Java学习笔记Day10 Java常用类
字符串相关的类
String类及其常用方法
String类是一个final类,代表不可变的字符序列
String实现了Serializable接口表示字符串是可被序列化的
实现了Comparable接口,表示String是可以比较大小的
字符串是常量,用双引号引起来表示。它们的值在创建之后不能更改
String对象的字符内容是存储在一个字符数组value[ ]中的
value[ ]是final修饰的char类型数组,表示是数组不可被重新赋值,数组元素也不可被修改的
String不可变性的体现
@Test
public void test1() {
//通过字面量的方式(不同于new)给一个字符串赋值,此时的字符串值声明在字符串常量池中
//字符串常量池会存储相同内容的字符串
String s1 = "abc";//字面量的定义方式
String s2 = "hello";
s1 = "hello";
System.out.println(s1 == s2);//比较s1和s2的地址值 为true
System.out.println(s1);//hello
System.out.println(s2);//hello
System.out.println("------------");
//对现有字符串进行连接操作时,需要指定内存区域赋值。不能在原位置
String s3 = "hello";
s3 += ",gyq";
System.out.println(s3);//hello,gyq
System.out.println(s1);//hello
System.out.println("------------");
//替换字符串的指定字符,也需要指定内存区域赋值。不能在原位置
String s4 = "hello";
String s5 = s4.replace('e', 'a');
System.out.println(s4);//hello
System.out.println(s5);//hallo
}
}String不同实例化方式的对比
package string;
import org.junit.Test;
public class StringTest {
@Test
public void test2() {
//通过字面量定义的方式
String s1 = "gyq";
String s2 = "gyq";
System.out.println(s1 == s2);//true
System.out.println("----------");
//通过new + 构造器的方式
String s3 = new String("gyq");
String s4 = new String("gyq");
System.out.println(s3 == s4);//false
System.out.println(s3 == s1);//false
System.out.println("----------");
//字符串对象如何存储
Person p1 = new Person("gyq", 10);
Person p2 = new Person("gyq", 20);
System.out.println(p1.name == p2.name);//true 比较地址
System.out.println(p1.name.equals(p2.name));//true 比较值
p1.name = "gyqq";
System.out.println(p2.name);//gyq
}
}
class Person {
String name;
int age;
public Person() {
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}String不同拼接操作的对比
@Test
public void test2() {
String s1 = "hello,";
String s2 = "gyq";
String s3 = "hello,gyq";
//没有变量参与,存储在常量池中
String s4 = "hello," + "gyq";
//有变量参与,相当于是new,存在堆中
String s5 = s1 + "gyq";
String s6 = "hello," + s2;
String s7 = s1 + s2;
//调用intern()方法 则返回值是常量池中已存在的 "hello,gyq"
String s8 = (s1 + s2).intern();
System.out.println(s3 == s4);//true
System.out.println(s3 == s5);//false
System.out.println(s3 == s6);//false
System.out.println(s3 == s7);//false
System.out.println(s5 == s6);//false
System.out.println(s5 == s7);//false
System.out.println(s3 == s8);//true
}String的常用方法
public class StringTest {
@Test
public void test() {
String str = " wDoshAi yiEgFSezifuAichuan ";
String str1 = new String("GYQ");
String str2 = new String("gyq");
//返回字符串长度
System.out.println(str.length());
//返回指定索引的字符
System.out.println(str.charAt(8));
//判断当前字符串是否为空
System.out.println(str.isEmpty());
//将字符串转化为大写/小写
String s1 = str.toUpperCase(Locale.ROOT);
String s2 = str.toLowerCase(Locale.ROOT);
System.out.println(s1);
System.out.println(s2);
//填补字符串首尾的空白部分
String s3 = str.trim();
System.out.println(s3);
//比较字符串内容是否相同 后者忽略大小写
System.out.println(str1.equals(str2));
System.out.println(str1.equalsIgnoreCase(str2));
//将指定字符串连接到此字符串的结尾 等价于 +
System.out.println(str1.concat(str2));
//比较两个字符串的大小
System.out.println(str1.compareTo(str2));
//返回字符串的 [begin,end) 子串 第一个参数是开始索引,第二个是结束索引
System.out.println(str.substring(5));
System.out.println(str.substring(5, 15));
//测试字符串是否以指定后缀/前缀结尾
//第三个是判断以1索引开始的子串,是否以“Y”为前缀
System.out.println(str1.endsWith("YQ"));
System.out.println(str1.startsWith("GY"));
System.out.println(str1.startsWith("Y", 1));
//判断当前字符串是否含有指定字符串
System.out.println(str.contains("chuan"));
//返回指定字符串在当前字符串中第一次出现的索引 没有则返回-1
System.out.println(str.indexOf("chua"));
//返回指定字符串在当前字符串从5开始的子串中第一次出现的索引 没有则返回-1
System.out.println(str.indexOf("chua", 5));
//返回指定字符串在当前字符串中最后一次出现的索引 没有则返回-1
System.out.println(str.lastIndexOf("i"));
//返回指定字符串在当前字符串中以5结束的子串中最后一次出现的索引 没有则返回-1
System.out.println(str.lastIndexOf("w", 5));
//新字符替换指定字符串中的旧字符
System.out.println(str.replace('w', 'n'));
//用新的字符串替换指定字符串中的旧字符串
System.out.println(str.replace("Ai", "Dog"));
//将当前字符串中符合正则表达式的部分替换为指定字符串
System.out.println(str.replaceAll("\\w+", "Dog"));
//将当前字符串中(第一个)符合正则表达式的部分替换为指定字符串
System.out.println(str.replaceFirst("\\w+", "Dog"));
//将当前字符串以指定分隔符分隔
String[] a = str1.split("Y");
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
System.out.println(a[i]);
}
}
}String类与其他结构之间的转换
public class StringTest {
@Test
public void test() throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
String str1 = "123";
String str2 = "123aad大撒啊";
//String转基本数据类型
int a = Integer.parseInt(str1);
System.out.println(a);
Double b = Double.parseDouble(str1);
System.out.println(b);
//基本数据类型转String
String str = String.valueOf(a);
String str3 = a + "";
//String转char[]
char[] array = str2.toCharArray();
for (char c : array) {
System.out.println(c);
}
//char[]转String
char[] array1 = new char[]{'1', '2', '3', '4', '5'};
String str4 = new String(array1);
System.out.println(str4);
//String转byte[] 编码 默认不写也是UTF-8
byte[] bytes = str2.getBytes("UTF-8");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes));
//byte[]转String 解码 默认不写也是UTF-8
System.out.println(new String(bytes, "UTF-8"));
}
}StringBuffer和StringBuilder
常用方法
@Test
public void test() {
StringBuffer sb1 = new StringBuffer("GYQ");
//进行字符串拼接
System.out.println(sb1.append("yy"));
System.out.println(sb1.append("ds"));
//删除指定位置元素
System.out.println(sb1.delete(1, 3));
//用指定字符替换元素
System.out.println(sb1.replace(0, 2, "GYQy"));
//在指定索引位置插入字符
System.out.println(sb1.insert(2, "q"));
//反转当前字符序列
System.out.println(sb1.reverse());
}indexOf(),substring(),length(),charAt(),setCharAt()等方法与字符串用法相同
String,StringBuffer和StringBuilder的异同
String:不可变的字符序列,底层使用char[ ]存储 效率最低(比下两种慢很多)
StringBuffer:可变的字符序列,线程安全的,效率低,底层使用char[ ]存储
StringBuilder:可变的字符序列,线程不安全的,效率高 jdk5.0新增,底层使用char[ ]存储
源码分析:
@Test
public void test() {
String str = new String(); //char[] value = new char[0];
String str1 = new String("abc"); //char[] value = new char[]{'a','b','c'};
StringBuffer sb1 = new StringBuffer();//char[] value = new char[16];
sb1.append("a");//value[0] = ’a‘;
sb1.append("b");//value[1] = ’b‘;
//扩容问题:如果要添加的数据底层数组盛不下了,那就需要扩容底层的数组。
//默认情况下扩容为原来容量的2倍+2,同时将原有数组中的元素复制到新的数组中
//指导建议:在开发中使用StringBuffer(int capacity)或
//StringBuilder(int capacity)减少扩容的情况
StringBuffer sb2 = new StringBuffer("abc");//char[] value = new char["abc".length() + 16];
System.out.println(sb2.length());// 3
}日期时间类API
JDK8之前
System.currentTimeMillis();java.util.Date;java.sql.Date;SimpleDateFormat;java.util.Calendar
@Test
public void test() {
//System类中的currentTimeMillis()
//返回 1970.01.01 00:00:00 到现在的毫秒数 称为时间戳
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis());
//java.util.Date
Date date1 = new Date();
System.out.println(date1);
//与上方第一个方法作用相同 日期对象对应的时间戳
System.out.println(date1.getTime());//Fri Mar 11 13:19:26 CST 2022
//创建指定毫秒数的Date对象
Date date2 = new Date(1646875556137L);
System.out.println(date2);
//java.sql.Date
Date date3 = new java.sql.Date(1546875556137L);//2019-01-07
System.out.println(date3);
//java.text.SimpleDateFormat 不与语言环境有关的方式来格式化和解析日期的具体类
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat();
//日期转化为字符串 格式化
Date date = new Date();
System.out.println(date);
System.out.println(sdf.format(date));
//将字符串转化为日期 解析
String str = "2022/3/11 下午7:21";
try {
System.out.println(sdf.parse(str));
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//将日期格式化为指定格式的字符串
SimpleDateFormat sdf1 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy.MM.dd hh:mm aaa");
System.out.println(sdf1.format(new Date()));
//解析 要求字符串符合SimpleDateFormat的格式(通过带参构造器定义的)
String str2 = "2023.11.08 23:55 下午";
try {
System.out.println(sdf1.parse(str2));
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//java.util.Calendar
//获取Calendar实例的两种方法
Calendar calendar1 = Calendar.getInstance();
System.out.println(calendar1.getClass());
Calendar calendar2 = new GregorianCalendar();
//常用方法
//这个月/周/年的第几天
int dayOfMonth = calendar1.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);
System.out.println(dayOfMonth);
int dayOfYear = calendar1.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_YEAR);
System.out.println(dayOfYear);
//更改当前对象中的属性
calendar1.set(Calendar.DAY_OF_YEAR, 300);
System.out.println(calendar1.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_YEAR));
//对当前对象中的属性加或减
calendar1.add(Calendar.DAY_OF_YEAR, 5);
System.out.println(calendar1.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_YEAR));
calendar1.add(Calendar.DAY_OF_YEAR, -5);
System.out.println(calendar1.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_YEAR));
//日历类->Date 返回的对象是一个日历类
System.out.println(calendar1.getTime());
//Date->日历类
calendar1.setTime(new Date());
System.out.println(calendar1.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_YEAR));
}JDK8之中
新引入的java.time API纠正了过去的缺陷,建议使用
@Test
public void test() {
//LocalDate,LocalTime,LocalDateTime
//实例化 now()
LocalDate date = LocalDate.now();
LocalTime time = LocalTime.now();
LocalDateTime dateTime = LocalDateTime.now();
System.out.println(date + "\n" + time + "\n" + dateTime);
//获取指定时间的LocalDateTime对象 of()
LocalDateTime dateTime1 = LocalDateTime.of(2222, 2, 22, 22, 22);
System.out.println(dateTime1);
//获取对象的具体信息
System.out.println(dateTime1.getDayOfYear());
System.out.println(dateTime1.getDayOfMonth());
System.out.println(dateTime1.getDayOfWeek());
System.out.println(dateTime1.getMinute());
//更改对象的信息 体现不可变性
LocalDateTime dateTime2 = dateTime1.withDayOfMonth(28);
System.out.println(dateTime2);
System.out.println(dateTime1);
//修改 体现不可变性
LocalDateTime dateTime3 = dateTime1.plusDays(-2);
System.out.println(dateTime3);
System.out.println(dateTime1);
}Instant类 瞬时
可能被用来记录应用程序中的事件时间戳
@Test
public void test() {
//Instant类
//实例化
Instant instant = Instant.now();//获取本初子午线对应的标准时间
System.out.println(instant);//需要加8个小时才是东八区
//设置偏移量
OffsetDateTime offsetDateTime = instant.atOffset(ZoneOffset.ofHours(8));
System.out.println(offsetDateTime);
//获取时间戳(s)
long l = instant.getEpochSecond();
System.out.println(l);
//根据给定时间戳,获取Instant实例
Instant instant1 = Instant.ofEpochSecond(1540000002L);
System.out.println(instant1);
}java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter类 格式化,解析 日期或时间
@Test
public void test() {
//DateTimeFormatter
//预定义的标准格式 格式化
DateTimeFormatter formatter1 = DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_DATE_TIME;
String str1 = formatter1.format(LocalDateTime.now());
System.out.println(LocalDateTime.now());
System.out.println(str1);
//解析
TemporalAccessor parse = formatter1.parse(str1);
System.out.println(parse);
//本地相关的格式
DateTimeFormatter formatter2 = DateTimeFormatter.ofLocalizedDateTime(FormatStyle.LONG).withZone(ZoneOffset.ofHours(8));
String str2 = formatter2.format(LocalDateTime.now());
System.out.println(str2);
//自定义的格式
DateTimeFormatter formatter3 = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss E");
String str3 = formatter3.format(LocalDateTime.now());
System.out.println(str3);
}Java比较器
Java中的对象,正常情况下,只能进行比较:== 或 != ,不能使用 > 或 <
但是在开发场景中,我们需要对多个对象进行排序,也就是需要比较对象的大小
如何实现?实现Comparable或Comparator接口
自定义类实现Comparable自然排序
public class CompareTest {
@Test
public void test() {
//Comparable的使用举例
String[] arr = new String[]{"zzz", "aaa", "fff", "sss", "vvv", "ccc"};
Arrays.sort(arr);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
//String实现了Comparable接口,重写了compareTo(obj)方法
//重写compareTo(obj)的规则:
//如果当前对象this大于形参对象obj,则返回正整数
//如果当前对象this等于形参对象obj,则返回零
//如果当前对象this小于形参对象obj,则返回负整数
Goods[] goodsArr = new Goods[5];
goodsArr[0] = new Goods("电动玩具", 20.12);
goodsArr[1] = new Goods("娃娃", 15.88);
goodsArr[2] = new Goods("tank", 200.51);
goodsArr[3] = new Goods("airplane", 200.51);
goodsArr[4] = new Goods("航母", 9999.99);
Arrays.sort(goodsArr);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(goodsArr));
}
}
//自定义类实现Comparable自然排序
class Goods implements Comparable {
private String name;
private double price;
public Goods() {
}
public Goods(String name, double price) {
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Goods{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
//比较大小的方式:按价格从低到高排序 如果价格一样再根据name排
@Override
public int compareTo(Object o) {
if (o instanceof Goods) {
Goods anotherGoods = (Goods) o;
//方式一
if (this.price > anotherGoods.price) {
return 1;
} else if (this.price < anotherGoods.price) {
return -1;
} else {
return this.name.compareTo(anotherGoods.name);
}
//方式二
//return Double.compare(this.price,anotherGoods.price);
}
throw new RuntimeException("传入数据类型不一致!");
}
}
使用Comparator实现定制排序
当元素的类型没有实现java.lang.Comparable接口二又不方便修改代码,或者实现java.lang.Comparable接口的排序规则不适合当前操作,那么可以考虑使用Comparator的对象来排序
public class CompareTest {
@Test
public void test() {
//Comparator的使用举例
String[] arr = new String[]{"zzz", "aaa", "fff", "sss", "vvv", "ccc"};
//反向自然排序
Arrays.sort(arr, new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(String o1, String o2) {
return -o1.compareTo(o2);
}
});
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
Goods[] goodsArr = new Goods[5];
goodsArr[0] = new Goods("电动玩具", 20.12);
goodsArr[1] = new Goods("娃娃", 15.88);
goodsArr[2] = new Goods("tank", 200.51);
goodsArr[3] = new Goods("airplane", 200.51);
goodsArr[4] = new Goods("tank", 9999.99);
//根据Goods的name排序,如果name相同根据价格从高到低排 汉字不适应
Arrays.sort(goodsArr, new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
if (o1 instanceof Goods && o2 instanceof Goods) {
Goods good1 = (Goods) o1;
Goods good2 = (Goods) o2;
if (good1.getName().equals(good2.getName())) {
return -Double.compare(good1.getPrice(), good2.getPrice());
} else {
return good1.getName().compareTo(good2.getName());
}
}
throw new RuntimeException("类型错误!");
}
});
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(goodsArr));
}
}
//自定义类实现Comparable自然排序
class Goods implements Comparable {
private String name;
private double price;
public Goods() {
}
public Goods(String name, double price) {
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Goods{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
//比较大小的方式:按价格从低到高排序 如果价格一样再根据name排
@Override
public int compareTo(Object o) {
if (o instanceof Goods) {
Goods anotherGoods = (Goods) o;
//方式一
if (this.price > anotherGoods.price) {
return 1;
} else if (this.price < anotherGoods.price) {
return -1;
} else {
return this.name.compareTo(anotherGoods.name);
}
//方式二
//return Double.compare(this.price,anotherGoods.price);
}
throw new RuntimeException("传入数据类型不一致!");
}
} Comparable接口和Comparator接口的使用对比
Comparable接口的方式一旦使用,保证Comparable接口实现类的对象在任何位置都可以比较大小
Comparator接口属于临时性的比较
System,Math,BigInteger,BigDecimal类的使用
public class CompareTest {
@Test
public void test() {
//System
//时间戳
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis());
//退出当前程序,参数为0正常退出,非零异常退出 在图形界面编程中实现程序退出
//System.exit(0);
//请求系统进行垃圾回收,至于系统是否立即回收,取决于系统中垃圾回收算法的实现以及系统执行时的情况
System.gc();
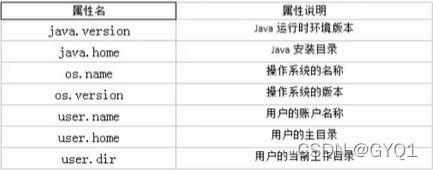
//获取系统中属性名为key的属性对应的值,常见属性名及其作用如代码下图
System.out.println(System.getProperty("java.version"));
//Math 提供了一系列的静态方法用于科学计算,方法参数和返回值一般为Double
//绝对值
System.out.println(Math.abs(-55.0));
//三角函数
System.out.println(Math.sin(45.0));
//第一个参数的第二个参数次幂
System.out.println(Math.pow(2.0, 5.0));
//自然对数
System.out.println(Math.log(20.0));
//e为底指数
System.out.println(Math.exp(2.0));
//最大数
System.out.println(Math.max(10, 50));
//最小数
System.out.println(Math.min(55.0, 22.0));
//返回范围在[0.0,1.0)的随机数
System.out.println(Math.random());
//double型数据转换为long型(四舍五入)
System.out.println(Math.round(25.823));
//弧度->角度
System.out.println(Math.toDegrees(0.5));
//角度->弧度
System.out.println(Math.toRadians(180));
//BigInteger&BigDecimal
//BigInteger可以表示不可变的任意精度的整数 Integer和Long类不够用时使用它
//BigDecimal表示不可变的,任意精度的有符号十进制定点数,商业计算中要求数字精度较高时使用
//常用方法见下图
}
}String getProperty(String key) 方法
系统的常见属性名及其作用