【数据结构day04--静态链表】
文章目录
-
- 前言
- 一、静态链表的定义
-
-
- 结构描述
- 代码描述
-
- 二、静态链表的基本操作
-
-
- 初始化
- 打印链表
- 静态链表的插入
- 静态链表的删除
-
- 三、完整代码及运行截图
-
-
- 完整代码如下:
- 运行截图
-
- 四、闵版(略改)
前言
C语言的指针能十分方便的描述链表,但在一些语言,如Basic、Fortran等早期语言中由于没有指针,链表结构就不能用指针来描述,因此便出现了用数组来代替指针来描述单链表的方法。
一、静态链表的定义
结构描述
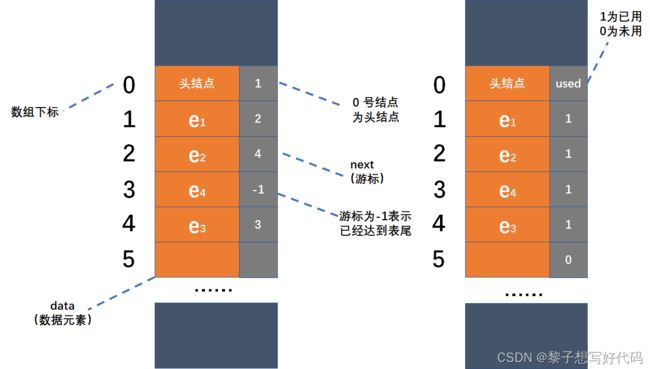
此处用于描述链表的数组由两个数据域组成,data和next。即数组的每个下标都对应一个data和一个next。其中,数据域data用来存放数据元素,而next相当于单链表中的next指针,用来存放该元素的后继元素在数组中的下标。这种用数组描述的链表叫做静态链表。静态链表的结构图示如下:
代码描述
typedef struct StaticLinkedNode
{
char data;
int next;
} *NodePtr,Node;
typedef struct StaticLinkedList
{
NodePtr node;
int* used;
} *ListPtr,List;
注意:为了方便插入数据,通常会把数组建立的大一些,以便有空闲空间可以便于插入时不至于溢出。
二、静态链表的基本操作
初始化
//初始化链表
ListPtr initLinkedList()
{
ListPtr tempPtr = (ListPtr)malloc(sizeof(List));
tempPtr->node = (NodePtr)malloc(sizeof(Node)*MAXSIZE);
tempPtr->used = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*MAXSIZE);
tempPtr->node[0].data = '\0';
tempPtr->node[0].next = -1;
tempPtr->used[0] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < MAXSIZE; ++i)
{
tempPtr->used[i] = 0;
}
return tempPtr;
}
打印链表
//打印链表
void printList(ListPtr tempPtr)
{
int p = 0;
while (p != -1)
{
printf("%c",tempPtr->node[p].data);
p = tempPtr->node[p].next;
}
printf("\n");
}
静态链表的插入
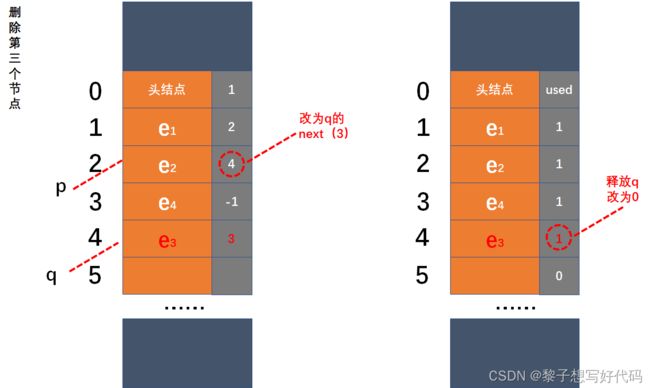
在动态链表中,结点的申请和释放分别借用malloc()和free()两个函数实现,而在静态链表中,操作的是数组,不存在像动态链表的结点申请和释放问题,为了辨别数组中空间是否被使用,用一个used数组来存储值,其中1为被使用,0为未使用,图示如下:
代码如下:
//插入
void ListInsert(ListPtr tempPtr, int insertPosition, char insertChar)
{
if(insertPosition <= 0)
{
printf("The position %d out of range of linked list!\n",insertPosition);
return ;
}
int p,q,i;
p = 0;
for(i = 1; i < insertPosition; ++i)
{
p = tempPtr->node[p].next;
if(p == -1)
{
printf("The position %d out of range of linked list!\n",insertPosition);
return ;
}
}
for(i = 1; i < MAXSIZE; ++i)
{
if(tempPtr->used[i] == 0)
{
tempPtr->used[i] = 1;
q = i;
break;
}
}
if(i == MAXSIZE)
{
printf("There is no space to insert new nodes!\n");
return ;
}
tempPtr->node[q].data = insertChar;
tempPtr->node[q].next = tempPtr->node[p].next;
tempPtr->node[p].next = q;
}
静态链表的删除
有了对静态链表插入的理解,对于静态链表的删除就容易理解了,图示如下:
代码如下:
//删除第一个数据域为x的节点
void ListDeleteByData(ListPtr tempPtr, char DeleteChar)
{
int p,q;
p = 0;
while((tempPtr->node[p].next != -1) && (tempPtr->node[tempPtr->node[p].next].data) != DeleteChar)
{
p = tempPtr->node[p].next;
}
if(tempPtr->node[p].next == -1)
{
printf("Can't delete %c!\n",DeleteChar);
return ;
}
q = tempPtr->node[p].next;
tempPtr->node[p].next = tempPtr->node[q].next;
tempPtr->used[q] = 0;
}
//删除第Position个节点
void ListDeleteByPosition(ListPtr tempPtr, int Position)
{
int j = 1;
int p,q;
p = 0;
while((tempPtr->node[p].next != -1) && j < Position)
{
p = tempPtr->node[p].next;
++j;
}
if((tempPtr->node[p].next == -1) || j > Position)
{
printf("The position %d out of range of linked list!\n",Position);
return ;
}
q = tempPtr->node[p].next;
tempPtr->node[p].next = tempPtr->node[q].next;
tempPtr->used[q] = 0;
}
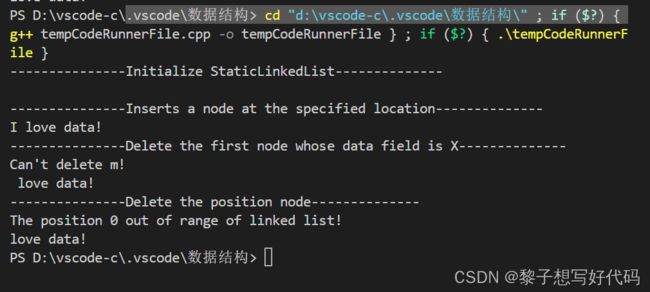
三、完整代码及运行截图
完整代码如下:
#include 运行截图
四、闵版(略改)
#include