LinuxC进程编程
文章目录
- 一、fork
- 二、exec函数族
- 三、system
- 四、wait和waitpid
- 五、无名管道
- 六、有名管道
- 七、消息队列
- 八、共享内存
- 九、信号量
- 十、信号
一、fork
#include fork()函数用于创建一个和当前进程映像相同的子进程。fork执行一次,返回两次,可能有三种不同的值。如果执行成功,在父进程中返回子进程的ID,在子进程中返回0,如果执行失败返回-1;
vfork()函数功能与fork类似,二者区别如下:
- fork子进程拷贝父进程的数据段;vfork子进程与父进程共享数据段。
- fork父、子进程的执行次序不确定;vfork子进程先运行,父进程后运行。
#include 运行结果
atreus@atreus-virtual-machine:~/code/220317$ make
gcc -Wall main.c -o main
atreus@atreus-virtual-machine:~/code/220317$ ./main
I am a parent process, my pid is 8480, my child is 8481.
I am a child process, my pid is 8481, my parent is 8480.
atreus@atreus-virtual-machine:~/code/220317$
二、exec函数族
#include exec函数族用被执行的程序替换调用它的程序,以上六个函数均为库函数,最终都要执行系统调用execve来实现相应功能。
与fork创建一个新的进程,产生一个新的PID不同,exec会启动一个新程序,替换原有的进程,因此进程的PID不会改变。如果调用成功,exec不会有返回值,否则返回-1。
函数参数如下:
pathname:要执行的程序路径,可以是绝对路径或者是相对路径。在execl、execle和execv这3个函数中,使用带路径名的文件名作为参数。file:要执行的程序名称。如果该参数中包含/字符,则视为路径名直接执行。否则视为单独的文件名,系统将根据PATH环境变量指定的路径顺序搜索指定的文件。argv:被执行程序所需的命令行参数数组。envp:带有该参数的exec函数可以在调用时指定一个环境变量数组,其他不带该参数的exec函数则使用调用进程的环境变量,类似于main函数中的第三个参数。arg:要执行的程序的首个参数,即程序名本身,相当于argv[O]。...:命令行参数列表,调用相应程序时有多少命令行参数就需要有多少个输入参数项。注意:在使用此类函数时,在所有命令行参数的最后应该增加一个空的参数项NULL,表明命令行参数结束。
main.c
#include show.c
#include 运行结果
atreus@atreus-virtual-machine:~/code/220317$ gcc -Wall main.c -o main
main.c: In function ‘main’:
main.c:16:11: warning: unused variable ‘arg_vpe’ [-Wunused-variable]
16 | char *arg_vpe[MAX_SIZE] = {"show", "execvpe", NULL};
| ^~~~~~~
main.c:15:11: warning: unused variable ‘arg_vp’ [-Wunused-variable]
15 | char *arg_vp[MAX_SIZE] = {"show", "execvp", NULL};
| ^~~~~~
main.c:14:11: warning: unused variable ‘arg_v’ [-Wunused-variable]
14 | char *arg_v[MAX_SIZE] = {"show", "execv", NULL};
| ^~~~~
atreus@atreus-virtual-machine:~/code/220317$ gcc -Wall show.c -o show
atreus@atreus-virtual-machine:~/code/220317$ ./main
Parent porcess is 6753, my child porcess is 6754.
Show is execued by execle.
Child porcess is 6754, my parent porcess is 6753.
env[0] = my_path
atreus@atreus-virtual-machine:~/code/220317$
三、system
#include system()是一个封装好的库函数,而不是系统调用,它通过调用fork产生子进程,由子进程来执行execl("/bin/sh", "sh", "-c", command, (char *) NULL);,进而来执行参数command中的命令。
#include 运行结果
atreus@atreus-virtual-machine:~/code/220317$ make
gcc -Wall main.c -o main
atreus@atreus-virtual-machine:~/code/220317$ ./main
总用量 52
393231 -rwxrwxr-x 1 atreus atreus 16736 3月 21 10:24 main
393268 -rw-rw-r-- 1 atreus atreus 70 3月 21 10:24 main.c
393270 -rw-rw-r-- 1 atreus atreus 38 3月 21 09:54 makefile
393257 -rwxrwxr-x 1 atreus atreus 16872 3月 21 10:11 show
393620 -rw-rw-r-- 1 atreus atreus 521 3月 21 10:10 show.c
atreus@atreus-virtual-machine:~/code/220317$
四、wait和waitpid
#include wait()函数和waitpid()函数会使父进程等待子进程的退出,主要用于解决僵尸进程和孤儿进程。
僵尸进程和孤儿进程:
- 僵尸进程:一个父进程利用fork创建子进程,如果子进程退出,而父进程没有利用wait或者waitpid来获取子进程的状态信息,那么子进程的状态描述符依然保存在系统中。
- 孤儿进程:一个父进程退出,而它的一个或几个子进程仍然还在运行,那么这些子进程就会变成孤儿进程,孤儿进程将被init进程(PID为1)所收养,并由init进程对它们完成状态收集的工作。
UID PID PPID C STIME TTY TIME CMD
root 1 0 0 08:29 ? 00:00:01 /sbin/init splash
waitpid()函数函数参数如下:
pid:参数pid是需要等待的一个或多个进程的pid,它必须是下面这四种情况之一:
①<-1:等待所有这样的子进程,他们的组ID是参数pid的绝对值。例如传递-100表示等待所有在进程组100中的子进程。
②-1:等待任意子进程,和wait等效。
③0:等待与调用进程处于同一进程组的任意进程。
④>0:等待进程pid等于传入值的那个子进程。例如传递100表示等待pid为100的子进程。wstatus:与wait一样,这个参数可以用来包含一些关于子进程的附加信息,如果只是想把进程回收,可以设定为NULL。option:此参数要么为0,要么是下面选项进行或运算:
①WNOHANG:如果要等待的子进程已经结束,或者停止,或者处于继续运行的状态,则waitpid不会阻塞,而是立刻返回。
②WUNTRACED。
③WCONTINUED。
在调用成功时,waitpid返回状态发生改变的那个进程的pid。如果设置了WNOHANG参数,那么等待的进程状态没有改变时返回0。发生错误时返回-1。
五、无名管道
pipe()函数用于创建一个无名管道:
#include 参数pipefd是一个长度为2的整型数组,用于存放调用该函数所创建的管道的文件描述符。其中 pipefd[0]存放管道读取端的文件描述符,pipefd[1]存放管道写入端的文件描述符。调用成功时,返回值为0;调用失败时,返回值为-1。
由于管道里面是字节流,父子进程同时读写会导致内容混在一起,对于读管道的一方,解析起来就比较困难。常规的使用方法是父子进程一方只能写入,另一方只能读出,管道变成一个单向的通道,以方便使用。因此管道在创建成功后,要在分别关闭读端和写端后再使用。
管道的特点:
①管道只允许具有血缘关系的进程间通信,如父子进程间通信。
②管道只允许单向通信。
③读管道时,如果管道没有数据,读操作会被阻塞;写数据时,如果管道被写满,写操作也会被阻塞。
无名管道实现父子进程间通信
#include 运行结果
atreus@atreus-virtual-machine:~/code/220317$ make
gcc -Wall main.c -o main
atreus@atreus-virtual-machine:~/code/220317$ ./main
Write pipe:Hello world!
Read pipe:Hello world!
Write pipe:Hello
Read pipe:Hello
Write pipe:end
Read pipe:end
atreus@atreus-virtual-machine:~/code/220317$
六、有名管道
匿名管道应用的一个限制就是只能在具有亲缘关系的进程间通信,如果我们想在不相关的进程之间交换数据,可以使用FIFO文件来做这项工作,它经常被称为命名管道。
mkfifo()用来创建一个有名管道:
#include 前一个参数是管道文件的文件名,后一个参数为文件权限。
注意事项:
①为了保证管道一定被创建,最好两个进程都包含创建管道的代码,谁先运行谁先创建,后运行的直接打开使用。
②不能以O_RDWR模式打开命名管道文件,其行为是未定义的,管道是单向的,不能同时读写。
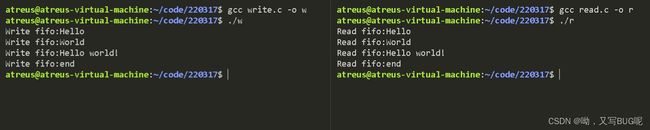
有名管道实现非血缘进程间通信
写进程write.c
#include 读进程read.c
#include 七、消息队列
消息队列传送的是有格式的数据,可以实现多进程网状交叉通信以及大规模数据的通信。消息队列建立前必须为其指定一个键值key,通过ftok()(file to key)函数生成这个键值:
#include ftok.c
#include 执行结果
atreus@atreus-virtual-machine:~/code/220317$ ls -li ./
总用量 36
393231 -rwxrwxr-x 1 atreus atreus 16736 3月 22 12:45 ftok
393257 -rw-rw-r-- 1 atreus atreus 314 3月 22 12:46 ftok.c
393270 -rw-rw-r-- 1 atreus atreus 38 3月 21 09:54 makefile
393619 -rw-rw-r-- 1 atreus atreus 942 3月 22 12:31 receive.c
393276 -rw-rw-r-- 1 atreus atreus 1007 3月 22 12:31 send.c
atreus@atreus-virtual-machine:~/code/220317$ ls -li ../
总用量 4
393265 drwxrwxrwx 3 atreus atreus 4096 3月 22 12:45 220317
atreus@atreus-virtual-machine:~/code/220317$ gcc ftok.c -o ftok
atreus@atreus-virtual-machine:~/code/220317$ ./ftok
key is 0x8050031.
key_ is 0x10050031.
key__ is 0x8050029.
atreus@atreus-virtual-machine:~/code/220317$
其中pathname用于指定一个已经存在的文件,proj_id为子序号,实际上只取其低8位。通过上述代码和执行结果可以大致看出这个key值的生成过程:高位是proj_id转化为十六进制,低位是pathname文件的索引结点转化为16进制(393265D = 60031H)后修改最高位,因此通过同一个消息队列通信的进程必须指定相同的文件和子序号。
在获取到key值后通过msgget()函数获取消息队列标识符:
#include 其中msgflg是一个权限标志,标识消息队列的访问权限,权限标志可以与IPC_CREAT进行或运算,表示指定消息队列不存在时新创建一个消息队列。函数执行成功时返回一个以key命名的消息队列的标识符(非零整数),失败时返回-1。
msgsnd()函数和msgrcv()函数分别用于发送和接收消息:
#include 参数如下:
msqid:由msgget返回的消息队列标识符。msgp:一个指向准备发送或接收的消息的指针,消息必须按照上图中msgbuf的形式定义。msgsz:发送或接收的消息中的数据部分的长度,即不包括长整型消息类型成员变量。msgtyp: 实现接收优先级,如果等于零,就获取队列中的第一个消息;如果它大于零,将获取具有相同消息类型的第一个信息;如果它小于零,就获取类型等于或小于msgtype的绝对值的第一个消息。msgflg:用于控制当前消息队列满或没有符合接收条件的消息时的操作,为0则表示阻塞发送或接收操作。
在调用成功时,msgsnd返回0,msgrcv返回接收的字节数。发生错误时返回-1。
msgctl()可以用来删除消息队列或进行其他操作:
#include 其中cmd参数是将要采取的动作,buf是一个指向消息队列模式和访问权限的结构的指针,如果是想要删除消息队列,参数分别设置为IPC_RMID和0;
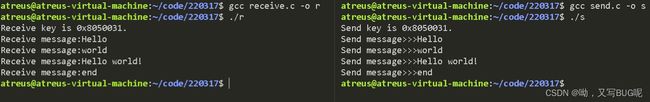
消息队列实现通信
send.c
#include receive.c
#include 八、共享内存
管道和消息队列的使用需要频繁地访问内核,共享内存可以减少进入内核的次数,从而提高通信效率。与消息队列类似,共享内存在创建之前也需要通过ftok()生成一个键值,然后通过shmget()函数获取共享内存标识符。
在得到共享内存标识符后,可以通过shmat()函数把共享内存区映射到调用进程的地址空间中,通过shmdt()函数解除映射:
#include 其中shmid是共享内存标识符,shmflag一般设置为0,表示读写模式,在映射函数中,shmaddr指定共享内存出现在进程内存地址的什么位置,指定为NULL的话内核会自己决定,在解除映射函数中,shmaddr指向连接的共享内存地址。
同样的,在使用结束后要通过shmctl()函数将共享内存删除,效果等同于ipcrm -m shmid命令
共享内存实现进程间通信
send.c
#include receive.c
#include 执行结果
atreus@atreus-virtual-machine:~/code/220317$ ipcs -m
------------ 共享内存段 --------------
键 shmid 拥有者 权限 字节 连接数 状态
atreus@atreus-virtual-machine:~/code/220317$ gcc send.c -o s
atreus@atreus-virtual-machine:~/code/220317$ gcc receive.c -o r
atreus@atreus-virtual-machine:~/code/220317$ ./s
Send key is 0x8050031.
Send message>>>Hello world!
atreus@atreus-virtual-machine:~/code/220317$ ipcs -m
------------ 共享内存段 --------------
键 shmid 拥有者 权限 字节 连接数 状态
0x08050031 23 atreus 644 4096 0
atreus@atreus-virtual-machine:~/code/220317$ ./r
Send key is 0x8050031.
Receive message:Hello world!.
atreus@atreus-virtual-machine:~/code/220317$ ipcs -m
------------ 共享内存段 --------------
键 shmid 拥有者 权限 字节 连接数 状态
atreus@atreus-virtual-machine:~/code/220317$
九、信号量
信号量在通过ftok()函数获取键值,semget()函数获取信号量之后,需要先通过semctl()将信号量初始化:
#include 这是一个系统调用:
semid是信号量集的标识符。semnum是操作信号在信号集中的编号,第一个信号的编号是0。cmd是要执行的操作,一般取SETVAL设置信号量集中的一个单独的信号量的值,或取GETVAL返回信号量集中的一个单个的信号量的值,在上述两种操作中最后一个参数置0。
初始化后由semop()函数执行P操作和V操作:
#include nsops指出要操作的信号个数,sops指向一个sembuf结构体数组,这个结构体的三个成员变量如下:
sem_num:操作信号在信号集中的编号,第一个信号的编号是0。sem_op:如果其值为正数,该值会加到现有的信号内含值中,通常用于释放所控资源的使用权;如果其值为负数,而其绝对值又大于信号的现值,操作将会阻塞,通常用于获取资源的使用权;如果其值为0且没有设置IPC_NOWAIT,则调用该操作的进程或者线程将暂时睡眠,直到信号量的值为0。sem_flg:信号操作标志,可能的选择有两种:
①IPC_NOWAIT:对信号的操作不能满足时,semop()不会阻塞,并立即返回,同时设定错误信息。
②SEM_UNDO:不论程序正常还是非正常结束,可以保证信号值会被重设为semop()调用前的值,这样做的目的在于避免程序在异常情况下结束时未将锁定的资源解锁,造成该资源永远锁定。
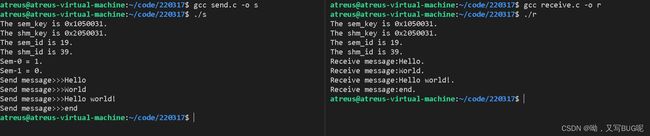
通过信号量实现共享内存读写同步
send.c
#include receive.c
#include 十、信号
信号有默认处理、忽略、执行用户需要执行的动作三种处理方式,常用信号如下:
| 信号编号 | 信号名 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | SIGINT | Ctrl+C |
| 3 | SIGQUIT | Ctrl+Z |
| 9 | SIGKILL | 此信号不能被阻塞、处理和忽略 |
| 11 | SIGSEGV | 一般由段错误产生 |
| 14 | SIGALRM | 时钟定时信号,alarm()函数使用此信号 |
| 15 | SIGTERM | kill命令缺省产生此信号 |
kill()函数用于向任意进程或进程组发信号:
#include 参数如下:
pid:用来指定接收信号的进程,有如下四种取值情况:
①>0:将信号传给进程识别码为pid的进程。
②=0:将信号传给和目前进程位于相同进程组的所有进程。
③=-1:将信号像广播一样传送给系统内所有进程。
④<0:将信号传给进程组识别码为pid绝对值的所有进程。sig:待发送的信号。
signal()函数用于改变信号的处理方式:
#include 参数如下:
signum指明要处理的信号编号。handler指定一个函数指针,它有如下三种情况:
①SIG_DFL:默认的信号处理程序。
②SIG_IGN:忽视信号。
③指向一个自定义信号处理函数的指针。
signal函数的使用
#include 执行结果
atreus@atreus-virtual-machine:~/code/220317$ make
gcc -Wall main.c -o m
atreus@atreus-virtual-machine:~/code/220317$ ./m
^C
SIGINT.
atreus@atreus-virtual-machine:~/code/220317$ ./m
SIGALRM.
atreus@atreus-virtual-machine:~/code/220317$