开始
又是很久很久没写新东西了,刚好最近时间都比较空闲,终于能有时间整理之前的阅读源码的笔记;不知不觉React都发布了18的版本了,还好React整体架构还是没太大的变化,16版本应该还有一定的参考性。
先带着问题
在我还没阅读源码前或者在我阅读源码的时候记录好几个问题,基本上就是带着这些问题去一步步深入了解源码的实现的:
- Virtual Dom是如何转化Fiber结构的?
- workInProgress 和 current 为什么要有两个fiber树?
- fiber是怎么暂停和恢复执行的?
- fiber更新在什么情况下会被暂停或者抢占?
- 同一fiber节点树被重复标记,低优先级被高优先级覆盖会怎样?
- 为什componentWillMount会重复触发?
逐步分析
直接从代码开始
ReactDOM.redner(, '#root');下一步:
funciton legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer(...) {
let root: Root = (container._reactRootContainer: any);
if(!root) {
// 开始初始渲染,创建ReactRoot
root = container._reactRootContainer = legacyCreateRootFromDOMContainer(container,forceHydrate,);
unbatchedUpdates(() => {
if (parentComponent != null) {
...
} else {
// 调起ReactRoot的渲染方法
root.render(children, callback);
}
});
} else {
...
}
}ReactRoot创建:
function ReactRoot(
container: DOMContainer,
isConcurrent: boolean,
hydrate: boolean,
) {
const root = createContainer(container, isConcurrent, hydrate);
this._internalRoot = root;
}这里createContainer,实际创建的是createFiberRoot:
export function createFiberRoot(
containerInfo: any,
isConcurrent: boolean,
hydrate: boolean,
): FiberRoot {
const uninitializedFiber = createHostRootFiber(isConcurrent);
let root;
root = ({
current: uninitializedFiber, // HostRoot类型的fiber节点
containerInfo: containerInfo, // dom节点
pendingChildren: null,
pingCache: null,
earliestPendingTime: NoWork, // 各种等待更新的优先级
latestPendingTime: NoWork,
earliestSuspendedTime: NoWork,
latestSuspendedTime: NoWork,
latestPingedTime: NoWork,
didError: false, // 更新出错标记位
pendingCommitExpirationTime: NoWork,
finishedWork: null, // 已经完成diff的wip fiber树,等待最后commit
timeoutHandle: noTimeout,
context: null,
pendingContext: null,
hydrate,
nextExpirationTimeToWorkOn: NoWork, // 下次更新的优先级
expirationTime: NoWork,
firstBatch: null,
nextScheduledRoot: null, // 下个调度的Root,FiberRoot会串起一个单向链表,调度器会不停遍历查看是否需要更新
}: BaseFiberRootProperties);
}
uninitializedFiber.stateNode = root;
return ((root: any): FiberRoot);
}这里的FiberRoot才是实际的调度单位,这里有很多字段都是跟调度更新相关的,就大概注释一下。
这里React已经创建了一个ReactRoot->FiberRoot的关系,再回到legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer方法,开始直接调起ReactRoot.render方法,可以想像为什么不在FiberRoot上实现类似render的方法,而在ReactRoot上做,大概是为了让整个Fiber树都是一个非常简单的对象结构组成方便以后使用其他语言直接实现类似的结构吧。
在顺便看一下FiberNode结构:
function FiberNode(
tag: WorkTag,
pendingProps: mixed,
key: null | string,
mode: TypeOfMode,
) {
// Instance
this.tag = tag; // 类型标签
this.key = key;
this.elementType = // 虚拟dom的类型,一般为字符串或者函数,class; 或者是REACT_SUSPENSE_TYPE,REACT_FRAGMENT_TYPE等内置类型
this.type = null; // resolve后的最终类型一般跟elementType是一样的
this.stateNode = null; // 组件实例或者Dom节点
// Fiber
this.return = null;
this.child = null;
this.sibling = null;
this.index = 0;
this.ref = null;
this.pendingProps = pendingProps;
this.memoizedProps = null;
this.updateQueue = null; // 更新队列,记录了更新的请求
this.memoizedState = null; // 对应hook状态链表
this.contextDependencies = null;
this.mode = mode;
// Effects
this.effectTag = NoEffect;
this.nextEffect = null;
this.firstEffect = null;
this.lastEffect = null;
this.expirationTime = NoWork;
this.childExpirationTime = NoWork;
this.alternate = null;
}接着来到ReactFiberReconciler的updateContainer:
function updateContainer(
element: ReactNodeList,
container: OpaqueRoot,
parentComponent: ?React$Component,
callback: ?Function,
): ExpirationTime {
const current = container.current;
const currentTime = requestCurrentTime();
const expirationTime = computeExpirationForFiber(currentTime, current);
return updateContainerAtExpirationTime(
element,
container,
parentComponent,
expirationTime,
callback,
);
} 这里requestCurrentTime方法是很特别的,并不是单纯的是调用类似Data.now或者Performance.now方法获取时间。
function requestCurrentTime() {
if (isRendering) {
// 要是渲染中,直接返回之前已经计算调度好的时间
return currentSchedulerTime;
}
findHighestPriorityRoot();
if (
nextFlushedExpirationTime === NoWork ||
nextFlushedExpirationTime === Never
) {
// 要是没有其他等待中的工作才计算并更新currentRendererTime
recomputeCurrentRendererTime();
currentSchedulerTime = currentRendererTime;
return currentSchedulerTime;
}
// 要是有工作在等待中,则直接返回之前已经计算调度好的时间
return currentSchedulerTime;
}因为这个计算的时间会影响最后工作的优先级的计算,所以React里面的优先级是包含两种含义的:任务的优先级和超时的时间,这里requestCurrentTime目标就是尽可能把其他同一阶段(如在渲染过程中触发的,或者一个事件处理器里面触发的)触发的更新都计算为同一个优先级,然后在一次调度更新中处理。
再继续看recomputeCurrentRendererTime是如何计算这个时间的:
function recomputeCurrentRendererTime() {
const currentTimeMs = now() - originalStartTimeMs;
currentRendererTime = msToExpirationTime(currentTimeMs);
}
const UNIT_SIZE = 10;
const MAGIC_NUMBER_OFFSET = MAX_SIGNED_31_BIT_INT - 1;
export function msToExpirationTime(ms: number): ExpirationTime {
return MAGIC_NUMBER_OFFSET - ((ms / UNIT_SIZE) | 0);
}首先获取当前页面加载的时间差,然后每10ms内作为一个级别,再与MAGIC_NUMBER_OFFSET相减。
这样可以总结两点:
- 一般也是往后触发的工作任务,它的优先级是会越低的
- 每10ms内间隔触发的任务都视为同一个优先级的任务
继续回到updateContainer,接着调用computeExpirationForFiber,再根据调度的上下文来确定实际的优先级:
function computeExpirationForFiber(currentTime: ExpirationTime, fiber: Fiber) {
const priorityLevel = getCurrentPriorityLevel();
let expirationTime;
if ((fiber.mode & ConcurrentMode) === NoContext) {
expirationTime = Sync;
} else if (isWorking && !isCommitting) {
expirationTime = nextRenderExpirationTime;
} else {
switch (priorityLevel) {
case ImmediatePriority:
expirationTime = Sync;
break;
case UserBlockingPriority:
expirationTime = computeInteractiveExpiration(currentTime);
break;
case NormalPriority:
// This is a normal, concurrent update
expirationTime = computeAsyncExpiration(currentTime);
break;
case LowPriority:
case IdlePriority:
expirationTime = Never;
break;
default:
invariant(
false,
'Unknown priority level. This error is likely caused by a bug in ' +
'React. Please file an issue.',
);
}
if (nextRoot !== null && expirationTime === nextRenderExpirationTime) {
expirationTime -= 1;
}
}
if (
priorityLevel === UserBlockingPriority &&
(lowestPriorityPendingInteractiveExpirationTime === NoWork ||
expirationTime < lowestPriorityPendingInteractiveExpirationTime)
) {
lowestPriorityPendingInteractiveExpirationTime = expirationTime;
}
return expirationTime;
}这里的上下文主要包括:是否是并发模式以及当前的priorityLevel是什么。
- 如果不是并发模式,更新的优先级永远都是Sync
- 如果是并发模式下,正在render的过程中,那优先级等同于当前render的工作优先级nextRenderExpirationTime
- getCurrentPriorityLevel获取当前priorityLevel,这里就有
ImmediatePriority:对应就是Sync = MAX_SIGNED_31_BIT_INT
UserBlockingPriority: 通过computeInteractiveExpiration计算
NormalPriority:通过computeAsyncExpiration计算
LowPriority,IdlePriority:对应就是Never = 1,优先级最低
分别再看computeInteractiveExpiration和computeAsyncExpiration的计算
export const HIGH_PRIORITY_EXPIRATION = __DEV__ ? 500 : 150;
export const HIGH_PRIORITY_BATCH_SIZE = 100;
export function computeInteractiveExpiration(currentTime: ExpirationTime) {
return computeExpirationBucket(
currentTime,
HIGH_PRIORITY_EXPIRATION,
HIGH_PRIORITY_BATCH_SIZE,
);
}
export const LOW_PRIORITY_EXPIRATION = 5000;
export const LOW_PRIORITY_BATCH_SIZE = 250;
export function computeAsyncExpiration(
currentTime: ExpirationTime,
): ExpirationTime {
return computeExpirationBucket(
currentTime,
LOW_PRIORITY_EXPIRATION,
LOW_PRIORITY_BATCH_SIZE,
);
}
function computeExpirationBucket(
currentTime,
expirationInMs,
expirationInMs,
): ExpirationTime {
return (
MAGIC_NUMBER_OFFSET -
ceiling(
MAGIC_NUMBER_OFFSET - currentTime + expirationInMs / UNIT_SIZE,
bucketSizeMs / UNIT_SIZE,
)
);
}感觉computeExpirationBucket这个方法计算有点绕,但是把之前currentTime的计算合并在一起就会清晰一点:
MAGIC_NUMBER_OFFSET -
ceiling(
MAGIC_NUMBER_OFFSET - (MAGIC_NUMBER_OFFSET - ((ms / UNIT_SIZE) | 0)) + expirationInMs / UNIT_SIZE,
bucketSizeMs / UNIT_SIZE,
)
合并等于:
MAGIC_NUMBER_OFFSET - ceiling((ms + expirationInMs) / UNIT_SIZE, bucketSizeMs / UNIT_SIZE)也就是说以computeInteractiveExpiration为例,都是任务触发的时间加150ms作为优先级和超时的时间,而且每100ms作为一个级别间隔,
而computeAsyncExpiration则是延后5000ms,250ms作为间隔。
最后来到updateContainerAtExpirationTime方法,这里直接调起scheduleRootUpdate方法
function scheduleRootUpdate(
current: Fiber,
element: ReactNodeList,
expirationTime: ExpirationTime,
callback: ?Function,
) {
const update = createUpdate(expirationTime);
update.payload = {element};
callback = callback === undefined ? null : callback;
if (callback !== null) {
warningWithoutStack(
typeof callback === 'function',
'render(...): Expected the last optional `callback` argument to be a ' +
'function. Instead received: %s.',
callback,
);
update.callback = callback;
}
flushPassiveEffects();
enqueueUpdate(current, update);
scheduleWork(current, expirationTime);
return expirationTime;
}经过之前一堆准备工作,这里才算是进入调度更新:
- 创建一个update对象,记录这次触发的更新信息
- flushPassiveEffects,触发useEffect这些hook,放在以后hook分析的文章再细说
- enqueueUpdate,把update对象加入到fiber的updateQueue上,这里要是存在wip fiber节点同样是需要加入到wip fiber节点的updateQueue,因为整个更新过程有可能会被抢占而中断,也有可能顺利完成更新wip fiber tree会替换为current fiber tree;所以两边队列都需要加入防止丢失更新
然后就是scheduleWork调度工作:
function scheduleWork(fiber: Fiber, expirationTime: ExpirationTime) {
// 1
const root = scheduleWorkToRoot(fiber, expirationTime);
if (root === null) {
return;
}
// 2
if (
!isWorking &&
nextRenderExpirationTime !== NoWork &&
expirationTime > nextRenderExpirationTime
) {
interruptedBy = fiber;
resetStack();
}
// 3
markPendingPriorityLevel(root, expirationTime);
if (
!isWorking ||
isCommitting ||
nextRoot !== root
) {
const rootExpirationTime = root.expirationTime;
requestWork(root, rootExpirationTime);
}
}继续分步分析:
- scheduleWorkToRoot,主要更新fiber的childExpirationTime属性,该属性标记的是子fiber里面最高的优先级
- 如果不是在diff或者commit过程中,而且要是将要更新的优先级比当前处理的优先级更高,就意味着要中断了,所以要resetStack
- markPendingPriorityLevel主要更新root的两个属性earliestPendingTime和latestPendingTime,这两个属性就是标记等待更新的工作的优先级范围,因为等待更新的优先级其实也是分为几种类型的:pending,pinged,suspended,这些类型从高到低顺序处理,所以优先处理pending的。
- findNextExpirationTimeToWorkOn开始寻找优先级最高的工作去处理并更新root的nextExpirationTimeToWorkOn和expirationTime,记录当前要处理的优先级
- 如果不是diff或者commit过程中,则开始requestWork,否则直接返回等着下次调度执行就好
接着看requestWork:
function requestWork(root: FiberRoot, expirationTime: ExpirationTime) {
addRootToSchedule(root, expirationTime);
if (isRendering) {
return;
}
if (expirationTime === Sync) {
performSyncWork();
} else {
scheduleCallbackWithExpirationTime(root, expirationTime);
}
}- addRootToSchedule加入到root单向调度链表
- 如果是优先级是Sync立马调起performSyncWork,否则scheduleCallbackWithExpirationTime等待调度更新
这里就分开两条线路,一条是传统模式下的同步更新,另外一条就是fiber架构最终目标并发模式下的异步更新。
先看同步更新:
function performWork(minExpirationTime: ExpirationTime, isYieldy: boolean) {
// 寻找最高优先级的Root准备执行
findHighestPriorityRoot();
if (isYieldy) {
// 异步更新逻辑
} else {
// 同步更新逻辑
// 1. 存在等待处理的工作
// 2. 等待处理的工作的优先级要大于等于这次调度的优先级
while (
nextFlushedRoot !== null &&
nextFlushedExpirationTime !== NoWork &&
minExpirationTime <= nextFlushedExpirationTime
) {
performWorkOnRoot(nextFlushedRoot, nextFlushedExpirationTime, false);
findHighestPriorityRoot();
}
}
// 执行清理工作
finishRendering();
}performWork的逻辑也非常简单,不停循环寻找存在最高优先级的工作任务的Root调起performWorkOnRoot执行:
function performWorkOnRoot(
root: FiberRoot,
expirationTime: ExpirationTime,
isYieldy: boolean,
) {
isRendering = true;
if (!isYieldy) {
// 同步更新逻辑
let finishedWork = root.finishedWork;
if (finishedWork !== null) {
completeRoot(root, finishedWork, expirationTime);
} else {
root.finishedWork = null;
const timeoutHandle = root.timeoutHandle;
if (timeoutHandle !== noTimeout) {
cancelTimeout(timeoutHandle);
}
renderRoot(root, isYieldy);
finishedWork = root.finishedWork;
if (finishedWork !== null) {
completeRoot(root, finishedWork, expirationTime);
}
}
} else {
// 异步更新逻辑
}
}到了performWorkOnRoot,可以明显看到主要分为两个阶段来处理工作的:renderRoot和completeRoot。
先看renderRoot:
function renderRoot(root: FiberRoot, isYieldy: boolean): void {
// 1. 触发useEffect hook
flushPassiveEffects();
isWorking = true;
const previousDispatcher = ReactCurrentDispatcher.current;
// 2. 设置hook dispatcher
ReactCurrentDispatcher.current = ContextOnlyDispatcher;
const expirationTime = root.nextExpirationTimeToWorkOn;
// 3. 如果调度优先级跟当前的处理的优先级不一样或者处理的root不一样,又或者是一个全新的调度,就开始重置执行栈,创建wip fiber节点
if (
expirationTime !== nextRenderExpirationTime ||
root !== nextRoot ||
nextUnitOfWork === null
) {
resetStack();
nextRoot = root;
nextRenderExpirationTime = expirationTime;
nextUnitOfWork = createWorkInProgress(
nextRoot.current,
null,
nextRenderExpirationTime,
);
root.pendingCommitExpirationTime = NoWork;
}
do {
try {
// 4. 开始处理工作任务主循环
workLoop(isYieldy);
} catch (thrownValue) {
resetContextDependences();
resetHooks();
if (nextUnitOfWork === null) {
didFatal = true;
onUncaughtError(thrownValue);
} else {
const sourceFiber: Fiber = nextUnitOfWork;
let returnFiber = sourceFiber.return;
if (returnFiber === null) {
didFatal = true;
onUncaughtError(thrownValue);
} else {
throwException(
root,
returnFiber,
sourceFiber,
thrownValue,
nextRenderExpirationTime,
);
nextUnitOfWork = completeUnitOfWork(sourceFiber);
continue;
}
}
}
break;
} while (true);
...
onComplete(root, rootWorkInProgress, expirationTime);
}再进入看workLoop,performUnitOfWork不停处理遍历fiber节点处理
function workLoop(isYieldy) {
if (!isYieldy) {
// Flush work without yielding
while (nextUnitOfWork !== null) {
nextUnitOfWork = performUnitOfWork(nextUnitOfWork);
}
} else {
// Flush asynchronous work until there's a higher priority event
while (nextUnitOfWork !== null && !shouldYieldToRenderer()) {
nextUnitOfWork = performUnitOfWork(nextUnitOfWork);
}
}
}继续performUnitOfWork:
function performUnitOfWork(workInProgress: Fiber): Fiber | null {
const current = workInProgress.alternate;
let next;
next = beginWork(current, workInProgress, nextRenderExpirationTime);
workInProgress.memoizedProps = workInProgress.pendingProps;
if (next === null) {
next = completeUnitOfWork(workInProgress);
}
ReactCurrentOwner.current = null;
return next;
}现在先总结一下FiberRoot和Fiber各个阶段: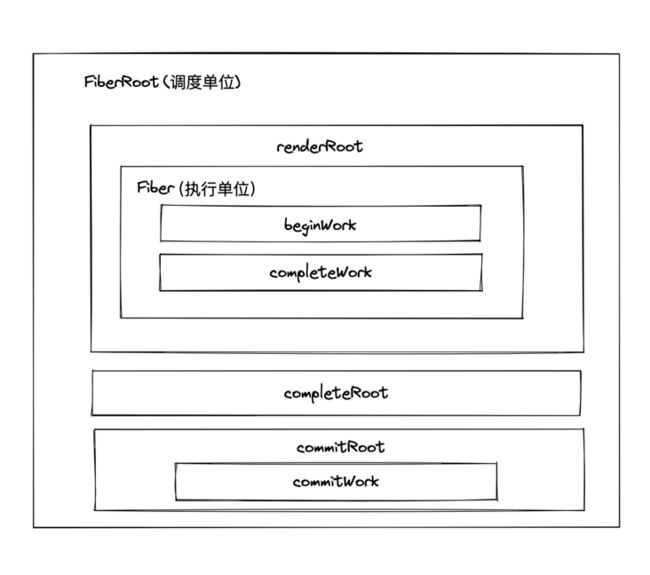
所以FiberRoot和Fiber也各自都会有render,complete, commit阶段,不同的阶段都会有不一样的工作目的。
现在到了beginWork阶段:
function beginWork(
current: Fiber | null,
workInProgress: Fiber,
renderExpirationTime: ExpirationTime,
): Fiber | null {
if (current !== null) {
const oldProps = current.memoizedProps;
const newProps = workInProgress.pendingProps;
// 如果pros有变化或者依赖的context有改变
if (oldProps !== newProps || hasLegacyContextChanged()) {
didReceiveUpdate = true;
} else if (updateExpirationTime < renderExpirationTime) {
didReceiveUpdate = false;
// 如果fiber的优先级没有当前处理的优先级更高的更新则跳过,直接进入bailoutOnAlreadyFinishedWork,bailoutOnAlreadyFinishedWork里面会判断childExpirationTime有没有处理的更新,如果没有则返回null,然后遍历sibling,要是存在则继续深度遍历
...
}
} else {
didReceiveUpdate = false;
}
workInProgress.expirationTime = NoWork;
switch(workInProgress.tag) {
....
case HostRoot:
return updateHostRoot(current, workInProgress, renderExpirationTime);
case FunctionComponent: {
const Component = workInProgress.type;
const unresolvedProps = workInProgress.pendingProps;
const resolvedProps =
workInProgress.elementType === Component
? unresolvedProps
: resolveDefaultProps(Component, unresolvedProps);
return updateFunctionComponent(
current,
workInProgress,
Component,
resolvedProps,
renderExpirationTime,
);
}
}
}beginWork,第一步先判断是否有更新,然后第二步接着根据不同组件类型调用更新的方法,因为根节点是HostRoot类型的,先看updateHostRoot方法,后面再回头跟进
updateFunctionComponent;
function updateHostRoot(current, workInProgress, renderExpirationTime) {
pushHostRootContext(workInProgress);
const updateQueue = workInProgress.updateQueue;
const nextProps = workInProgress.pendingProps;
const prevState = workInProgress.memoizedState;
const prevChildren = prevState !== null ? prevState.element : null;
// 处理updteQueue,把高于当前优先级的update对象移出队列并处理,处理完后根据需要移入到effectList队列中等待后续处理
processUpdateQueue(
workInProgress,
updateQueue,
nextProps,
null,
renderExpirationTime,
);
const nextState = workInProgress.memoizedState;
const nextChildren = nextState.element;
if (nextChildren === prevChildren) {
resetHydrationState();
return bailoutOnAlreadyFinishedWork(
current,
workInProgress,
renderExpirationTime,
);
}
const root: FiberRoot = workInProgress.stateNode;
if (
(current === null || current.child === null) &&
root.hydrate &&
enterHydrationState(workInProgress)
) {
workInProgress.child = mountChildFibers(
workInProgress,
null,
nextChildren,
renderExpirationTime,
);
} else {
reconcileChildren(
current,
workInProgress,
nextChildren,
renderExpirationTime,
);
resetHydrationState();
}
return workInProgress.child;
}updateHostRoot方法的第一步就是处理updateQueue,把高于当前优先级的update对象移出队列并处理,处理完后根据需要移入到effectList队列(effectList队列都是commit阶段的包含这次更新的所有副作用:例如各种生命周期方法,hook回调,dom操作等)中等待后续处理,然后再根据是否是初始挂载而调用mountChildFibers或者reconcileChildren;而实际mountChildFibers和reconcileChildren都是一样的逻辑,唯一不一样的是mountChildFibers不会记录增删改这些副作用,因为这个fiber本身effectTag已经标记为Placement,后续commit阶段会不停遍历子节点插入到dom上,而mountChildFibers最大的目标就是把jsx element转换为fiber结构。
回头再看updateFunctionComponent:
export const reconcileChildFibers = ChildReconciler(true);
export const mountChildFibers = ChildReconciler(false);function updateFunctionComponent(
current,
workInProgress,
Component,
nextProps: any,
renderExpirationTime,
) {
// 获取context,后面context分析再细说
const unmaskedContext = getUnmaskedContext(workInProgress, Component, true);
const context = getMaskedContext(workInProgress, unmaskedContext);
let nextChildren;
prepareToReadContext(workInProgress, renderExpirationTime);
// 执行函数组件
nextChildren = renderWithHooks(
current,
workInProgress,
Component,
nextProps,
context,
renderExpirationTime,
);
if (current !== null && !didReceiveUpdate) {
bailoutHooks(current, workInProgress, renderExpirationTime);
return bailoutOnAlreadyFinishedWork(
current,
workInProgress,
renderExpirationTime,
);
}
workInProgress.effectTag |= PerformedWork;
// diff算法
reconcileChildren(
current,
workInProgress,
nextChildren,
renderExpirationTime,
);
return workInProgress.child;
}进入renderWithHooks:
export function renderWithHooks(
current: Fiber | null,
workInProgress: Fiber,
Component: any,
props: any,
refOrContext: any,
nextRenderExpirationTime: ExpirationTime,
): any {
renderExpirationTime = nextRenderExpirationTime;
currentlyRenderingFiber = workInProgress;
nextCurrentHook = current !== null ? current.memoizedState : null;
// 切换hook上下文
ReactCurrentDispatcher.current =
nextCurrentHook === null
? HooksDispatcherOnMount
: HooksDispatcherOnUpdate;
let children = Component(props, refOrContext);
if (didScheduleRenderPhaseUpdate) {
do {
didScheduleRenderPhaseUpdate = false;
numberOfReRenders += 1;
nextCurrentHook = current !== null ? current.memoizedState : null;
nextWorkInProgressHook = firstWorkInProgressHook;
currentHook = null;
workInProgressHook = null;
componentUpdateQueue = null;
ReactCurrentDispatcher.current = __DEV__
? HooksDispatcherOnUpdateInDEV
: HooksDispatcherOnUpdate;
children = Component(props, refOrContext);
} while (didScheduleRenderPhaseUpdate);
renderPhaseUpdates = null;
numberOfReRenders = 0;
}
const renderedWork: Fiber = (currentlyRenderingFiber: any);
// 更新节点当前的信息
renderedWork.memoizedState = firstWorkInProgressHook;
renderedWork.expirationTime = remainingExpirationTime;
renderedWork.updateQueue = (componentUpdateQueue: any);
renderedWork.effectTag |= sideEffectTag;
}renderWithHook会首先切换hook的上下文(分为mount和update两种上下文),然后直接调用函数组件,如果函数组件在调用的时候又触发了更新,就会再一次重复调用;最后更新节点信息,主要是查看hook上还有没有其他等待的更新,如果有就把该优先级更新到节点上,等待下一轮更新。
当renderWithHook得到新的jsx elements,就会进入reconcileChildren,与current fiber树一起进行diff然后更新到wip fiber树上,直接介绍一下React的diff算法吧:
function reconcileChildrenArray(
returnFiber: Fiber,
currentFirstChild: Fiber | null,
newChildren: Array<*>,
expirationTime: ExpirationTime,
): Fiber | null {
let resultingFirstChild: Fiber | null = null;
let previousNewFiber: Fiber | null = null;
let oldFiber = currentFirstChild;
let lastPlacedIndex = 0;
let newIdx = 0;
let nextOldFiber = null;
for (; oldFiber !== null && newIdx < newChildren.length; newIdx++) {
if (oldFiber.index > newIdx) {
nextOldFiber = oldFiber;
oldFiber = null;
} else {
nextOldFiber = oldFiber.sibling;
}
const newFiber = updateSlot(
returnFiber,
oldFiber,
newChildren[newIdx],
expirationTime,
);
if (newFiber === null) {
if (oldFiber === null) {
oldFiber = nextOldFiber;
}
break;
}
if (shouldTrackSideEffects) {
if (oldFiber && newFiber.alternate === null) {
deleteChild(returnFiber, oldFiber);
}
}
lastPlacedIndex = placeChild(newFiber, lastPlacedIndex, newIdx);
if (previousNewFiber === null) {
resultingFirstChild = newFiber;
} else {
previousNewFiber.sibling = newFiber;
}
previousNewFiber = newFiber;
oldFiber = nextOldFiber;
}
if (newIdx === newChildren.length) {
deleteRemainingChildren(returnFiber, oldFiber);
return resultingFirstChild;
}
if (oldFiber === null) {
for (; newIdx < newChildren.length; newIdx++) {
const newFiber = createChild(
returnFiber,
newChildren[newIdx],
expirationTime,
);
if (!newFiber) {
continue;
}
lastPlacedIndex = placeChild(newFiber, lastPlacedIndex, newIdx);
if (previousNewFiber === null) {
resultingFirstChild = newFiber;
} else {
previousNewFiber.sibling = newFiber;
}
previousNewFiber = newFiber;
}
return resultingFirstChild;
}对比vue2,最大的不同点大概就是不是使用前后游标遍历的算法,直接是从开头开始遍历对比,这主要就是因为fiber结构,兄弟节点是是采用单链表的形式而不是数组(为什么是单链表而不能是数组?因为diff是可以中途打断的,而且遍历算法是深度优先遍历,如果采用数组无法或者很难存每一层级遍历的当前位置,其实fiber的return就是充当这个遍历位置记录),当然是不能前后游标遍历的算法了;其他的例如没有key则按照顺序或如果有key则根据key map找到对应元素就更新,遍历结束,旧列表还剩元素就是清除,新列表还剩元素就插入,都是大体没有变化的。
当diff算法结束后,fiber上的effectTag会标记这次更新后所需要做的操作,然后在completeUnitOfWork上:
function completeUnitOfWork(workInProgress: Fiber): Fiber | null {
while (true) {
const current = workInProgress.alternate;
const returnFiber = workInProgress.return;
const siblingFiber = workInProgress.sibling;
if ((workInProgress.effectTag & Incomplete) === NoEffect) {
nextUnitOfWork = workInProgress;
// 调用completeWork,弹出context
nextUnitOfWork = completeWork(
current,
workInProgress,
nextRenderExpirationTime,
);
// 重置childExpirationTime
resetChildExpirationTime(workInProgress, nextRenderExpirationTime);
if (nextUnitOfWork !== null) {
return nextUnitOfWork;
}
// 把需要增加删除更新的fiber节点添加道父节点的effectList上
if (
returnFiber !== null &&
(returnFiber.effectTag & Incomplete) === NoEffect
) {
if (returnFiber.firstEffect === null) {
returnFiber.firstEffect = workInProgress.firstEffect;
}
if (workInProgress.lastEffect !== null) {
if (returnFiber.lastEffect !== null) {
returnFiber.lastEffect.nextEffect = workInProgress.firstEffect;
}
returnFiber.lastEffect = workInProgress.lastEffect;
}
const effectTag = workInProgress.effectTag;
if (effectTag > PerformedWork) {
if (returnFiber.lastEffect !== null) {
returnFiber.lastEffect.nextEffect = workInProgress;
} else {
returnFiber.firstEffect = workInProgress;
}
returnFiber.lastEffect = workInProgress;
}
}
}
if (siblingFiber !== null) {
return siblingFiber;
} else if (returnFiber !== null) {
workInProgress = returnFiber;
continue;
} else {
return null;
}
} else {
// 节点没有完成,可能有错误抛出
const next = unwindWork(workInProgress, nextRenderExpirationTime);
if (next !== null) {
next.effectTag &= HostEffectMask;
return next;
}
if (returnFiber !== null) {
returnFiber.firstEffect = returnFiber.lastEffect = null;
returnFiber.effectTag |= Incomplete;
}
}
}主要有三个工作:
- 清理协程栈,准备执行下一个fiber
- 重置fiber的childExpirationTime标记
- 把需要增加删除更新的fiber节点添加到父节点的effectList上,后面只要遍历根节点的effcetList就可以完成最后的commit,就不需要再深度遍历
到此renderRoot的工作基本完成,进入completeRoot阶段:
function completeRoot(
root: FiberRoot,
finishedWork: Fiber,
expirationTime: ExpirationTime,
): void {
root.finishedWork = null;
runWithPriority(ImmediatePriority, () => {
commitRoot(root, finishedWork);
});
}completeRoot主要还是直接调度执行commitRoot方法,commitRoot已经是最后一步了,但是也是最复杂,最多步骤,代码太长就不贴了直接分析步骤:
- markCommittedPriorityLevels, 传入的参数expirationTime是root.expirationTime或者root.childExpirationTime
如果expirationTime是NoWork证明所有work都已经完成
如果expirationTime都低于latestPingedTime,证明之前latestPingedTime优先级已经完成,设置为NoWork
如果expirationTime都低于latestPendingTime,证明之前latestPendingTime优先级已经完成,设置为NoWork
如此类推
findNextExpirationTimeToWorkOn 重新设置root.expirationTime和root.nextExpirationTimeToWorkOn
// 2,3,5 都是不停在遍历effect链表
commitBeforeMutationLifecycles
如果是FunctionComponent, ForwardRef, SimpleMemoComponent
(1) commitHookEffectList,遍历查看是否存在UnmountSnapshot的effectTag
如果是ClassComponent
(2) 调用ClassComponent的getSnapshotBeforeUpdate方法- commitAllHostEffects这个阶段开始对真实dom节点造成影响,对dom树增删改处理
执行useLayoutEffect的清理函数, 执行dom的属性更新 - 把wip切换为current //现在已经更新完了dom
- commitAllLifeCycles
如果是FunctionComponent, ForwardRef, SimpleMemoComponent
(1) 执行useLayoutEffect hook //dom已经是更新了,这个时候还在js代码的线程,还没渲染,所以这个时候修改dom,用户是感知不到的,而useEffect是dom更新完,已经渲染到界面后才触发
如果是ClassComponent
(2) 执行ClassComponent的componentDidMount/componentDidUpdate方法
commitUpdateQueue flushPassiveEffects方法会调起passiveEffectCallback,而passiveEffectCallback其实就是commitPassiveEffects
所以flushPassiveEffects调用点会有几个地方;- scheduleRootUpdate方法 // 下一次schedule 更新的时候
- renderRoot方法 // 执行下一个Root的更新的时候,会把前一个的passiveEffects清空
- dispatchAction方法 // setState方法触发,不在当前渲染中 会触发flushPassiveEffects,在当前渲染中则不会
- commitRoot方法 // 设置定一个调度,一个宏任务中更新
passiveEffectCallbackHandle = scheduler.unstable_runWithPriority(scheduler.unstable_NormalPriority, function () {
return schedulePassiveEffects(callback);
});
// 所以passiveEffect不一定是延后调用的,但是如果有多个Root等待更新,前一个Root会先清空PassiveEffect,再接着进入更新流程
// 这里Root的意思是带有HostRoot标记的组件,也就是reactDom.render的根节点
// 至少在一个组件树里面是延后调用的
// flushPassiveEffects 保证在下一轮更新前调用,但是执行时机可能是同步的也可能是异步的
- 最后再更新root.expirationTime
// commit完成之后是不会把root移除出调度队列的,会在下次调度,findHighestPriorityRoot的时候移除
- commitAllHostEffects这个阶段开始对真实dom节点造成影响,对dom树增删改处理
到此commitRoot完成,一次完整的渲染结束,后面再会循环查找还有没有等待处理的Root。
问题解答
了解了整个渲染流程之后,可以开始回答一开始的问题了
Virtual Dom是如何转化Fiber结构的?
Virtual Dom是在reconcile的过程中转换到fiber结构的
workInProgress 和 current 为什么要有两个fiber树
如果只有一棵树的话,因为渲染过程是可以中断的,渲染过程中又可能会触发新的优先级的渲染,而这些优先级都标记在fiber树上,还有fiber节点上的effectList保存的都是渲染过程中产生后续处理的fiber节点;如果被中断,fiber树上就会有脏的状态,难以清理。
同一fiber节点树被重复标记,低优先级被高优先级覆盖会怎样?
并不会又问题,因为hook是有updateQueue来记录每个更新,这个更新对象还有expirationTime记录这个更新的优先级,
每次执行的更新的时候,会遍历updateQueue,会挑出高于这个渲染优先级的update来进行更新,低于这次渲染优先级的会跳过
最后更新的时候fiber的优先级会设置成剩余的remainingExpirationTime
为什componentWillMount会重复触发
因为在beginWork阶段调起的,在异步执行环境,work有可能多次中断重新执行,所以会多次执行
fiber更新在什么情况下会被暂停或者抢占
- 当前的时间片用完
- 结束diff过程或者commit过程
也就是不是随便就能发生中断,必须等当前时间片结束
判断是否需要中断, - 渲染的优先级跟当前的优先级不一样
- 渲染Root跟当前的Root不一样
结束
整个渲染分析真的是挺漫长,但是分析完之后又会觉得没有想象中那么复杂,基本原理还是很好理解,但是细节的地方确实很多,后面再继续分析hook实现原理。