逃脱只会部署集群系列 —— Istio实现微服务流量治理以及envoy剖析
目录
一、利用istio进行微服务流量分配
1、模拟流量分配规则场景
2、使用Istio实现
二、服务网格细节剖析
1、宏观角度剖析
2、认识envoy
3、envoy的xDS
4、envoy在微服务治理中的工作环境
三、envoy实现原理
1、工作原理
四、envoy实现流量转发剖析 (重要)
1、istio-init容器作用
2、init容器进行入站出站流量监控
3、envoy接管出口流量剖析
1、监听15001端口跳转路由
2、route规则跳转cluster配置
3、cluster规则跳转endpoint配置
4、endpoint规则跳转pod配置
4、envoy接管入口流量剖析
1、iptables转发入口请求到15006
2、15006监听流量并转发至本地80端口
3、逻辑图总结
五、ingressgateway访问网格服务
1、场景描述
2、为啥不用ingress
3、利用ingress访问
4、利用ingressgateway访问网格服务
5、配置nginx转发域名请求
一、利用istio进行微服务流量分配
1、模拟流量分配规则场景
集群默认流量访问是50%规则的,如果场景是后台账单服务更新v2版本,前期规划90%的流量访问v1版本,导入10%的流量到v2版本,或者是主备节点的流量分配,此时怎么实现呢?
模型图
2、使用Istio实现
istio注入:
# 注入的意思就是获取代理权 $ istioctl kube-inject -f bill-service-dpl-v1.yaml|kubectl apply -f - $ istioctl kube-inject -f bill-service-dpl-v2.yaml|kubectl apply -f - $ istioctl kube-inject -f front-tomcat-dpl-v1.yaml|kubectl apply -f -
# 每个pod增加边车容器数量变2
[root@k8s-master demo]# kubectl get po -n istio-demo
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
bill-service-v1-78974677c-zgh8f 2/2 Running 0 7m15s
bill-service-v2-5d9c7f875d-gf6r5 2/2 Running 0 7m10s
front-tomcat-v1-8649f6fd68-rtzwf 2/2 Running 0 6m35s
若想实现上述需求,需要解决如下两个问题:
让访问账单服务的流量按照我们期望的比例,其实是一条路由规则,如何定义这个规则
如何区分两个版本的服务
两个新的资源类型:
VirtualService和DestinationRule
bill-service-destnation-rule.yaml
定义v1跳转至bill-service的服务下的label为version=v1的pod
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: dest-bill-service
namespace: istio-demo
spec:
host: bill-service
subsets:
- name: v1
labels:
version: v1
- name: v2
labels:
version: v2bill-service-virtualservice.yaml
定义90%流量跳转至destnation的v1上面
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: vs-bill-service
namespace: istio-demo
spec:
hosts:
- bill-service
http:
- name: bill-service-route
route:
- destination:
host: bill-service
subset: v1
weight: 90
- destination:
host: bill-service
subset: v2
weight: 10使用client验证流量分配是否生效。
$ kubectl apply -f bill-service-virtualservice.yaml $ kubectl apply -f bill-service-destnation-rule.yaml [root@k8s-master demo]# kubectl -n istio-demo get vs NAME GATEWAYS HOSTS AGE vs-bill-service [bill-service] 4m46s [root@k8s-master demo]# kubectl -n istio-demo get destinationrule NAME HOST AGE dest-bill-service bill-service 4m41s $ kubectl -n istio-demo exec front-tomcat-v1-8649f6fd68-rtzwf -c front-tomcat -- curl -s bill-service:9999 此时发现访问规则已经变了,流量调度成功。
二、服务网格细节剖析
1、宏观角度剖析
执行的操作:
-
使用istioctl为pod注入了sidecar
-
创建了virtualservice和destinationrule
如何最终影响到了pod的访问行为?
可以看到注入后yaml中增加了很多内容:
pod被istio注入后,被纳入到服务网格中,每个pod都会添加一个名为istio-proxy的容器(常说的sidecar容器),istio-proxy容器中有两个进程,一个是piolot-agent,一个是envoy
$ kubectl -n istio-demo exec -ti front-tomcat-v1-8649f6fd68-rtzwf -c istio-proxy bash
istio-proxy@front-tomcat-v1-8649f6fd68-rtzwf:/$ ps aux
USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND
istio-p+ 1 0.0 1.5 782916 78044 ? Ssl 14:30 0:01 /usr/local/bin/pilot-agent proxy sidecar --domain istio-demo.svc.cluster.local --serviceCluster front-tom
istio-p+ 13 0.2 1.1 185940 55584 ? Sl 14:30 0:06 /usr/local/bin/envoy -c etc/istio/proxy/envoy-rev0.json --restart-epoch 0 --drain-time-s 45 --parent-shut
目前已知:
-
在istio网格内,每个Pod都会被注入一个envoy代理
-
envoy充当nginx的角色,做为proxy代理,负责接管pod的入口和出口流量
目前,还需要搞清楚几个问题:
-
istio-init初始化容器作用是什么?
-
istio-proxy如何接管业务服务的出入口流量?
2、认识envoy
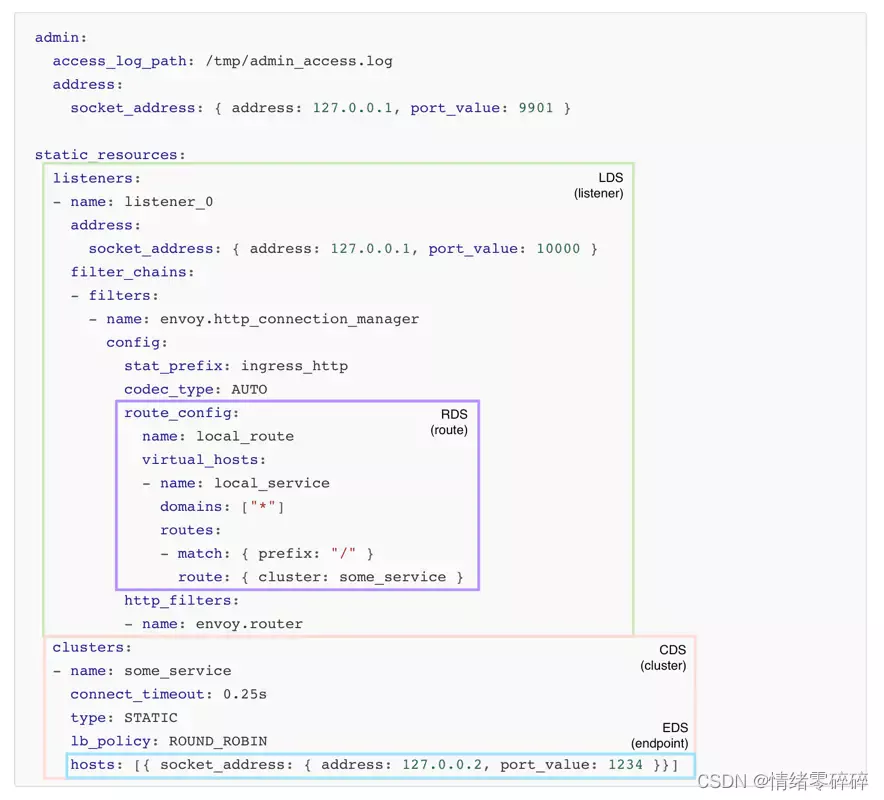
Envoy 是为云原生应用设计的代理。网络代理程序的流程:比如作为一个代理,首先要能获取请求流量,通常是采用监听端口的方式实现;其次拿到请求数据后需要对其做微处理,例如附加 Header 或校验某个 Header 字段的内容等,这里针对来源数据的层次不同,可以分为 L3/L4/L7,然后将请求转发出去;转发这里又可以衍生出如果后端是一个集群,需要从中挑选一台机器,如何挑选又涉及到负载均衡等。
listener: Envoy 的监听地址。Envoy 会暴露一个或多个 Listener 来监听客户端的请求。
filter: 过滤器。在 Envoy 中指的是一些“可插拔”和可组合的逻辑处理层,是 Envoy 核心逻辑处理单元。
route_config: 路由规则配置。即将请求路由到后端的哪个集群。
cluster: 服务提供方集群。Envoy 通过服务发现定位集群成员并获取服务,具体路由到哪个集群成员由负载均衡策略决定。
3、envoy的xDS
Envoy的启动配置文件分为两种方式:静态配置和动态配置。
-
静态配置是将所有信息都放在配置文件中,启动的时候直接加载。
-
动态配置需要提供一个Envoy的服务端,用于动态生成Envoy需要的服务发现接口,这里叫XDS,通过发现服务来动态的调整配置信息,Istio就是实现了v2的API。
Envoy 接收到请求后,会先走 FilterChain,通过各种 L3/L4/L7 Filter 对请求进行微处理,然后再路由到指定的集群,并通过负载均衡获取一个目标地址,最后再转发出去。
其中每一个环节可以静态配置,也可以动态服务发现,也就是所谓的 xDS。这里的 x 是一个代词,类似云计算里的 XaaS 可以指代 IaaS、PaaS、SaaS 等。
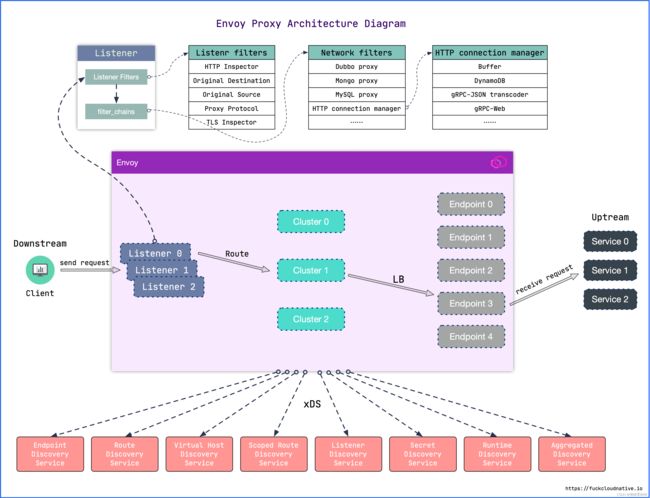
所以,envoy的架构大致的样子如下:
Downstream
下游(downstream)主机连接到 Envoy,发送请求并或获得响应。
Upstream
上游(upstream)主机获取来自 Envoy 的链接请求和响应。
监听器
-
除了过滤器链之外,还有一种过滤器叫监听器过滤器(Listener filters),它会在过滤器链之前执行,用于操纵连接的元数据。这样做的目的是,无需更改 Envoy 的核心代码就可以方便地集成更多功能。
-
每个监听器都可以配置多个过滤器链(Filter Chains),监听器会根据
filter_chain_match中的匹配条件将流量转交到对应的过滤器链,其中每一个过滤器链都由一个或多个网络过滤器(Network filters)组成。这些过滤器用于执行不同的代理任务,如速率限制,TLS客户端认证,HTTP连接管理,MongoDB嗅探,原始 TCP 代理等。
4、envoy在微服务治理中的工作环境
可以在服务旁运行,以平台无关的方式提供必要的特性,所有到服务的流量都通过 Envoy 代理,这里 Envoy 扮演的就是 Sidecar 的角色。
在istio中,envoy的位置:
很明显,istio中,envoy进行流量治理,更多的使用的是XDS进行配置更新,而我们知道,XDS需要有服务端来提供接口,istiod中的pilot组件则提供了xDS服务端接口的实现 。
三、envoy实现原理
1、工作原理
目前为止,我们可以知道大致的工作流程:
用户端,通过创建服务治理的规则(VirtualService、DestinationRule等资源类型),存储到ETCD中
istio控制平面中的Pilot服务监听上述规则,转换成envoy可读的规则配置,通过xDS接口同步给各envoy
envoy通过xDS获取最新的配置后,动态reload,进而改变流量转发的策略
思考两个问题:
istio中envoy的动态配置到底长什么样子?
在istio的网格内,front-tomcat访问到bill-service,流量的流向是怎么样的?
针对问题1:
每个envoy进程启动的时候,会在
127.0.0.1启动监听15000端口$ kubectl -n istio-demo exec -ti front-tomcat-v1-78cf497978-ppwwk -c istio-proxy bash # netstat -nltp # curl localhost:15000/help # curl localhost:15000/config_dump
针对问题2:
$ kubectl -n istio-demo exec -ti front-tomcat-v1-78cf497978-ppwwk -c front-tomcat bash # curl bill-service:9999
按照之前的认知,
现在为什么流量分配由5:5 变成了9:1?流量经过envoy了的处理
四、envoy实现流量转发剖析 (重要)
我们已经知道利用istio注入可以为每个pod添加istio-init容器和istio-proxy的容器(常说的sidecar容器),istio-proxy容器中有两个进程,一个是piolot-agent,一个是envoy,并且可以实现流量的调度,那么重点来了:
为什么我发起请求会跑到istio调度上面去,策略具体是如何实现的?
1、istio-init容器作用
Istio 给应用 Pod 注入的配置主要包括:
-
Init 容器
istio-initIstio 在 pod 中注入的 Init 容器名为
istio-init,作用是为 pod 设置 iptables 端口转发。我们在上面 Istio 注入完成后的 YAML 文件中看到了该容器的启动命令是:
istio-iptables -p 15001 -z 15006 -u 1337 -m REDIRECT -i '*' -x "" -b '*' -d 15090,15021,15020
Init 容器的启动入口是
istio-iptables命令行,该命令行工具的用法如下:$ istio-iptables [flags] -p: 指定重定向所有 TCP 出站流量的 sidecar 端口(默认为 $ENVOY_PORT = 15001) -m: 指定入站连接重定向到 sidecar 的模式,“REDIRECT” 或 “TPROXY”(默认为 $ISTIO_INBOUND_INTERCEPTION_MODE) -b: 逗号分隔的入站端口列表,其流量将重定向到 Envoy(可选)。使用通配符 “*” 表示重定向所有端口。为空时表示禁用所有入站重定向(默认为 $ISTIO_INBOUND_PORTS) -d: 指定要从重定向到 sidecar 中排除的入站端口列表(可选),以逗号格式分隔。使用通配符“*” 表示重定向所有入站流量(默认为 $ISTIO_LOCAL_EXCLUDE_PORTS) -o:逗号分隔的出站端口列表,不包括重定向到 Envoy 的端口。 -i: 指定重定向到 sidecar 的 IP 地址范围(可选),以逗号分隔的 CIDR 格式列表。使用通配符 “*” 表示重定向所有出站流量。空列表将禁用所有出站重定向(默认为 $ISTIO_SERVICE_CIDR) -x: 指定将从重定向中排除的 IP 地址范围,以逗号分隔的 CIDR 格式列表。使用通配符 “*” 表示重定向所有出站流量(默认为 $ISTIO_SERVICE_EXCLUDE_CIDR)。 -k:逗号分隔的虚拟接口列表,其入站流量(来自虚拟机的)将被视为出站流量。 -g:指定不应用重定向的用户的 GID。(默认值与 -u param 相同) -u:指定不应用重定向的用户的 UID。通常情况下,这是代理容器的 UID(默认值是 1337,即 istio-proxy 的 UID)。 -z: 所有进入 pod/VM 的 TCP 流量应被重定向到的端口(默认 $INBOUND_CAPTURE_PORT = 15006)。
以上传入的参数都会重新组装成 iptables 规则,关于 Istio 中端口用途请参考 Istio 官方文档。
这条启动命令的作用是:
-
将应用容器的所有入站流量都转发到 envoy的 15006 端口(15090 端口(Envoy Prometheus telemetry)和 15020 端口(Ingress Gateway)除外,15021(sidecar健康检查)端口)
-
将所有出站流量都重定向到 sidecar 代理(通过 15001 端口)
-
上述规则对id为1337用户除外,因为1337是istio-proxy自身的流量
该容器存在的意义就是让 sidecar 代理可以拦截pod所有的入站(inbound)流量以及出站(outbound)流量,这样就可以实现由sidecar容器来接管流量,进尔实现流量管控。
-
2、init容器进行入站出站流量监控
因为 Init 容器初始化完毕后就会自动终止,因为我们无法登陆到容器中查看 iptables 信息,但是 Init 容器初始化结果会保留到应用容器和 sidecar 容器中。
# 查看front-tomcat服务的istio-proxy容器的id $ docker ps |grep front-tomcat d02fa8217f2f consol/tomcat-7.0 "/bin/sh -c /opt/tom…" 2 days ago Up 2 days k8s_front-tomcat_front-tomcat-v1-78cf497978-ppwwk_istio-demo_f03358b1-ed17-4811-ac7e-9f70e6bd797b_0
# 根据容器id获取front-tomcat容器在宿主机中的进程
$ docker inspect f67195afaf5a|grep -i pid
"Pid": 28834,
"PidMode": "",
"PidsLimit": null,
# 进入该进程的网络命名空间
$ nsenter -n --target 110502
# 查看命名空间的iptables规则
$ iptables -t nat -vnL
# 2、PREROUTING 链:用于目标地址转换(DNAT),将所有入站 TCP 流量跳转到 ISTIO_INBOUND 链上。
Chain PREROUTING (policy ACCEPT 2616 packets, 157K bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
2615 157K ISTIO_INBOUND tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
# 1、INPUT 链:处理输入数据包,非 TCP 流量将继续 OUTPUT 链。
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 2615 packets, 157K bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
# 5、OUTPUT 链:将所有出站数据包跳转到 ISTIO_OUTPUT 链上。
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 1324 packets, 125K bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
33 1980 ISTIO_OUTPUT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
# 8、POSTROUTING 链:所有数据包流出网卡时都要先进入POSTROUTING 链,内核根据数据包目的地判断是否需要转发出去,我们看到此处未做任何处理。5-8实现了出站流量的15001端口监控
Chain POSTROUTING (policy ACCEPT 1343 packets, 126K bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
# 3、ISTIO_INBOUND 链:将所有入站流量重定向到 ISTIO_IN_REDIRECT 链上,目的地为 15090,15020,15021端口的流量除外,发送到以上两个端口的流量将返回 iptables 规则链的调用点,即 PREROUTING 链的后继 POSTROUTING。过滤特殊的直接返回,剩下需要调度的继续往下走
Chain ISTIO_INBOUND (1 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 RETURN tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:15008
0 0 RETURN tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:22
0 0 RETURN tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:15090
2615 157K RETURN tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:15021
0 0 RETURN tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:15020
0 0 ISTIO_IN_REDIRECT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
# 4、ISTIO_IN_REDIRECT 链:将所有入站流量REDIRECT跳转到本地的 15006 端口,至此成功的拦截了流量到sidecar中。前四步实现了入站流量的15006端口监控。
Chain ISTIO_IN_REDIRECT (3 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 REDIRECT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 redir ports 15006
# 6、ISTIO_OUTPUT 链:选择需要重定向到 Envoy(即本地) 的出站流量,所有非 localhost 的流量全部转发到 ISTIO_REDIRECT。为了避免流量在该 Pod 中无限循环,所有到 istio-proxy 用户空间的流量都返回到它的调用点中的下一条规则,本例中即 OUTPUT 链,因为跳出 ISTIO_OUTPUT 规则之后就进入下一条链 POSTROUTING。如果目的地非 localhost 就跳转到 ISTIO_REDIRECT;如果流量是来自 istio-proxy 用户空间的,那么就跳出该链,返回它的调用链继续执行下一条规则(OUTPUT 的下一条规则,无需对流量进行处理);所有的非 istio-proxy 用户空间的目的地是 localhost 的流量就跳转到 ISTIO_REDIRECT。
Chain ISTIO_OUTPUT (1 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 RETURN all -- * lo 127.0.0.6 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 ISTIO_IN_REDIRECT all -- * lo 0.0.0.0/0 !127.0.0.1 owner UID match 1337
0 0 RETURN all -- * lo 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 ! owner UID match 1337
14 840 RETURN all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 owner UID match 1337
0 0 ISTIO_IN_REDIRECT all -- * lo 0.0.0.0/0 !127.0.0.1 owner GID match 1337
0 0 RETURN all -- * lo 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 ! owner GID match 1337
0 0 RETURN all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 owner GID match 1337
0 0 RETURN all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 127.0.0.1
19 1140 ISTIO_REDIRECT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
# 7、ISTIO_REDIRECT 链:将所有流量重定向到 Sidecar(即本地) 的 15001 端口。
Chain ISTIO_REDIRECT (1 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
19 1140 REDIRECT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 redir ports 15001说明pod内的入站流量请求被监听在15006端口,出站流量请求被监听在15001端口的envoy的进程接收到,进而就走到了envoy的Listener -> route -> cluster -> endpoint 转发流程。
问题就转变为:如何查看envoy的配置,跟踪转发的过程?
3、envoy接管出口流量剖析
我们知道,envoy的配置非常复杂,直接在config_dump里去跟踪xDS的过程非常繁琐。因此istio提供了调试命令,方便查看envoy的流量处理流程。
$ istioctl proxy-config -h
1、监听15001端口跳转路由
# 1、既然出口流量都被15001监听,查看15001的监听
[root@k8s-master demo]# istioctl pc listener front-tomcat-v1-8649f6fd68-rtzwf.istio-demo --port 15001
ADDRESS PORT MATCH DESTINATION
0.0.0.0 15001 ALL PassthroughCluster
# virtualOutbound的监听不做请求处理,hiddenEnvoyDeprecatedUseOriginalDst: true, 直接转到原始的请求对应的监听器中
### 请求过来先给monitor15001过目,已阅,继续该去哪去哪
# 2、查看访问端口是9999的监听器
[root@k8s-master demo]# istioctl pc listener front-tomcat-v1-8649f6fd68-rtzwf.istio-demo --port 9999 -ojson
...
{
"name": "0.0.0.0_9999",
"address": {
"socketAddress": {
"address": "0.0.0.0",
"portValue": 9999
}
},
"filterChains": [
{
"filterChainMatch": {
"applicationProtocols": [
"http/1.0",
"http/1.1",
"h2c"
]
},
"filters": [
{
"name": "envoy.filters.network.http_connection_manager",
"typedConfig": {
"@type": "type.googleapis.com/envoy.extensions.filters.network.http_connection_manager.v3.HttpConnectionManager",
"statPrefix": "outbound_0.0.0.0_9999",
"rds": {
"configSource": {
"ads": {},
"resourceApiVersion": "V3"
},
"routeConfigName": "9999" #重点是这个
},
...
envoy收到请求后,会转给监听器进行处理请求,监听器先匹配address和port和socket都一致的Listener,如果没找到再找port一致,address==0.0.0.0的Listener
发现istio会为网格内的Service Port创建名为
0.0.0.0_的虚拟监听器,本例中为0.0.0.0_9999。envoy的15001端口收到请求后,直接转到了
0.0.0.0_9999,进而转到了"routeConfigName": "9999",即9999这个route中。
###利用http_connection_manager模块将包请求转换为http,然后发送到名字叫9999的route上面了,此时完成监听端口到路由的过渡
2、route规则跳转cluster配置
下面,看下route的内容:
$ istioctl pc route front-tomcat-v1-8649f6fd68-rtzwf.istio-demo --name 9999
NOTE: This output only contains routes loaded via RDS.
NAME DOMAINS MATCH VIRTUAL SERVICE
9999 bill-service /* vs-bill-service.istio-demo
# 发现了前面创建的virtual service
istioctl pc route front-tomcat-v1-8649f6fd68-rtzwf.istio-demo --name 9999 -ojson
[
{
"name": "9999",
"virtualHosts": [
{
"name": "allow_any",
"domains": [
"*"
],
"routes": [
{
"name": "allow_any",
"match": {
"prefix": "/"
},
"route": {
"cluster": "PassthroughCluster",
"timeout": "0s",
"maxGrpcTimeout": "0s"
}
}
],
"includeRequestAttemptCount": true
},
{
"name": "bill-service.istio-demo.svc.cluster.local:9999",
"domains": [
"bill-service.istio-demo.svc.cluster.local",
"bill-service.istio-demo.svc.cluster.local:9999",
"bill-service",
"bill-service:9999",
"bill-service.istio-demo.svc.cluster",
"bill-service.istio-demo.svc.cluster:9999",
"bill-service.istio-demo.svc",
"bill-service.istio-demo.svc:9999",
"bill-service.istio-demo",
"bill-service.istio-demo:9999",
"10.1.122.241",
"10.1.122.241:9999"
],
"routes": [
{
"name": "bill-service-route",
"match": {
"prefix": "/"
},
"route": {
"weightedClusters": {
"clusters": [
{
"name": "outbound|9999|v1|bill-service.istio-demo.svc.cluster.local",
"weight": 90
},
{
"name": "outbound|9999|v2|bill-service.istio-demo.svc.cluster.local",
"weight": 10
}
]
},
...
满足访问domains列表的会优先匹配到,访问10.111.219.247:9999或者bill-service:9999时就会匹配到下面的规则,因此匹配bill-service.istio-demo.svc.cluster.local:9999这组虚拟hosts,进而使用到基于weight的集群配置。;访问www.baidu.com:9999就会匹配到上面的规则也就是allow_any放行,这样可以防止别的流量被拦截,此时完成了route到cluster的过渡
我们看到,流量按照预期的配置进行了转发:
90% -> outbound|9999|v1|bill-service.istio-demo.svc.cluster.local 10% -> outbound|9999|v2|bill-service.istio-demo.svc.cluster.local
3、cluster规则跳转endpoint配置
$ istioctl pc cluster front-tomcat-v1-8649f6fd68-rtzwf.istio-demo --fqdn bill-service.istio-demo.svc.cluster.local -ojson
# --fqdn根据域名访问
...
"name": "outbound|9999|v1|bill-service.istio-demo.svc.cluster.local",
"type": "EDS",
"edsClusterConfig": {
"edsConfig": {
"ads": {},
"resourceApiVersion": "V3"
},
"serviceName": "outbound|9999|v1|bill-service.istio-demo.svc.cluster.local"
},
...
我们发现,endpoint列表是通过eds获取的,因此,查看endpoint信息:
###此时完成了cluster到endpoint的转换,此时规则已经到了具体的pod的80端口了
4、endpoint规则跳转pod配置
[root@k8s-master demo]# istioctl pc endpoint front-tomcat-v1-8649f6fd68-rtzwf.istio-demo --cluster 'outbound|9999|v1|bill-service.istio-demo.svc.cluster.local' -ojson
[
{
"name": "outbound|9999|v1|bill-service.istio-demo.svc.cluster.local",
"addedViaApi": true,
"hostStatuses": [
{
"address": {
"socketAddress": {
"address": "10.244.0.53",
"portValue": 80
}
},
[root@k8s-master demo]# kubectl get po -n istio-demo -owide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
bill-service-v1-78974677c-zgh8f 2/2 Running 0 167m 10.244.0.53 k8s-master
bill-service-v2-5d9c7f875d-gf6r5 2/2 Running 0 167m 10.244.1.170 k8s-node2
front-tomcat-v1-8649f6fd68-rtzwf 2/2 Running 0 167m 10.244.1.171 k8s-node2
目前为止,经过envoy的规则,流量从front-tomcat的pod中知道要发往10.244.0.53:80 这个pod地址。也就是说我们已经实现了请求到目的pod的80端口的过程。现在相当于在front的istio-proxy容器里面curl 10.244.0.53:80地址
此时envoy接管出站流量完成。
4、envoy接管入口流量剖析
envoy不止接管出站流量,入站流量同样会接管。
此时只是把流量携带权重规则发到了正确的bill-service的80端口,完成了envoy出口流量的过程,接下来我们剖析下,bill-service容器是如果处理入口流量的。
下面看下流量到达bill-service-v1的pod后的处理:
###刚才在发起方把策略转到目的方80端口,默认所有流入请求都被15006拦截
先回顾前面的iptables规则,除特殊情况以外,所有的出站流量被监听在15001端口的envoy进程拦截处理,同样的,分析bill-service-v1的iptables规则可以发现,监听在15006端口的envoy进程通过在PREROUTING链上添加规则,同样将进入pod的入站流量做了拦截。
1、iptables转发入口请求到15006
# PREROUTING 链:用于目标地址转换(DNAT),将所有入站 TCP 流量跳转到 ISTIO_INBOUND 链上。
Chain PREROUTING (policy ACCEPT 148 packets, 8880 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
148 8880 ISTIO_INBOUND tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0# INPUT 链:处理输入数据包,非 TCP 流量将继续 OUTPUT 链。
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 148 packets, 8880 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination# ISTIO_INBOUND 链:将所有入站流量重定向到 ISTIO_IN_REDIRECT 链上,目的地为 15090,15020,15021端口的流量除外,发送到以上两个端口的流量将返回 iptables 规则链的调用点,即 PREROUTING 链的后继 POSTROUTING。
Chain ISTIO_INBOUND (1 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 RETURN tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:15008
0 0 RETURN tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:22
0 0 RETURN tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:15090
143 8580 RETURN tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:15021
5 300 RETURN tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:15020
0 0 ISTIO_IN_REDIRECT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0# ISTIO_IN_REDIRECT 链:将所有入站流量跳转到本地的 15006 端口,至此成功的拦截了流量到sidecar中。
Chain ISTIO_IN_REDIRECT (3 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 REDIRECT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 redir ports 15006
2、15006监听流量并转发至本地80端口
15006端口是一个名为 virtualInbound虚拟入站监听器, 15006监听80端口,然后转到route,再到cluster
$ istioctl pc listener bill-service-v1-78974677c-zgh8f.istio-demo --port 15006 -ojson
"name": "virtualInbound-catchall-http" #
},
{
"filterChainMatch": {
"destinationPort": 80,
"applicationProtocols": [
"istio",
"istio-http/1.0",
"istio-http/1.1",
"istio-h2"
]
},
"filters": [
{
"name": "istio.metadata_exchange",
"typedConfig": {
"@type": "type.googleapis.com/udpa.type.v1.TypedStruct",
"typeUrl": "type.googleapis.com/envoy.tcp.metadataexchange.config.MetadataExchange",
"value": {
"protocol": "istio-peer-exchange"
}
}
},
{
"name": "envoy.filters.network.http_connection_manager",
"typedConfig": {
"@type": "type.googleapis.com/envoy.extensions.filters.network.http_connection_manager.v3.HttpConnectionManager",
"statPrefix": "inbound_0.0.0.0_80",
"routeConfig": {
"name": "inbound|9999|http|bill-service.istio-demo.svc.cluster.local",
"virtualHosts": [
{
"name": "inbound|http|9999",
"domains": [
"*"
],
"routes": [
{
"name": "default",
"match": {
"prefix": "/"
},
"route": {
"cluster": "inbound|9999|http|bill-service.istio-demo.svc.cluster.local",
"timeout": "0s",
"maxGrpcTimeout": "0s"
},
"decorator": {
"operation": "bill-service.istio-demo.svc.cluster.local:9999/*"
}
}
]
}
相比于
VirtualOutbound,virtualInbound不会再次转给别的虚拟监听器,而是直接由本监听器的filterChains处理,本例中我们可以发现本机目标地址为80的http请求,转发到了inbound|9999|http|bill-service.istio-demo.svc.cluster.local这个集群中。###最终转到本地的80端口,也就是tomcat的80端口
查看该集群的信息
$ istioctl pc cluster bill-service-v1-6c95ccb747-vwt2d.istio-demo -h
$ istioctl pc cluster bill-service-v1-6c95ccb747-vwt2d.istio-demo --direction inbound -ojson
[
{
"name": "inbound|9999|http|bill-service.istio-demo.svc.cluster.local",
"type": "STATIC",
"connectTimeout": "10s",
"loadAssignment": {
"clusterName": "inbound|9999|http|bill-service.istio-demo.svc.cluster.local",
"endpoints": [
{
"lbEndpoints": [
{
"endpoint": {
"address": {
"socketAddress": {
"address": "127.0.0.1",
"portValue": 80
}
}
}
}
]
}
]
},
"circuitBreakers": {
"thresholds": [
{
"maxConnections": 4294967295,
"maxPendingRequests": 4294967295,
"maxRequests": 4294967295,
"maxRetries": 4294967295
}
]
}
}
]
3、逻辑图总结 
至此,我们实现了流量从front端发起,经过iptables转发至15001出口监听,经过 envoy的Listener -> route -> cluster -> endpoint 转发流程确定目的pod的地址端口,service端的istio-proxy容器收到流量的入口请求,再次经过iptables转发至15006监听,经过规则识别到转发127.0.0.1后到达bill-service容器的80端口,实现访问。
五、ingressgateway访问网格服务
1、场景描述
目前我们实现了后台服务层面,前端front调用后端service的流量策略,现在实现下客户访问前端的流量策略注入,区别是前端界面访问需要配置ingress域名。
2、为啥不用ingress
Ingress:对接ingress controller,实现外部流量进入集群内部,只适用于 HTTP 流量,使用方式也很简单,只能对 service、port、HTTP 路径等有限字段匹配来路由流量,这导致它无法路由如 MySQL、Redis 和各种私有 RPC 等 TCP 流量。要想直接路由南北向的流量,只能使用 Service 的 LoadBalancer 或 NodePort,前者需要云厂商支持,后者需要进行额外的端口管理。有些 Ingress controller 支持暴露 TCP 和 UDP 服务,但是只能使用 Service 来暴露,Ingress 本身是不支持的,例如 nginx ingress controller,服务暴露的端口是通过创建 ConfigMap 的方式来配置的。
ingressgateway访问网格服务
对于入口流量管理,您可能会问: 为什么不直接使用 Kubernetes Ingress API ? 原因是 Ingress API 无法表达 Istio 的路由需求。 Ingress 试图在不同的 HTTP 代理之间取一个公共的交集,因此只能支持最基本的 HTTP 路由,最终导致需要将代理的其他高级功能放入到注解(annotation)中,而注解的方式在多个代理之间是不兼容的,无法移植。
Istio
Gateway通过将 L4-L6 配置与 L7 配置分离的方式克服了Ingress的这些缺点。Gateway只用于配置 L4-L6 功能(例如,对外公开的端口,TLS 配置),所有主流的L7代理均以统一的方式实现了这些功能。 然后,通过在Gateway上绑定VirtualService的方式,可以使用标准的 Istio 规则来控制进入Gateway的 HTTP 和 TCP 流量。
3、利用ingress访问
既然要实现前端的流量调控,需要新增front:v2,front-svc,front-ingress服务
资源清单
front-tomcat-service.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
app: front-tomcat
name: front-tomcat
namespace: istio-demo
spec:
ports:
- name: http
port: 8080
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 8080
selector:
app: front-tomcat
type: ClusterIPfront-tomcat-v2-dpl.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app: front-tomcat
version: v2
name: front-tomcat-v2
namespace: istio-demo
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: front-tomcat
version: v2
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: front-tomcat
version: v2
spec:
containers:
- image: consol/tomcat-7.0:latest
name: front-tomcat
command: ["/bin/sh", "-c", "echo 'hello tomcat version2'>/opt/tomcat/webapps/ROOT/index.html;/opt/tomcat/bin/deploy-and-run.sh;"]front-tomcat-virtualservice.yaml
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: front-tomcat
namespace: istio-demo
spec:
hosts:
- front-tomcat
http:
- name: front-tomcat-route
route:
- destination:
host: front-tomcat
subset: v1
weight: 90
- destination:
host: front-tomcat
subset: v2
weight: 10
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: front-tomcat
namespace: istio-demo
spec:
host: front-tomcat
subsets:
- name: v1
labels:
version: v1
- name: v2
labels:
version: v2front-tomcat-ingress.yaml
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: front-tomcat
namespace: istio-demo
spec:
rules:
- host: tomcat.istio-demo.com
http:
paths:
- backend:
serviceName: front-tomcat
servicePort: 8080
path: /
status:
loadBalancer: {}$ kubectl apply -f front-tomcat-service.yaml $ kubectl apply -f <(istioctl kube-inject -f front-tomcat-v2-dpl.yaml) $ kubectl apply -f front-tomcat-virtualservice.yaml $ kubectl apply -f front-tomcat-ingress.yaml
使用ingress来访问网格服务
使用浏览器访问查看效果。
只有网格内部访问会遵从
virtualservice的规则,在宿主机中直接访问Service的ClusterIP还是按照默认的规则转发。此时还是各0.5权重,没有调度到istio
4、利用ingressgateway访问网格服务
front-tomcat-gateway.yaml
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: front-tomcat-gateway
namespace: istio-demo
spec:
selector:
istio: ingressgateway # use istio default controller
servers:
- port:
number: 80
name: http
protocol: HTTP
hosts:
- tomcat.istio-demo.com效果是在Istio的ingress网关上加了一条规则,允许
`tomcat.istio-demo.com的外部http流量进入到网格中,但是只是接受访问和流量输入,当流量到达这个网关时,它还不知道发送到哪里去。
网关已准备好接收流量,我们必须告知它将收到的流量发往何处,这就用到了前面使用过的
VirtualService。要为进入上面的 Gateway 的流量配置相应的路由,必须为同一个 host 定义一个
VirtualService,并使用配置中的gateways字段绑定到前面定义的Gateway上
front-tomcat-gateway-virtualservice.yaml
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: gateway-front-tomcat
namespace: istio-demo
spec:
gateways:
- front-tomcat-gateway
hosts:
- tomcat.istio-demo.com
http:
- name: front-tomcat-route
route:
- destination:
host: front-tomcat
subset: v1
weight: 90
- destination:
host: front-tomcat
subset: v2
weight: 10该网关列表指定,只有通过我们指定的网关 front-tomcat-gateway 的流量是允许的。所有其他外部请求将被拒绝,并返回 404 响应。
请注意,在此配置中,来自网格中其他服务的内部请求不受这些规则约束
$ kubectl apply -f front-tomcat-gateway-virtualservice.yaml $ kubectl apply -f front-tomcat-gateway.yaml
此时:
[root@k8s-master demo]# kubectl get vs -n istio-demo -owide
NAME GATEWAYS HOSTS AGE
front-tomcat [front-tomcat] 2m59s
gateway-front-tomcat [front-tomcat-gateway] [tomcat.istio-demo.com] 10m
vs-bill-service [bill-service] 23h
[root@k8s-master demo]# kubectl get gw -n istio-demo -owide
NAME AGE
front-tomcat-gateway 10m
[root@k8s-master demo]# kubectl get ingress -n istio-demo -owide
NAME CLASS HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE
front-tomcattomcat.istio-demo.com 80 39m
模拟访问:
# 此时我们已经走到ingressgateway上面了,所以要访问需要确认这里的svc是哪个映射端口,如下ingress映射80:80;ingressgateway映射80:32437,所以要访问域名:32437 [root@k8s-master demo]# kubectl -n istio-system get service istio-ingressgateway NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE istio-ingressgateway LoadBalancer 10.1.126.16515021:31356/TCP,80:32437/TCP,443:30389/TCP,31400:31099/TCP,15443:30765/TCP 26h # 也可以直接获取ingressgateway的nodeport $ kubectl -n istio-system get service istio-ingressgateway -o jsonpath='{.spec.ports[?(@.name=="http2")].nodePort}' 32437 # 访问 $ curl -HHost:tomcat.istio-demo.com 172.21.51.67:32437/
浏览器访问:
http://tomcat.istio-demo.com:32437/
此时已实现流量分配9:1的效果
5、配置nginx转发域名请求
如何实现不加端口访问网格内服务?
# 在一台80端口未被占用的机器中,如ip为192.168.0.121
$ docker run -d --restart=always -p 80:80 --name istio-nginx nginx:alpine
# 在容器的/etc/nginx/conf.d/目录中,新增配置文件
docker exec -it istio-nginx sh
$ cat front-tomcat.conf
upstream front-tomcat {
server 192.168.0.121:32437;
}
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
server_name tomcat.istio-demo.com;
location / {
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_pass http://front-tomcat;
}
}
$ nginx -s reload
win本地配置hosts,注意配置nginx部署的机器,而不是k8s集群ingress-nginx服务的机器
192.168.0.121 tomcat.istio-demo.com
直接访问
http://tomcat.istio-demo.com即可实现外部域名访问到网格内部服务