Pytorch学习笔记:GoogLeNet
Pytorch学习笔记:GoogLeNet
- 1.网络分析
-
- 1.1 网络亮点
- 1.2 Inception结构
- 1.3 辅助分类器
- 2.网络搭建
-
- 2.1 卷积模块
- 2.2 Inception模块
- 2.3 辅助分类器模块
- 2.4 全网络模块
- 3.网络训练
- 4.测试文件
主要参考b站up霹雳吧啦Wz视频,感谢up主做的极其详细并对小白友好的精彩分享。
GoogLeNet知识点视频
代码实现视频
代码来自up主的Github仓库开源项目,侵权删。
1.网络分析
1.1 网络亮点
1.2 Inception结构
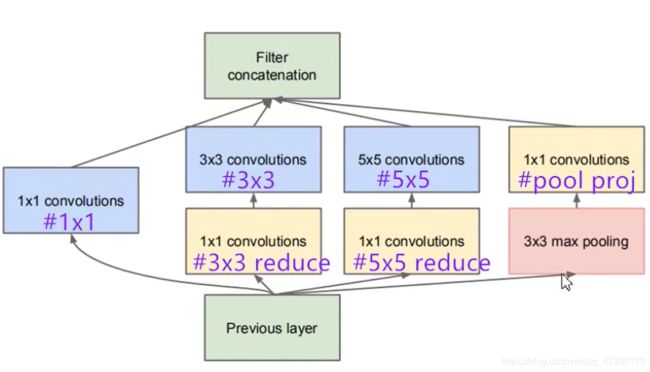
这是改进以后的Inception模块,与改进前相比引入了1×1卷积核进行降维,从而减少了网络的参数。
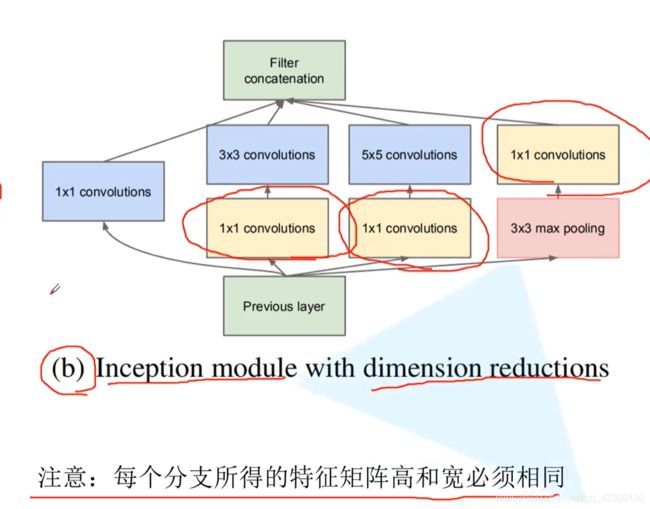
特征图输入后,经过4个分支。
分支1:直接进行1×1卷积降维;
分支2:先进行1×1卷积降维,再通过3×3卷积提取特征图;
分支3:先进行1×1卷积降维,再通过5×5卷积提取特征图;
分支4:先通过3×3最大池化层,再进行1×1卷积降维。
4个分支输出时在channels维度上进行拼接提升输出特征图的channels,丰富特征,这就要求输出的特征图长宽尺寸一致,需要通过padding填充来实现。
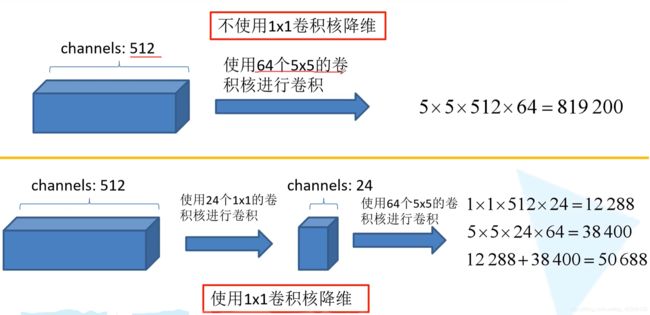
关于引入1×1卷积降维:
1.3 辅助分类器
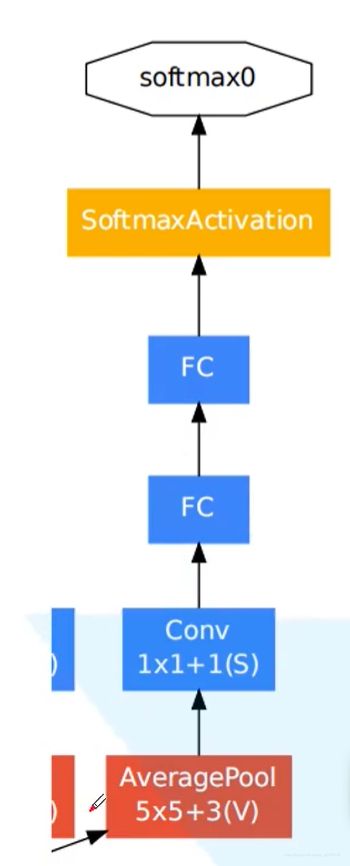
考虑到随着网络变深会有梯度消失的可能,且低维网络提取的低维特征也具有一定价值,故引出低维特征,通过一个辅助分类器输出,在训练网络时,辅助分类器的损失函数与最终的网络损失函数进行加权求和。
但要注意辅助分类器仅在训练时使用,在使用训练好的网络时会进行舍弃。
2.网络搭建
2.1 卷积模块
因为卷积层后面 总是跟着激活层,故将两者合一。
class BasicConv2d(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, **kwargs):
super(BasicConv2d, self).__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, **kwargs)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv(x)
x = self.relu(x)
return x
2.2 Inception模块
Inception模块需要确定的参数有:
1.输入图像的channels(in_channels);
2.分支一 1×1卷积核的个数(ch1x1),这决定了分支一输出的channels
3.分支二 1×1卷积核的个数(ch3x3red),这决定了分支二降维后输出的channels,3×3卷积核的个数(ch3x3),这决定了分支二最终输出的channels
4.分支三 1×1卷积核的个数(ch5x5red),这决定了分支三降维后输出的channels,5×5卷积核的个数(ch5x5),这决定了分支二最终输出的channels
5.分支四 1×1卷积核的个数(pool_proj),这决定了分支四降维后最终输出的channels
class Inception(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, ch1x1, ch3x3red, ch3x3, ch5x5red, ch5x5, pool_proj):
super(Inception, self).__init__()
self.branch1 = BasicConv2d(in_channels, ch1x1, kernel_size=1)
self.branch2 = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv2d(in_channels, ch3x3red, kernel_size=1),
BasicConv2d(ch3x3red, ch3x3, kernel_size=3, padding=1) # 保证输出大小等于输入大小
)
self.branch3 = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv2d(in_channels, ch5x5red, kernel_size=1),
BasicConv2d(ch5x5red, ch5x5, kernel_size=5, padding=2) # 保证输出大小等于输入大小
)
self.branch4 = nn.Sequential(
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
BasicConv2d(in_channels, pool_proj, kernel_size=1)
)
def forward(self, x):
branch1 = self.branch1(x)
branch2 = self.branch2(x)
branch3 = self.branch3(x)
branch4 = self.branch4(x)
outputs = [branch1, branch2, branch3, branch4]
return torch.cat(outputs, 1)
torch.cat是将两个张量(tensor)拼接在一起,cat是concatnate的意思,即拼接,联系在一起。
使用torch.cat((A,B),dim)时,除拼接维数dim数值可不同外其余维数数值需相同,方能对齐。dim = 1即为channels,其0维度(batch),2,3维度(图像尺寸)均相等。
2.3 辅助分类器模块
class InceptionAux(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, num_classes):
super(InceptionAux, self).__init__()
self.averagePool = nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=5, stride=3)
self.conv = BasicConv2d(in_channels, 128, kernel_size=1) # output[batch, 128, 4, 4]
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(2048, 1024)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(1024, num_classes)
def forward(self, x):
# aux1: N x 512 x 14 x 14, aux2: N x 528 x 14 x 14
x = self.averagePool(x)
# aux1: N x 512 x 4 x 4, aux2: N x 528 x 4 x 4
x = self.conv(x)
# N x 128 x 4 x 4
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = F.dropout(x, 0.5, training=self.training)
# N x 2048
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x), inplace=True)
x = F.dropout(x, 0.5, training=self.training)
# N x 1024
x = self.fc2(x)
# N x num_classes
return x
2.4 全网络模块
class GoogLeNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes=1000, aux_logits=True, init_weights=False):
super(GoogLeNet, self).__init__()
self.aux_logits = aux_logits
self.conv1 = BasicConv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3)
self.maxpool1 = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2, ceil_mode=True)
self.conv2 = BasicConv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=1)
self.conv3 = BasicConv2d(64, 192, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.maxpool2 = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2, ceil_mode=True)
self.inception3a = Inception(192, 64, 96, 128, 16, 32, 32)
self.inception3b = Inception(256, 128, 128, 192, 32, 96, 64)
self.maxpool3 = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2, ceil_mode=True)
self.inception4a = Inception(480, 192, 96, 208, 16, 48, 64)
self.inception4b = Inception(512, 160, 112, 224, 24, 64, 64)
self.inception4c = Inception(512, 128, 128, 256, 24, 64, 64)
self.inception4d = Inception(512, 112, 144, 288, 32, 64, 64)
self.inception4e = Inception(528, 256, 160, 320, 32, 128, 128)
self.maxpool4 = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2, ceil_mode=True)
self.inception5a = Inception(832, 256, 160, 320, 32, 128, 128)
self.inception5b = Inception(832, 384, 192, 384, 48, 128, 128)
if self.aux_logits:
self.aux1 = InceptionAux(512, num_classes)
self.aux2 = InceptionAux(528, num_classes)
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(0.4)
self.fc = nn.Linear(1024, num_classes)
if init_weights:
self._initialize_weights()
def forward(self, x):
# N x 3 x 224 x 224
x = self.conv1(x)
# N x 64 x 112 x 112
x = self.maxpool1(x)
# N x 64 x 56 x 56
x = self.conv2(x)
# N x 64 x 56 x 56
x = self.conv3(x)
# N x 192 x 56 x 56
x = self.maxpool2(x)
# N x 192 x 28 x 28
x = self.inception3a(x)
# N x 256 x 28 x 28
x = self.inception3b(x)
# N x 480 x 28 x 28
x = self.maxpool3(x)
# N x 480 x 14 x 14
x = self.inception4a(x)
# N x 512 x 14 x 14
if self.training and self.aux_logits: # eval model lose this layer
aux1 = self.aux1(x)
x = self.inception4b(x)
# N x 512 x 14 x 14
x = self.inception4c(x)
# N x 512 x 14 x 14
x = self.inception4d(x)
# N x 528 x 14 x 14
if self.training and self.aux_logits: # eval model lose this layer
aux2 = self.aux2(x)
x = self.inception4e(x)
# N x 832 x 14 x 14
x = self.maxpool4(x)
# N x 832 x 7 x 7
x = self.inception5a(x)
# N x 832 x 7 x 7
x = self.inception5b(x)
# N x 1024 x 7 x 7
x = self.avgpool(x)
# N x 1024 x 1 x 1
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
# N x 1024
x = self.dropout(x)
x = self.fc(x)
# N x 1000 (num_classes)
if self.training and self.aux_logits: # eval model lose this layer
return x, aux2, aux1
return x
nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d可以通过设置输出尺寸来自适应调整池化的大小与步长。
nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))表示输出的图像尺寸变为1×1。
3.网络训练
import os
import json
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torchvision import transforms, datasets
import torch.optim as optim
from tqdm import tqdm
from model import GoogLeNet
def main():
#device = "cpu"
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
print("using {} device.".format(device))
data_transform = {
"train": transforms.Compose([transforms.RandomResizedCrop(224),
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))]),
"val": transforms.Compose([transforms.Resize((224, 224)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))])}
data_root = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.getcwd(), "../..")) # get data root path
image_path = os.path.join(data_root, "dataSet", "flower_data") # flower data set path
assert os.path.exists(image_path), "{} path does not exist.".format(image_path)
train_dataset = datasets.ImageFolder(root=os.path.join(image_path, "train"),
transform=data_transform["train"])
train_num = len(train_dataset)
# {'daisy':0, 'dandelion':1, 'roses':2, 'sunflower':3, 'tulips':4}
flower_list = train_dataset.class_to_idx
cla_dict = dict((val, key) for key, val in flower_list.items())
# write dict into json file
json_str = json.dumps(cla_dict, indent=4)
with open('class_indices.json', 'w') as json_file:
json_file.write(json_str)
batch_size = 16
nw = 0
#nw = min([os.cpu_count(), batch_size if batch_size > 1 else 0, 8]) # number of workers
print('Using {} dataloader workers every process'.format(nw))
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True,
num_workers=nw)
validate_dataset = datasets.ImageFolder(root=os.path.join(image_path, "val"),
transform=data_transform["val"])
val_num = len(validate_dataset)
validate_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(validate_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False,
num_workers=nw)
print("using {} images for training, {} images for validation.".format(train_num,
val_num))
net = GoogLeNet(num_classes=5, aux_logits=True, init_weights=True)
net.to(device)
loss_function = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=0.0003)
epochs = 30
best_acc = 0.0
save_path = './googleNet.pth'
train_steps = len(train_loader)
for epoch in range(epochs):
# train
net.train()
running_loss = 0.0
train_bar = tqdm(train_loader)
for step, data in enumerate(train_bar):
images, labels = data
optimizer.zero_grad()
logits, aux_logits2, aux_logits1 = net(images.to(device))
loss0 = loss_function(logits, labels.to(device))
loss1 = loss_function(aux_logits1, labels.to(device))
loss2 = loss_function(aux_logits2, labels.to(device))
loss = loss0 + loss1 * 0.3 + loss2 * 0.3
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# print statistics
running_loss += loss.item()
train_bar.desc = "train epoch[{}/{}] loss:{:.3f}".format(epoch + 1,
epochs,
loss)
# validate
net.eval()
acc = 0.0 # accumulate accurate number / epoch
with torch.no_grad():
val_bar = tqdm(validate_loader)
for val_data in val_bar:
val_images, val_labels = val_data
outputs = net(val_images.to(device)) # eval model only have last output layer
predict_y = torch.max(outputs, dim=1)[1]
acc += torch.eq(predict_y, val_labels.to(device)).sum().item()
val_accurate = acc / val_num
print('[epoch %d] train_loss: %.3f val_accuracy: %.3f' %
(epoch + 1, running_loss / train_steps, val_accurate))
if val_accurate > best_acc:
best_acc = val_accurate
torch.save(net.state_dict(), save_path)
print('Finished Training')
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
几点说明:
1.训练时损失函数的设置是网络输出的损失与辅助分类器的损失加权和;
logits, aux_logits2, aux_logits1 = net(images.to(device))
loss0 = loss_function(logits, labels.to(device))
loss1 = loss_function(aux_logits1, labels.to(device))
loss2 = loss_function(aux_logits2, labels.to(device))
loss = loss0 + loss1 * 0.3 + loss2 * 0.3
2.进行精度计算时,因为使用了 net.eval()所以网络只输出网络末端的结果进行分类。
4.测试文件
import os
import json
import torch
from PIL import Image
from torchvision import transforms
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from model import GoogLeNet
def main():
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
data_transform = transforms.Compose(
[transforms.Resize((224, 224)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))])
# load image
img_path = "2.jpg"
assert os.path.exists(img_path), "file: '{}' dose not exist.".format(img_path)
img = Image.open(img_path)
plt.imshow(img)
# [N, C, H, W]
img = data_transform(img)
# expand batch dimension
img = torch.unsqueeze(img, dim=0)
# read class_indict
json_path = './class_indices.json'
assert os.path.exists(json_path), "file: '{}' dose not exist.".format(json_path)
json_file = open(json_path, "r")
class_indict = json.load(json_file)
# create model
model = GoogLeNet(num_classes=5, aux_logits=False).to(device)
# load model weights
weights_path = "./googleNet.pth"
assert os.path.exists(weights_path), "file: '{}' dose not exist.".format(weights_path)
missing_keys, unexpected_keys = model.load_state_dict(torch.load(weights_path, map_location=device),
strict=False)
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
# predict class
output = torch.squeeze(model(img.to(device))).cpu()
predict = torch.softmax(output, dim=0)
predict_cla = torch.argmax(predict).numpy()
print_res = "class: {} prob: {:.3}".format(class_indict[str(predict_cla)],
predict[predict_cla].numpy())
plt.title(print_res)
print(print_res)
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
几点说明:
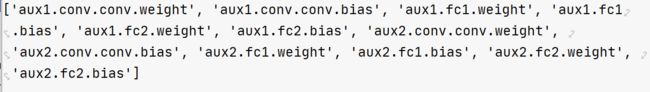
1.载入训练好的模型参数时,参数strict=False表明非严格匹配,因为训练好的模型中还有辅助分类层的参数,而我们用来分类的模型不需要这些参数。通过unexpected_keys可以得知损失的参数。
missing_keys, unexpected_keys = model.load_state_dict(
torch.load(weights_path, map_location=device),strict=False)