周志华《机器学习》课后习题4.3(决策树)
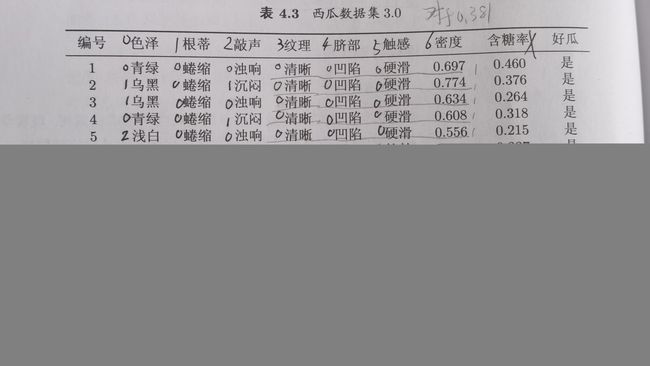
作业使用了如下数据集(不包括含糖率)
对各特征及取值进行编号
根据书上的方法进行编写

Divide_Select.py:
import math
data = [[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0.697, 1],
[1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0.774, 1],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0.634, 1],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0.608, 1],
[2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0.556, 1],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0.403, 1],
[1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0.481, 1],
[1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0.437, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0.666, 0],
[0, 2, 2, 0, 2, 1, 0.243, 0],
[2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 0, 0.245, 0],
[2, 0, 0, 2, 2, 1, 0.343, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0.639, 0],
[2, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0.657, 0],
[1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0.360, 0],
[2, 0, 0, 2, 2, 0, 0.593, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0.719, 0]]
divide_point = [0.244, 0.294, 0.351, 0.381, 0.420, 0.459, 0.518, 0.574, 0.600, 0.621, 0.636, 0.648, 0.661, 0.681, 0.708,
0.746]
# 计算信息熵
def Entropy(melons):
melons_num = len(melons)
pos_num = 0
nag_num = 0
for i in range(melons_num):
if melons[i][7] == 1:
pos_num = pos_num + 1
nag_num = melons_num - pos_num
p_pos = pos_num / melons_num
p_nag = nag_num / melons_num
entropy = -(p_pos * math.log(p_pos, 2) + p_nag * math.log(p_nag, 2))
return entropy
# 计算第charac项特征的的信息熵
# charac = 0~5
# 输出:[信息增益,第几个特征]
def Entropy_Gain(melons, charac):
charac_entropy = 0
entropy_gain = 0
melons_num = len(melons)
# 密度特征是连续特征
if charac >= 6:
# 对于某一个划分点,划分后的信息增益
density_entropy = list()
density0 = list()
density1 = list()
class0_small_num = 0 # 是否大于第i个划分点用big和small表示,是否是好瓜用0和1表示
class0_big_num = 0
class1_small_num = 0
class1_big_num = 0
for i in range(melons_num):
if melons[i][7] == 1:
if melons[i][6] > divide_point[charac - 6]:
class1_big_num = class1_big_num + 1
else:
class1_small_num = class1_small_num + 1
else:
if melons[i][6] > divide_point[charac - 6]:
class0_big_num = class0_big_num + 1
else:
class0_small_num = class0_small_num + 1
# 防止除零报错
if class0_small_num == 0 and class1_small_num == 0:
p0_small = 0
p1_small = 0
else:
p0_small = class0_small_num / (class0_small_num + class1_small_num)
p1_small = class1_small_num / (class0_small_num + class1_small_num)
if class0_big_num == 0 and class1_big_num == 0:
p0_big = 0
p1_big = 0
else:
p0_big = class0_big_num / (class0_big_num + class1_big_num)
p1_big = class1_big_num / (class0_big_num + class1_big_num)
# 防止log0的报错
if p0_small != 0 and p1_small != 0:
entropy_small = -(class0_small_num + class1_small_num) / melons_num * (
-(p0_small * math.log(p0_small, 2)
+ p1_small * math.log(p1_small, 2)))
elif p0_small == 0 and p1_small != 0:
entropy_small = -(class0_small_num + class1_small_num) / melons_num * (
-p1_small * math.log(p1_small, 2))
elif p0_small != 0 and p1_small == 0:
entropy_small = -(class0_small_num + class1_small_num) / melons_num * (
-p0_small * math.log(p0_small, 2))
else:
entropy_small = 0
#print(entropy_small)
if p0_big != 0 and p1_big != 0:
entropy_big = -(class0_big_num + class1_big_num) / melons_num * (
-(p0_big * math.log(p0_big, 2) + p1_big *
math.log(p1_big, 2)))
elif p0_big == 0 and p1_big != 0:
entropy_big = -(class0_big_num + class1_big_num) / melons_num * (
-p1_big * math.log(p1_big, 2))
elif p0_big != 0 and p1_big == 0:
entropy_big = -(class0_big_num + class1_big_num) / melons_num * (
-p0_big * math.log(p0_big, 2))
else:
entropy_big = 0
entropy_gain = Entropy(melons) + entropy_small + entropy_big
# 触感特征只有两种情况
elif charac == 5:
class0_melons = []
class1_melons = []
class_melons = [[], []]
for i in range(melons_num):
if melons[i][5] == 0:
class0_melons.append(melons[i][7])
else:
class1_melons.append(melons[i][7])
class_melons[0] = class0_melons
class_melons[1] = class1_melons
#print(class_melons)
for i in range(2):
class0_num = 0
class1_num = 0
total_num = len(class_melons[i])
for j in range(total_num):
if class_melons[i][j] == 0:
class0_num = class0_num + 1
else:
class1_num = class1_num + 1
p_class0 = class0_num / total_num
p_class1 = class1_num / total_num
if p_class0 != 0 and p_class1 != 0: # 防止log0的报错
entropy_class = -p_class0 * math.log(p_class0, 2) - p_class1 * math.log(p_class1, 2)
elif p_class0 == 0 and p_class1 != 0:
entropy_class = - p_class1 * math.log(p_class1, 2)
else:
entropy_class = -p_class0 * math.log(p_class0, 2)
charac_entropy = charac_entropy - total_num / melons_num * entropy_class
entropy_gain = Entropy(melons) + charac_entropy
# 其他特征有三种情况
else:
class0_melons = []
class1_melons = []
class2_melons = []
class_melons = [[], [], []]
for i in range(melons_num):
if melons[i][charac] == 0:
class0_melons.append(melons[i][7])
elif melons[i][charac] == 1:
class1_melons.append(melons[i][7])
else:
class2_melons.append(melons[i][7])
class_melons[0] = class0_melons
class_melons[1] = class1_melons
class_melons[2] = class2_melons
#print(class_melons)
for i in range(3):
class0_num = 0
class1_num = 0
total_num = len(class_melons[i])
# 避免除零报错
if total_num != 0:
for j in range(total_num):
if class_melons[i][j] == 0:
class0_num = class0_num + 1
else:
class1_num = class1_num + 1
p_class0 = class0_num / total_num
p_class1 = class1_num / total_num
if p_class0 != 0 and p_class1 != 0: # 防止log0的报错
entropy_class = -p_class0 * math.log(p_class0, 2) - p_class1 * math.log(p_class1, 2)
elif p_class0 == 0 and p_class1 != 0:
entropy_class = - p_class1 * math.log(p_class1, 2)
else:
entropy_class = -p_class0 * math.log(p_class0, 2)
charac_entropy = charac_entropy - total_num / melons_num * entropy_class
entropy_gain = Entropy(melons) + charac_entropy
else:
entropy_gain = 0
return [entropy_gain, charac]
# 输出:[信息增益,第几个特征]
def select_best_feature(melons, features):
best_feature = 0
max_entropy = Entropy_Gain(melons, features[0])
for i in range(len(features)):
entropy = Entropy_Gain(melons, features[i])
if entropy[0] > max_entropy[0]:
max_entropy = entropy
return max_entropy
tree.py:
from Divide_Select import *
import numpy as np
# 训练集data,属性集A
# 0色泽,1根蒂,2敲声,3纹理,4脐部,5触感,
# 对于密度,每个划分点算作一个特征,共16个划分点,即6~21
A = list(range(22))
def find_most(x):
return sorted([(np.sum(x == i), i) for i in np.unique(x)])[-1][-1]
def tree_generate(melons, features):
# 如果所有样本属于同一类别,返回该类别作为叶子节点
melons_y = [i[7] for i in melons]
if len(np.unique(melons_y)) == 1:
return melons_y[0]
# 如果features是空集或者所有样本在features上取值相同,返回多数类别作为叶子节点
same_flag = 1
for i in range(6): # 括号里填什么?
if len(np.unique([j[i] for j in melons])) > 1:
same_flag = 0
if not features or same_flag == 1:
return find_most(melons_y)
# 选出最优特征
[max_entropy, best_feature] = select_best_feature(melons, features)
node = {best_feature: {}}
division = list()
to_divide = list()
# 对于离散特征
if best_feature < 6:
division = [i[best_feature] for i in data] # 特征best_feature有division的可能性
to_divide = [i[best_feature] for i in melons] # 特征best_feature在melons中有to_divide的分支
# 对于连续特征
else:
for j in [i[6] for i in melons]:
if j > divide_point[best_feature - 6]:
to_divide.append(1)
else:
to_divide.append(0)
#to_divide = np.unique(to_divide)
division = [0, 1]
data_y = [i[7] for i in data]
for i in np.unique(division):
loc = list(np.where(to_divide == i))
if len(loc[0]) == 0: # 若该属性取此值的样本集为空,生成叶节点,其类别记为样本最多的类
test = find_most(melons_y)
node[best_feature][i] = find_most(melons_y)
else:
new_melons = []
for k in range(len(loc[0])):
new_melons.append(melons[loc[0][k]])
if best_feature in features: # 避免重复删除报错
features.remove(best_feature)
node[best_feature][i] = tree_generate(new_melons, features)
return node
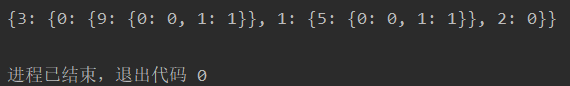
print(tree_generate(data, A))
与书上的答案一样
绘图的代码参考https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_40856057/article/details/89954058
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from pylab import *
# 定义文本框 和 箭头格式 【 sawtooth 波浪方框, round4 矩形方框 , fc表示字体颜色的深浅 0.1~0.9 依次变浅】
decisionNode = dict(boxstyle="square", pad=0.5,fc="0.8")
leafNode = dict(boxstyle="circle", fc="0.8")
arrow_args = dict(arrowstyle="<-")
# 控制显示中文
mpl.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
def getNumLeafs(myTree):
numLeafs = 0
firstStr = list(myTree.keys())[0]
secondDict = myTree[firstStr]
# 根节点开始遍历
for key in secondDict.keys():
# 判断子节点是否为dict, 不是+1
if type(secondDict[key]) is dict:
numLeafs += getNumLeafs(secondDict[key])
else:
numLeafs += 1
return numLeafs
def getTreeDepth(myTree):
maxDepth = 0
firstStr = list(myTree.keys())[0]
secondDict = myTree[firstStr]
# 根节点开始遍历
for key in secondDict.keys():
# 判断子节点是不是dict, 求分枝的深度
# ----------写法1 start ---------------
if type(secondDict[key]) is dict:
thisDepth = 1 + getTreeDepth(secondDict[key])
else:
thisDepth = 1
# ----------写法1 end ---------------
# ----------写法2 start --------------
# thisDepth = 1 + getTreeDepth(secondDict[key]) if type(secondDict[key]) is dict else 1
# ----------写法2 end --------------
# 记录最大的分支深度
maxDepth = max(maxDepth, thisDepth)
return maxDepth
def plotNode(nodeTxt, centerPt, parentPt, nodeType):
createPlot.ax1.annotate(nodeTxt, xy=parentPt, xycoords='axes fraction', xytext=centerPt, textcoords='axes fraction', va="center", ha="center", bbox=nodeType, arrowprops=arrow_args)
def plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt, txtString):
xMid = (parentPt[0] - cntrPt[0]) / 2 + cntrPt[0]
yMid = (parentPt[1] - cntrPt[1]) / 2 + cntrPt[1]
createPlot.ax1.text(xMid, yMid, txtString, va="center", ha="center", rotation=30)
def plotTree(myTree, parentPt, nodeTxt):
# 获取叶子节点的数量
numLeafs = getNumLeafs(myTree)
# 获取树的深度
# depth = getTreeDepth(myTree)
# 找出第1个中心点的位置,然后与 parentPt定点进行划线
cntrPt = (plotTree.xOff + (1 + numLeafs) / 2 / plotTree.totalW, plotTree.yOff)
# print(cntrPt)
# 并打印输入对应的文字
plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt, nodeTxt)
firstStr = list(myTree.keys())[0]
# 可视化Node分支点
plotNode(firstStr, cntrPt, parentPt, decisionNode)
# 根节点的值
secondDict = myTree[firstStr]
# y值 = 最高点-层数的高度[第二个节点位置]
plotTree.yOff = plotTree.yOff - 1 / plotTree.totalD
for key in secondDict.keys():
# 判断该节点是否是Node节点
if type(secondDict[key]) is dict:
# 如果是就递归调用[recursion]
plotTree(secondDict[key], cntrPt, str(key))
else:
# 如果不是,就在原来节点一半的地方找到节点的坐标
plotTree.xOff = plotTree.xOff + 1 / plotTree.totalW
# 可视化该节点位置
plotNode(secondDict[key], (plotTree.xOff, plotTree.yOff), cntrPt, leafNode)
# 并打印输入对应的文字
plotMidText((plotTree.xOff, plotTree.yOff), cntrPt, str(key))
plotTree.yOff = plotTree.yOff + 1 / plotTree.totalD
def createPlot(inTree):
# 创建一个figure的模版
fig = plt.figure(1, facecolor='green')
fig.clf()
axprops = dict(xticks=[], yticks=[])
# 表示创建一个1行,1列的图,createPlot.ax1 为第 1 个子图,
createPlot.ax1 = plt.subplot(111, frameon=False, **axprops)
plotTree.totalW = float(getNumLeafs(inTree))
plotTree.totalD = float(getTreeDepth(inTree))
# 半个节点的长度
plotTree.xOff = -0.1 / plotTree.totalW
plotTree.yOff = 0.5
plotTree(inTree, (0.5, 0.5), '')
plt.show()
# 根据tree.py输出的答案{3: {0: {9: {0: 0, 1: 1}}, 1: {5: {0: 0, 1: 1}}, 2: 0}}写出
myTree = {'纹理': {'清晰': {'密度大于0.381?': {'否': '坏瓜', '是': '好瓜'}}, '稍糊': {'触感': {'硬滑': '坏瓜', '软粘': '好瓜'}}, '模糊': '坏瓜'}}
createPlot(myTree)