['crazing', 'inclusion', 'patches', 'pitted_surface', 'rolled-in_scale', 'scratches']
train和val改成自己的路径
nc表示类别,我这里有六个缺陷类别,所以是6。names很明显是类别的名称。
4.开始训练
数据准备完毕了。我们开始训练。首先选择训练的模型,在moudles文件夹里:

假设我们选择yolov5s.yaml,打开之后,需要改的参数是那个nc,依然改成我们的分类数量。
接着运行
python3 train.py --data ../NEU-DET/data.yaml --cfg models/yolov5s.yaml --weights '' --batch-size 8
等待训练完成。
训练完成之后,会在runs文件夹生成train/exp文件夹,里面是这样:
里面的weights权重文件夹里的best.pt,是我们要用的权重文件。
值得注意的是,和yolov3和yolov4的权重文件.weight和模型文件.cfg都不同的是,yolov5的.pt同时包含了模型以及权重参数。
5.opencv4.5.0的C++部署yolov5的训练模型与权重。
5.1 opencv4.5.0里面配置的函数,没有直接读取.pt文件的,所以,我们要进行转化,将best.pt转为best.onnx。转化的方法:
python3 export.py --weights best.pt --opset 12
注意这只适用于6.0版本,要将参数opset由原来的13改为12,可以代码改,也可以参数改。
5.2 读取.onnx文件
string modelFile = "/home/cg/机器视觉与机器学习/工业缺陷检测项目/钢材表面缺陷检测/project/best";
modelFile += ".onnx";
this->net = readNet(modelFile);
当然啦路径要改。
5.3 检测函数
void YOLO::detect(Mat &frame)
{
Mat blob;
blobFromImage(frame, blob, 1 / 255.0, Size(this->inpWidth, this->inpHeight), Scalar(0, 0, 0), true, false);
this->net.setInput(blob);
vector outs;
this->net.forward(outs, this->net.getUnconnectedOutLayersNames());
//generate proposals
vector classIds;
vector confidences;
vector boxes;
cout << "classes:" << classes.size() << endl;
float ratioh = (float)frame.rows / this->inpHeight, ratiow = (float)frame.cols / this->inpWidth;
int n = 0, q = 0, i = 0, j = 0, nout = this->classes.size() + 5, row_ind = 0;
for (n = 0; n < 3; n++) //stride
{
int num_grid_x = (int)(this->inpWidth / this->stride[n]);
int num_grid_y = (int)(this->inpHeight / this->stride[n]);
cout << "num_grid_x:" << num_grid_x << endl;
cout << "num_grid_y:" << num_grid_y << endl;
for (q = 0; q < 3; q++) ///anchors
{
const float anchor_w = this->anchors[n][q * 2];
const float anchor_h = this->anchors[n][q * 2 + 1];
for (i = 0; i < num_grid_y; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < num_grid_x; j++)
{
float *pdata = (float *)outs[0].data + row_ind * nout;
float box_score = pdata[4]; //sigmoid_x(pdata[4])
if (box_score > this->objThreshold)
{
//评分框
cv::Mat scores(1, classes.size(), CV_32FC1, pdata + 5);
Point classIdPoint;
double max_class_socre;
// 获取最高分数的值和位置
minMaxLoc(scores, 0, &max_class_socre, 0, &classIdPoint);
max_class_socre = max_class_socre; // sigmoid_x((float)max_class_socre);
if (max_class_socre > this->confThreshold)
{
float cx = pdata[0]; //(sigmoid_x(pdata[0]) * 2.f - 0.5f + j) * this->stride[n]; ///cx
float cy = pdata[1]; // (sigmoid_x(pdata[1]) * 2.f - 0.5f + i) * this->stride[n]; ///cy
float w = pdata[2]; //powf(sigmoid_x(pdata[2]) * 2.f, 2.f) * anchor_w; ///w
float h = pdata[3]; //powf(sigmoid_x(pdata[3]) * 2.f, 2.f) * anchor_h; ///h
int left = (cx - 0.5 * w) * ratiow;
int top = (cy - 0.5 * h) * ratioh;
classIds.push_back(classIdPoint.x);
confidences.push_back(max_class_socre);
boxes.push_back(Rect(left, top, (int)(w * ratiow), (int)(h * ratioh)));
}
}
row_ind++;
}
}
}
}
// Perform non maximum suppression to eliminate redundant overlapping boxes with
// lower confidences
vector indices;
NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, this->confThreshold, this->nmsThreshold, indices);
cout << "num_grid_y:" << indices.size() << endl;
for (size_t i = 0; i < indices.size(); ++i)
{
int idx = indices[i];
Rect box = boxes[idx];
this->drawPred(classIds[idx], confidences[idx], box.x, box.y,
box.x + box.width, box.y + box.height, frame);
}
}
主要函数:
blobFromImage主要是用来对图片进行预处理。包含两个主要过程:
整体像素值减去平均值(mean)
通过缩放系数(scalefactor)对图片像素值进行缩放
详细参考:OpenCV中blobFromImage函数详细解释.
前向计算,检测结果存入outs:
this->net.forward(outs, this->net.getUnconnectedOutLayersNames());
5.4 绘制锚框
void YOLO::drawPred(int classId, float conf, int left, int top, int right, int bottom, Mat &frame) // Draw the predicted bounding box
{
//Draw a rectangle displaying the bounding box
rectangle(frame, Point(left, top), Point(right, bottom), Scalar(0, 0, 255), 3);
//Get the label for the class name and its confidence
string label = format("%.2f", conf);
label = this->classes[classId] + ":" + label;
//Display the label at the top of the bounding box
int baseLine;
Size labelSize = getTextSize(label, FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1, &baseLine);
top = max(top, labelSize.height);
//rectangle(frame, Point(left, top - int(1.5 * labelSize.height)), Point(left + int(1.5 * labelSize.width), top + baseLine), Scalar(0, 255, 0), FILLED);
putText(frame, label, Point(left, top), FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, Scalar(0, 255, 0), 2);
}
效果:
全部文件下载:
https://download.csdn.net/download/weixin_39735688/47481220
Cmake编译,记得有关加载文件的路径都要改。
