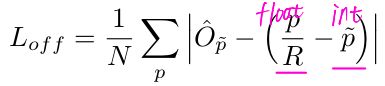[paper reading] CenterNet (Object as Points)
[paper reading] CenterNet (Object as Points)
GitHub:Notes of Classic Detection Papers
2020.11.09更新:更新了Use Yourself,即对于本文的理解和想法,详情参见GitHub:Notes-of-Classic-Detection-Papers
本来想放到GitHub的,结果GitHub不支持公式。
没办法只能放到CSDN,但是格式也有些乱
强烈建议去GitHub上下载源文件,来阅读学习!!!这样阅读体验才是最好的
当然,如果有用,希望能给个star!
| topic | motivation | technique | key element | math | use yourself | relativity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CenterNet (Object as Points) |
Problem to Solve Idea |
CenterNet Architecture | Center Point & Anchor Getting Ground-Truth Model Output Data Augmentation Inference TTA Compared with SOTA Additional Experiments |
Loss Function KeyPoint Loss L k \text{L}_k Lk Offset Loss L o f f \text{L}_{off} Loff Size Loss L s i z e \text{L}_{size} Lsize |
…… | Anchor-Based KeyPoint-Based |
文章目录
- [paper reading] CenterNet (Object as Points)
-
- Motivation
-
- Problem to Solve
- Idea
- Technique
-
- CenterNet Architecture
-
- Components
- Advantage
- Key Element
-
- Center Point & Anchor
-
- Connection
- Difference
- Getting Ground-Truth
-
- Keypoint Ground-Truth
-
- Ground-Truth:Input Image ==> Output Feature Map
- Gaussian Penalty Reduction
- Size Ground-Truth
- Model Output
- Data Augmentation
- Inference
- TTA
- Compared with SOTA
- Additional Experiments
-
- Center Point Collision
- NMS
- Training & Testing Resolution
- Regression Loss
- Bounding Box Size Weight
- Training Schedule
- Math
-
- Symbol Definition
- Loss Function
- KeyPoint Loss L k \text{L}_k Lk
- Offset Loss L o f f \text{L}_{off} Loff
- Size Loss L s i z e \text{L}_{size} Lsize
- Use Yourself
- Related work
-
- Anchor-Based Method
-
- Essence
- Two-Stage Method
- One-Stage Method
- Post-Processing(NMS)
- KeyPoint-Based Method
-
- Essence
- CornerNet
- ExtremeNet
- Drawback
Motivation
Problem to Solve
anchor-based method有以下的缺点:
-
wasteful & inefficient:
需要对object进行饱和式检测(饱和式地列出object的潜在位置)
-
need post-processing(e.g. NMS)
Idea
-
从本质上讲:
将Object Detection转化为Standard Keypoint Estimation
-
从思路上讲:
使用bounding box的center point表示一个object
-
从具体流程上讲:
使用keypoint estimation寻找center point,并根据center point回归其他的属性(因为其他的属性都和center point存在确定的数学关系)
Technique
CenterNet Architecture
Components
-
Backbone
-
Stacked Hourglass Network
详见 [CornerNet](./[paper reading] RetinaNet.md)
-
Upconvolutional Residual Netwotk
-
Deep Layer Aggregation(DLA)
-
-
Task-Specific Modality
- 1 个 3×3 Convolution
- ReLU
- 1 个 1×1 Convolution
Advantage
-
simpler & faster & accurate
-
end-to-end differential
所有的输出都是直接从keypoint estimation network输出,不需要NMS(以及其他post-processing)
Peak Keypoint Extraction由 3 × 3 Max Pooling 3×3 \ \text{Max Pooling} 3×3 Max Pooling 实现,足够用来替换NMS
-
estimate additional object properties in one single forward pass
在单次前向传播中,可以估计出多种object properties
Key Element
Center Point & Anchor
Connection
center point可以看作是shape-agnostic anchor(形状不可知的anchor)
Difference
-
center point仅仅与location有关(与box overlap无关)
即:不需要手动设置foreground和background的threshold
-
每个object仅对应1个center point
直接在keypoint heatmap上提取local peak,不存在重复检测的问题
-
CenterNet有更大的输出分辨率
降采样步长为4(常见为16)
Getting Ground-Truth
详见 [Symbol Definition](#Symbol Definition)
Keypoint Ground-Truth
Ground-Truth:Input Image ==> Output Feature Map
- p ∈ R 2 p \in \mathcal{R}^2 p∈R2 :ground-truth keypoint
- p ~ = ⌊ p R ⌋ \widetilde{p} = \lfloor\frac pR \rfloor p =⌊Rp⌋ :low-resolution equivalent
将image的ground-truth keypoint p p p 映射为output feature map上ground-truth keypoint p ~ \widetilde p p
p ~ = ⌊ p R ⌋ \widetilde{p} = \lfloor\frac pR \rfloor p =⌊Rp⌋
Gaussian Penalty Reduction
Y x y c = exp ( − ( x − p ~ x ) 2 + ( y − p ~ y ) 2 2 σ p 2 ) Y_{x y c}=\exp \left(-\frac{\left(x-\tilde{p}_{x}\right)^{2}+\left(y-\tilde{p}_{y}\right)^{2}}{2 \sigma_{p}^{2}}\right) Yxyc=exp(−2σp2(x−p~x)2+(y−p~y)2)
- σ p \sigma_{p} σp :object size-adaptive的标准差
如果同一个类别的2个Gaussian发生重叠,则取element-wise maximum
keypoint heatmap:
Y ^ ∈ [ 0 , 1 ] W R × H R × C \hat{Y}\in[0,1]^{\frac{W}{R}×\frac HR×C} Y^∈[0,1]RW×RH×C
- Y ^ x , y , c = 1 \hat Y _{x,y,c} =1 Y^x,y,c=1 ==> keypoint
- Y ^ x , y , c = 0 \hat Y _{x,y,c} =0 Y^x,y,c=0 ==> background
注意:这里的center是bounding box的几何中心,即center到左右边和上下边的距离是相等的
Size Ground-Truth
bounding box 用4个点表示(第 k k k 个object,类别为 c k c_k ck):
( x 1 ( k ) , y 1 ( k ) , x 2 ( k ) , y 2 ( k ) ) (x_1^{(k)}, y_1^{(k)}, x_2^{(k)}, y_2^{(k)}) (x1(k),y1(k),x2(k),y2(k))
Center 表示为:
p k = ( x 1 ( k ) + x 2 ( k ) 2 , y 1 ( k ) + y 2 ( k ) 2 ) p_k = \big( \frac{x_1^{(k)} + x_2^{(k)} }{2} , \frac{y_1^{(k)} + y_2^{(k)} }{2} \big) pk=(2x1(k)+x2(k),2y1(k)+y2(k))
Size Ground-Truth 表示为:
s k = ( x 2 ( k ) − x 1 ( k ) , y 2 ( k ) − y 1 ( k ) ) s_k = \big(x_2^{(k)} - x_1^{(k)}, y_2^{(k)}-y_1^{(k)} \big) sk=(x2(k)−x1(k),y2(k)−y1(k))
注意:不对scale进行归一化,而是直接使用raw pixel coordinate
Model Output
Input & Output Resolution:
- 512×512
- 128×128
所有的输出共享一个共用的全卷积网络
- keypoint Y ^ \hat Y Y^ ==> C C C
- offset O ^ \hat O O^ ==> 2
- size S ^ \hat S S^ ==> 2
即:每个location都有C+4个output
对于each modality,在将feature经过:
- 1 个 3×3 Convolution
- ReLU
- 1 个 1×1 Convolution
Data Augmentation
-
random flip
-
random scaling(0.6~1.3)
-
cropping
-
color jittering
Inference
CenterNet的Inference是single network forward pass
-
将image输入backbone(e.g. FCN),得到3个输出:
-
keypoint Y ^ \hat Y Y^ ==> C C C
heatmap的peak对应object的center(取top-100)
peak的判定:值 ≥ \ge ≥ 其8个邻居
-
offset O ^ \hat O O^ ==> 2
-
size S ^ \hat S S^ ==> 2
-
-
根据keypoint Y ^ \hat Y Y^、 offset O ^ \hat O O^、size S ^ \hat S S^ 计算bounding box
- ( δ x ^ i , δ x ^ i ) = O ^ x ^ i , y ^ i (\delta \hat x_i, \delta \hat x_i) = \hat O_{\hat x_i, \hat y_i} (δx^i,δx^i)=O^x^i,y^i :offset prediction
- ( w ^ i , h ^ i ) = S ^ x ^ i , y ^ i ( \hat w_i, \hat h_i) = \hat S _{\hat x_i, \hat y_i} (w^i,h^i)=S^x^i,y^i :size prediction
-
计算keypoint的confidence:keypoint对应位置的value
Y ^ x i , y i c \hat Y_{x_i,y_ic} Y^xi,yic
TTA
有3种TTA方式:
-
no augmentation
-
flip augmentation
flip:在decoding之前,进行output average
-
flip & multi-scale(0.5,0.75,1,1.25,1.5)
multi-scale:使用NMS对结果进行聚合
Compared with SOTA
Additional Experiments
Center Point Collision
多个object经过下采样,其center keypoint有可能重叠
CenterNet可以减少Center Keypoint的冲突
NMS
CenterNet使用了NMS提升很小,说明CenterNet不需要NMS
Training & Testing Resolution
- 低分辨率速度最快但是精度最差
- 高分辨率精度提高,但速度降低
- 原尺寸速度略高于高分辨率,但速度略慢
Regression Loss
smooth L1 Loss的效果略差于L1 Loss
Bounding Box Size Weight
λ s i z e \lambda_{size} λsize 为0.1时最佳,增大时AP快速衰减,减小时鲁棒
Training Schedule
训练时间更长,效果更好
Math
Symbol Definition
- I ∈ R W × H × 3 I \in R^{W×H×3} I∈RW×H×3 :image
- R R R :output stride,实验中为4
- C C C :keypoint的类别数
Loss Function
L d e t = L k + λ s i z e L s i z e + λ o f f L o f f \text{L}_{det} = \text{L}_k + \lambda_{size} \text{L}_{size} + \lambda_{off} \text{L}_{off} Ldet=Lk+λsizeLsize+λoffLoff
- λ s i z e = 0.1 \lambda_{size} = 0.1 λsize=0.1
- λ o f f = 1 \lambda_{off} = 1 λoff=1
KeyPoint Loss L k \text{L}_k Lk
penalty-reduced pixel-wise logistic regression with focal loss
.assets/image-20201105190626950.png)
![[paper reading] CenterNet (Object as Points)_第5张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/48c7b603039d4db782e15f9540e3ebee.jpg)
- Y ^ x y c \hat{Y}_{xyc} Y^xyc :predicted keypoint confidence
- α = 2 , β = 4 \alpha =2,\beta=4 α=2,β=4
Offset Loss L o f f \text{L}_{off} Loff
目的:恢复由下采样带来的离散化错误(discretization error)
- O ^ ∈ R W R × H R × 2 \hat O \in \mathcal R^{\frac{W}{R}×\frac HR×2} O^∈RRW×RH×2 :predicted local offset
注意:
- 仅仅对keypoint location(positive)计算
- 所有的类别共享相同的offset prediction
Size Loss L s i z e \text{L}_{size} Lsize
- S ^ p k ∈ R W R × H R × 2 \hat{S}_{p_{k}} \in \mathcal R^{\frac{W}{R}×\frac HR×2} S^pk∈RRW×RH×2
- s k = ( x 2 ( k ) − x 1 ( k ) , y 2 ( k ) − y 1 ( k ) ) s_k = \big(x_2^{(k)} - x_1^{(k)}, y_2^{(k)}-y_1^{(k)} \big) sk=(x2(k)−x1(k),y2(k)−y1(k))
Use Yourself
……
Related work
Anchor-Based Method
Essence
将detection降级为classification
Two-Stage Method
-
在image上放置anchor(同 [One-Stage Method](#One-Stage Method))
即:在low-resolution上dense & grid采样anchor,分类为foreground/background ==> proposal
具体的label:
-
foreground:
与任意ground-truth box有 > 0.7 的IoU
-
background:
与任意ground-truth box有 < 0.3 的IoU
-
ignored:
与任意ground-truth box 的IoU ∈ [ 0.3 , 0.7 ] \in [0.3, 0.7] ∈[0.3,0.7]
-
-
对anchor进行feature resample
比如:
- RCNN:在image上取crop
- Fast-RCNN:在feature map上取crop
One-Stage Method
- 在image上放置anchor
- 直接对anchor位置进行分类
one-stage method的一些改进:
- anchor shape prior
- different feature resolution(e.g. Feature Pyramid Network)
- loss re-weighting(e.g. Focal Loss)
Post-Processing(NMS)
-
Purpose:根据IoU,抑制相同instance的detections
-
Drawback:难以differentiate和train,导致绝大部分的detector无法做到end-to-end trainable
KeyPoint-Based Method
Essence
将detection转化为keypoint estimation
其Backbone均为KeyPoint Estimation Network
CornerNet
检测2个corner作为keypoints,表示1个bounding box
ExtremeNet
检测 top-most, left-most, bottom-most, right-most ,center 作为keypints
Drawback
对1个object检测多个keypoint,其需要额外的grouping stage(导致算法速度的降低)

![[paper reading] CenterNet (Object as Points)_第1张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/a13aa7136826416bae690a2ec3443f17.jpg)
![[paper reading] CenterNet (Object as Points)_第2张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/50068cbb287f4a6e8b63454eb31f5f4c.jpg)
![[paper reading] CenterNet (Object as Points)_第3张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/c8ce5210a3f34daeab218a1a9aee6fd6.jpg)
![[paper reading] CenterNet (Object as Points)_第4张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/ae367112af9c4d4c8cf8e2e718f42cc5.jpg)