数据结构(三)——详解栈和队列及完整代码实现
文章目录
- 一.栈
-
- 1.1 栈的逻辑结构
- 1.2 栈的顺序存储结构及实现
-
- 1.2.1 顺序栈的实现——入栈
- 1.2.2顺序栈的实现——出栈
- 1.2.3 两栈共享空间
- 1.3 栈的链接存储结构及实现
-
- 1.3.1 链栈的实现——入栈
- 1.3.2 链栈的实现——出栈
- 1.4 顺序栈和链栈的比较
- 二.队列
-
- 2.1 队列的逻辑结构
- 2.2 队列的顺序存储结构及实现
-
- 2.2.1 循环队列
- 2.2.2 循环队列的实现——入队
- 2.2.3 循环队列的实现——出队
- 2.2.4 循环队列的实现——读队头元素
- 2.3 队列的链接存储结构及实现
-
- 2.3.1 链队列的实现——构造函数
- 2.3.2 链队列的实现——入队
- 2.3.3 链队列的实现——出队
- 2.4 循环队列和链队列的比较
- 三 .栈和队列完整代码实现
-
- 3.1 顺序栈类模板实现:
- 3.2 链队列的代码实现:
- 3.3 循环队列实现代码
- 3.4 顺序栈,两栈共享,链栈的应用
两种特殊的线性表——栈和队列:
从数据结构角度看,栈和队列是操作受限的线性表,他们的逻辑结构相同。
从抽象数据类型角度看,栈和队列是两种重要的抽象数据类型。
一.栈
1.1 栈的逻辑结构
栈的相关定义:
1.栈:限定仅在表的一端进行插入和删除操作的线性表。
2.允许插入和删除的一端称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。
3. 空栈:不含任何数据元素的栈。
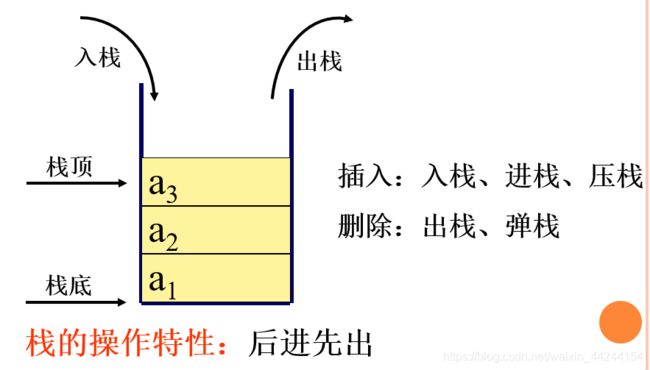
如上图所示,栈的插入和删除是有一定条件的,即栈顶的元素先出栈,下面的元素才能接着出,如果栈顶的元素 a 3 a3 a3没有出栈,那么下面的元素 a 2 、 a 1 a2、a1 a2、a1是不可能出栈的,就比如往弹夹里面压子弹一样,最上面的一发子弹没有射出去,下面的子弹自然不可能出去了——这就是栈的操作特性:后进先出
1.2 栈的顺序存储结构及实现
顺序栈是指栈的顺序存储结构,那么如何改造数组来实现栈的顺序存储呢?
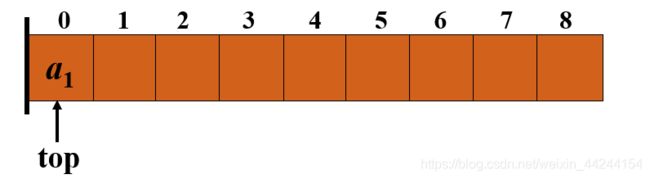
如上图所示,我们先确定用数组的哪一端表示栈底,假设我们用a[0]端作为栈底,附设指针top指示栈顶元素在数组中的位置。
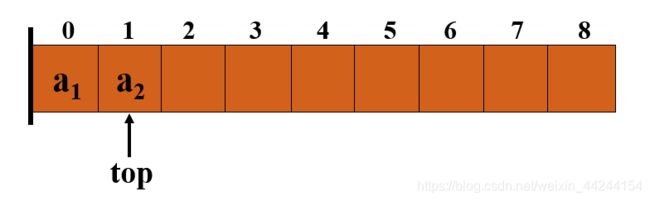
如果a2进栈的,就让top++,指向a2对应的位置

a3进栈,就让top++,指向a3对应的位置,同理,如果a3出栈了,就让top–,这样就用数组来实现栈的顺序存储,当栈空的适合,就让top=-1,而栈满的适合,则让top=数组的最大值-1.
1.2.1 顺序栈的实现——入栈
实现代码如下:
template <class DataType>
void seqStack<DataType> ::Push ( DataType x)
{
if (top == MAX_SIZE-1) throw “溢出”;
top++;
data[top] = x;
}
如果栈没有满的话,就让top++,然年把x压栈到数组中即可,而这两步可以合并为一步:

1.2.2顺序栈的实现——出栈
template <class DataType>
DataType seqStack<DataType> :: Pop ( )
{
if (top == -1) throw “溢出”;
x = data[top--];
return x;
}
原理很简单,再此处不多说啦
1.2.3 两栈共享空间
如果在一个程序中需要同时使用具有相同数据类型的两个栈,如何顺序存储这两个栈呢?
我们可以采用顺序栈单向延伸——使用一个数组来存储两个栈,即两栈共享空间:
使用一个数组来存储两个栈,让一个栈的栈底为该数组的始端,另一个栈的栈底为该数组的末端,两个栈从各自的端点向中间延伸。
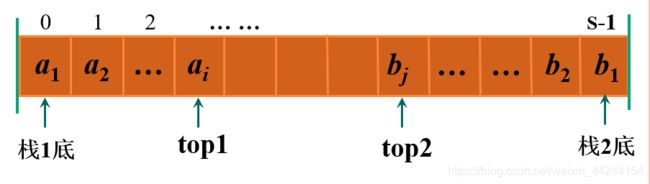
如上图所示,栈1的底固定在下标为0的一端;栈2的底固定在下标为StackSize-1的一端。
top1和top2分别为栈1和栈2的栈顶指针;Stack_Size为整个数组空间的大小(图中用S表示);
当top1== -1时,栈1为空
当top2= =Stack_Size时,栈2为空
而当top2= =top1+1时,栈满
1.3 栈的链接存储结构及实现
同理,我们应该如何改造链表实现栈的链接存储呢?
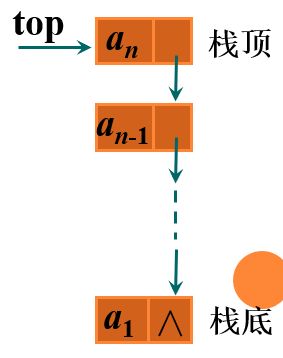
如上图所示,我们将链头作为栈顶,方便操作;且链栈不需要附设头结点。
1.3.1 链栈的实现——入栈
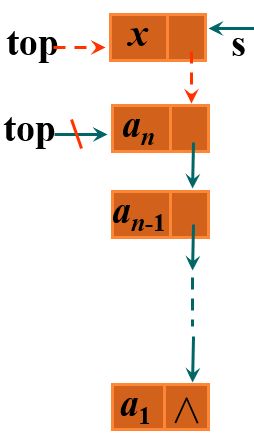
如上图所示,让入栈时,我们定义一个新的结点s,然后将x赋值给s的数据部分,然后让s的下一个结点指向top,再修改top指向新入栈的结点s即可。
实现代码如下:
template <class DataType>
void LinkStack<DataType> ::Push(DataType x)
{
s = new Node<DataType>;
s->data = x;
s->next = top;
top = s;
}
1.3.2 链栈的实现——出栈
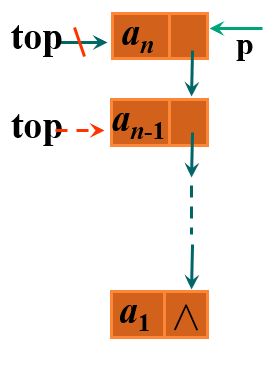
同理,出栈时,我们先存入x的值便于返回,然后让栈顶指针p指向结点top,修改top,让他指向他的下一个结点,删除结点p即可。
实现代码如下:
template <class DataType>
DataType LinkStack<DataType> ::Pop( )
{
if (top == NULL)
throw "下溢";
x = top->data;
p = top;
top = top->next;
delete p;
return x;
}
1.4 顺序栈和链栈的比较
时间性能:相同,都是常数时间O(1)。
空间性能:
顺序栈:有元素个数的限制和空间浪费的问题。
链栈:没有栈满的问题,只有当内存没有可用空间时才会出现栈满,但是每个元素都需要一个指针域,从而产生了结构性开销。
总之,当栈的使用过程中元素个数变化较大时,用链栈是适宜的,反之,应该采用顺序栈。
二.队列
2.1 队列的逻辑结构
队列的相关定义:
1.队列:只允许在一端进行插入操作,而另一端进行删除操作的线性表。
2. 允许插入(也称入队、进队)的一端称为队尾,允许删除(也称出队)的一端称为队头。
3. 空队列:不含任何数据元素的队列。

如上图所示,队列的特性是先出先进,也就和我们排队是一个道理。
2.2 队列的顺序存储结构及实现
如何才能改造数组实现队列的顺序存储呢?
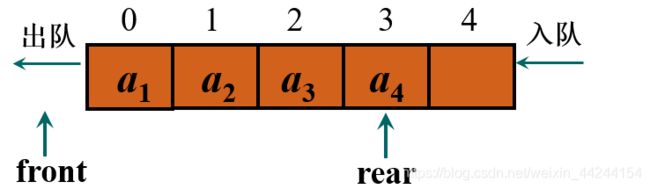
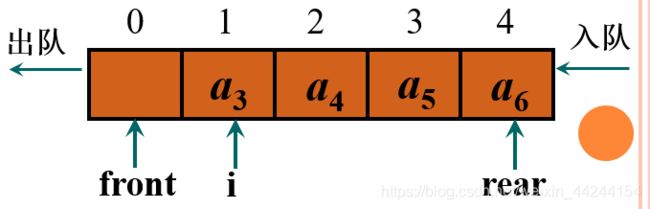
如上图所示,我们设置队头、队尾两个指针,分别约定:让队头指针front指向队头元素的前一个位置,让队尾指针rear指向队尾元素。
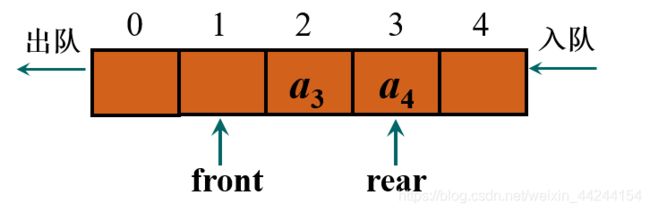
当a1、a2依次出队后,对头和队尾指针也跟着相应变化。
2.2.1 循环队列
假溢出:当元素被插入到数组中下标最大的位置上之后,队列的空间就用尽了,尽管此时数组的低端还有空闲空间,这种现象叫做假溢出。
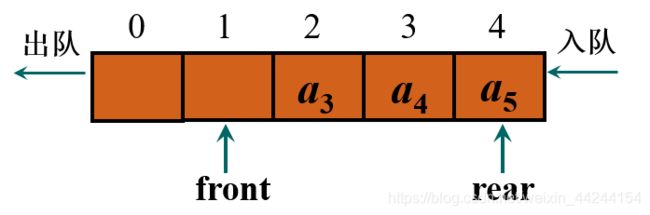
如上图所示,虽然0和1位置还空着,但由于rear指针已经到数组中下标最大的位置,便无法再插入了。
如何解决假溢出呢?
我们设置一个循环队列,将存储队列的数组头尾相接:
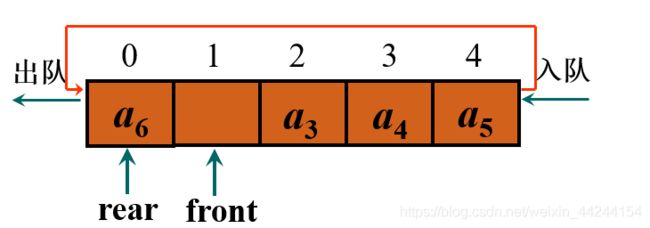
这样就能让rear指向前面的元素位置了。
但循环队列并不存在物理的循环结构,用软件方法求模实现,比如上图:
我们求模:(4+1)mod 5=0即可让rear指向0位置了
当需要执行出队操作,出队完成后,front==rear时,就表示队空了:
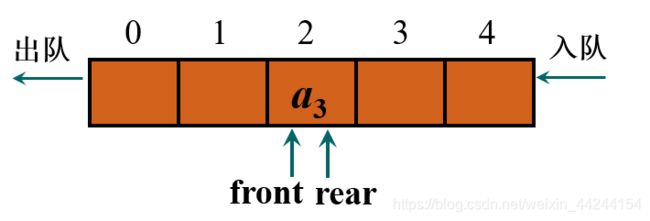

而当front==rear时,也能表示队满:
 如何才能确定不同的队空、队满的判定条件?有三种方法:
如何才能确定不同的队空、队满的判定条件?有三种方法:
方法一:附设一个存储队列中元素个数的变量num,
当num==0时队空,当num==QueueSize时为队满;
方法二:修改队满条件,浪费一个元素空间,队满时数组中只有一个空闲单元;
方法三:设置标志flag,当front==rear且flag==0时为队空,
当front==rear且flag==1时为队满。
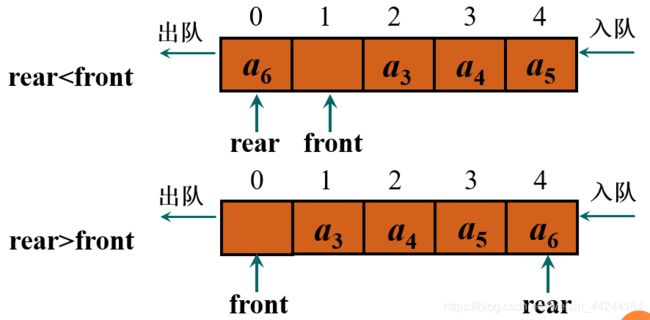
在此当(rear+1) mod QueueSize==front时为队满,当rear=front时队空
2.2.2 循环队列的实现——入队
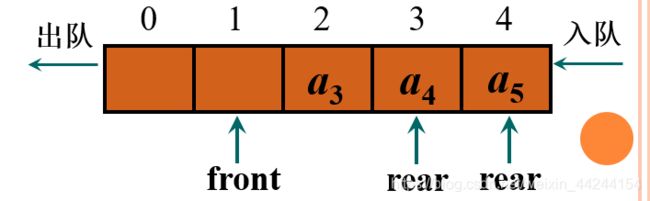
入队的适合,当(rear+1) % QueueSize与front相同时,就说明队满了,否则修改rear的指向,然后x赋值到rear对应的数组元素处即可。
实现代码如下:
template <class DataType>
void CirQueue<DataType> ::EnQueue(DataType x)
{
if ((rear+1) % QueueSize == front) throw "上溢";
rear =(rear+1) % QueueSize;
data[rear] = x;
}
2.2.3 循环队列的实现——出队

当a3进行出队操作时,当rear == front,表示队列为空,否则修改front的指向,返回data值即可,因为front指向的是队头元素的前一个位置。
代码实现如下:
template <class DataType>
DataType CirQueue<DataType> ::DeQueue( )
{
if (rear == front) throw "下溢";
front = (front + 1) % QueueSize;
return data[front];
}
2.2.4 循环队列的实现——读队头元素
template <class DataType>
DataType CirQueue<DataType> ::GetQueue( )
{
if (rear == front) throw "下溢";
i = (front + 1) % QueueSize;
return data[i];
}
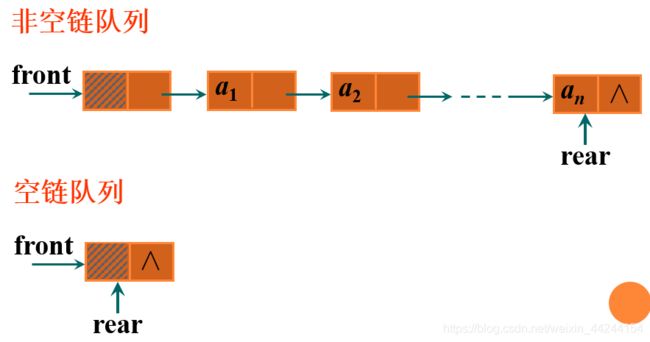
2.3 队列的链接存储结构及实现
2.3.1 链队列的实现——构造函数
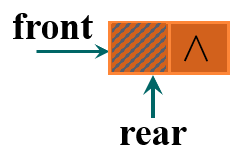
构造一个空链表,让队头和队尾指针都指向该结点即可
代码实现如下:
template <class DataType>
LinkQueue<DataType> ::LinkQueue( )
{
front = new Node<DataType>;
front->next = NULL;
rear = front;
}
2.3.2 链队列的实现——入队
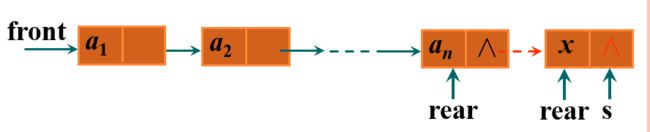
如上图所示,如果要插入结点s,那么让s的下一个结点为空,让rear的下一个结点指向s,再修改rear指向s即可
template <class DataType>
void LinkQueue<DataType> ::EnQueue(DataType x)
{
s = new Node<DataType>;
s->data = x;
s->next = NULL;
rear->next = s;
rear = s;
}
2.3.3 链队列的实现——出队
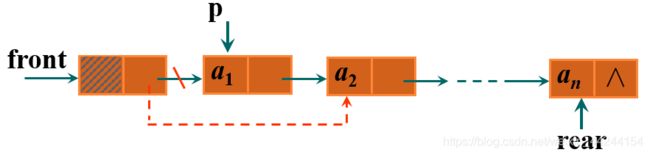
如上图所示,我们先让p结点为front的下一个结点,然后让front的下一个结点指向p的下一个结点,删除p结点即可
此处需要注意当队列中只有一个元素时,我们要让rear指向front,然后再删除p结点。
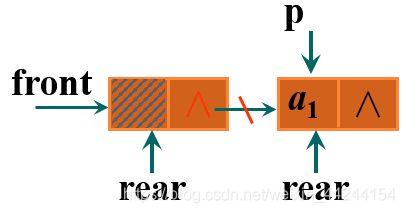
代码实现如下:
template <class DataType>
DataType LinkQueue<DataType> ::DeQueue( )
{
if (rear == front) throw "下溢";
p = front->next;
x = p->data;
front->next = p->next;
if (p->next == NULL) rear = front;
delete p;
return x;
}
2.4 循环队列和链队列的比较
时间性能:
循环队列和链队列的基本操作都需要常数时间O (1)。
空间性能:
循环队列:必须预先确定一个固定的长度,
所以有存储元素个数的限制和空间浪费的问题。
链队列:没有队列满的问题,只有当内存没有可用空间时才会出现队列满,
但是每个元素都需要一个指针域,从而产生了结构性开销。
三 .栈和队列完整代码实现
3.1 顺序栈类模板实现:
#include
}
template <class T>
T SqStack<T>::Pop()
{
T x;
if(top==-1) throw "栈空,不能出栈";
x=base[top--];
return x;
}
template <class T>
T SqStack<T>::GetTop()
{
if(top==-1)
throw "栈空,栈顶无元素";
return base[top];
}
template <class T>
int SqStack<T>::StackEmpty()
{
if(top==-1)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
template <class T>
void SqStack<T>::ClearStack()
{
top=-1;
}
template <class T>
void SqStack<T>::StackTop()
{//返回栈顶指针
cout<<"栈顶top= "<<top;
}
template <class T>
void SqStack<T>::StackTranverse()
{
int i=top;
while(i>=0)
cout<<base[i--]<<'\t';
cout<<endl;
}
char pause;
//主函数
int main()
{
int e;
SqStack<int> s(10);//建立容量为20、元素类型为整型的空栈
system("cls");//执行系统命令cls,清屏
int choice;
do
{//显示主菜单
cout<<"1-元素入栈\n";
cout<<"2-元素出栈\n";
cout<<"3-取栈顶元素\n";
cout<<"4-置栈空\n";
cout<<"5-测栈空\n";
cout<<"6-显示栈元素\n";
cout<<"7-显示栈顶指针\n";
cout<<"8-退出\n";
cout<<"Enter choice:";
cin>>choice;
switch(choice)
{
case 1://入栈
cout<<"请输入插入元素的值:";
cin>>e;//
cout<<endl;
try
{
s.Push(e);
}
catch(char *err)
{
cout<<err<<endl;
}
cin.get(pause);
system("pause");
break;
case 2://出栈
try
{
e=s.Pop ();
cout<<"出栈元素为:"<<e<<endl;
}
catch(char *err)
{
cout<<err<<endl;
}
cin.get(pause);
system("pause");
break;
case 3://获取栈顶元素
try
{
e=s.GetTop ();
cout<<"栈顶元素为:"<<e<<endl;
}
catch(char *err)
{
cout<<err<<endl;
}
cin.get(pause);
system("pause");
break;
case 4://清空栈
s.ClearStack();
cin.get(pause);
system("pause");
break;
case 5://测栈空
if(s.StackEmpty())
cout<<"栈空"<<endl;
else
cout<<"栈不空"<<endl;
cin.get(pause);
system("pause");
break;
case 6://遍历栈
s.StackTranverse();
cin.get(pause);
system("pause");
break;
case 7://显示栈顶指针
s.StackTop ();
break;
case 8://
cout<<"程序结束,Bye-Bye!"<<endl;
break;
default:
cout<<"Invalid choice\n";
break;
}
cout<<endl;
}while(choice!=8);
return 0;
}
3.2 链队列的代码实现:
# include3.3 循环队列实现代码
#include3.4 顺序栈,两栈共享,链栈的应用
#include