计算机视觉PyTorch实现风格迁移
神经网络风格迁移
它主要是通过神经网络,将一幅艺术风格画(style image)和一张普通的照片(content image)巧妙地融合,形成一张非常有意思的图片。
大白话说,图像往往由风格与内容组成,比如我们常常说画家的画风是怎么样的,毕加索的画风、动漫的画风。
风格迁移就是保留一张图片的内容(物体,人物),用另一张图片的色彩画图风格去填充。
风格迁移原理
在介绍原理之前先普及一个知识点:
通常将图像输出到卷积神经网络中,在神经网络第一层隐藏层通常会找出一些简单的特征,比如边缘或者颜色阴影。在神经网络深层部分的一个隐藏单元会看到一张图片更大的部分,在极端的情况下,可以假设图像中每一个像素都会影响到神经网络层更深层的输出,靠后的隐藏层可以看到更大的图片块。
也就是说在神经网络中隐藏单元里从第一层的边缘到第二层的质地再到更深层的复杂物体
原理:
首先我们需要获取一张内容图片和一张风格图片;然后定义二个度量,一个度量值为内容度量值,另一个度量为风格度量值,其中内容度量值通过生成代价函数来衡量二个图片之间的内容差异程度,风格度量也通过生成代价函数衡量图片之间风格差异程度,最后建立生成图像的神经网络模型,对内容图片中的内容和风格图片的风格进行提取,以内容图片为基准将其输入建立的模型中,通过代价函数梯度下降来调整内容度量值和风格度量值,让它们趋近于最小,最后输出的图片就是内容和风格融合的图片。

1.生成图像代价函数
想要生成出我们想要的图像,就需要定义一个代价函数,通过最小化代价函数,你可以生成任何图像
我们用C表示内容图像,用S表示风格图像,用G表示想要生成的图像
我们定义一个关于图像G的代价函数J,通过J来判断我们生成图像的好坏,使用梯度下降法来去最小化J(G),以便于生成更好的图像。
图像代价函数
J ( G ) J(G) J(G)= α \alpha α J c o n t e n t ( C , G ) J_{content}(C,G) Jcontent(C,G)+ β \beta β J s t y l e ( S , G ) J_{style}(S,G) Jstyle(S,G)
这里公式中使用二个超参数 α \alpha α, β \beta β表示二者之间的权重,其实对于风格迁移完全可以使用一个参数来权衡就可以。
梯度下降求导:
G = G − G=G- G=G− ∂ ∂ G \frac{\partial}{\partial G} ∂G∂ J ( G ) J(G) J(G)
下图是通过一张内容图像和一张风格图像进行梯度下降逐渐优化的过程,通过梯度下降图像可视化过程,可以更好的理解。

代价函数梯度下降优化过程,生成图像的变化:

2.内容代价函数
α \alpha α J c o n t e n t ( C , G ) J_{content}(C,G) Jcontent(C,G)
在卷积神经网络中如果选择的隐藏层是浅层,那上面的像素会非常接近你的内容图片,如果选择的是高层的,那么内容图片里就会判别像素是否存在一些物体(是否存在有狗),因此在选择内容图像的时候,选择网络隐藏层单元中既不要选很浅层也不要选很高层的。
内容代价函数:
α \alpha α J c o n t e n t ( C , G ) J_{content}(C,G) Jcontent(C,G)= 1 2 ∣ ∣ a [ l ] ( C ) − a [ l ] ( G ) ∣ ∣ 2 \frac12||a^{[l](C)}-a^{[l](G)}||^2 21∣∣a[l](C)−a[l](G)∣∣2
a [ l ] ( C ) a [ l ] ( G ) a^{[l](C)}a^{[l](G)} a[l](C)a[l](G)各自表示内容图经过I层卷积层得到的特征图、生成图经过卷积层生成的特征图。把他们两个作差并平方求和(不仅记录一层卷积层特征图的差异),使生成图的特征图越接近于内容图的特征图,这样就可以保留内容信息。在做代价函数梯度下降时,整个函数会激励内容代价函数算法来找到图像G,使隐藏层的激活值和内容图像相似。
3.风格代价函数
这里我们用Gram矩阵表示图像的风格特征,对于每一张图片,卷积层的输出形状为 C × H × W C\times H\times W C×H×W,C是卷积核的通道数,每个卷积核学习图像不同特征,每个卷积核输出 H × W H\times W H×W代表这张图像的一个feature map,这里把一张彩色图像看成RGB三个feature map拼接组合成的feature map。通过计算每一个通道的feature map之间相似性,得到图像风格特征。
Gram矩阵计算公式如下:
G k 1 k 2 [ l ] ( S ) G_{k_1k_2}^{[l](S)} Gk1k2[l](S)= ∑ i = 1 n i l ∑ j = 1 n j l a i j k 1 [ l ] ( S ) a i j k 2 [ l ] ( S ) \sum_{i=1}^{n_i^l}\sum_{j=1}^{n_j^l}a_{ijk_1}^{[l](S)}a_{ijk_2}^{[l](S)} ∑i=1nil∑j=1njlaijk1[l](S)aijk2[l](S)
其中:
a i j k 1 [ l ] ( S ) a_{ijk_1}^{[l](S)} aijk1[l](S)代表第 k 1 k_1 k1个feature map矩阵,位置是i,j的像素点。
G k 1 k 2 [ l ] ( S ) G_{k_1k_2}^{[l](S)} Gk1k2[l](S)代表二个feature map(二个通道)的第I层所有像素点乘积和。
风格代价函数:
J s t y l e l ( S , G ) J_{style}^l(S,G) Jstylel(S,G)= ∣ ∣ G [ l ] [ S ] − G [ l ] [ G ] ∣ ∣ 2 ||G^{[l][S]}-G^{[l][G]}||^2 ∣∣G[l][S]−G[l][G]∣∣2
J s t y l e l ( S , G ) J_{style}^l(S,G) Jstylel(S,G)= 1 ( 2 H l W l C l ) 2 1 \over (2H^lW^lC^l)^2 (2HlWlCl)21 ∑ k 1 ∑ k 2 ( G k 1 k 2 [ l ] ( S ) − G k 1 k 2 [ l ] ( G ) ) \sum_{k_1}\sum_{k_2}(G_{k_1k_2}^{[l](S)}-G_{k_1k_2}^{[l](G)}) ∑k1∑k2(Gk1k2[l](S)−Gk1k2[l](G))
其中 H l W l C l H^lW^lC^l HlWlCl代表第I层的长、宽、通道数。
风格迁移算法实现
2016年Justin Johnson提出一种快速风格迁移算法,这种算法称之为Fast Neural Style。
Fast Neural Style网络结构如下图所示, x x x是输入图像,在风格迁移任务是 y c y_c yc表示内容图像, y s y_s ys表示风格图像,Image Transform Net f w f_w fw是设计出的风格迁移网络,针对输入的图像 x x x,能够返回一张新的图像 y ^ \hat{y} y^, y ^ \hat{y} y^在图像内容上与 y c y_c yc相似,但在风格上与 y s y_s ys相似,在损失网络下,采用VGG-16实现。
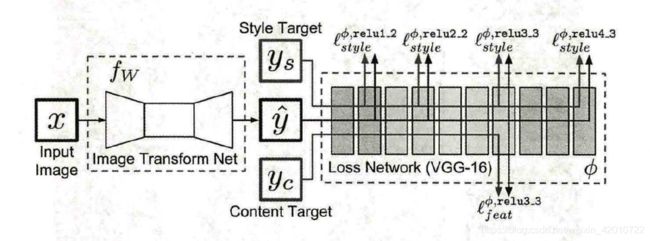
VGG-16网络结构如下图所示:

Fast Neuarl Style训练步骤如下:
- 输入一张图片 x x x到 f w f_w fw中得到结果 y ^ \hat{y} y^。
- 将 y ^ \hat{y} y^和 y c y_c yc输入到loss network(VGG-16)中,计算它在relu3_3的输出,并计算它们之间的均方差content loss。
- 将 y ^ \hat{y} y^和 y s y_s ys输入到loss network中,计算它在relu1_2、relu2_2、relu3_3和relu4_3的输出,再计算它们的Gram Matrix的均方差作为style loss。
- 两个损失相加,并反向传播,更新 f w f_w fw参数
- 跳回第一步,继续训练 f w f_w fw
PyTorch代码实现如下:
from __future__ import print_function
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torchvision
from torchvision import transforms,models
from PIL import Image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from torch.autograd import Variable
import copy
#%% 图像预处理
transform=transforms.Compose([transforms.Scale([128,128]),
transforms.ToTensor()])
def loadimg(path=None):
img=Image.open(path)
img=transform(img)
img=Variable(img)
img=img.unsqueeze(0)
return img
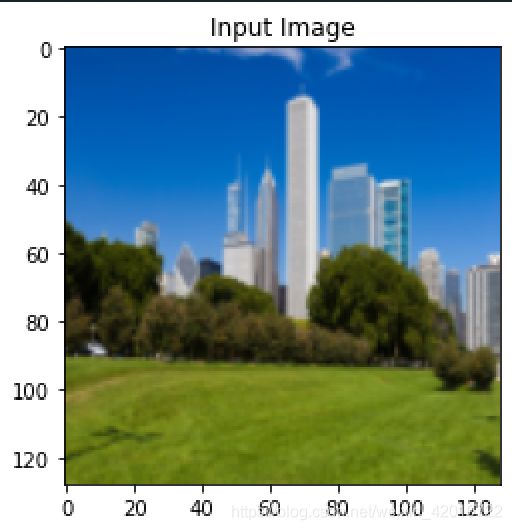
content_img=loadimg("3.jpg")
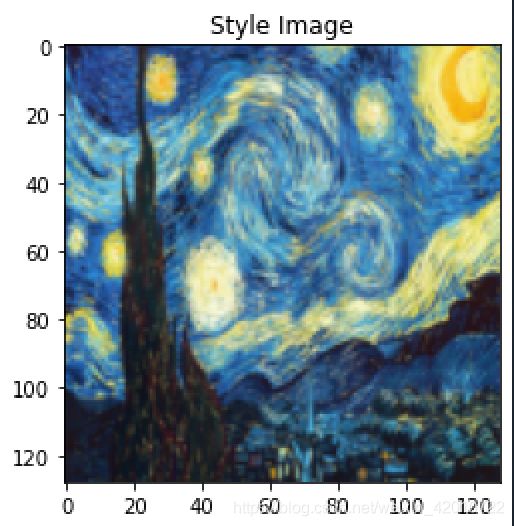
style_img=loadimg("1.jpg")
#%% 显示图片
unloader = transforms.ToPILImage() # 重新转换成PIL图像
plt.ion()
def imshow(tensor, title=None):
image = tensor.clone().cpu() # 我们克隆张量以不对其进行修改
image = image.view(3, 128, 128) # 删除批量处理维度
image = unloader(image)
plt.imshow(image)
if title is not None:
plt.title(title)
plt.pause(0.001) # pause a bit so that plots are updated
plt.figure()
imshow(style_img.data, title='Style Image')
plt.figure()
imshow(content_img.data, title='Content Image')
#%% 内容损失
class Content_loss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,target,weight):
super(Content_loss, self).__init__()
self.weight=weight
self.target=target.detach()*weight
self.loss_fn=nn.MSELoss()
def forward(self,input):
self.loss=self.loss_fn(input*self.weight,self.target)
self.output = input
return self.output
def backward(self, retain_graph=True):
self.loss.backward(retain_graph=retain_graph)
return self.loss
#%% 风格损失
class Style_loss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, target, weight):
super(Style_loss, self).__init__()
self.target = target.detach() * weight
self.weight = weight
self.gram = Gram_matrix()
self.loss_fn = nn.MSELoss()
def forward(self, input):
self.output = input.clone()
self.G = self.gram(input)
self.G.mul_(self.weight)
self.loss = self.loss_fn(self.G, self.target)
return self.output
def backward(self, retain_graph=True):
self.loss.backward(retain_graph=retain_graph)
return self.loss
class Gram_matrix(nn.Module):
def forward(self,input):
a,b,c,d=input.size()
feature=input.view(a*b,c*d)
gram=torch.mm(feature, feature.t())
return gram.div(a*b*c*d)
#%% 模型搭建
vgg=models.vgg19(pretrained=True).features
content_layer=["Conv_4"]
style_layer=['conv_1', 'conv_2', 'conv_3', 'conv_4', 'conv_5']
def get_style_model_and_losses(vgg, style_img, content_img,
style_weight=1000, content_weight=1,
content_layers=content_layer,
style_layers=style_layer):
vgg = copy.deepcopy(vgg)
# just in order to have an iterable access to or list of content/syle
# losses
content_losses = []
style_losses = []
model = nn.Sequential() # the new Sequential module network
gram = Gram_matrix() # we need a gram module in order to compute style targets
# move these modules to the GPU if possible:
i = 1
for layer in list(vgg):
if isinstance(layer, nn.Conv2d):
name = "conv_" + str(i)
model.add_module(name, layer)
if name in content_layers:
# add content loss:
target = model(content_img).clone()
content_loss = Content_loss(target, content_weight)
model.add_module("content_loss_" + str(i), content_loss)
content_losses.append(content_loss)
if name in style_layers:
# add style loss:
target_feature = model(style_img).clone()
target_feature_gram = gram(target_feature)
style_loss = Style_loss(target_feature_gram, style_weight)
model.add_module("style_loss_" + str(i), style_loss)
style_losses.append(style_loss)
if isinstance(layer, nn.ReLU):
name = "relu_" + str(i)
model.add_module(name, layer)
if name in content_layers:
# add content loss:
target = model(content_img).clone()
content_loss = Content_loss(target, content_weight)
model.add_module("content_loss_" + str(i), content_loss)
content_losses.append(content_loss)
if name in style_layers:
# add style loss:
target_feature = model(style_img).clone()
target_feature_gram = gram(target_feature)
style_loss = Style_loss(target_feature_gram, style_weight)
model.add_module("style_loss_" + str(i), style_loss)
style_losses.append(style_loss)
i += 1
if isinstance(layer, nn.MaxPool2d):
name = "pool_" + str(i)
model.add_module(name, layer) # ***
return model, style_losses, content_losses
#%%输入图像
input_img = content_img.clone()
# if you want to use a white noise instead uncomment the below line:
# input_img = Variable(torch.randn(content_img.data.size())).type(dtype)
# add the original input image to the figue:
plt.figure()
imshow(input_img.data, title='Input Image')
#%%梯度下降
def get_input_param_optimizer(input_img):
# this line to show that input is a parameter that requires a gradient
input_param = nn.Parameter(input_img.data)
optimizer = torch.optim.LBFGS([input_param])
return input_param, optimizer
input_param,optimizer=get_input_param_optimizer(input_img)
#%%参数优化
def run_style_transfer(cnn, content_img, style_img, input_img, num_steps=300,
style_weight=1000, content_weight=1):
"""Run the style transfer."""
print('Building the style transfer model..')
model, style_losses, content_losses = get_style_model_and_losses(cnn,
style_img, content_img, style_weight, content_weight)
input_param, optimizer = get_input_param_optimizer(input_img)
print('Optimizing..')
run = [0]
while run[0] <= num_steps:
def closure():
# correct the values of updated input image
input_param.data.clamp_(0, 1)
optimizer.zero_grad()
model(input_param)
style_score = 0
content_score = 0
for sl in style_losses:
style_score += sl.backward()
for cl in content_losses:
content_score += cl.backward()
run[0] += 1
if run[0] % 50 == 0:
print("run {}:".format(run))
print('Style Loss : {:5f} Content Loss: {:5f}'.format(
style_score, content_score))
return style_score + content_score
optimizer.step(closure)
# a last correction...
input_param.data.clamp_(0, 1)
return input_param.data
#%% 输出图像
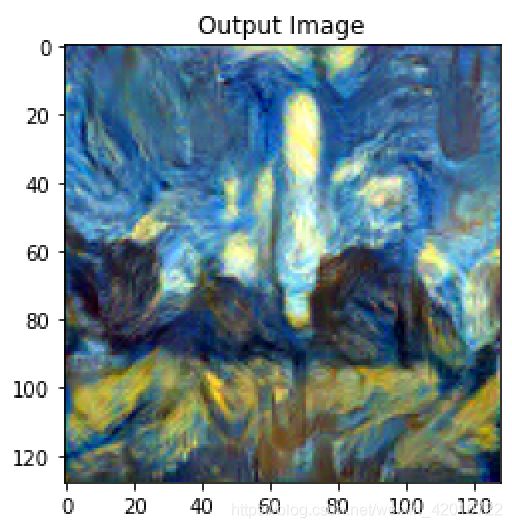
output = run_style_transfer(vgg, content_img, style_img, input_img)
plt.figure()
imshow(output,title="Output Image")
# sphinx_gallery_thumbnail_number = 4
plt.ioff()
plt.show()