机器学习入门
1.必要的库和工具
①NumPy:可实现多维数组、高级数学函数(线性代数、傅里叶变换)的实现。
import numpy as np
x = np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]])
print("打印矩阵:")
print(x)
打印矩阵:
[[1 2 3]
[4 5 6]]
②SciPy:用于稀疏矩阵(即矩阵中除少量元素外,其余大部分元素都是0).
from scipy import sparse
eye = np.eye(4)
print("创建一个4行4列单位矩阵:\n{}".format(eye))
创建一个4行4列单位矩阵:
[[1. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 1. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 1. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. 1.]]
sparse_matrix = sparse.csr_matrix(eye)
print("该表示方法意为在几行几列有何元素:\n{}".format(sparse_matrix))
该表示方法意为在几行几列有何元素:
(0, 0) 1.0
(1, 1) 1.0
(2, 2) 1.0
(3, 3) 1.0
data = np.ones(4)
row_indices = np.arange(4)
col_indices = np.arange(4)
eye_coo = sparse.coo_matrix((data,(row_indices,col_indices)))
print("同上:\n{}".format(eye_coo))
同上:
(0, 0) 1.0
(1, 1) 1.0
(2, 2) 1.0
(3, 3) 1.0
③matpoltlib:科学绘图库.
在 jupyter 中使用 %matplotlib inline 或者 %matplotlib notebook 可将图像直接显示在浏览器中。
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = np.linspace(-10, 10, 100)
y = np.sin(x)
plt.plot(x, y)
[]
④pandas:可用于输出数据表格.
import pandas as pd
from IPython.display import display
data = {'Name':["John", "Arthur","Hosea","Charles"],
'Location':["Mexico","England","America","Canada"],
'Age':[30, 35, 60, 32]}
data_pandas = pd.DataFrame(data)
display(data_pandas)
|
Name |
Location |
Age |
| 0 |
John |
Mexico |
30 |
| 1 |
Arthur |
England |
35 |
| 2 |
Hosea |
America |
60 |
| 3 |
Charles |
Canada |
32 |
display(data_pandas[data_pandas.Age > 34])
|
Name |
Location |
Age |
| 1 |
Arthur |
England |
35 |
| 2 |
Hosea |
America |
60 |
2.第一个机器学习例子
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
iris_dataset = load_iris()
print("鸢尾花数据集的键:\n{}".format(iris_dataset.keys()))
鸢尾花数据集的键:
dict_keys(['data', 'target', 'frame', 'target_names', 'DESCR', 'feature_names', 'filename'])
要明确数据集的键值对,目标名:
data – 数据集本身
target – 标签编号
target_names – 标签名称
feature_names – 特征名称
print("预测目标分类名:{}".format(iris_dataset['target_names']))
预测目标分类名:['setosa' 'versicolor' 'virginica']
print("特征名:{}".format(iris_dataset['feature_names']))
特征名:['sepal length (cm)', 'sepal width (cm)', 'petal length (cm)', 'petal width (cm)']
print("数据类型:{}".format(type(iris_dataset['data'])))
数据类型:
print("样本数, 特征数:{}".format(iris_dataset['data'].shape))
样本数, 特征数:(150, 4)
print("前五行的数据:\n{}".format(iris_dataset['data'][:5]))
前五行的数据:
[[5.1 3.5 1.4 0.2]
[4.9 3. 1.4 0.2]
[4.7 3.2 1.3 0.2]
[4.6 3.1 1.5 0.2]
[5. 3.6 1.4 0.2]]
print("目标值规模:{}".format(iris_dataset['target'].shape))
目标值规模:(150,)
print("目标:\n{}".format(iris_dataset['target']))
print("0-品种A,1-品种B,2-品种C")
目标:
[0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
2 2]
0-品种A,1-品种B,2-品种C
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
"""在sklearn中X表示数据, y表示标签"""
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(iris_dataset['data'], iris_dataset['target'], random_state=0)
在原始数据中所有的数据都是按标签排列的(即假设不经过打乱直接选取测试集,如果选取最后的25%作为测试集,可能获得的标签都是相同的).
函数 train_test_split()能够利用伪随机数生成器将数据集打乱顺序。
参数 random_state是为了确保多次运行同意函数后仍能够得到同样的输出(即保持第一次打乱后的数据顺序)
该函数输出X_train(75%), X_test(25%), y_train, y_test.
print("X_train shape:{}".format(X_train.shape))
print("y_train shape:{}".format(y_train.shape))
X_train shape:(112, 4)
y_train shape:(112,)
print("X_test shape:{}".format(X_test.shape))
print("y_test shape:{}".format(y_test.shape))
X_test shape:(38, 4)
y_test shape:(38,)
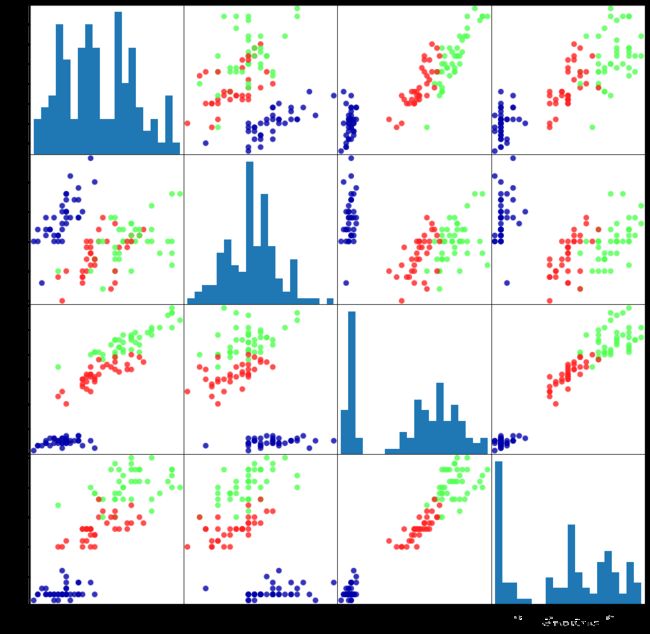
iris_dataframe = pd.DataFrame(X_train, columns=iris_dataset.feature_names)
grr = pd.plotting.scatter_matrix(iris_dataframe, c = y_train, figsize = (15, 15), marker = 'o', hist_kwds = {'bins':20},s=60,alpha=.8,cmap=mglearn.cm3)
K近邻算法
图自bilbil KonwingAI知智
“物以类聚”,如果要对一个新的数据点进行预测,那么KNN算法会寻找离该新数据点最近的数据点来判断其分类结果。
其中, k表示离需要预测的数据点最近的k个邻居。
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
knn = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=1)
knn.fit(X_train, y_train)
KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=1)
做出预测
import numpy as np
X_new = np.array([[5, 2.9, 1, 0.2]])
print("显示该数据规模:\n{}".format(X_new.shape))
显示该数据规模:
(1, 4)
prediction = knn.predict(X_new)
print("预测结果:{}".format(prediction))
print("属于标签:{}".format(iris_dataset['target_names'][prediction]))
预测结果:[0]
属于标签:['setosa']
评估模型
y_pred = knn.predict(X_test)
print(y_pred)
[2 1 0 2 0 2 0 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 2 1 0 0 2 0 0 1 1 0 2 1 0 2 2 1 0
2]
print(knn.score(X_test, y_test))
0.9736842105263158
print(np.mean(y_pred == y_test))
0.9736842105263158
总结