js手写数组api
本文涉及数组的api有 slice、concat、push、pop、shift、unshift、reverse、copyWithin、entries、every、fill、filter、find、findIndex、forEach、from、includes、indexOf、isArray、join、lastIndexOf、map、reduce、reduceRight、some、sort、splice、toString、valueOf
slice
选取数组的一部分,并返回一个新数组
Array.prototype.mySlice = function(start, end = this.length) {
const arr = this;
const result = [];
if (start < 0) {
for (let i = start + end; i < end; i++) {
result.push(arr[i]);
}
}
else {
for (let i = start; i < end; i++) {
result.push(arr[i]);
}
}
return result;
};
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6];
let newArr = arr.mySlice(-4);
console.log(arr, newArr); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6] [3, 4, 5, 6]
newArr = arr.mySlice(1);
console.log(newArr); // [2, 3, 4, 5, 6]concat
连接两个或更多的数组,并返回结果
Array.prototype.myConcat = function () {
const arr = this;
for (let i = 0; i < arguments.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < arguments[i].length; j++) {
arr[this.length] = arguments[i][j];
}
}
return arr;
};
const arr = ['123', '456'];
const arr1 = ['1', '2', '3'];
const arr2 = ['4', '5', '6'];
const res = arr.myConcat(arr1, arr2);
console.log(arr); // ['123', '456', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6']push
向数组的末尾添加一个或更多元素,并返回新的长度
Array.prototype.myPush = function () {
for (let i = 0; i < arguments.length; i++) {
this[this.length] = arguments[i];
}
return this.length;
};
const arr = [1, 2, 3];
const res = arr.myPush(4);
console.log(arr, res); // [1, 2, 3, 4] 4pop
删除数组的最后一个元素并返回删除的元素
Array.prototype.myPop = function () {
const arr = this;
if (arr.length === 0) return undefined;
const ans = arr[this.length - 1];
this.length = this.length - 1;
return ans;
};
const arr = [1, 2, 3];
const res = arr.myPop();
console.log(arr, res); // [1, 2] 3shift
删除并返回数组的第一个元素
Array.prototype.myShift = function () {
const arr = this;
if (arr.length === 0) return undefined;
const ans = arr[0];
for (let i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i - 1] = arr[i];
}
this.length = this.length - 1;
return ans;
};
const arr = [1, 2, 3];
const ans = arr.myShift();
console.log(arr, ans); // [2, 3] 1unshift
向数组的开头添加一个或更多元素,并返回新的长度
Array.prototype.myUnshift = function () {
const arrLength = this.length;
const arr = this;
for (let i = arrLength + arguments.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (i > arguments.length - 1) {
arr[i] = arr[i - arguments.length];
}
else {
arr[i] = arguments[i];
}
}
return arr.length;
};
const arr = [1, 2, 3];
const res = arr.myUnshift(4);
console.log(arr, res); // [4, 1, 2, 3] 4reverse
将数组的前后顺序进行调换
Array.prototype.myReverse = function () {
const arr = this;
const arrLength = arr.length;
const copyArr = Array.from(arr);
for (let i = 0; i < arrLength; i++) {
arr[arrLength - i - 1] = copyArr[i];
}
return arr;
};
const arr = [1, 2, 3];
const ans = arr.myReverse();
console.log(ans); // [3, 2, 1]copyWithin
从数组的指定位置拷贝元素到数组的另一个指定位置中
Array.prototype.myCopyWithin = function (target, start, end = this.length) {
const arr = this;
for (let i = start; i < end; i++) {
arr[target] = arr[i];
target++;
}
return arr;
};
let arr = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e'];
arr.copyWithin(0, 3, 4);
console.log(arr); // ['d', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e']
arr = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e'];
arr.myCopyWithin(0, 3, 4);
console.log(arr); // ['d', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e']
arr.myCopyWithin(1, 3);
console.log(arr); // ['d', 'd', 'e', 'd', 'e']entries
返回数组的可迭代对象
Array.prototype.myEntries = function () {
const ans = [];
for (let i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
ans[i] = [];
ans[i].push(i);
ans[i].push(this[i]);
}
return ans;
};
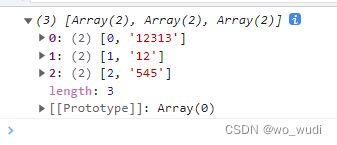
const arr = ['12313', '12', '545'];
console.log(arr.myEntries());every
检测数值元素的每个元素是否都符合条件
Array.prototype.myEvery = function (fn) {
const arr = this;
let count = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (fn(arr[i])) {
count++;
}
}
if (count === arr.length) {
return true;
}
return false;
};
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8];
let res = arr.myEvery(value => value > 4);
console.log(arr, res); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8] false
res = arr.myEvery(value => value > 0);
console.log(res); // truefill
使用一个固定值来填充数组
Array.prototype.myFill = function (value, start = 0, end = this.length) {
const arr = this;
for (let i = start; i < end; i++) {
arr[i] = value;
}
return arr;
};
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4];
arr.myFill(0, 2, 4);
console.log(arr); // [1, 2, 0, 0]
arr.myFill(5, 1);
console.log(arr); // [1, 5, 5, 5]
arr.myFill(6);
console.log(arr); // [6, 6, 6, 6]filter
检测数值元素,并返回符合条件所有元素的数组
Array.prototype.myFilter = function (fn) {
if (Object.prototype.toString.call(fn).slice(8, -1) !== 'Function') {
throw new error('ths first argument must be Function!');
}
const arr = this;
const res = [];
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (fn(arr[i], i, arr)) {
res.push(arr[i]);
}
}
return res;
};
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9];
const res = arr.myFilter((value, index, arr) => value > 4);
console.log(arr, res); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] [5, 6, 7, 8, 9]find
返回符合传入测试(函数)条件的第一个数组元素
Array.prototype.myFind = function (fn) {
if (typeof fn !== 'function') {
return new Error(`${fn} is no a function`);
}
const self = this;
for (let i = 0; i < self.length; i++) {
if (fn(self[i], i, self)) {
// 如果当前元素满足,则返回此元素
return self[i];
}
}
};
const arr = [1, 2, 5, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9];
const res = arr.myFind((value, index, arr) => value > 4);
console.log(arr, res); // [1, 2, 5, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] 5findIndex
返回符合传入测试(函数)条件的数组元素索引
Array.prototype.myFindIndex = function (fn) {
if (typeof fn !== 'function') {
throw TypeError('err function');
}
for (let i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
if (fn(this[i])) {
return i;
}
}
return undefined;
};
const arrFindIndex = [12, 15, 19];
const findIndex = arrFindIndex.myFindIndex(item =>
item > 12);
console.log('findIndex:' + findIndex); // findIndex:1forEach
数组每个元素都执行一次回调函数
Array.prototype.myForEach = function (fn, thisArg) {
const arr = this;
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
fn.call(thisArg, arr[i]);
}
};
const obj = {
num: 10
};
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6];
arr.myForEach(function (value, index, arr) {
console.log(value + this.num); // 依次打印:11 12 13 14 15 16
}, obj);
console.log(arr); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]from
通过给定的对象中创建一个数组
Array.prototype.myFrom = function (object, mapFunction, thisValue) {
const obj = thisValue || this;
let result = [];
// 没有length属性 或者 length 为0的 直接返回空数组
if (!object.length) {
return result;
}
if (typeof object === 'string') {
result = object.split('');
}
else {
object.forEach(item => result.push(item));
}
if (typeof mapFunction !== 'function') {
throw new TypeError(mapFunction + ' is not a function');
}
return result.map(mapFunction, thisValue);
};
const r1 = Array.prototype.myFrom([1, 2, 3], x => x * 10);
console.log(r1); // [10, 20, 30, 40]
const r2 = Array.prototype.myFrom('1234', x => x * 10);
console.log(r2); // [10, 20, 30]includes
判断一个数组是否包含一个指定的值
Array.prototype.myIncludes = function (searchElement, fromIndex = 0) {
const arr = this;
if (fromIndex >= arr.length || !arr.length) {
return false;
}
for (let i = fromIndex; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] === searchElement) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
};
const arr = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'];
const result = arr.myIncludes('b');
console.log(result); // trueindexOf
搜索数组中的元素,并返回它所在的位置
Array.prototype.myIndexOf = function (num) {
const arr = this;
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] === num) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
};
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6];
console.log(arr.myIndexOf(5)); // 4isArray
判断对象是否为数组
Array.prototype.myIsArray = function (item) {
/*
* 这里使用Object.prototype.toString.call来判断是否为数组
* 不能使用typeof来判断,因为不准确,而Object.prototype.toString.call判断类型的方法是最准确的
*/
return Object.prototype.toString.call(item) === '[object Array]';
};
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4];
console.log(Array.prototype.myIsArray(arr)); // truejoin
把数组的所有元素以某个中间值连接并放入一个字符串
Array.prototype.myJoin = function (separator = ',') {
const arr = this;
let str = '';
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
str += arr[i];
if (i != arr.length - 1) {
str += separator;
}
}
return str;
};
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6];
const res = arr.myJoin('-');
console.log(arr, res); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6] '1-2-3-4-5-6'lastIndexOf
搜索数组中的元素,并返回它最后出现的位置
Array.prototype.myLastIndexOf = function (num) {
const arr = this;
for (let i = arr.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (arr[i] === num) return i;
}
return -1;
};
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 4];
console.log(arr.myLastIndexOf(4)); // 5map
通过指定函数处理数组的每个元素,并返回处理后的数组
Array.prototype.myMap = function (fn, thisArg) {
if (Object.prototype.toString.call(fn).slice(8, -1) !== 'Function') {
throw new error('The first argument must be a function!');
}
const result = [];
const currentArr = this;
for (let i = 0; i < currentArr.length; i++) {
result[i] = fn.call(thisArg, currentArr[i], i, currentArr);
}
return result;
};
arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6];
console.log(arr.map((item, index, arr) => item * 2)); // [2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12]
console.log(arr.myMap((item, index, arr) => item + 1)); // [2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]reduce
将数组元素计算为一个值(从左到右)
const arrReduce = [12, 15, 19];
Array.prototype.myReduce = function (fn, obj) {
if (typeof fn !== 'function') {
throw new TypeError(`error ${fn} no a function `);
}
for (let i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
obj = fn(obj, this[i]);
}
return obj;
};
const reduce = arrReduce.myReduce((pre, item) => {
pre = pre + item;
return pre;
}, 0);
console.log('reduce:' + reduce); // reduce:46reduceRight
将数组元素计算为一个值(从右到左)
const arrReduce = [12, 15, 19];
Array.prototype.myReduceRight = function (fn, obj) {
if (typeof fn !== 'function') {
throw new TypeError(`error ${fn} no a function `);
}
for (let i = this.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
obj = fn(obj, this[i]);
}
return obj;
};
const reduce = arrReduce.myReduceRight((pre, item) => {
pre = pre + item;
return pre;
}, 0);
console.log('reduce:' + reduce); // reduce:46some
检测数组元素中是否有元素符合指定条件
Array.prototype.mySome = function (fn) {
if (typeof fn !== 'function') {
throw new TypeError(`error ${fn} no a function `);
}
for (let i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
if (fn(this[i])) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
};
const arrSome = [12, 15, 19];
const some = arrSome.mySome(item => item > 19);
console.log('some:' + some); // some:falsesort
对数组的元素进行排序(此api可涉及多种排序算法,感兴趣可以去了解,此处使用冒泡排序)
Array.prototype.mySort = function () {
let arr = this;
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < arr.length - i; j++) {
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) {
let temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
return arr;
};
const arrSort = [1, 5, 65, 78, 44, 0, 2, 3, 1, 0, 44, 12, 15, 19];
console.log(arrSort.mySort()); // [0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 12, 15, 19, 44, 44, 65, 78]splice
从数组中添加或删除元素
Array.prototype.mySplice = function (index, howmany = 0) {
const arr = this;
const left = arr.slice(0, index); // 截取左边的数组
const right = arr.slice(index + howmany, arr.length); // 截取右边的数组
const subArr = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments, 2); // 截取参数里面需要添加的数组
let result = [];
// 合并数组
result = [...left, ...subArr, ...right];
// 这里改变 this, 就是改变原数组
for (let i = 0; i < result.length; i++) {
this[i] = result[i];
}
// 返回删除的数据
return this.slice(index, index + howmany);
};
const arr = ['Banana', 'Orange', 'Lemon', 'Apple', 'Mango'];
const result = arr.mySplice(2, 1, 'sss', 'xxx');
console.log(result); // ["sss"]
console.log(arr); // ["Banana", "Orange", "sss", "xxx", "Apple", "Mango"]toString
把数组转换为字符串,并返回结果
Array.prototype.myToString = function (separator = ',') {
const arr = this;
let str = '';
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
str += arr[i];
if (i != arr.length - 1) {
str += separator;
}
}
return str;
};
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6];
const arr1 = [1, 2, 'a', 'b'];
res = arr1.myToString();
console.log(arr1, res); // [1, 2, 'a', 'b'] '1,2,a,b'valueOf
返回数组对象的原始值
Array.prototype.myValueOf = function () {
return this;
};
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
console.log(arr.myValueOf()); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]