1 应用
日志、事务、限流、统计、上下文切换、异步等非业务功能的逻辑处理都可以用
2 例子
网上随处可见,这里只是简单举个例子
@Aspect
@Component
public class DemoAspect {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.example.demo2.controller.DemoController.sayDemo())")
public void aa(){
System.out.println("pointcut");
}
@Before("aa()")
public void beforeDemo(JoinPoint joinPoint){
System.out.println(joinPoint);
System.out.println("before demo");
}
@After("aa()")
public void afterDemo(){
System.out.println("after demo");
}
@Around("aa()")
public void zaroundDemo(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint){
System.out.println("demo around1 ");
try {
joinPoint.proceed();
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
throwable.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("demo around2");
}
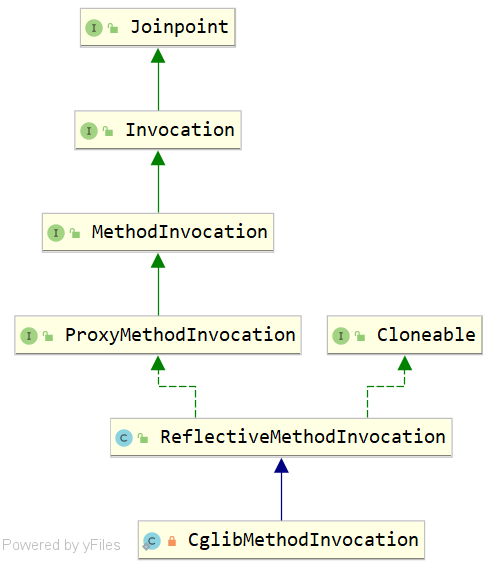
}3 相关重要类
AbstractAspectJAdvise
AspectJAroundAdvice
AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice
AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice
AspectJAfterAdvice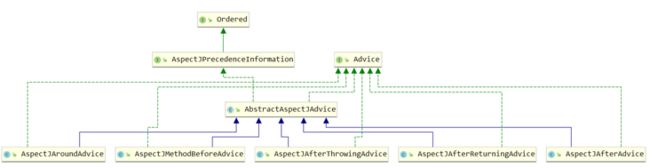
AspectjAroundAdvice -- 继承自methodInterceptor
AspectjMethodBeforeAdvice --- 这还有一个MethodBeforeInterceptor 用来实现动态代理
4 调用过程
- 通过cglib代理生成代理类,里面重写父类的方法,加入拦截器DynamicCglibMethodInterceptor,这里面加入了对于这个类的所有织入通知(advice)对应的拦截器,比如:AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice---MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor;AspectJAroundAdvice的拦截器就是本身;
- 在进行调用的时候,会先遍历所有的Advice对应的拦截器,调用里面的invoke方法;把当前的CglibMethodInvocation对象传下去;(典型责任链模式)
3.重点:AspectJAroundAdvise里面有一个ProceedingJoinPoint参数,这个是如何调用的呢? 实际上里面在Advice里面都是通过返回调用了切面类中的通知方法,method.invoke(obj,args);为了实现环绕通知呢?在初始化MethodInvokcationProceedingJoinPoint的时候,就把CglibMethodInvocation也传入进去了,方便调用链的继续运行;如果是调用链最后一个,那么methodInvocationProceedingJoinPoint调用完成后,直接返回到环绕通知方法里面,然后继续向下执行,直至结束即可。
5 源码解析
5.1 动态代理类
根据
System.setProperty(DebuggingClassWriter.DEBUG_LOCATION_PROPERTY,fileName);生成的动态代理对象,可以看出,里面会有一个DemoController$$EnhanceByCglib这个对象,里面有一个callback[]数组,这个就是记录的所有拦截器;
通过动态生成的代理类调用demo方法的时候,实际上走的流程是:
public final void sayDemo() {
MethodInterceptor var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
if (var10000 == null) {
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
}
# 如果有拦截器,则调用拦截器方法,
if (var10000 != null) {
var10000.intercept(this, CGLIB$sayDemo$0$Method, CGLIB$emptyArgs, CGLIB$sayDemo$0$Proxy);
} else {
super.sayDemo();
}
}可以看到动态代理产生的类重写了父类的DemoController中的sayDemo方法,然后有写了一个方法叫
final void CGLIB$sayDemo$0() {
super.sayDemo();
}来调用父类的方法;
重点看下拦截器是什么?怎么调用的?
5.2 DynamicAdvisedInterceptor
注入的拦截器,
在intercept方法中,会判断advice是否为空,如果不为空,则会调用
retVal = new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy).proceed();5.3 CglibMethodInvocation
调用父类proceed方法
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
// We start with an index of -1 and increment early.
// 如果是最后一个,那么就完事了。
if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) {
return invokeJoinpoint();
}
// 根据index 找下一个advice是什么?
Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice =
this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex);
if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) {
// Evaluate dynamic method matcher here: static part will already have
// been evaluated and found to match.
InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm =
(InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice;
Class targetClass = (this.targetClass != null ? this.targetClass : this.method.getDeclaringClass());
if (dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, targetClass, this.arguments)) {
return dm.interceptor.invoke(this);
}
else {
// Dynamic matching failed.
// Skip this interceptor and invoke the next in the chain.
return proceed();
}
}
else {
// It's an interceptor, so we just invoke it: The pointcut will have
// been evaluated statically before this object was constructed.
// 走到这里,调用advice对应的MethodInterceptor
return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this);
}
}假设:第一个是环绕通知对应的拦截器
5.4 AspectJAroundAdvice
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
if (!(mi instanceof ProxyMethodInvocation)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("MethodInvocation is not a Spring ProxyMethodInvocation: " + mi);
}
// 把当前的CglibMethodInvocation 实例对象传到ProceedingJoinPoint中,方便后面来用;
ProxyMethodInvocation pmi = (ProxyMethodInvocation) mi;
ProceedingJoinPoint pjp = lazyGetProceedingJoinPoint(pmi);
JoinPointMatch jpm = getJoinPointMatch(pmi);
// 利用反射调用切面中的环绕通知方法,(即上文的zaroundDemo方法)
return invokeAdviceMethod(pjp, jpm, null, null);
}代码如下
@Around("aa()")
public void zaroundDemo(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint){
System.out.println("demo around1 ");
try {
// 这里就是调用MethodInvocationProceedingJoinPoint;
joinPoint.proceed();
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
throwable.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("demo around2");
}MethodInvocationProceedingJoinPoint.proceed方法,可以发现,实际上它调用的是上面作为成员变量传进来的CglibMethodInvocation对象;形成一个调用链;
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
return this.methodInvocation.invocableClone().proceed();
}5.5 AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice--MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor
拦截器里面的逻辑:
- 先调用前置通知的before方法,
- 再返回调用链的CglibMethodInvocation--继续责任链的调用;
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
this.advice.before(mi.getMethod(), mi.getArguments(), mi.getThis());
return mi.proceed();
}AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice.proceed
也是利用反射进行调用切面中的前置通知;
@Override
public void before(Method method, Object[] args, @Nullable Object target) throws Throwable {
invokeAdviceMethod(getJoinPointMatch(), null, null);
}5.6 AspectJAfterAdvice
在finally里面在反射调用织入的后置通知;
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
try {
return mi.proceed();
}
finally {
invokeAdviceMethod(getJoinPointMatch(), null, null);
}
}5.7 责任链的最后一步:--invokeJoinpoint
if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) {
return invokeJoinpoint();
}invokeJoinPoint
protected Object invokeJoinpoint() throws Throwable {
// 如果经过cglib代理,则调用动态代理方法
if (this.methodProxy != null) {
try {
return this.methodProxy.invoke(this.target, this.arguments);
}
catch (CodeGenerationException ex) {
logFastClassGenerationFailure(this.method);
}
}
// 否则就通过反射调用
return super.invokeJoinpoint();
}6 总结
- AOP 大量使用反射,诸如:调用织入通知
- spring将所有的通知放到一个list中,利用责任链模式进行逐一调用;
- 最后在触发cglib的动态代理,调用MethodProxy.invoke方法