Pytorch学习笔记6——训练分类器
Pytorch学习笔记6——TRAINING A CLASSIFIER
-
- **Pytorch Learning Notes**
-
- TRAINING A NEURAL NETWORK
-
- 1 **Load Data**
- 2 **定义神经网络**
- 3 **定义损失函数和优化器**
- 4 **训练神经网络**
- 5 **保存模型**
- 6 **测试模型**
- 7 **在GPU上训练**
- 8 **最终代码**(GPU版本)
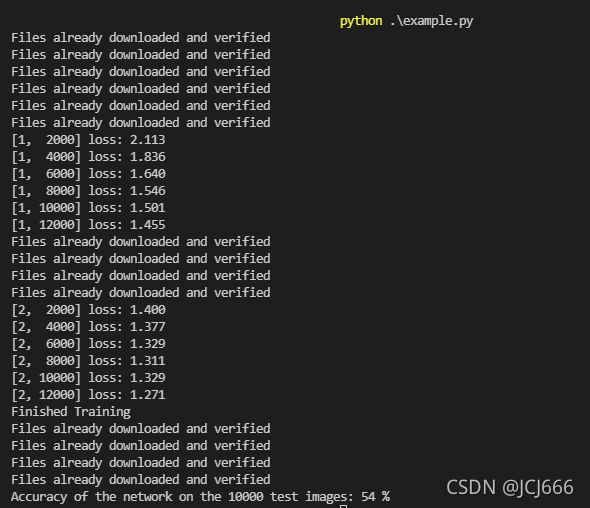
- 9 **输出**
Pytorch Learning Notes
Reference:
Pytorch官方文档——TRAINING A CLASSIFIER
以上是Pytorch官方的文档,本文主要对其进行翻译整理,并加入一些自己的理解,仅作日后复习查阅所用。
TRAINING A NEURAL NETWORK
1 Load Data
import torch
import torchvision
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
#torchvision.transforms是pytorch中的图像预处理包。用Compose把多个变换整合到一起
transform = transforms.Compose(
[transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))])
batch_size = 4
#获得训练集和测试集
trainset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root='./data', train=True,
download=True, transform=transform)
trainloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(trainset, batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=True, num_workers=2)
testset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root='./data', train=False,
download=True, transform=transform)
testloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(testset, batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=False, num_workers=2)
#定义label
classes = ('plane', 'car', 'bird', 'cat','deer', 'dog', 'frog', 'horse', 'ship', 'truck')
2 定义神经网络
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class Net(nn.Module):
#定义卷积层、池化层、线性映射等
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 6, 5)
self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(16 * 5 * 5, 120)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(120, 84)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(84, 10)
#定义前向运算
def forward(self, x):
x = self.pool(F.relu(self.conv1(x)))
x = self.pool(F.relu(self.conv2(x)))
x = torch.flatten(x, 1) # flatten all dimensions except batch
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = F.relu(self.fc2(x))
x = self.fc3(x)
return x
net = Net()
3 定义损失函数和优化器
import torch.optim as optim
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.001, momentum=0.9)
4 训练神经网络
for epoch in range(2): # loop over the dataset multiple times
running_loss = 0.0
for i, data in enumerate(trainloader, 0):
# get the inputs; data is a list of [inputs, labels]
inputs, labels = data
# zero the parameter gradients
optimizer.zero_grad()
# forward + backward + optimize
outputs = net(inputs)
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# print statistics
running_loss += loss.item()
if i % 2000 == 1999: # print every 2000 mini-batches
print('[%d, %5d] loss: %.3f' %
(epoch + 1, i + 1, running_loss / 2000))
running_loss = 0.0
print('Finished Training')
5 保存模型
PATH = './cifar_net.pth'
torch.save(net.state_dict(), PATH)
6 测试模型
correct = 0
total = 0
# since we're not training, we don't need to calculate the gradients for our outputs
with torch.no_grad():
for data in testloader:
images, labels = data
# calculate outputs by running images through the network
outputs = net(images)
# the class with the highest energy is what we choose as prediction
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)
total += labels.size(0)
correct += (predicted == labels).sum().item()
print('Accuracy of the network on the 10000 test images: %d %%' % (
100 * correct / total))
7 在GPU上训练
在cpu上训练则无需做如下改动
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
#将网络移到gpu上
net.to(device)
#将数据移到gpu上
inputs, labels = data[0].to(device), data[1].to(device)
8 最终代码(GPU版本)
import torch
import torchvision
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
transform = transforms.Compose([transforms.ToTensor(),transforms.Normalize((0.5,0.5,0.5),(0.5,0.5,0.5))])
batch_size = 4
trainset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root='./data',train=True,download=True,transform=transform)
trainloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(trainset,batch_size=batch_size,shuffle=True,num_workers=2)
testset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root='./data',train=False,download=True,transform=transform)
testloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(testset,batch_size=batch_size,shuffle=False,num_workers=2)
classes = ('plane', 'car', 'bird', 'cat','deer', 'dog', 'frog', 'horse', 'ship', 'truck')
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 6, 5)
self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(16 * 5 * 5, 120)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(120, 84)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(84, 10)
def forward(self,x):
x = self.pool(F.relu(self.conv1(x)))
x = self.pool(F.relu(self.conv2(x)))
x = torch.flatten(x, 1) # flatten all dimensions except batch
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = F.relu(self.fc2(x))
x = self.fc3(x)
return x
net = Net()
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
net.to(device)
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.001, momentum=0.9)
if __name__ == '__main__':
for epoch in range(2):
running_loss = 0.0
for i,data in enumerate(trainloader,0):
inputs, labels = data[0].to(device), data[1].to(device)
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = net(inputs)
loss = criterion(outputs,labels)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
running_loss+= loss.item()
if i%2000 ==1999:
print('[%d, %5d] loss: %.3f' %
(epoch + 1, i + 1, running_loss / 2000))
running_loss = 0.0
print('Finished Training')
PATH = './cifar_net.pth'
torch.save(net.state_dict(), PATH)
correct = 0
total = 0
# since we're not training, we don't need to calculate the gradients for our outputs
with torch.no_grad():
for data in testloader:
images, labels = data[0].to(device), data[1].to(device)
# calculate outputs by running images through the network
outputs = net(images)
# the class with the highest energy is what we choose as prediction
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)
total += labels.size(0)
correct += (predicted == labels).sum().item()
print('Accuracy of the network on the 10000 test images: %d %%' % (
100 * correct / total))