【javaScript】学完js基础,顺便把js高级语法学了(尚硅谷视频学习笔记)
文章目录
-
- 【1】基本总结深入
-
- 一、什么是数据
-
- 1、数据类型
-
- 基本(值)类型
- 对象(引用)类型
- 2、判断
- 相关问题
- 二、什么是内存
-
-
- 1、什么是数据
- 2、什么是内存?
- 3、什么是变量
- 4、内存、数据、变量三者之间的关系
- 相关问题
-
- 1、问题:var a = xxx,a内存中到底保存的是什么?
- 2、关于引用变量赋值问题
- 3、在js调用函数传递变量参数时,是值传递还是引用传递
- 4、JS引擎如何管理内存
-
- 三、什么是对象
-
-
- 1、什么是对象
- 2、为什么要用对象
- 3、对象的组成
- 4、如何访问对象内部数据
- 5、什么时候必须使用[‘属性值’]的方式
-
- 四、什么是函数
-
-
- 1、什么是函数
- 2、为什么用函数
- 3、如何定义函数
- 4、如何调用(执行)函数
- 5、回调函数
-
- 1、什么函数才是回调函数
- 2、常见的回调函数
- 6、IIFE
-
- 1、理解
- 2、作用
- 7、函数中的this
-
- 1、this是什么
- 2、如何让确定this的值
-
- 【2】函数高级
-
- 一、原型与原型链
-
- 1、原型
-
- (1)函数的prototype属性
- (2)给原型对象添加属性(一般都是方法)
- 2、显示原型与隐式原型
-
- (1)每个函数function都有一个prototype,即显示原型(属性)默认指向一个空的Object对象
- (2)每个实例对象都有一个‘ _ _ proto _ _’,可称为隐式原型(属性)
- (3)对象的隐式原型的值为其对应构造函数的显式原型的值
- (4)内存构造(图)
- (5)总结
- 3、原型链
-
- (1)原型链
- (2)构造函数/原型实例对象的关系
- (3)构造函数/原型实例对象的关系2
- (4)相关问题
- 4、原型链属性问题
- 5、探索instanceof
-
- 1、instanceof是如何判断的?
- 2、Function是通过new自己产生的实例
- 6、面试题
- 二、执行上下文与执行上下文栈
-
- 1、变量提升与函数提升
-
- (1)变量声明提升
- (2)函数声明提升
- 2、执行上下文
-
- (1)代码分类(位置)
- (2)全局执行上下文
- (3)函数执行上下文
- 3、执行上下文栈
-
- (1)在全局代码执行前,JS引擎就会创建一个栈来存储管理所有的执行上下文对象
- (2)在全局执行上下文(window)确定后,将其添加到栈中(压栈)
- (3)在函数执行上下文创建后,将其添加到栈中(压栈)
- (4)在当前函数执行完后,将栈顶的对象移除(出栈)
- (5)当所有的代码执行完后,栈中只剩下window
- 4、面试题
- 三、作用域与作用域链
-
- 1、作用域
-
- (1)理解
- (2)分类
- (3)作用
- 2、作用域与执行上下文
-
- (1)区别1
- (2)区别2
- (3)联系
- 3、作用域链
-
- (1)理解
- (2)查找一个变量的查找规则
- 四、闭包
-
- 1、理解闭包
-
- (1)如何产生闭包
- (2)闭包到底是什么
- (3)产生闭包的条件
- 2、常见闭包
- 3、闭包作用
-
- (1)使用函数内部的变量在函数执行完后,仍然存活在内存中(延长了局部变量的声明周期)
- (2)让函数外部可以操作(读写)到函数内部的数据(变量/函数)
- (1)函数执行完后,函数内部声明的局部变量是否还存在?
- (2)在函数外部能直接访问函数内部的局部变量吗?
- 4、闭包生命周期
-
- (1)产生:在嵌套内部函数定义执行完时就产生了(不是在调用)
- (2)死亡:在嵌套的内部函数成为垃圾对象时
- 5、闭包应用
-
- 闭包的应用:定义JS模块
- 6、闭包缺点
-
- (1)缺点
- (2)解决
- (3)内存溢出
- (4)内存泄漏
- 五、面试题
- 【3】对象高级
-
- 一、对象创建模式
-
- 方式一:Object构造函数模式
- 方式二:对象字面量模式
- 方式三:工厂模式
- 方式四:自定义构造函数模式
- 二、继承模式
-
- 1、原型链继承
-
- (1)套路
- (2)关键
- 2、借用构造函数继承(假的)
-
- (1)套路
- (2)关键
- 3、组合继承
-
- (1)原型链+借用构造函数的组合继承
- 【4】线程机制与事件机制
-
- 一、进程与进程
-
- 1、进程
-
- 2、线程
- 3、图解
- 4、相关知识
- 5、相关问题
-
- (1)何为多进程与多线程
- (2)JS是单线程还是多线程
- (3)比较单线程与多线程
- (4)浏览器运行是单线程还是多线程
- 二、浏览器内核
- 三、定时器引发的思考
-
- 1、定时器真的是定时执行的吗?
- 2、定时器回调函数是在哪个线程执行的?
- 3、定时器是如何实现的?
- 四、JS是单线程执行
- 五、浏览器的事件循环(轮询)模型
【1】基本总结深入
一、什么是数据
1、数据类型
-
基本(值)类型
- String:任意的字符串
- Nubmer:任意数字
- booleans :true/false
- underfine :underfine
- null:null
-
对象(引用)类型
- Object:任意对象
- Function:一种特别的对象(可以执行)
- Array:一种特别的对象(数值下标,内部数据是有序的)
2、判断
-
typeof 返回数据类型的字符串表达
- 可以判断:underfine/数值/字符串/布尔值/function
- 不能判断:null与object, object与array
var b1 = { b2:[1,'abc',console.log], b3:function(){ console.log('b3') return function(){ return 'xfzhang' } } } console.log(typeof b1.b2)//'object' -
instanceof
- 判断对象的基本类型
-
===
- 可以判断:undefine,null
相关问题
1、underfine与null的区别
- underfine 代表定义未赋值
- null定义了并赋值,值为null
2、 什么时候给变量赋值为null呢?
- 初始赋值,表明将要赋值为对象
- 结束前,让对象成为垃圾对象(被垃圾回收器回收)
3、严格区别变量类型与数据类型
-
数据类型
- 基本类型
- 对象类型
-
变量的类型(变量内存值的类型)
- 基本类型:保存就是基本类型的数据
- 引用类型:保存的是地址值
二、什么是内存
1、什么是数据
- 存储在内存中代表特定信息的东西,本质上是0101……
- 数据的特点:可传递,可运算
- 一切皆数据
- 内存中所有操作的目标:数据
- 算术运算
- 逻辑运算
- 赋值
- 运行函数
2、什么是内存?
-
内存条通电后产生的可存储数据的空间(临时的)
-
内存的产生和死亡:内存条==>通电==>产生内存空间==>存储数据==>处理数据==>断电==>内存空间和数据都消失
-
一块小内存的2个数据
- 内部存储的数据
- 地址值
-
内存分类
- 栈:全局变量/局部变量(空间较小)
- 堆:对象(空间较大)
3、什么是变量
- 可变化的量,由变量名和变量值组成
- 每个变量都对应的一块小内存,变量名用来查找对应的内存,变量值就是内存中保存的数据
4、内存、数据、变量三者之间的关系
- 内存是用来存储数据的空间
- 变量是内存的标识
相关问题
1、问题:var a = xxx,a内存中到底保存的是什么?
- xxx是基本数据,保存的就是这个数据
- xxx是对象,保存的是对象的地址值
- xxx是一个变量,保存的xxx的内存内容(可能是基本数据,也可能是地址值)
2、关于引用变量赋值问题
- 2个引用变量指向同一个对象,通过一个变量修改对象内部数据,另一个变量看到的是修改之后的数据
- 2个引用变量指向同一个对象,让其中一个引用变量指向另一个对象,另一个对象依然指向前一个对象。
var obj1 = {name:'Tom'}
var obj2 = obj1;
function fn1(obj) {
obj.name = 'A';
}
fn1(obj1)
console.log(obj2.name)//A
function fn2(obj) {
obj = {name: 'B'}
}
fn2(obj1)
console.log(obj1.name) //A
3、在js调用函数传递变量参数时,是值传递还是引用传递
- 理解1:都是值(基本/地址值)传递
- 理解2:可能值传递,也可能是引用传递(地址值)
4、JS引擎如何管理内存
1、内存生命周期
- 分配小内存空间,得到它的使用权
- 存储数据,可以反复进行操作
- 释放小内存空间
2、释放内存
- 局部变量:函数执行完自动释放
- 对象:成为垃圾对象==>由垃圾回收器回收
var a = 3
var obj = {}
function fn() {
var b = {}
}
fn()//b是自动释放,b所指向的对象是在后面的某个时刻由垃圾回收器回收
三、什么是对象
1、什么是对象
- 多个数据的封装体
- 用来保存多个数据的容器
- 一个对象代表现实中的一个事物
2、为什么要用对象
- 统一管理多个数据
3、对象的组成
- 属性:属性名(字符串)和属性值(任意)组成
- 方法:一种特别的属性(属性值是函数)
4、如何访问对象内部数据
- 属性名:编码简单,有时不能用
- [‘属性名’]:编码麻烦,能通用
5、什么时候必须使用[‘属性值’]的方式
1、属性名包含特殊字符: - 空格
2、属性值不确定
var p = {}
//1、给p对象添加一个属性:content type: text/json
//p.content-type = 'text/json' //不能用
p['content-type'] = 'text/json'
var propName = 'myAge'
var value = 18
//p.propName = value //不能用
p[propName] = value
console.log(p[propName])
四、什么是函数
1、什么是函数
- 实现特定功能的n条语句的封装体
- 只有函数是可以执行的,其他类型的数据不能执行
2、为什么用函数
-
提高代码复用
-
便于阅读交流
3、如何定义函数
//1.函数声明
function fn1() {
console.log(1)
}
//2.表达式
fn2 = function() {
console.log(2)
}
4、如何调用(执行)函数
- test():直接调用
- obj.test():通过对象调用
- new test():new调用
- test.call/apply(obj):临时让test成为obj的方法调用
var obj = {}
function test(){
this.xxx="atguigu"
}
//obj.test() 不能直接调用
test.call(obj) //相当于obj.test()
console.log(obj.xxx) // atguigu
5、回调函数
1、什么函数才是回调函数
- 你定义的
- 你没有调用
- 最终它执行了
2、常见的回调函数
- dom事件回调函数
- 定时器回调函数
- ajax请求回调函数
- 生命周期回调函数
6、IIFE
1、理解
- 全称:Imm-Invoked Function Expression
2、作用
- 隐藏实现
- 不会污染外部(全局)命名空间
(function () { //匿名函数调用
var a = 3
console.log(a + 3)
})()
var a = 4
console.log(a)
;(function () {
var a = 1
function test () {
console.log(++a)
}
window.$ = function () { //向外暴露一个全局函数
return {
test:test
}
}
})()
$.test() //1. $是一个函数 2.$执行后返回的是一个对象
//6
//4
//2
7、函数中的this
1、this是什么
- 任何函数本质上都是通过某个对象来调用的,如果没有直接指定就是window
- 所有函数内部都有一个变量this
- 它的值是调用函数的当前对象
2、如何让确定this的值
- test():window
- p.test():p
- new test():新创建的对象
- p.call(obj):obj
function Person(color) {
console.log(this)
this.color = color;
this.getColor = function () {
console.log(this)
return this.color
};
this.setColor = function () {
console.log(this)
return this.color
};
}
Person("red"); //this是谁? window
var p = new Person("yello"); //this是谁? p
p.getColor(); //this是谁? p
var obj = {};
p.serColor.call(obj,"black"); //this是谁? obj
var test = p.setColor;
test(); //this是谁? window
function fn1() {
function fn2() {
console.log(this);
}
fn2();//this是谁? window
}
fn1;
【2】函数高级
一、原型与原型链
1、原型
(1)函数的prototype属性
- 每个函数都有一个prototype属性,它默认指向一个Object空对象(原型对象)
- 原型对象中一个属性constructor,它指向函数对象
(2)给原型对象添加属性(一般都是方法)
- 作用:函数的所有实例对象自动拥有原型中的属性(方法)
//每个函数都有一个prototype属性,它默认指向一个Object空对象(原型对象)
console.log(Data.prototype, typeof Date.prototype) //... object
function Fun {}
console.log(Fun.prototype) //默认指向一个Object空对象
//原型对象中由一个属性constructor,它指向函数对象
console.log(Fun.prototype.constructor === Fun) //true
console.log(Date.prototype.constructor === Date) //true
//给原型对象添加属性(一般是方法) ===> 实例对象可以访问
Fun.prototype.test = function() {
console.log('test()')
}
var fun = new Fun()
fun.test() //test()
2、显示原型与隐式原型
(1)每个函数function都有一个prototype,即显示原型(属性)默认指向一个空的Object对象
(2)每个实例对象都有一个‘ _ _ proto _ _’,可称为隐式原型(属性)
(3)对象的隐式原型的值为其对应构造函数的显式原型的值
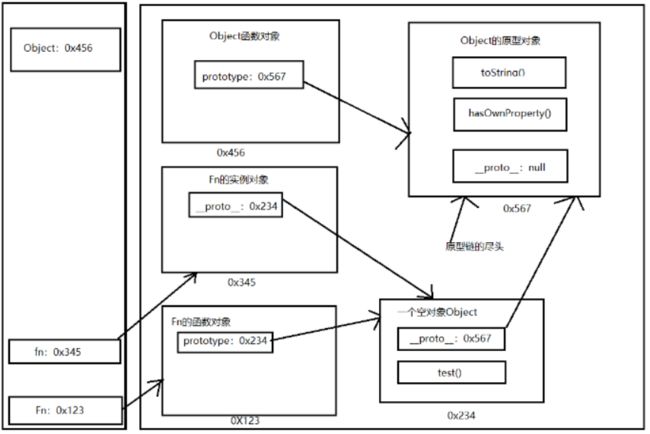
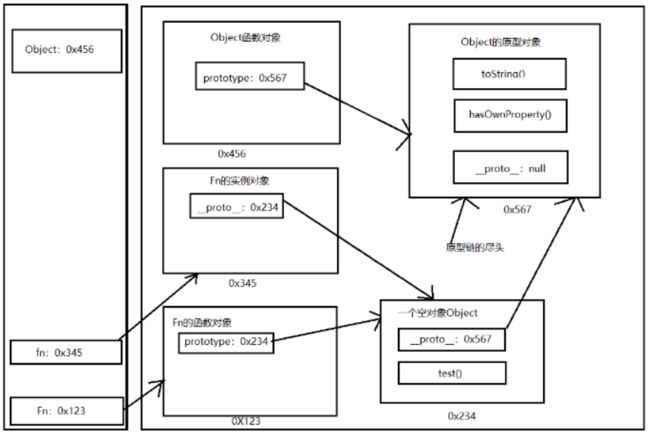
(4)内存构造(图)
function Fn() {
//内部语句:this.prototype = {}
}
//1、每个函数function都有一个prototype,即显示原型(属性)默认指向一个空的Object对象
console.log(Fn.prototype)
//2、每个实例对象都有一个__ proto__,可称为隐式原型(属性)
//创造实例对象
var fn = new Fn() //内部语句:this.__proto__ = Fn.prototype
//3、对象的隐式原型的值为其对应构造函数的显式原型的值
console.log(fn.__proto__ == Fn.prototype) // true
//给原型添加方法
Fn.prototype.test = function() {
console.log('test()')
}
fn.test() // test()
(5)总结
- 函数的prototype属性:定义函数时自动添加的,默认值时一个空Object对象
- 对象的_ _ proto _ _属性:创建对象时自动添加到,默认值为构造函数的prototype属性值
- 程序员能直接操作显示原型,但不能直接操作隐式原型(ES6之前)
3、原型链
(1)原型链
- 访问一个对象的属性值
- 先在自身属性中查找,找到返回
- 如果没有,再沿着 _ _ proto _ _ 这条链向上查找,找到返回
- 如果最终没找到,返回underfined
- 别名:隐式原型链
- 作用:查找对象的属性(方法)
function Fn() {
this.test1 = function() {
console.log('test1()')
}
}
Fn.prototype.test2 = function() {
console.log('test1()')
}
var fn = new Fn()
fn.test1()
fn.test2()
console.log(fn.toString())
fn.test3() //报错
(2)构造函数/原型实例对象的关系
(3)构造函数/原型实例对象的关系2
(4)相关问题
//1.函数的显示原型指向的对象默认时空Object实例对象(但Object不满足)
console.log(Fn.prototype instanceof Object) //true
console.log(Object.prototype instanceof Object) // false
console.log(Function.prototype instanceof Object) // true
//2.所有函数都是Function的实例(包含Function)
console.log(Function.__protp__ === Function.prototype) // true
//3.Object的原型对象是原型链尽头
console.log(Object.prototype.__proto__) //null
4、原型链属性问题
- 读取对象的属性值时:会自动到原型链中查找
- 设置对象的属性值时:不会查找原型链,如果当前对象中没有此属性,直接添加此属性并设置其值
- 方法一般定义在原型中,属性一般通过构造函数定义在对象本身上
function Fn() {}
Fn.prototype.a = 'xxx'
var fn1 = new Fn()
console.log(fn1.a, fn1) // xxx
var fn2 = new Fn()
fn2.a = 'yyy'
console.log(fn1.a,fn2.a,fn2) // xxx yyy
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name
this.age = age
}
Person.prototype.setName = function(name) {
this.name = name
}
var p1 = new Person('Tom', 12)
p1.setName('Bob')
console.log(p1) //Bob 12
var p2 = new Person('jack', 12)
p2.setName('Cat')
console.log(p2) // Cat 12
console.log(p1.__proto__ == p2.__proto__) // true 实例对象的隐式原型对象指向构造函数的显示原型对象
5、探索instanceof
1、instanceof是如何判断的?
- 表达式:A instanceof B
- 如果B函数的显示原型对象在A对象的原型链上,返回true,否则返回false
2、Function是通过new自己产生的实例
function Foo() {}
var f1 = new Foo()
console.log(f1 instanceof Foo) //true
console.log(f1 instanceof Obeject) // true
console.log(Object instanceof Function) //true
console.log(Object instanceof Object) //true
console.log(Function instanceof Function) //true
console.log(Function instanceof Object) //true
function Foo(){}
console.log(Object instaenceof Foo) //false
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-968lJYs1-1650793106729)(C:\Users\hello world\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\1643304158857.png)]
6、面试题
//测试1
function A(){}
A.prototype.n = 1
var b = new A()
A.prototype = {
n: 2,
m: 3
}
var c = new A()
console.log(b.n, b.m, c.n, c.m) // 1 undenfine 2 3
//测试2
var F = function() {}
Object.prototype.a = function() {
console.log('a()')
}
Function.prototype.b = function() {
console.log('b()')
}
var f = new F()
f.a() //a()
f.b() //报错
F.a() //a()
F.b() //b()
二、执行上下文与执行上下文栈
1、变量提升与函数提升
(1)变量声明提升
- 通过var定义(声明)的变量,在定义语句之前就可以访问到
- 值:undefined
(2)函数声明提升
- 通过function声明的函数,在之前就可以直接调用
- 值:函数定义(对象)
var a = 3
function fn1() {
console.log(a)
var a = 4
}
fn1() //undenfine 变量提升,fn1函数相当于 var a; console.log(a); a = 4
console.log(b) //undefined 变量提升
var b = 3
fn2() //可调用 函数提升
function fn2() {
console.log('fn2()')
}
fn3() //不能 变量提升
var fn3 = function(){}
2、执行上下文
(1)代码分类(位置)
- 全局代码
- 函数(局部)代码
(2)全局执行上下文
- 在执行全局代码前将window确定为全局执行上下文
- 对全局数据进行预处理
- var定义的全局变量 ==>underfined,添加为window的属性
- function声明的全局函数 ==> 赋值(fun),添加为window的方法
- this ==> 赋值(window)
(3)函数执行上下文
- 在调用函数,准备执行函数体之前,创建对应的函数执行上下文对象
- 对局部数据进行预处理
- 形参变量 > 赋值(实参)> 添加为执行上下文的属性
- argument ==>赋值(实参列表),添加为执行上下文的属性
- var定义的局部变量 ==> undefined,添加为执行上下文的属性
- function声明的函数 ==>赋值(fun),添加为执行上下文的方法
- this ==> 赋值(调用函数的对象)
- 开始执行函数体代码
3、执行上下文栈
(1)在全局代码执行前,JS引擎就会创建一个栈来存储管理所有的执行上下文对象
(2)在全局执行上下文(window)确定后,将其添加到栈中(压栈)
(3)在函数执行上下文创建后,将其添加到栈中(压栈)
(4)在当前函数执行完后,将栈顶的对象移除(出栈)
(5)当所有的代码执行完后,栈中只剩下window
//1.进入全局执行上下文
var a = 10
var bar = function (x) {
var b = 5
//3.进入foo函数执行上下文
foo(x + b)
}
var foo = function (y) {
var c== 5
console.log(a + c + y)
}
//2.进入bar函数执行上下文
bar(10)
4、面试题
console.log('gb: '+i)
var i = 1
foo(1)
function foo(i) {
if(i == 4) {
return
}
console.log('fb: ' + i)
foo(i + 1)
console.log('fe: ' + i)
}
console.log('ge: ' + i)
//gb: undefine
//fb: 1
//fb: 2
//fb: 3
//fe: 3
//fe: 2
//fe: 1
//ge: 4
//执行上下文5个
//测试题1
function a() {}
var a;
console.log(typeof a)
//测试题2
if(!(b in window)) {
var b = 1
}
console.log(b) //undefine
//测试题3
var c = 1
function c(c) {
console.log(c)
var c = 3
}
c(2) //报错,c不是一个函数
//其实代码相当于
var c
function c(c) {
console.log(c)
var c = 3
}
c = 1
c(2)
三、作用域与作用域链
1、作用域
(1)理解
- 就是一块“地盘”,一个代码段所在区域
- 它是静态的(相对于上下文对象),在编写代码时就确定
(2)分类
- 全局作用域
- 函数作用域
- 没有块作用域(ES6有了)
(3)作用
- 隔离变量,不用作用域下同名变量不会冲突
2、作用域与执行上下文
(1)区别1
- 全局作用域之外,每个函数都会创建自己的作用域,作用域在函数定义时就已经确定了,而不是在函数调用时
- 全局执行上下文环境是在全局作用域确定之后,js代码马上执行之前创建
- 函数执行上下文环境是在调用函数时,函数体代码执行之前创建
(2)区别2
- 作用域是静态的,只要函数定义好了就一直存在,且不会在变化
- 上下文环境是动态的,调用函数时创建,函数调用结束时上下文环境就会被释放
(3)联系
- 执行上下文(对象)是从属于所在的作用域
- 全局上下文环境 ==>全局作用域
- 函数上下文环境 ==> 对应的函数使用域
3、作用域链
(1)理解
- 多个上下级关系的作用域形成的链,它的方向是从下向上的(从内到外)
- 查找变量时就是沿着作用域链来查找的
(2)查找一个变量的查找规则
- 在当前作用域下的执行上下文中查找对应的属性,如果有直接返回,否则进入2
- 在上一级作用域的执行上下文中查找对应的属性,如果有直接返回,否则进入3
- 再次执行2的相同操作,直到全局作用域,如果还找不到就抛出找不到的异常
var x = 10
function fn() {
console.log(x)
}
function show(f) {
var x = 20
f()
}
show(fn)//10
var fn = function() {
console.log(fn)
}
fn() //输出函数
var obj = {
fn2: function() {
console.log(fn2) // 报错
console.log(this.fn2) //正常输出函数
}
}
obj.fn2()
四、闭包
1、理解闭包
(1)如何产生闭包
- 当一个嵌套内部(子)函数引用了嵌套的外部(父)函数的变量(或函数)是,就产生了闭包
(2)闭包到底是什么
- 理解1:闭包是嵌套的内部函数
- 理解2:包含被引用变量(或函数)的对象
- 注意:闭包存在于嵌套的内部函数中
function fn1() {
var a = 2
var b = 'abc'
function fn2() { //执行函数定义就会产生闭包(不用调用内部函数)
console.log(a)
}
fn2()
}
fn1() //需要调用外部函数
(3)产生闭包的条件
- 函数嵌套
- 内部函数引用了外部函数的数据(变量/函数)
2、常见闭包
//1.将函数作为另一个函数的返回值
function fn1() {
var a = 2
function fn2() {
a++
console.log(a)
}
return fn2
}
var f = fn1() //执行外部函数
f() //3 执行内部函数
f() //4 执行内部函数
//2.将函数作为实参传递给另一个函数调用
function showDelay(msg, time) {
setTimeout(function() {
alert(msg)
},time)
}
showDelay('atguigu',2000)
3、闭包作用
(1)使用函数内部的变量在函数执行完后,仍然存活在内存中(延长了局部变量的声明周期)
(2)让函数外部可以操作(读写)到函数内部的数据(变量/函数)
问题:
(1)函数执行完后,函数内部声明的局部变量是否还存在?
- 一般不存在,存在于闭包中的变量才存在
(2)在函数外部能直接访问函数内部的局部变量吗?
- 不能,但我们可以通过闭包让外部操作它
//1.将函数作为另一个函数的返回值
function fn1() {
var a = 2
function fn2() {
a++
console.log(a)
}
return fn2
}
var f = fn1() //执行外部函数 指向fn2,导致fn2不释放
f() //3 执行内部函数
f() //4 执行内部函数
4、闭包生命周期
(1)产生:在嵌套内部函数定义执行完时就产生了(不是在调用)
(2)死亡:在嵌套的内部函数成为垃圾对象时
function fn1() {
//此时闭包就已经产生了(函数提升,内部函数对象已经创建了)
var a = 2
function fn2() {
a++
console.log(a)
}
//var fn2 = function () {
// a++
// console.log(a)
//} 闭包在此句完成才产生
return fn2
}
var f = fn1() //执行外部函数 指向fn2,导致fn2不释放
f() //3 执行内部函数
f() //4 执行内部函数
f = null // 闭包死亡(包含闭包的函数对象成为垃圾对象)
5、闭包应用
闭包的应用:定义JS模块
- 具有特定功能的js文件
- 将所有的数据和功能封装在一个函数内部(私有的)
- 只向外暴露一个包含n个方法的对象或函数
- 模块的使用者,只需要通过模块暴露的对象调用方法来实现对应的功能
function myModule() {
//私有数据
var msg = 'My atguigu'
//操作数据的函数
function doSomething() {
console.log('doSomething()' + msg.toUpperCase)
}
function doOtherting() {
console.log('doOtherting()' + msg.toLowerCase)
}
//向外暴露对象(给外部使用的方法)
return {
doSomething: doSomething,
doOtherthing:doOtherting
}
}
//
var module = myModule()
module.doSomething()
module.doOtherthing()
(function(window) {
//私有数据
var msg = 'My atguigu'
//操作数据的函数
function doSomething() {
console.log('doSomething()' + msg.toUpperCase)
}
function doOtherting() {
console.log('doOtherting()' + msg.toLowerCase)
}
//向外暴露对象(给外部使用的方法)
window.myModule = {
doSomething: doSomething,
doOtherthing:doOtherting
}
})(window)
myModule.doSomething()
mymodule.doOtherthing()
6、闭包缺点
(1)缺点
- 函数执行完后,函数内的局部变量没有释放,占用内存时间会变长
- 容易造成内存泄漏
(2)解决
- 能不用闭包就不用
- 及时释放
function fn1(){
var arr = new Array[10000]
function fn2() {
console.log(arr.length)
}
return fn2
}
var f = fn1()
f()
f = null//让内部函数成为垃圾对象 -->回收闭包
(3)内存溢出
- 一种程序运行出现的错误
- 当程序运行需要的内存超过了剩余的内存时,就抛出内存溢出的错误
(4)内存泄漏
- 占用的内存没有及时释放
- 内存泄漏积累多了就容易导致内存溢出
- 常见的内存泄露
- 意外的全局变量
- 没有及时清理的计时器或回调函数
- 闭包
//意外的全局变量
function fn1() {
a = new Array(1000)
}
//没有及时清理的计时器或回调函数
var intervalId = setInterval(function(){ //启动循环定时器后不清理
console.log('------')
},1000)
//clearInterval(intervalId)
//闭包
function fn1() {
var a = 1;
function fn2() {
a++
console.log(a)
}
return fn2
}
var f = fn1()
f()
//f = null
五、面试题
var name1 = "the window"
var object1 = {
name1: "my Object"
getNameFunc: function() {
//没有闭包
return function() {
return this.name
}
}
}
console.log(object1.getNameFunc()()) //the window
var name2 = "the window"
var object1 = {
name2: "my Object"
getNameFunc: function() {
var that = this // 闭包
return function() {
return that.name2
}
}
}
console.log(object2.getNameFunc()()) //my object
function fun(n,o) {
console.log(o)
return {
fun: function(m){
return fun(m,n) //
}
}
}
var a = fun(0); a.fun(1); a.fun(2); a.fun(3) //undefine 0 0 0
var b = fun(0).fun(1).fun(2).fun(3); //undefine 0 1 2
var c = fun(0).fun(1); c.fun(2); c.fun(3); //undefine 0 1 1
【3】对象高级
一、对象创建模式
方式一:Object构造函数模式
- 套路:先创建空Object对象,在动态添加属性/方法
- 适用场景:起始时不确定对象内部数据
- 问题:语句太多
var p = new Object()
p.name = 'Tom'
p.age = 12
p.setName = function(name) {
this.name = name
}
方式二:对象字面量模式
- 套路:使用{}创建对象,同时指定属性/方法
- 适用场景:起始时对象内部数据是确定的
- 问题:如果创建多个对象,有重复代码
var p = {
name: 'Tom',
age: 12,
setName: function(name) {
this.name = name
}
}
方式三:工厂模式
- 套路:通过工厂函数动态创建对象并返回
- 适用场景:需要创建多个对象
- 问题:对象没有一个具体的类型,都是Object类型
function createPerson(name,age) {
var obj = {
name: name,
age: age,
setName: function(name) {
this.name = name
}
}
return obj
}
//创建
var p1 = createPerson('Tome',12)
var p1 = createPerson('BOb',12)
-
方式四:自定义构造函数模式
-
套路:自定义构造函数,通过new创建对象
-
适用场景:需要创建多个类型确定的对象
-
问题:每个对象都有相同的数据,浪费内存
function Person(name,age) {
this.name = name
this.age = age
this.setName = function(name) {
this.name = name
}
}
function Student(name,age) {
this.name = name
this.age = age
this.setName = function(name) {
this.name = name
}
}
var p = new Person('Tom',12)
var s = new Student('Jack',12)
console.log(p instanceof Person) // true
console.log(s instanceof Student) // true
二、继承模式
1、原型链继承
(1)套路
- 定义父类型构造函数
- 给父类的原型添加方法
- 定义子类型的构造函数
- 创建父类型的对象赋值给子类型的原型
- 将子类型原型的构造属性设置为子类型
- 给子类型原型添加方法
- 创建子类型的对象:可以调用父类型的方法
(2)关键
- 子类型的原型为父类型的一个实例对象
//父类型
function Supper() {
this.supProp = 'Supper property'
}
Supper.prototype.showSupperProp = function() {
console.log(this.supProp)
}
//子类型
function Sub() {
this.supProp = 'Sub property'
}
//子类型的原型为父类的一个实例对象
Sub.proeotype = new Supper()
//让子类型的原型的constructor指向SUb
Sub.proeotype.constructor = Sub
Sub.prototype.showSubProp = function() {
console.log(this.supProp)
}
var sub = new Sub()
sub.showSupperProp() //Supper property'
2、借用构造函数继承(假的)
(1)套路
- 定义父类型构造函数
- 定义子类型的构造函数
- 在子类型构造函数中调用父类型构造
(2)关键
- 在子类型构造函数中通用supper()调用父类型构造函数
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name
this.age = age
}
function Student(name, age, price) {
Person.call(this,name, age) //相当于:this.Preson(name, age)
this.price = price
}
var s = new Student('Jack', 12, 14000)
3、组合继承
(1)原型链+借用构造函数的组合继承
- 利用原型链实现对父类型对象的方法继承
- 利用super()借用父类型构建函数初始化相同属性
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name
this.age = age
}
Person.prototype.setName = function (name) {
this.name = name
}
function Student(name, age, price) {
Person.call(this,name, age) //为了得到属性
this.price = price
}
Student.prototype = new Person() //为了看见父类型的方法
Student.prototype.constructor = Student //修正constructor属性
Student.prototype.setPrice = {
this.price = price
}
var s = new Student('Jack', 12, 14000)
【4】线程机制与事件机制
一、进程与进程
1、进程
- 程序的一次执行,它占有一片独有的内存空间
- 可以通过windows任务管理查看进程
2、线程
- 是进程内的一个独立执行单元
- 是程序执行的一个完整流程
- 是CPU的最小调度单元
3、图解
4、相关知识
- 应用程序必须运行在某个进程的某个线程上
- 一个进程中至少有有一个运行的线程:主线程,进程启动后自动创建
- 一个进程中也可以同时运行多个线程,我们会说程序是多线程运行的
- 一个进程内的数据可以供其中的多个线程直接共享
- 多个进程之间的数据是不能直接共享的
- 线程池(thread pool):保存多个线程对象的容器,实现线程对象的反复利用
5、相关问题
(1)何为多进程与多线程
- 多进程运行:一应用层序可以同时启动多个实例运行
- 多线程:在一个进程内,同时有多个线程运行
(2)JS是单线程还是多线程
- js是单线程运行的
- 但使用H5中的Web Workers可以多线程运行
(3)比较单线程与多线程
- 多线程
- 优点
- 能有效提升CPU的利用率
- 缺点
- 创建多线程开销
- 线程间切换开销
- 死锁与状态同步问题
- 优点
- 单线程
- 优点
- 顺序编程简单易懂
- 缺点
- 效率低
- 优点
(4)浏览器运行是单线程还是多线程
有的单线程有的多线程
- 单:firefox、老版IE
- 多:chrome、新版IE
二、浏览器内核
支持浏览器运行的最核心的程序
三、定时器引发的思考
1、定时器真的是定时执行的吗?
- 定时器并不能保证真正定时执行
- 一般会延时一点(可以接收),也有可能延迟很长时间(不能接收)
2、定时器回调函数是在哪个线程执行的?
- 在主线程执行的,js是单线程的
3、定时器是如何实现的?
- 事件循环模型